Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Razones Trigonométricas de Ángulos Compuestos
Uploaded by
carlos_kard0322688Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Razones Trigonométricas de Ángulos Compuestos
Uploaded by
carlos_kard0322688Copyright:
Available Formats
ACADEMIA PREUNIVERSITARIA ALPHA
TRIGONOMETRIA
RAZONES TRIGONOMTRICAS DE NGULOS COMPUESTOS
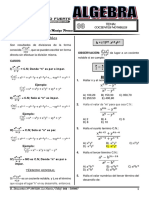
1. RAZONES TRIGONOMTRICAS DE LA SUMA Y DIFERENCIA DE NGULOS EJERCICIOS DE APLICACIN 1. Simplifique: sen (15 + x ). cos x - cos (15 + x ).senx E = cos x . cos (15 - x ) - senx .sen (15 - x ) A) 2 - 3 D) B) 2 + 3 C) E)
se n ( x y ) = senx.seny cos x .seny cos( x y ) = cos x . cos y m senx.seny
tg x tg y tg ( x y ) = ; 1 m tg x.tg y c tg ( x y ) =
tg x.tg y 1;-1
ctg x.ctg y m 1 ; ctgx m ctgy ctg y ctg y
3 6 2. Si: t g (3 x - 2 y ) = 4
Halle: t g ( x + y ) A)
3 2 t g (2 x - 3 y ) = 5
2. OTRAS IDENTIDADES
se n ( x + y ).se n ( x - y ) = se n 2 x - se n 2 y cos( x + y ). cos( x - y ) = cos 2 x - se n 2 y
tg x tg y t g ( x y ).tg x.tg y = t g ( x y )
1 21 1 D) 10 3. Si: sen ( x + y ) =
B) -1
1 21 1 E) 10
C) -
tg x tg y =
se n( x y ) cos x . cos y
ctg x ctg y =
se n( x y ) senx.seny
4 y 5 Halle: se n ( x - y )
A)
senx . cos y =
3 5
se n ( x + y + z ) = senx. cos y . cos z - seny . cos x . cos z + senz . cos x . cos y - senx .seny .senz cos( x + y + z ) = cos x . cos y . cos z - cos x .seny .sen z
- cos y .senx.senz - cos z .senx.seny
tg ( x + y + z ) = tg x + tg y + tg z - tg x .tg y .tg z 1 - tg x .tg y - tg y .tg z - tg x .tg z
1 1 2 B) C) 5 6 5 3 4 E) D) 5 5 4. Los ngulos y son agudos con menor que , tales que la razn de sus tangentes es 7/18 y sen(+)=4/5. Calcule 25sen(-). A) 6,6 B) 4,8 C) 8,8 D) 7,6 E) 5,4
5. Si a y b son ngulos complementarios, adems: 3sena = 7senb. Halle: tg(a-b)
3. PROPIEDADES PARA 3 NGULOS I. Si: x + y + z = n p ; n
tg x + tg y + tg z = tg x .tg y .tg z
ctgx.ctgy + ctgy.ctg z + ctgx.ctg z = 1
19 21 20 D) 21
A)
B)
17 21
C)
23 21 22 E) 21
p II. Si: x + y + z = (2n + 1) ; n 2
ctg x + ctg y + ctg z = ctg x .ctg y .ctg z
6. Si: x+y+z=p y cosx-cosy.cosz=0. Hallar E=ctgy.ctgz A) 1/2 B) 1/4 C) -1/2 D) 1 E) 2 7. En un tringulo ABC, se reduce
tg x.tg y + tg y.tg z + tg x.tg z = 1
E =
A) 1 D) 4
cos( A - B ) cos( B - C ) cos(C - A ) + + senA.senB senB.senC senC.senA
B) 2 C) 3 E) 5
M(o). CARLOS KASELY VILLEGAS ROSALES
CICLO SEMESTRAL 2011
ACADEMIA PREUNIVERSITARIA ALPHA
TRIGONOMETRIA
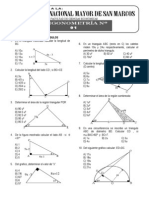
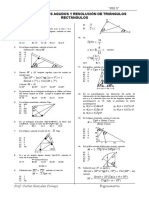
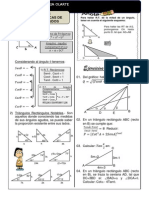
8. De la figura mostrada, calcular: tg A) -5/3 B) -55/3 C) 4/3 D) 55/3 E) 5/3
15. Del grfico, halle: tgq A) 10/11 B) 9/11 C) 12/11 D) 8/11 E) 7/11 16. Calcule el valor de:
9. Un tringulo de ngulos internos , y q, satisface la relacin A) 1/7 D) 4/7
tg a tg b = = 1. Calcule: Tgq. 3 5
B) 7/4 C) -1/2 E) -7/6
E =
A) 1/8 D) 1
tg 14 tg 52 - tg 38 B) 1/6
C) 1/4 E) 1/2
10. En la figura mostrada, calcular: tg A) 5/11 B) 5/3 C) 4/14 D) 55/3 E) 5/14
17. Simplifique la expresin sen (a + b + 75 ) cos (a + b + 75 ) + E = 3 -1 3 +1 A) 2 se n (a + b C)
)
)
)
B) D)
2 cos (a + b 2 se n (a + b
E) 2 cos (a + b
6 cos (a + b
