Professional Documents
Culture Documents
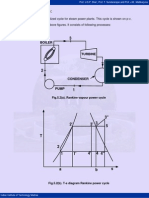
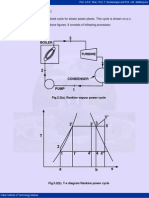
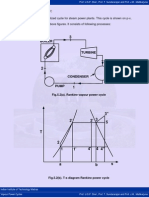
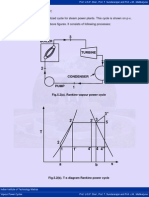
Fig.5.5 (A) - P-V Diagram of Modified Rankine Cycle
Uploaded by
api-3830954Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fig.5.5 (A) - P-V Diagram of Modified Rankine Cycle
Uploaded by
api-3830954Copyright:
Available Formats
Vapour Power Cycles Prof. U.S.P. Shet , Prof. T. Sundararajan and Prof. J.M .
Mallikarjuna
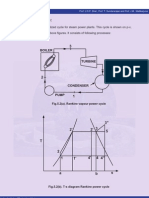
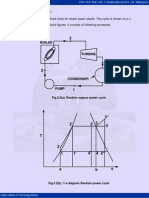
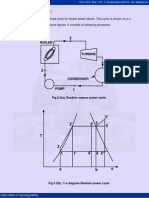
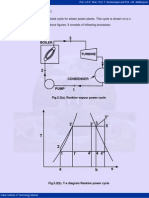
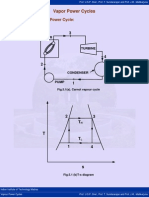
5.5 Modified Rankine Cycle:
1 2
4 3
6
Fig.5.5(a). p-v diagram of modified Rankine cycle
2
T
1 5
4 6 3
s
Fig.5.5(b). T-s diagram of modified Rankine cycle
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
Vapour Power Cycles Prof. U.S.P. Shet , Prof. T. Sundararajan and Prof. J.M . Mallikarjuna
Process 1-2 represents the admission of high pressure steam into the engine cylinder,
process 2-3 is the reversible adiabatic expansion of steam in the cylinder and process
3-4 is the exhaust of steam into condenser. Net work done is represented by the area 1-
2-3-4-1.
Observe that the area 3-6-5 is very small and in order to obtain this small work, the
cylinder volume must be increased from v6 to v3.This makes cylinder very bulky. For this
reason, the expansion process is terminated at point 5. So that indicator diagram
becomes 1-2-5-6-4. The work lost is small but there is large saving in cylinder volume.
Process 5-6 represents the release of steam into the condenser, thus causing the
cylinder pressure to drop from P5 to P6. Process 6-4 is the exhaust of steam at constant
pressure. Cycle 1-2-5-6-4 is called as the “modified Rankine cycle”.
Thermal Efficiency:
Considering the unit mass of working fluid,
Heat supplied = h 2 - h1
Net workdone = {w 2-5 + w 5-6 + w 4-1 }
6
= ( h 2 - h 5 ) - ∫ vdp + ( h 4 - h1 )
5
= ( h 2 - h 5 ) + v5 ( p5 - p6 ) + ( h 4 - h1 )
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
Vapour Power Cycles Prof. U.S.P. Shet , Prof. T. Sundararajan and Prof. J.M . Mallikarjuna
v5 = specific volume of steam at state 5.
