Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TSL 3102
Uploaded by
swordmy2523Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TSL 3102
Uploaded by
swordmy2523Copyright:
Available Formats
TESL3102
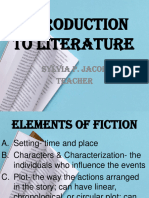
Notebook: PPG Created: URL: 19/11/2011 11:01 PM http://www.ppg.tesl.net Literature Genres Non-Fiction narrative Non-Fiction : based on fact, tells a story Biography: a written account of another person's life Autobiography: written by oneself Fiction Drama: Stories in verse or prose- for theaterical Poetry: verse and rhythmic writing with imagery that evoked emotions Fantasy: forming of mental images, strange Fable: supernatural, narrated - useful truth Fairy Tales: magical, fairies - for children Science Fiction: potential science - actual or imagined Realistic fiction: can actually happen, true to real life Folklore: songs, myths, proverbs - mouth to mouth Historical Fiction: fictional characters with historical setting Horror: evokes feeling of dread and fear Literary Criticism Def: involves reading, interpretation of and commentary on a specific text Literary text Literary criticism Literary / critical theory Functions of a critic: to to to to to introduce unknown authors encourage us to re-evaluate a work compare different works / ages / cultures increase the understanding of a work relate art to life / religion etc. Updated: 20/11/2011 12:47 AM
Layman VS Professional Critics Layman to kill time to enjoy fanciful visions to be amused to explore different ways of feelings to learn about self Theories of Literary Criticism Historical Studies within historical context If the writer is influenced by social context Is it only the writer's version of past events As a basis for a criticism of a society Connected past and present / offered value judgment Professional Critics to work from assumptions that are highly conscious to read through the lens of a particular theory to focus on particular details
Cultural To break down boundaries between high and low in cultures to dismantle the hierarchy that the distinction implies to discover why something is better than others originated from Marxist critics Social Criticism (Marxism) History as a struggle between socioeconomic classes Literature is a material product in particular society celebrates the values it represents Political Criticism the political situations Gender Criticism (Lesbian/Gay & Feminist) Do men and women read in different ways Do they write in different ways Structuralism a way of thinking that human activities is constructed What is Poetry A piece of literature written by a poet in meter or verse expressing various emotions. Using various techniques including metaphors, similes and onomatopoeia. Forms of Poetry Lyrical Poetry Consists of Poem, sonnets or ode Expresses the thoughts and feelings of the poet Nowadays: Songs Ballads folk-song or orally transmitted poem direct and dramatic manner Local history / legends normally composed in Quatrains Sonnets A lyric poem of a single stanza - 14 lines Italian or Petrarchan sonnets - One octave and One sestet - abbaabba and cdecde or cdccdc Shakespearean or English sonnets - 3 quatrains and 1 couplet Epics Long narrative poem elevated style hero-centered (semi-divine) historical legends Haiku 3 short lines 1st line - 5 syllable 2nd line - 7 syllable 3rd line - 5 syllable Must paint a mental image
