Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aesthetic Etc.
Uploaded by
Nhojlem RamosOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Aesthetic Etc.
Uploaded by
Nhojlem RamosCopyright:
Available Formats
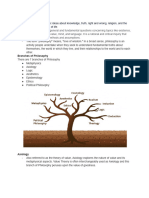
Aesthetics is the branch of philosophy which deals with the nature of art and of artistic judgment.
Some of the central questions of aesthetics focus on the beautiful: under what circumstances it may be said to exist, what criteria are to be used to judge the beautiful, and whether or not these criteria apply equally to literature and music. http://www.answers.com/topic/aesthetics
The term Logic comes from the Greek word logos. The variety of senses that logos possesses may suggest the difficulties to be encountered in characterizing the nature and scope of logic. http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/346240/philosophy-of-logic
Political is the study of human social organization and of the nature of man/woman in society. A political philosopher is likely to ponder the following question: What is the ideal form of government? Is it aristocracy, monarchy, theocracy, democracy, some mix of the different systems, or absolutely no government at all (anarchy)? http://www.philosophicalsociety.com/Political%20Philosophy.htm
Metaphysics is a branch of philosophy very much concerned with explaining the fundamental nature of being and the world, although the term is not easily defined. Traditionally, metaphysics attempts to answer two basic questions in the broadest possible terms: "What is there?" "What is it like?" http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metaphysics
Ethics is also called moral philosophy and is the discipline concerned with what is morally good and bad, right and wrong. The term is also applied to any system or theory of moral values or principles. Meta-ethics investigates where our moral principles come from, and what they mean. Normative ethics is more practical and is concerned with finding moral principles to govern how we should act. Applied ethics considers applying our moral principles to particular real world situations. http://www.philosophyarchive.com/index.php?title=Philosophy_of_Ethics
Epistemology, the study of the nature, origin, and limits of human knowledge. The term is derived from the Greekepistm (knowledge) and logos (reason), and accordingly the field is sometimes referred to as the theory of knowledge. Epistemology has a long history, beginning with the ancient Greeks and continuing to the present. Along with metaphysics, logic, and ethics, it is one of the four main branches of philosophy, and nearly every great philosopher has contributed to it. http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/190219/epistemology
You might also like
- Introduction To The Five Branches of PhilosophyDocument8 pagesIntroduction To The Five Branches of PhilosophyMina Lily100% (1)
- Fatima Assignment PhilosophyDocument27 pagesFatima Assignment PhilosophyAbdullah HabibNo ratings yet
- The Branches of PhilosophyDocument23 pagesThe Branches of Philosophyvicente ferrer100% (1)
- Branches of PhilosophyDocument3 pagesBranches of Philosophyyvette18latagNo ratings yet
- The Main Branches of Philosophy AreDocument2 pagesThe Main Branches of Philosophy AreMeynard BatasNo ratings yet
- Branches of PhilosophyDocument2 pagesBranches of PhilosophyMary GleyneNo ratings yet
- Branches of PhilosophyDocument4 pagesBranches of PhilosophyJui Aquino ProvidoNo ratings yet
- What is Philosophy? - An Introduction to its Four Major BranchesDocument4 pagesWhat is Philosophy? - An Introduction to its Four Major BranchesLetlie Zoilo SemblanteNo ratings yet
- Greek Philosophers' ContributionsDocument5 pagesGreek Philosophers' ContributionsMark Louie DagamacNo ratings yet
- The Branches of PhilosophyDocument3 pagesThe Branches of PhilosophyFor Use Web (My Web)No ratings yet
- What Are The 7 Branches of Philosophy?Document4 pagesWhat Are The 7 Branches of Philosophy?Muzaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Branches of PhilosophyDocument2 pagesBranches of PhilosophyFlorenio Mediavillo JaballasNo ratings yet
- The Field of PhilosophyDocument11 pagesThe Field of PhilosophyRed Hood100% (1)
- Ethics 101: From Altruism and Utilitarianism to Bioethics and Political Ethics, an Exploration of the Concepts of Right and WrongFrom EverandEthics 101: From Altruism and Utilitarianism to Bioethics and Political Ethics, an Exploration of the Concepts of Right and WrongRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Philosophy: The Study of Fundamental ProblemsDocument5 pagesPhilosophy: The Study of Fundamental ProblemsJohn Henry Morga PetalinoNo ratings yet
- Med TechDocument3 pagesMed TechblickenstaffNo ratings yet
- PhiloDocument17 pagesPhiloJudy PatenoNo ratings yet
- ETHICSDocument2 pagesETHICSEla Daniel MuñezNo ratings yet
- Philosoph_MiralpesDocument2 pagesPhilosoph_MiralpesFiona MiralpesNo ratings yet
- Key Terminology (ETHICS)Document6 pagesKey Terminology (ETHICS)Apeksha SuranaNo ratings yet