Net workdone (h 2 - h 5 ) + v5 (p5 - p6 ) + (h 4 - h1 )
ηth = =
Heat sup plied (h 2 - h1 )
If pump work is neglected, then h 4 ≈ h1
(h 2 - h 5 ) + v5 (p5 - p6 )
ηth =
(h 2 - h 4 )
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
You might also like
- Phase Equilibrium in Mixtures: International Series of Monographs in Chemical EngineeringFrom EverandPhase Equilibrium in Mixtures: International Series of Monographs in Chemical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- 5 Modified Rankine CycleDocument3 pages5 Modified Rankine CycleMohammad Mussavvir100% (1)
- Rankine CycleDocument4 pagesRankine CycleyuvrajsinghvloggingNo ratings yet
- Basic Thermodynamic CyclesDocument4 pagesBasic Thermodynamic Cyclesapi-3830954No ratings yet
- 6 Deviation of Actual Cycle From Ideal CycleDocument5 pages6 Deviation of Actual Cycle From Ideal CyclecaptainhassNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Rankine Cycle:: BoilerDocument4 pages5.2 Rankine Cycle:: BoilerAruni KantNo ratings yet
- 2 - RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 - RankinecyclekenankerimNo ratings yet
- 2 Rankinecycle-2Document4 pages2 Rankinecycle-2Anonymous gS6JtOfaNo ratings yet
- 2 RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 RankinecycleAmit PandeyNo ratings yet
- 2 RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 RankinecycleMantript SinghNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Rankine Cycle:: BoilerDocument4 pages5.2 Rankine Cycle:: BoilerVidyut KumarNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Rankine Cycle:: BoilerDocument4 pages5.2 Rankine Cycle:: BoilerSasi GunaNo ratings yet
- 2 RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 Rankinecyclesoubhadra nagNo ratings yet
- 2 RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 RankinecycleJohn FredyNo ratings yet
- 2 RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 RankinecycleSami UllahNo ratings yet
- 2 - RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 - RankinecycleAnonymous BHBWQIcClNo ratings yet
- 2 - RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 - RankinecycleAtanu Brainless RoyNo ratings yet
- 2 - RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 - RankinecyclePrasad KhatiNo ratings yet
- 2 - RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 - RankinecyclePrasad KhatiNo ratings yet
- 2 - RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 - RankinecycletpplantNo ratings yet
- 2 - RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 - RankinecycleamdevaNo ratings yet
- 2 - RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 - Rankinecycledurga345No ratings yet
- 2 - RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 - RankinecycleRishabh VermaNo ratings yet
- Applied Termo 122424Document4 pagesApplied Termo 122424rjrahul25No ratings yet
- 2 - RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 - RankinecycleamdevaNo ratings yet
- 2 - RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 - RankinecycleamdevaNo ratings yet
- PVT Diagram Rankine CycleDocument4 pagesPVT Diagram Rankine CycleEnny Rosmawar PurbaNo ratings yet
- 2 - RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 - RankinecycleRishabh VermaNo ratings yet
- Rankine CycleDocument4 pagesRankine Cyclerishav43No ratings yet
- MSBVCDocument3 pagesMSBVCapi-3830954No ratings yet
- Molier Diagram ConceptDocument37 pagesMolier Diagram ConceptMONER MANUSNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbines (Rankine Cycle) : Dr. S. SaboorDocument25 pagesSteam Turbines (Rankine Cycle) : Dr. S. SaboorHrithik RathiNo ratings yet
- 11 Mercury Steam Binary VCDocument3 pages11 Mercury Steam Binary VCSekhar Babu PendyalaNo ratings yet
- محطات ٥Document11 pagesمحطات ٥عبير ابوصالحهNo ratings yet
- SAT # 13 (Thermal Physics) - Paper (E+H) PDFDocument18 pagesSAT # 13 (Thermal Physics) - Paper (E+H) PDFTanvir NosaNo ratings yet
- ME411 (Ideal Models of Engine Cycles) (160215)Document13 pagesME411 (Ideal Models of Engine Cycles) (160215)Eftaykhar AhmedNo ratings yet
- First Checking: Mass Balance Checking in TurbineDocument17 pagesFirst Checking: Mass Balance Checking in TurbineTrisha Mae BelmonteNo ratings yet
- Principles of Energy Conversion Homework #4 February 12, 2018Document5 pagesPrinciples of Energy Conversion Homework #4 February 12, 2018Kishore KrishNo ratings yet
- 2 Carnot CycleDocument6 pages2 Carnot CycleSamujawal Kumar SumanNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 - Reservoir Fluid Flow Semisteady FlowDocument9 pagesChapter-3 - Reservoir Fluid Flow Semisteady FlowOmer IkhlasNo ratings yet
- Reheat RegenerativeDocument8 pagesReheat RegenerativeBenjamin MabuteNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermodynamics C211 PDFDocument173 pagesApplied Thermodynamics C211 PDFSubham AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Pressure Build-Up Analysis, Variable-Rate CaseDocument5 pagesPressure Build-Up Analysis, Variable-Rate CaseBolsec14No ratings yet