Limerick a 5-line poem, funny, rhyme- aabba 1 couplet and one triplet Line 1: rhyme /a/ 3 beats Line 2: rhyme /a/ 3 beats Line 3: rhyme /b/ 2 beats Line 4: rhyme /b/ 2 beats Line 5: rhyme /a/ 3 beats Contains hyperboles, onomatopoeia, idioms, puns Last line must be the Punch Line Poetic Devices Alliteration - The repetition of a beginning sound Allusion - a casual reference to someone or something that paints a mental picture Analogy - Comparisons of two things : explaining one to show the similarities Caesura - pausing or stopping within a line of poetry, by punctuation Enjambement - the continuation of thought from one line to another without punctuation Hyperbole - extreme exaggeration for effect Metaphor - comparison of two unlike things. eg: Clouds are ships in full sail Metonym - substitution of a word for another that is closely associated. eg: White House to the President Onomatopoeia - the sound things make Oxymoron - use of contradictory items for effect. eg: Freezing fires of hell Personification - giving human traits to non-human things. eg: The sun smiles Simile - comparison of two unlikely things as one is like the other Symbol - something representing other than itself. eg: Dove-Peace Elegy - poem of extreme sorrow (lament) Free Verse - poem without any rhymes or rhythm imagery - use of words to create mental picture mood - the emotional effect Theme - the controlling idea
You might also like
- AP Lit Critical Analysis TermsDocument8 pagesAP Lit Critical Analysis Termsunknown racerx50No ratings yet
- POETRYDocument5 pagesPOETRYHamida KherNo ratings yet
- Literature Is A Term Used To Describe Written or Spoken MaterialDocument7 pagesLiterature Is A Term Used To Describe Written or Spoken MaterialIrish Ochiai100% (1)
- Canadian Poetry Student HandoutDocument18 pagesCanadian Poetry Student Handoutromil monisNo ratings yet
- Poetry: Alcantara, R.LDocument26 pagesPoetry: Alcantara, R.LCJ Klein BautistaNo ratings yet
- Types of PoetryDocument7 pagesTypes of Poetrysaadboss0345No ratings yet
- Literary Terms and Techniques ExplainedDocument4 pagesLiterary Terms and Techniques ExplainedVic AbandoNo ratings yet
- 2324 - Songs of Ourselves - Level N - ADV - Teacher GuideDocument121 pages2324 - Songs of Ourselves - Level N - ADV - Teacher GuidelayanNo ratings yet
- Literary Devices ExplainedDocument2 pagesLiterary Devices Explainedayesha juheerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Poetry PresentationDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Poetry Presentationdiana scottNo ratings yet
- To Autumn - John Keats - 3Document5 pagesTo Autumn - John Keats - 3Sara SlimaniNo ratings yet
- Poetry 11 TerminologyDocument6 pagesPoetry 11 Terminologyasala123aaupNo ratings yet
- Lecture-Literatures of The WorldDocument14 pagesLecture-Literatures of The WorldpatpaterNo ratings yet
- Poetry Powerpoint FinalDocument23 pagesPoetry Powerpoint Finalapi-268373101No ratings yet
- Glossary of Literary TermsDocument6 pagesGlossary of Literary TermsMichael Brian TorresNo ratings yet
- 21 Century Literature: FictionDocument36 pages21 Century Literature: FictionJhon Keneth NamiasNo ratings yet
- Winter Program DictionaryDocument6 pagesWinter Program Dictionaryapi-280992392No ratings yet
- NotesDocument11 pagesNotesOm PatelNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Poetry CommentaryDocument14 pagesHow To Write A Poetry CommentaryTom BombadilNo ratings yet
- Intro To LiteratureDocument28 pagesIntro To LiteratureZac Rhysin AlfecheNo ratings yet
- Slides On Types of Poems and Poetic DevicesDocument19 pagesSlides On Types of Poems and Poetic DevicesIbrahim AbuNo ratings yet
- Truth: The Ordered Pattern of Rhymes at The Ends of The Lines of A Poem or VerseDocument4 pagesTruth: The Ordered Pattern of Rhymes at The Ends of The Lines of A Poem or VerseaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Intro. Reviewer in World LitDocument2 pagesChapter 1 Intro. Reviewer in World LitLAGRANA, MA. ANGELICA A.No ratings yet
- SAT II LiteratureDocument7 pagesSAT II Literaturemanorville95No ratings yet
- Material - 2Document20 pagesMaterial - 2John Fritz DiamosNo ratings yet
- English LiteratureDocument8 pagesEnglish LiteratureErfan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Seminar 2 WorksheetDocument6 pagesSeminar 2 WorksheetЮлія ГородицькаNo ratings yet
- Poetry: Basic Terms: Poem: StanzaDocument6 pagesPoetry: Basic Terms: Poem: Stanzapapar58954No ratings yet
