Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Substance Abuse NCP
Uploaded by
Bryan Baynosa ArabianaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Substance Abuse NCP
Uploaded by
Bryan Baynosa ArabianaCopyright:
Available Formats
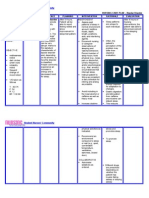
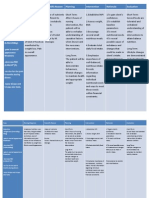
ASSESSMENT Subjective: Hindi ko kayang tumugil sa pagiinum ko as verbalized by the patient Objective: -fear -helplessness -tension - nausea and
vomiting -rapid heart rate (130bpm) -loss of appetite -insomnia
DIAGNOSIS Anxiety related to cessation of alcohol intake, physiological withdrawal as evidenced by increased helplessness, fear, tension, hopelessness with loss of control of own life.
PLANNING After 4 hours of nursing interventions, the patient will verbalize reduction of fear and anxiety to an acceptable and manageable level.
IMPLEMENTATION Identify cause of anxiety, involving client in the process. Explain that alcohol withdrawal increases anxiety and uneasiness. Reassess level of anxiety on an ongoing basis. Develop a trusting relationship through frequent contact and being honest and nonjudgmental. Project an accepting attitude about alcoholism.
RATIONALE Persons in acute phase of withdrawal may be unable to identify and/or accept what is happening. Anxiety may be physiologically or environmentally caused. Provides client with a sense of humanness, helping to decrease paranoia and distrust. Client will be able to detect biased or condescending attitude of caregivers. Enhances sense of trust, and explanation may increase cooperation and reduce anxiety. Provides sense of control over self in circumstance where loss of control is a significant factor. Client may experience periods of confusion, resulting in increased anxiety Anti-anxiety agents are given during acute withdrawal to help client relax, be less hyperactive, and feel
EVALUATION After 4 hours of nursing interventions, the patient verbalized reduction of fear and anxiety to an acceptable and manageable level
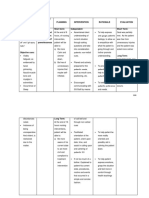
Inform client about what you plan to do and why. Include client in planning process and provide choices when possible
Reorient frequently
Administer medications, as indicated, for example: Benzodiazepines, such as chlordiazepoxide
(Librium), and diazepam (Valium).
more in control..
Administer Barbiturates, such as phenobarbital, or possibly secobarbital (Seconal) or pentobarbital (Nembutal)
These drugs are sometimes used to treat or prevent alcohol withdrawal seizures, but need to be used with caution because they are respiratory depressants and REM sleep cycle inhibitors. Client is more likely to contract for treatment while still hurting and experiencing fear and anxiety from last drinking episode. Motivation decreases as well-being increases and person again feels able to control the problem.
Provide consultation or referral to detoxification or crisis center for ongoing treatment program as soon as medically stable
You might also like
- NCPDocument8 pagesNCPTrixia Diaz67% (3)
- NCP BSN 3rd Yr Psychiatric WardDocument9 pagesNCP BSN 3rd Yr Psychiatric WardMary Margarett BoadoNo ratings yet
- Xi. Nursing Care PlansDocument4 pagesXi. Nursing Care PlansNic Ji100% (1)
- NURSING CARE PLAN-EditDocument14 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN-EditRene John Francisco100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For "Alcohol Acute Withdrawal"Document15 pagesNursing Care Plan For "Alcohol Acute Withdrawal"jhonroks86% (21)
- Bipolar NCPDocument2 pagesBipolar NCPweehdinga89% (9)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care Planautoeroticasphaxia50% (8)