11. Si: x+y+z=2p y cosx=-cosy.cosz. Calcule Tgy.Tgz A) 1/2 B) 1 C) 2 D) 1/4 E) 4 12. Simplifique:
K =
A) D)
3 sen 7 + 3 cos 7 sen 8 - cos 8
B) - 6 C)
6
4 6 3
3 6 4
18. En un tringulo ABC se cumple: 3ctgB-7ctgC=2mtgA 8ctgA-9ctgB=ntgC 10ctgC-2ctgA=ptgB Determinar la relacin que se cumple entre m, n y p. A) 2m-n=2p B) 2m+n+p=1 C) m+n=2p D) 2m+n+p=2 E) 2m+2n+p=1 19. En la figura mostrada calcular Tg A) 1/2 B) 1/6 C) 3/2 D) 2 E) 5/2 20. Si ABCD es un cuadrado, hallar: Tgmxq A) 3/4 B) 1 C) 5/4 D) 4/3 E) 4/5
CICLO SEMESTRAL 2011
E) 5 6
13. Si: ctg x + 2 = tg y Halle: E = A) 1/2 D) -2
2 cos( x + y ) se n ( x + y ) + se n ( x - y )
B) 1 C) 2 E) -1/2
14. Si: a+b=c Simplifique: cos2a+cos2b-2cosa.cosb.cosc A) sen(a-b) B) cosc D) cos(a-b)
M(o). CARLOS KASELY VILLEGAS ROSALES
C) cos2c E) sen2c
You might also like
- Angulos CompuestosDocument3 pagesAngulos CompuestosDenis MoralesNo ratings yet
- Circunferencia Trigonometrica - EjerciciosDocument4 pagesCircunferencia Trigonometrica - EjerciciosYuri Quihui100% (2)
- Ejercicios de SegmentosDocument2 pagesEjercicios de SegmentosJuan Marcavillaca LaurenteNo ratings yet
- T 4 Año Angulo Trigonometrico s1Document3 pagesT 4 Año Angulo Trigonometrico s1Pepe Pesantez RomeroNo ratings yet
- Geometria Anual 2015 PDFDocument15 pagesGeometria Anual 2015 PDFcrisar10100% (1)
- Angulos en Posicion NormalDocument4 pagesAngulos en Posicion NormalRonald Cruz50% (2)
- Anual IntegralDocument5 pagesAnual IntegralJhonatan GoNo ratings yet
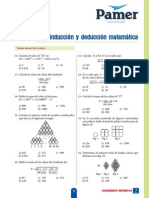
- RM - 5°AÑO - S2 - Induccion y Deduccion Matemática PDFDocument2 pagesRM - 5°AÑO - S2 - Induccion y Deduccion Matemática PDFJuan Carlos Apari Dueñas100% (3)
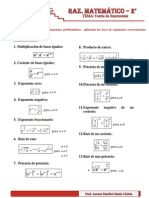
- Teoria de ExponentesDocument4 pagesTeoria de ExponentesMarco Quispe100% (1)
- TrigonometríaDocument22 pagesTrigonometríaCarlos Alberto Colque GarciaNo ratings yet
- Razones TrigonométricasDocument5 pagesRazones TrigonométricasAlex Flores Osorio100% (1)
- Practica de Reducción Al Primer CuadranteDocument4 pagesPractica de Reducción Al Primer CuadranteCarlos Supo88% (16)
- Cepuns 2013-II Semana 03Document8 pagesCepuns 2013-II Semana 03boc_55No ratings yet
- Semestral VallejoDocument12 pagesSemestral VallejoRuyelMasgoCamposNo ratings yet
- División Algebraica - CepasDocument2 pagesDivisión Algebraica - CepasWalterMincholaNo ratings yet
- 06 - Raz MatematicoDocument15 pages06 - Raz MatematicoHenry Araujo Salas0% (1)
- Razones Trigonometricas de Angulos Notables IDocument1 pageRazones Trigonometricas de Angulos Notables IDenis Morales100% (1)
- Razones TrigonometricasDocument4 pagesRazones TrigonometricasEdgar Marquez Laura67% (3)
- Separata TrigonometríaDocument20 pagesSeparata TrigonometríaPercy Torres Avalos KeplerNo ratings yet
- Reducción de Ángulos Al Primer CuadranteDocument4 pagesReducción de Ángulos Al Primer CuadranteEdinsson R. Javier Villanueva100% (1)
- Semana 1 Leyes de Exponentes Ciclo PREUNMSM 2013 IIDocument5 pagesSemana 1 Leyes de Exponentes Ciclo PREUNMSM 2013 IIJimmy Marcelo GuzmanNo ratings yet
- S Matematica IIDocument15 pagesS Matematica IIJustinianoSalazarBarrientosNo ratings yet
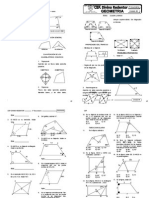
- CuadrilaterosDocument4 pagesCuadrilaterosGino Gonzales100% (1)