- Tools To Analyze A PoemDocument3 pagesTools To Analyze A PoemtijouNo ratings yet
- Elements of PoetryDocument10 pagesElements of PoetryIsha CeriseNo ratings yet
- Literary Terms - Official List (Alphabetized)Document5 pagesLiterary Terms - Official List (Alphabetized)Jonah DamayatiNo ratings yet
- Tspfastt PDFDocument2 pagesTspfastt PDFDewy VerenNo ratings yet
- Poetic Terminology: IB EditionDocument41 pagesPoetic Terminology: IB EditionmslenihanNo ratings yet
- Written Report Maam Joan JN - 093016Document1 pageWritten Report Maam Joan JN - 093016Jella GarzonNo ratings yet
- LITR 102 ReviewerDocument4 pagesLITR 102 Reviewerbautistajolina0317No ratings yet
- Apuntes Textos PoéticosDocument35 pagesApuntes Textos PoéticosGisela Herrera AfonsoNo ratings yet
- 1-Introduction To LiteratureDocument52 pages1-Introduction To LiteratureReina100% (3)
- Differences between drama and other literary formsDocument6 pagesDifferences between drama and other literary formsSeenauth Veeraj80% (5)
- WWW - Kutub.info 11799Document7 pagesWWW - Kutub.info 11799hassankchNo ratings yet
- T.me/englishnetjrf: Basic TerminologyDocument2 pagesT.me/englishnetjrf: Basic TerminologyMohsin IftikharNo ratings yet
- Literary Forms Elements and DevicesDocument38 pagesLiterary Forms Elements and Devicesallen alabaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. What Is LiteratureDocument24 pagesUnit 1. What Is LiteratureSopheakdey HormNo ratings yet
- Analyzing PoemDocument15 pagesAnalyzing Poemabc100% (1)
- FORMALISMDocument7 pagesFORMALISMZunaira KhanNo ratings yet
- Philippine LiteratureDocument17 pagesPhilippine LiteratureChristopher Lorence M. MercadoNo ratings yet
- 2 - PoetryDocument49 pages2 - PoetryChristian JP Lijayan RobertsonNo ratings yet
- Poetic TermsDocument3 pagesPoetic TermsmslenihanNo ratings yet
- 5 6230914381513752736 PDFDocument245 pages5 6230914381513752736 PDFRahmi AmiladiniNo ratings yet
- What Is PoetryDocument7 pagesWhat Is PoetryDM Riel100% (1)
- 02 Elements of POETRY Review MergedDocument226 pages02 Elements of POETRY Review MergedDenverrsNo ratings yet
- Week 3 & 4Document5 pagesWeek 3 & 4divya brahmaNo ratings yet
- Basic Approach To Text AnalysisDocument6 pagesBasic Approach To Text AnalysisMaría Regal CarballoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02Document10 pagesChapter 02Gwehn RevillaNo ratings yet
- What is poetry? The kinds, genres, modes and tonesDocument3 pagesWhat is poetry? The kinds, genres, modes and tonesKri ZaNo ratings yet
- 21st-PPT1 2Document38 pages21st-PPT1 2Johana Dahod MaligaNo ratings yet
- Literature: Introduction To English Literature By: Jehan SherDocument47 pagesLiterature: Introduction To English Literature By: Jehan Sherimran100% (1)
- List of Literary DevicesDocument3 pagesList of Literary DevicesNidhi NandaNo ratings yet
- List KJP Kimpalan 2018Document1 pageList KJP Kimpalan 2018swordmy2523No ratings yet
- Overview of The Eng Lang Curriculum Y4 050413Document15 pagesOverview of The Eng Lang Curriculum Y4 050413karimahNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Eng Lang Curriculum Y4 050413Document15 pagesOverview of The Eng Lang Curriculum Y4 050413karimahNo ratings yet
- 15 Leadership Traits Mnemonic JJ DID TIE BUCKLE-HDocument1 page15 Leadership Traits Mnemonic JJ DID TIE BUCKLE-Hswordmy2523No ratings yet
- Primary Year 2 Syllabus PDFDocument16 pagesPrimary Year 2 Syllabus PDFteachernizzNo ratings yet
- Lesson 31 Multimedia Production TeamDocument31 pagesLesson 31 Multimedia Production Teamswordmy2523No ratings yet
- Primary Year 2 Scheme of Work PhonicsDocument36 pagesPrimary Year 2 Scheme of Work PhonicsNoor Athirah Qurratu' Aini100% (8)
- D Internet Myiemorgmy Iemms Assets Doc Alldoc Document 2354 YES 04051212 CDocument2 pagesD Internet Myiemorgmy Iemms Assets Doc Alldoc Document 2354 YES 04051212 Cswordmy2523No ratings yet
- Cudbas FlyersDocument1 pageCudbas Flyersswordmy2523100% (1)