- Care Plan For SchizophreniaDocument6 pagesCare Plan For SchizophreniaAllea Likestolaugh Brown100% (2)
- Dementia Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesDementia Nursing Care Planmp175767% (3)
- NCP PsychosisDocument3 pagesNCP Psychosisinagasi100% (7)
- Ineffective CopingDocument5 pagesIneffective CopingIrish_Joy_Ari__301983% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan - SchizophreniaDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan - SchizophreniaJasmin Jacob76% (46)
- Risk for Self-Harm Assessment and InterventionsDocument1 pageRisk for Self-Harm Assessment and InterventionskyreNo ratings yet
- Care Plan 27Document10 pagesCare Plan 27Oroma TobiasNo ratings yet
- NCP Disturbed Thought Process Related To SchizophreniaDocument6 pagesNCP Disturbed Thought Process Related To Schizophrenianaishel0% (1)
- Bipolar NCPDocument2 pagesBipolar NCPGenevieve VLs100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanJewelyn Bronda100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan - SchizophreniaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan - SchizophreniaJasmin Jacob80% (5)
- ND - Disturbed Thought ProcessDocument2 pagesND - Disturbed Thought ProcessHu DawiNo ratings yet
- NCP - Suicidal TendencyDocument2 pagesNCP - Suicidal Tendencyяoxel яayмoи eитяeиa100% (5)
- Nursing Care Plan 1 Risk For Violence, Self DirectedDocument9 pagesNursing Care Plan 1 Risk For Violence, Self Directeddbryant010193% (14)
- Adhd NCPDocument2 pagesAdhd NCPGooph Buster83% (6)
- N C PDocument3 pagesN C PTrixia Diaz100% (1)
- Improving Social Interaction in a Child with Impaired Social SkillsDocument2 pagesImproving Social Interaction in a Child with Impaired Social Skills4kscribd80% (5)
- NCP DisturbedThoughtProcessesDocument1 pageNCP DisturbedThoughtProcessesJoan KarlaNo ratings yet
- NCP Psyche2Document6 pagesNCP Psyche2Nica RTNo ratings yet
- Assessing Auditory Hallucinations in SchizophreniaDocument3 pagesAssessing Auditory Hallucinations in SchizophreniaJames Lozano83% (6)
- Paranoid Schizophrenia NCPDocument8 pagesParanoid Schizophrenia NCPCherubim Lei DC Flores67% (3)
- NCP For Bipolar Risk For Injury Related To Extreme Hyperactivity As Evidenced by Excessive and Constant Motor ActivityDocument3 pagesNCP For Bipolar Risk For Injury Related To Extreme Hyperactivity As Evidenced by Excessive and Constant Motor Activitydana75% (4)
- Risk For InjuryDocument4 pagesRisk For InjuryJanina Patricia BuddleNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Bipolar Disorder NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Bipolar Disorder NCPderic94% (36)
- NCP: Alcohol Acute WithdrawlDocument11 pagesNCP: Alcohol Acute WithdrawlJavie100% (2)
- NCP - BipolarDocument2 pagesNCP - BipolarSasha FongNo ratings yet
- NCP DEPRESSION DIAGNOSISDocument4 pagesNCP DEPRESSION DIAGNOSIS'SheenMarkReal'No ratings yet
- NCP For Bipolar DisorderDocument1 pageNCP For Bipolar DisorderJohn Carlo Santos100% (7)
- Ineffective CopingDocument3 pagesIneffective CopingCalimlim Kim100% (2)
- Self Care DeficitDocument1 pageSelf Care DeficitWilly EstacionNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Nursing Diagnosis Anxiety (Mild)Document4 pagesNursing Care Plan Nursing Diagnosis Anxiety (Mild)yvenette_kris871881% (27)
- Care Plan For Schizoaffective DisorderDocument2 pagesCare Plan For Schizoaffective DisorderThalia Peart100% (13)
- Schizophrenia Care Plan RNDocument8 pagesSchizophrenia Care Plan RNlisa75% (4)
- Defensive coping nursing diagnosisDocument3 pagesDefensive coping nursing diagnosisRoch Oconer100% (1)