- Examen Admision Factorizacion UNMSMDocument2 pagesExamen Admision Factorizacion UNMSMHumberto Coz100% (4)
- Angulos VerticalesDocument4 pagesAngulos Verticalescarlos_kard0322688100% (1)
- Tri Razones - TrigonometricasDocument3 pagesTri Razones - TrigonometricasCesar Augusto Alocen Longoria56% (9)
- IV BIM - 4to. A o - GEOM - Gu¡a 7 - CilindrosDocument5 pagesIV BIM - 4to. A o - GEOM - Gu¡a 7 - CilindrosJuan Taza Villa100% (1)
- PreU - 14 - Analisis Combinatorio IDocument2 pagesPreU - 14 - Analisis Combinatorio IDaniel Pariapaza Sumi100% (1)
- TRIGONOMETRÍA-2°-2018 (Sesiones)Document60 pagesTRIGONOMETRÍA-2°-2018 (Sesiones)Neisser Arturo Soto FernándezNo ratings yet
- Libro Trilce Trigonometria I PDFDocument43 pagesLibro Trilce Trigonometria I PDFArturo CubasNo ratings yet
- CronometriaDocument57 pagesCronometriaJenner Huaman Callirgos83% (18)
- Angulo Trigonometrico IDocument2 pagesAngulo Trigonometrico IDenis MoralesNo ratings yet
- 1 - Triangulos Uni TareaDocument4 pages1 - Triangulos Uni TareaManowar JcNo ratings yet
- R.T de Ángulos AgudosDocument3 pagesR.T de Ángulos AgudosCarlos Alberto Gonzales CornejoNo ratings yet
- Boletin Cesar Vallejo - TrigonometriaDocument15 pagesBoletin Cesar Vallejo - TrigonometriaJesusVasquez67% (3)
- Poligonos EjerciciosDocument3 pagesPoligonos EjerciciosDavid LLontopNo ratings yet
- Relacion de TiempoDocument3 pagesRelacion de TiempodilsonllalleNo ratings yet
- Operaciones Con Fracciones para Segundo Grado de SecundariaDocument4 pagesOperaciones Con Fracciones para Segundo Grado de SecundariaManuel Ruiz BenavidesNo ratings yet
- Sistema de Medida AngularDocument2 pagesSistema de Medida AngularCirculo Es Nivel0% (1)
- 02 Sector CircularDocument4 pages02 Sector Circulararnold cristobalNo ratings yet
- Sectores CircularesDocument5 pagesSectores CircularesEduardoMedinaSequeiros100% (2)
- Miscelánea AritméticaDocument2 pagesMiscelánea AritméticaOMAR FELIPE HERRERA CÁCERES0% (1)
- Cocientes NotablesDocument4 pagesCocientes NotablesLuis Franklin Mendoza Floreano0% (1)
- Semana 05 Álgebra Cepuns 2012-III Productos NotablesDocument9 pagesSemana 05 Álgebra Cepuns 2012-III Productos NotablesGuillermo Salazar Castillo0% (1)
- 11 Operadores MatematicosDocument4 pages11 Operadores MatematicosAnonymous 8pLnCcsppNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument128 pagesPDFFernando MezaNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios de SegmentosDocument1 pageEjercicios de SegmentosLuis Miguel RV0% (1)
- Producto Notables VeranoDocument3 pagesProducto Notables VeranoAlvaro Ore EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Habilidad OperativaDocument2 pagesHabilidad OperativaMATE PRÁCTICANo ratings yet
- Guia2 (Suma y Diferencia)Document4 pagesGuia2 (Suma y Diferencia)Carlos SupoNo ratings yet
- Trigonometria Ident Trigon de Arcos CompuestosDocument3 pagesTrigonometria Ident Trigon de Arcos Compuestosmarco leonNo ratings yet
- Propiedades de Las Razones TrigonometricasDocument4 pagesPropiedades de Las Razones TrigonometricasAna Maria Atuncar Peña0% (1)
- 09 Identidades Trigonometricas de Angulos CompuestosDocument9 pages09 Identidades Trigonometricas de Angulos CompuestosOscar Pier Delgado PezoNo ratings yet