- Primary Curriculum Framework 2018 PDFDocument44 pagesPrimary Curriculum Framework 2018 PDFYanie JamalNo ratings yet
- DigestionDocument6 pagesDigestionswordmy2523No ratings yet
- Overview of The Eng Lang Curriculum Y4 050413Document15 pagesOverview of The Eng Lang Curriculum Y4 050413karimahNo ratings yet
- Hot Self Shot GirlsDocument14 pagesHot Self Shot Girlsleo1u42aspNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives: Introduction WDocument238 pagesLearning Objectives: Introduction Wswordmy2523No ratings yet
- Photography ShotsDocument2 pagesPhotography Shotsswordmy2523No ratings yet
- How To Draw StoryboardsDocument4 pagesHow To Draw StoryboardssdfhsdkfhksNo ratings yet
- Photography InfoDocument5 pagesPhotography Infoswordmy2523No ratings yet
- Videography BasicShotTypesDocument10 pagesVideography BasicShotTypesswordmy2523100% (2)
- Continuity Logging SheetDocument1 pageContinuity Logging Sheetswordmy2523No ratings yet
- Cabling Best Practices GA BP 036 02Document35 pagesCabling Best Practices GA BP 036 02Justin FisherNo ratings yet
- Osi LayerDocument13 pagesOsi Layerswordmy2523No ratings yet
- Ipad User GuideDocument144 pagesIpad User Guidepm_barnesNo ratings yet
- Action Script Note 2Document6 pagesAction Script Note 2swordmy2523No ratings yet
- Hipaa Cow Example Small Practice Network Diagram: InternetDocument1 pageHipaa Cow Example Small Practice Network Diagram: Internetswordmy2523No ratings yet
- NeuronDocument1 pageNeuronswordmy2523No ratings yet
- Flash Cs3 Animation 2 STDocument14 pagesFlash Cs3 Animation 2 STswordmy2523No ratings yet
- Windows History DiagramDocument25 pagesWindows History Diagramswordmy2523No ratings yet
- A Year of Nursery Rhymes: Lyrics and Actions Inside!Document16 pagesA Year of Nursery Rhymes: Lyrics and Actions Inside!swordmy2523No ratings yet
- Beginning Action Script 3Document77 pagesBeginning Action Script 3aboodkingsizeNo ratings yet
- Flash cs3 Animation 1 MTDocument18 pagesFlash cs3 Animation 1 MTswordmy2523No ratings yet
- Indian Institute OF Management, BangaloreDocument20 pagesIndian Institute OF Management, BangaloreGagandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Questions & AnswersDocument161 pagesMechanical Questions & AnswersTobaNo ratings yet
- Dell EMC VPLEX For All-FlashDocument4 pagesDell EMC VPLEX For All-Flashghazal AshouriNo ratings yet
- Levels of Attainment.Document6 pagesLevels of Attainment.rajeshbarasaraNo ratings yet
- Brooks Cole Empowerment Series Becoming An Effective Policy Advocate 7Th Edition Jansson Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesBrooks Cole Empowerment Series Becoming An Effective Policy Advocate 7Th Edition Jansson Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFlois.guzman538100% (12)
- Rescue Triangle PDFDocument18 pagesRescue Triangle PDFrabas_No ratings yet
- CHEM206 Answers 1Document3 pagesCHEM206 Answers 1Shiro UchihaNo ratings yet
- Global 6000 SystemsDocument157 pagesGlobal 6000 SystemsJosé Rezende100% (1)
- Technical File D13-MH, MG IMO Tier 11 GLDocument18 pagesTechnical File D13-MH, MG IMO Tier 11 GLsfsdffdsdfsdfsdfNo ratings yet
- Eudragit ReviewDocument16 pagesEudragit ReviewlichenresearchNo ratings yet
- Merchandise Floor Ready Standards - Supplier InformationDocument46 pagesMerchandise Floor Ready Standards - Supplier InformationGarmentLearner100% (1)
- Delhi Public School: Class: XI Subject: Assignment No. 3Document1 pageDelhi Public School: Class: XI Subject: Assignment No. 3Aman Kumar BhagatNo ratings yet
- Module 4-Answer KeyDocument100 pagesModule 4-Answer KeyAna Marie Suganob82% (22)
- Write 10 Lines On My Favourite Subject EnglishDocument1 pageWrite 10 Lines On My Favourite Subject EnglishIrene ThebestNo ratings yet
- PowerhouseDocument10 pagesPowerhouseRanjan DhungelNo ratings yet
- Complete Hemi Sync Gateway Experience ManualDocument43 pagesComplete Hemi Sync Gateway Experience Manualapi-385433292% (92)