- A NCP SchizoDocument5 pagesA NCP SchizoJoseph Wilson Macasa50% (4)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesNursing Care PlanNeza AgdalesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Goal Interventions (3) (Reference) Rationale (Reference) EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Goal Interventions (3) (Reference) Rationale (Reference) EvaluationJulvica HeuwNo ratings yet
- NCP AsthmaDocument3 pagesNCP AsthmaGellie Santos68% (19)
- NCP IsoDocument4 pagesNCP IsoBriccio Calingin IIINo ratings yet
- Nursing Interventions in AnxietyDocument7 pagesNursing Interventions in Anxietymindreader19No ratings yet
- Psych HESI Hints: Members For The Client's Safety (E.g., Suicide Plan) and Optimal TherapyDocument7 pagesPsych HESI Hints: Members For The Client's Safety (E.g., Suicide Plan) and Optimal TherapyChristina100% (10)
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPLeolene Grace BautistaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Cues: Treatment Options and Body ImageDocument12 pagesNursing Diagnosis Cues: Treatment Options and Body ImageJohn Michael FernandezNo ratings yet
- NCP Group 4Document5 pagesNCP Group 4Ynaffit Alteza UntalNo ratings yet
- Drug Study BATAANDocument2 pagesDrug Study BATAANBryant Riego IIINo ratings yet
- Bipolar NCPDocument4 pagesBipolar NCPcandy19agustin100% (1)
- Treatment of Panic Disorder (AUS) PDFDocument3 pagesTreatment of Panic Disorder (AUS) PDFBrian HarrisNo ratings yet
- NCP - Perinatal FinalsDocument6 pagesNCP - Perinatal FinalsJanette L. Ortega0% (1)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationKatrina Ponce86% (7)
- General Nursing Care Plan PDFDocument17 pagesGeneral Nursing Care Plan PDFTmanoj Praveen100% (1)
- GBS Nursing MangementDocument21 pagesGBS Nursing MangementJoseph Namita SunnyNo ratings yet
- NCP Copd4Document15 pagesNCP Copd4Alessa Marie Crisostomo Salazar100% (1)
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPChrisTine M. MoralesNo ratings yet
- H.A. 2 Lymph Nodes EtcDocument10 pagesH.A. 2 Lymph Nodes EtcBryan Baynosa ArabianaNo ratings yet
- List of Foods No. of Exchanges Cho G Pro G Fat EnergyDocument3 pagesList of Foods No. of Exchanges Cho G Pro G Fat EnergyBryan Baynosa ArabianaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Urinary System (JOse Reyes)Document2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Urinary System (JOse Reyes)Bryan Baynosa ArabianaNo ratings yet
- ADHD Can Be Diagnosed in Kids From Age 4Document4 pagesADHD Can Be Diagnosed in Kids From Age 4Bryan Baynosa ArabianaNo ratings yet
- Ambulatory DevicesDocument3 pagesAmbulatory DevicesBryan Baynosa ArabianaNo ratings yet
- Theories of Labor OnsetDocument1 pageTheories of Labor OnsetWeng Maesa MontemayorNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY CefuroximeDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY CefuroximeLyana Stark92% (39)
- French RevolutionDocument8 pagesFrench RevolutionBryan Baynosa ArabianaNo ratings yet
- DengueDocument1 pageDengueBryan Baynosa ArabianaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Patient's Bill of RightsDocument6 pagesPhilippine Patient's Bill of Rightsplethoraldork98% (49)
- CaduceusDocument2 pagesCaduceusBryan Baynosa ArabianaNo ratings yet
- VoodooDocument1 pageVoodooBryan Baynosa ArabianaNo ratings yet
- Research (Letter) 2013Document2 pagesResearch (Letter) 2013Bryan Baynosa ArabianaNo ratings yet
- Ambulatory DevicesDocument3 pagesAmbulatory DevicesBryan Baynosa ArabianaNo ratings yet
- Ambulatory DevicesDocument3 pagesAmbulatory DevicesBryan Baynosa ArabianaNo ratings yet
- How To Be A Mentally Health Person?Document3 pagesHow To Be A Mentally Health Person?Bryan Baynosa ArabianaNo ratings yet