- What is PhilosophyDocument1 pageWhat is PhilosophyiLoveMarshaNo ratings yet
- Textbook in PhilosophyDocument4 pagesTextbook in PhilosophyBrynn Vern PedroNo ratings yet
- The NotionDocument2 pagesThe NotionSilvan telaumbanuaNo ratings yet
- Uas FilsafatDocument16 pagesUas FilsafatIRFANSYAH ANAK SIRAITNo ratings yet
- Branches of OfPhilosophyDocument19 pagesBranches of OfPhilosophyrax dearNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Philosophy - The Branches of Philosophy - Wikibooks, Open Books For An Open WorldDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Philosophy - The Branches of Philosophy - Wikibooks, Open Books For An Open WorldAbdul HameedNo ratings yet
- Logic: True, and More With What Kinds of Meanings Can Be True or FalseDocument4 pagesLogic: True, and More With What Kinds of Meanings Can Be True or FalseminmorNo ratings yet
- PhilosophyDocument4 pagesPhilosophyCharmszelNo ratings yet
- 8,556,600,748 Visitors Served: Dictionary, Encyclopedia and Thesaurus - The Free DictionaryDocument21 pages8,556,600,748 Visitors Served: Dictionary, Encyclopedia and Thesaurus - The Free DictionarySamson SeiduNo ratings yet
- Definition, Nature, and Branches of PhilosophyDocument15 pagesDefinition, Nature, and Branches of Philosophysir jj73% (11)
- Introduction To The Philosophy of Human PersonDocument3 pagesIntroduction To The Philosophy of Human Personنجشو گحوشNo ratings yet
- Q.1 Discuss The Branches of PhilosophyDocument18 pagesQ.1 Discuss The Branches of PhilosophySajjad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonDocument10 pagesIntroduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonAguinaldo MeridaNo ratings yet
- The Nature of AestheticsDocument1 pageThe Nature of AestheticsAli AhmedNo ratings yet
- Exploring The Fundamentals of MetaphysicsDocument5 pagesExploring The Fundamentals of MetaphysicsMark Russel Sean LealNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To PhilosophyDocument8 pagesAn Introduction To Philosophylamarra100% (1)
- Briefly Explain PhilosophyDocument6 pagesBriefly Explain PhilosophyAshenPereraNo ratings yet
- Intellectual: Philosophy, (From Greek, by Way of Latin, Philosophia, "Love ofDocument4 pagesIntellectual: Philosophy, (From Greek, by Way of Latin, Philosophia, "Love ofSteak ONo ratings yet
- Branches of OfPhilosophyDocument23 pagesBranches of OfPhilosophyDonald Roland Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lesson 1 The Study of Philosophy and EthicsDocument44 pagesModule 1 Lesson 1 The Study of Philosophy and Ethicszzrot1No ratings yet
- MetaphysicsDocument12 pagesMetaphysicsDummy AccountNo ratings yet
- Lecture-Philosopy of Ethics PDFDocument5 pagesLecture-Philosopy of Ethics PDFMUHAMMAD SALEEM RAZANo ratings yet
- The Decision. Who Are Philosophers?Document3 pagesThe Decision. Who Are Philosophers?kenshei07No ratings yet
- Branches of Philosophy PDF 1Document17 pagesBranches of Philosophy PDF 1KayeAnn Posadas100% (2)
- Philosophy WPS OfficeDocument5 pagesPhilosophy WPS OfficeannejeninepNo ratings yet
- ZTS Philosophy Lecture 1Document5 pagesZTS Philosophy Lecture 1Isaiah MakurunjeNo ratings yet
- Philosophy's Main Branches in 40 CharactersDocument10 pagesPhilosophy's Main Branches in 40 CharactersVince Louanne Tabilon100% (1)
- PhiloDocument10 pagesPhiloEduc. FilesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Five Branches of Philosophy: MetaphysicsDocument17 pagesIntroduction To The Five Branches of Philosophy: MetaphysicsGretchen GultianoNo ratings yet
- ESL INtro. 1Document16 pagesESL INtro. 1Gleemor MakeNo ratings yet
- What Is Philosophy Intro ArticleDocument15 pagesWhat Is Philosophy Intro ArticleKyrha Joy LaysonNo ratings yet
- Six Branches of Philosophy AssignmentDocument3 pagesSix Branches of Philosophy Assignmentfrancis dungcaNo ratings yet
- PhiloDocument9 pagesPhiloJihane Tanog100% (1)
- Philosophy NotesDocument3 pagesPhilosophy NotesLadyrose SalazarNo ratings yet
- PHILOSOPHYDocument9 pagesPHILOSOPHYAlnadzrin Janadil JabaraniNo ratings yet
- What Questions About Your Life Are You Struggling To Find Answers To?Document13 pagesWhat Questions About Your Life Are You Struggling To Find Answers To?DP BPNo ratings yet
- Ethics Prelim ReviewerDocument16 pagesEthics Prelim ReviewerLJ RamirezNo ratings yet
- Ethics Module 1 - IntroductionDocument15 pagesEthics Module 1 - IntroductionFainted Hope100% (1)
- The Life Philosophy of the Master of Existentialism: 蛻變:生命存在與昇華的實相(國際英文版:卷三)From EverandThe Life Philosophy of the Master of Existentialism: 蛻變:生命存在與昇華的實相(國際英文版:卷三)No ratings yet
- Reason and Emotion: Essays on Ancient Moral Psychology and Ethical TheoryFrom EverandReason and Emotion: Essays on Ancient Moral Psychology and Ethical TheoryRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Earned Value ManagementDocument2 pagesEarned Value ManagementNhojlem RamosNo ratings yet
- Soft WenDocument4 pagesSoft WenNhojlem RamosNo ratings yet
- NVPDocument8 pagesNVPNhojlem RamosNo ratings yet
- ModelingDocument28 pagesModelingNhojlem RamosNo ratings yet