- Tema 11Document10 pagesTema 11Totti Di Franchesco PelaezNo ratings yet
- Trigonometria Semana 6,7,8,9,10,11,12Document14 pagesTrigonometria Semana 6,7,8,9,10,11,12AndreeVillegasFarfan100% (1)
- Trigo.10 Ident. Trigon - Arc CompuestosDocument4 pagesTrigo.10 Ident. Trigon - Arc CompuestosJulio César GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Trig Verano (Reparado)Document11 pagesTrig Verano (Reparado)Juan Carlos Muñoz De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Guia 6 - Propiedades de Las Razones TrigonométricasDocument3 pagesGuia 6 - Propiedades de Las Razones TrigonométricasJuan Taza Villa0% (1)
- Trigonometria PrepaDocument9 pagesTrigonometria PrepaZOSIMO ZANABRIA OLARTENo ratings yet
- Logaritmos - Teoría y ProblemasDocument3 pagesLogaritmos - Teoría y Problemascarlos_kard0322688No ratings yet
- Trigonometria CEPREVIDocument69 pagesTrigonometria CEPREVIjessica58% (12)
- Guia 03 - Productos NotablesDocument3 pagesGuia 03 - Productos Notablescarlos_kard0322688No ratings yet
- Polinomios - Teoría y ProblemasDocument2 pagesPolinomios - Teoría y Problemascarlos_kard0322688No ratings yet
- Guia 05 - Cocientes NotablesDocument2 pagesGuia 05 - Cocientes Notablescarlos_kard0322688No ratings yet
- Balotario Algebra 1º Sec.Document3 pagesBalotario Algebra 1º Sec.carlos_kard0322688No ratings yet
- Productos Notables RUBIÑOS PDFDocument10 pagesProductos Notables RUBIÑOS PDFcarlos_kard0322688No ratings yet
- Teoría de Exponentes - Teoría y ProblemasDocument2 pagesTeoría de Exponentes - Teoría y Problemascarlos_kard0322688No ratings yet
- División Algebraica - Teoría y ProblemasDocument2 pagesDivisión Algebraica - Teoría y Problemascarlos_kard0322688No ratings yet
- Leyes de ExponentesDocument4 pagesLeyes de Exponentescarlos_kard0322688100% (1)
- Movimientos en El Plano PDFDocument18 pagesMovimientos en El Plano PDFferney10No ratings yet
- Practica de La Flor OriginalDocument2 pagesPractica de La Flor Originalcarlos_kard0322688No ratings yet
- Examen 5º - OlimpiadaDocument2 pagesExamen 5º - Olimpiadacarlos_kard0322688No ratings yet
- Examen 4º - OlimpiadaDocument2 pagesExamen 4º - Olimpiadacarlos_kard0322688No ratings yet
- Guia 01 - Ángulo Trigonométrico - Full PracticaDocument2 pagesGuia 01 - Ángulo Trigonométrico - Full Practicacarlos_kard0322688100% (1)
- Examen 1º - OlimpiadaDocument2 pagesExamen 1º - Olimpiadacarlos_kard0322688No ratings yet
- Examen 2º - OlimpiadaDocument2 pagesExamen 2º - Olimpiadacarlos_kard0322688No ratings yet
- 03 - Razones Trigonométricas de Ángulos Agudos IDocument2 pages03 - Razones Trigonométricas de Ángulos Agudos Icarlos_kard032268867% (3)
- Semana 1 - Conceptos Básicos de EstadísticaDocument3 pagesSemana 1 - Conceptos Básicos de Estadísticacarlos_kard0322688100% (1)
- Simulacro 2°Document12 pagesSimulacro 2°carlos_kard0322688No ratings yet
- Ecuaciones TrigonometricasDocument4 pagesEcuaciones Trigonometricascarlos_kard0322688No ratings yet
- Educación Bancaria VS Educación LiberadoraDocument2 pagesEducación Bancaria VS Educación Liberadoracarlos_kard0322688No ratings yet
- Cabeza FetalDocument12 pagesCabeza Fetalcarlos_kard0322688No ratings yet
- HIDRAULICADocument3 pagesHIDRAULICAcarlos_kard0322688No ratings yet