- Cole Crops and Other Brassicas: Organic Production: AttraDocument20 pagesCole Crops and Other Brassicas: Organic Production: AttraRebecca SheaNo ratings yet
- Vol. 2 No. 10Document58 pagesVol. 2 No. 10Lindsey RobbinsNo ratings yet
- 1536106348Document144 pages1536106348Saman SarKoNo ratings yet
- By Dr. James C. Ekwensi, Dr. Thomas Gray, Dr. Abdulhalim Khan, and Khadijat B. MomohDocument71 pagesBy Dr. James C. Ekwensi, Dr. Thomas Gray, Dr. Abdulhalim Khan, and Khadijat B. MomohChukwu NedumNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Management of Patients With A Short BowelDocument12 pagesGuidelines For Management of Patients With A Short BowelMarselya GaniNo ratings yet
- Alemitu MequanintDocument125 pagesAlemitu MequanintshegawNo ratings yet
- Narrative TextDocument20 pagesNarrative Textdika grayNo ratings yet
- CytologyDocument12 pagesCytologyEsther HutagalungNo ratings yet
- ADA Guideline - Chronic Kidney Disease Evidence-Based Nutrition Practice GuidelineDocument19 pagesADA Guideline - Chronic Kidney Disease Evidence-Based Nutrition Practice GuidelineJorge SánchezNo ratings yet
- Nakshatra DhanishtaDocument7 pagesNakshatra DhanishtaANTHONY WRITER100% (3)
- Klenner Protocol For 2013Document10 pagesKlenner Protocol For 2013jcoppala4476No ratings yet
- Essay On AidsDocument6 pagesEssay On AidsBharat SinghNo ratings yet
- Full Download High Acuity Nursing 6th Edition Wagner Test BankDocument18 pagesFull Download High Acuity Nursing 6th Edition Wagner Test Bankassapancopepodmhup100% (38)
- Chloride: Colorimetric MethodDocument2 pagesChloride: Colorimetric MethodFariz KasyidiNo ratings yet
- 1 N-109 MCN 2 LEC Syllabus (2 S, AY 19-20) REVISED PDFDocument7 pages1 N-109 MCN 2 LEC Syllabus (2 S, AY 19-20) REVISED PDFCayla Mae CarlosNo ratings yet
- 3rdQ Health DLLDocument4 pages3rdQ Health DLLMichelle Handumon Alviar85% (13)
- Growing Plants / GerminationDocument62 pagesGrowing Plants / GerminationJulia Katrina RoxasNo ratings yet
- Caesarean SectionDocument20 pagesCaesarean Sectionapi-3705046100% (3)
- Antidiuretic HormoneDocument13 pagesAntidiuretic Hormonesadia ahmadNo ratings yet
- Procedure Checklist Chapter 22: Providing Denture CareDocument1 pageProcedure Checklist Chapter 22: Providing Denture Caremacs_smacNo ratings yet
- Prak Ospe PK FMS 3 2021Document7 pagesPrak Ospe PK FMS 3 2021Angelique NatalieNo ratings yet
- Rabipur - (EMC) Print FriendlyDocument8 pagesRabipur - (EMC) Print Friendlyshreyas_chandor3802No ratings yet
- Health Education - Reviewer (Prelims)Document9 pagesHealth Education - Reviewer (Prelims)Frances Nicole FloresNo ratings yet
- Universal Credit Work Capability QuestionnaireDocument24 pagesUniversal Credit Work Capability QuestionnaireSteven Preece100% (2)
- Mechanical Treatment For The Cervical SpineDocument36 pagesMechanical Treatment For The Cervical SpineMohamed ElMeligieNo ratings yet
- CogwheelDocument4 pagesCogwheelRimsha RanaNo ratings yet
- Homeopathy Mother Tinctures Internal and External UseDocument8 pagesHomeopathy Mother Tinctures Internal and External Useyogeshydd50% (2)
- 3911515Document1 page3911515Gemmelle CangcoNo ratings yet
- Dengue Clinical Presentation - History, Physical ExaminationDocument6 pagesDengue Clinical Presentation - History, Physical Examinationm.m.m.mNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Garlic (Allium Sativum) As Antimicrobial Agent Against Bacteria Causing Urinary Tract InfectionDocument4 pagesEffectiveness of Garlic (Allium Sativum) As Antimicrobial Agent Against Bacteria Causing Urinary Tract InfectionSabrina JonesNo ratings yet