- Executive Education Portfolio Soft Copy-INSEADDocument58 pagesExecutive Education Portfolio Soft Copy-INSEADОля КусраеваNo ratings yet
- E Learning: A Student Guide To MoodleDocument16 pagesE Learning: A Student Guide To MoodleHaytham Abdulla SalmanNo ratings yet
- CIGB B164 Erosion InterneDocument163 pagesCIGB B164 Erosion InterneJonathan ColeNo ratings yet
- DNT Audit Cash CountDocument2 pagesDNT Audit Cash CountAnonymous Pu7TnbCFC0No ratings yet
- Youth, Time and Social Movements ExploredDocument10 pagesYouth, Time and Social Movements Exploredviva_bourdieu100% (1)
- France: French HistoryDocument16 pagesFrance: French HistoryMyroslava MaksymtsivNo ratings yet
- Models of Health BehaviorDocument81 pagesModels of Health BehaviorFrench Pastolero-ManaloNo ratings yet
- Body Scan AnalysisDocument9 pagesBody Scan AnalysisAmaury CosmeNo ratings yet
- Rakpoxy 150 HB PrimerDocument1 pageRakpoxy 150 HB Primernate anantathatNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 CMADocument10 pagesLesson 5 CMAAssma SabriNo ratings yet
- The Rich Hues of Purple Murex DyeDocument44 pagesThe Rich Hues of Purple Murex DyeYiğit KılıçNo ratings yet
- Useful Coaching Questions: Questions To Create A State Change Questions To Ask When Something Goes WrongDocument2 pagesUseful Coaching Questions: Questions To Create A State Change Questions To Ask When Something Goes WrongAntonioNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Algorithms Prof. Madhavan Mukund Chennai Mathematical Institute Week - 01 Module - 01 Lecture - 01Document8 pagesDesign and Analysis of Algorithms Prof. Madhavan Mukund Chennai Mathematical Institute Week - 01 Module - 01 Lecture - 01SwatiNo ratings yet
- Conserve O Gram: Understanding Histograms For Digital PhotographyDocument4 pagesConserve O Gram: Understanding Histograms For Digital PhotographyErden SizgekNo ratings yet
- Summary: Atomic Habits by James Clear: An Easy & Proven Way to Build Good Habits & Break Bad OnesFrom EverandSummary: Atomic Habits by James Clear: An Easy & Proven Way to Build Good Habits & Break Bad OnesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1632)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- How To Win Friends and Influence People by Dale Carnegie - Book SummaryFrom EverandHow To Win Friends and Influence People by Dale Carnegie - Book SummaryRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (555)
- The Compound Effect by Darren Hardy - Book Summary: Jumpstart Your Income, Your Life, Your SuccessFrom EverandThe Compound Effect by Darren Hardy - Book Summary: Jumpstart Your Income, Your Life, Your SuccessRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (456)
- The War of Art by Steven Pressfield - Book Summary: Break Through The Blocks And Win Your Inner Creative BattlesFrom EverandThe War of Art by Steven Pressfield - Book Summary: Break Through The Blocks And Win Your Inner Creative BattlesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (273)
- The One Thing: The Surprisingly Simple Truth Behind Extraordinary ResultsFrom EverandThe One Thing: The Surprisingly Simple Truth Behind Extraordinary ResultsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (708)
- Can't Hurt Me by David Goggins - Book Summary: Master Your Mind and Defy the OddsFrom EverandCan't Hurt Me by David Goggins - Book Summary: Master Your Mind and Defy the OddsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (382)
- Summary of The Anxious Generation by Jonathan Haidt: How the Great Rewiring of Childhood Is Causing an Epidemic of Mental IllnessFrom EverandSummary of The Anxious Generation by Jonathan Haidt: How the Great Rewiring of Childhood Is Causing an Epidemic of Mental IllnessNo ratings yet
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (327)
- Surrounded by Idiots: The Four Types of Human Behavior and How to Effectively Communicate with Each in Business (and in Life) (The Surrounded by Idiots Series) by Thomas Erikson: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSurrounded by Idiots: The Four Types of Human Behavior and How to Effectively Communicate with Each in Business (and in Life) (The Surrounded by Idiots Series) by Thomas Erikson: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Summary: How to Know a Person: The Art of Seeing Others Deeply and Being Deeply Seen By David Brooks: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: How to Know a Person: The Art of Seeing Others Deeply and Being Deeply Seen By David Brooks: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Summary of 12 Rules for Life: An Antidote to ChaosFrom EverandSummary of 12 Rules for Life: An Antidote to ChaosRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (294)
- Stonewalled: My Fight for Truth Against the Forces of Obstruction, Intimidation, and Harassment in Obama's WashingtonFrom EverandStonewalled: My Fight for Truth Against the Forces of Obstruction, Intimidation, and Harassment in Obama's WashingtonRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Learn French with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: French Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachFrom EverandLearn French with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: French Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (80)
- Essentialism by Greg McKeown - Book Summary: The Disciplined Pursuit of LessFrom EverandEssentialism by Greg McKeown - Book Summary: The Disciplined Pursuit of LessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (187)
- Summary of The Galveston Diet by Mary Claire Haver MD: The Doctor-Developed, Patient-Proven Plan to Burn Fat and Tame Your Hormonal SymptomsFrom EverandSummary of The Galveston Diet by Mary Claire Haver MD: The Doctor-Developed, Patient-Proven Plan to Burn Fat and Tame Your Hormonal SymptomsNo ratings yet
- Writing Screenplays That Sell: The Complete Guide to Turning Story Concepts into Movie and Television DealsFrom EverandWriting Screenplays That Sell: The Complete Guide to Turning Story Concepts into Movie and Television DealsNo ratings yet
- 1000 Words: A Guide to Staying Creative, Focused, and Productive All-Year RoundFrom Everand1000 Words: A Guide to Staying Creative, Focused, and Productive All-Year RoundRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (13)
- Learn Italian with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Italian Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachFrom EverandLearn Italian with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Italian Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (47)
- Learn Spanish with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Spanish Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachFrom EverandLearn Spanish with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Spanish Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (136)
- Summary of Supercommunicators by Charles Duhigg: How to Unlock the Secret Language of ConnectionFrom EverandSummary of Supercommunicators by Charles Duhigg: How to Unlock the Secret Language of ConnectionNo ratings yet
- Designing Your Life by Bill Burnett, Dave Evans - Book Summary: How to Build a Well-Lived, Joyful LifeFrom EverandDesigning Your Life by Bill Burnett, Dave Evans - Book Summary: How to Build a Well-Lived, Joyful LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (61)
- Summary of Slow Productivity by Cal Newport: The Lost Art of Accomplishment Without BurnoutFrom EverandSummary of Slow Productivity by Cal Newport: The Lost Art of Accomplishment Without BurnoutRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Summary of Million Dollar Weekend by Noah Kagan and Tahl Raz: The Surprisingly Simple Way to Launch a 7-Figure Business in 48 HoursFrom EverandSummary of Million Dollar Weekend by Noah Kagan and Tahl Raz: The Surprisingly Simple Way to Launch a 7-Figure Business in 48 HoursNo ratings yet