- Excercise2-Fluid DynamicsDocument3 pagesExcercise2-Fluid DynamicsShabana ferozNo ratings yet
- 7 Limited Pressure CycleDocument4 pages7 Limited Pressure CyclecaptainhassNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Rankine Cycle With FWHS: Engineering Solution To Pure Thoughts .. .Document36 pagesAnalysis of Rankine Cycle With FWHS: Engineering Solution To Pure Thoughts .. .Stage2 C&I ShiftNo ratings yet
- Bell Coleman CycleDocument5 pagesBell Coleman CycleAshara Aakash100% (2)
- Cet-I Unit 5Document29 pagesCet-I Unit 5mathanm1101No ratings yet
- Performance of Steam Turbine With Feedwater HeatersDocument42 pagesPerformance of Steam Turbine With Feedwater Heatersذال شراحبئيلNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Rankine Cycle With FWHS: P M V Subbarao Professor Mechanical Engineering Department IitdelhiDocument36 pagesAnalysis of Rankine Cycle With FWHS: P M V Subbarao Professor Mechanical Engineering Department Iitdelhikidanemariam teseraNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Rankine Cycle With FWHS: P M V Subbarao Professor Mechanical Engineering Department IitdelhiDocument36 pagesAnalysis of Rankine Cycle With FWHS: P M V Subbarao Professor Mechanical Engineering Department IitdelhiBintang Lepas KendaliNo ratings yet
- Project 1 - Parsing NASA Thermodynamic Data - Skill-LyncDocument9 pagesProject 1 - Parsing NASA Thermodynamic Data - Skill-LyncShlok DixitNo ratings yet
- Session 1 - Basic ThermodynamicsDocument30 pagesSession 1 - Basic ThermodynamicsArjun Mac100% (1)
- 4 Capacity of Steam Power PlantDocument4 pages4 Capacity of Steam Power PlantcaptainhassNo ratings yet
- COFSPPDocument4 pagesCOFSPPapi-3830954No ratings yet
- Limited Pressure CycleDocument4 pagesLimited Pressure Cyclecasu19No ratings yet
- Group 15. Mechanics of Fluids: Vocabulary of Mechanics in Five Languages: English/German/French/Polish/Russian, Vol. 2From EverandGroup 15. Mechanics of Fluids: Vocabulary of Mechanics in Five Languages: English/German/French/Polish/Russian, Vol. 2Rating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (3)
- MTOFHADocument1 pageMTOFHAapi-3830954No ratings yet
- OFWHDocument2 pagesOFWHapi-3830954No ratings yet
- MSRCDocument3 pagesMSRCapi-3830954No ratings yet
- MSBVCDocument3 pagesMSBVCapi-3830954No ratings yet
- CVPCDocument2 pagesCVPCapi-3830954No ratings yet
- COFSPPDocument4 pagesCOFSPPapi-3830954No ratings yet
- Basic ThermodynamicsDocument284 pagesBasic Thermodynamicsikneo100% (10)
- CFWHDocument2 pagesCFWHapi-3830954No ratings yet
- Chemical Cleaning Procedure of Boiler Pressure Part R4Document15 pagesChemical Cleaning Procedure of Boiler Pressure Part R4Halim IrhamiNo ratings yet
- Carryover in BoilerDocument2 pagesCarryover in Boilershan877No ratings yet
- W1 Energy and Energy BalanceDocument32 pagesW1 Energy and Energy BalanceFatinnnnnnNo ratings yet
- InTech-Fundamentals of Paper Drying Theory and Application From Industrial PerspectiveDocument49 pagesInTech-Fundamentals of Paper Drying Theory and Application From Industrial PerspectiveSushil MeshramNo ratings yet
- Humidifier - ManualDocument66 pagesHumidifier - Manualaddipolli100% (1)
- Steam Purity of 500 MWDocument1 pageSteam Purity of 500 MWLipika Ghosh BiswasNo ratings yet
- Auxiliary BoilerDocument7 pagesAuxiliary BoilerYasser BayoumyNo ratings yet
- SSMTGuide PDFDocument77 pagesSSMTGuide PDFChawanakorn NontapaNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Development of The Kamojang Geothermal Field: GeothermicsDocument9 pagesSustainable Development of The Kamojang Geothermal Field: Geothermicsmiftah hijriawanNo ratings yet
- Frequently Asked Questions: GeneralDocument3 pagesFrequently Asked Questions: GeneralRahul MoottolikandyNo ratings yet
- DR Naushad Forbes & MR Satyadeo Purohit, Forbes MarshallDocument16 pagesDR Naushad Forbes & MR Satyadeo Purohit, Forbes MarshallGaurav DahakeNo ratings yet
- Handbook VaporDocument435 pagesHandbook VaporRichardy GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Essential Oils - Small-Scale ProductionDocument7 pagesEssential Oils - Small-Scale ProductionKroya HunNo ratings yet
- Control Valve - DRAG 100DDocument11 pagesControl Valve - DRAG 100Damer_arauf100% (15)
- Controlling Steam HeatersDocument12 pagesControlling Steam HeatersSreedhar Patnaik.MNo ratings yet
- Curriculum of B. Tech. (Mechanical Engineering)Document36 pagesCurriculum of B. Tech. (Mechanical Engineering)KharaPrasadNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine Cycle and PerformanceDocument43 pagesSteam Turbine Cycle and PerformanceDivyank Arya100% (1)
- A10 Steam Turb - CC Plant Webnar (Rev 4-1-16)Document121 pagesA10 Steam Turb - CC Plant Webnar (Rev 4-1-16)FlamingorosadoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3. Steam Power Plant Cycle PDFDocument31 pagesChapter 3. Steam Power Plant Cycle PDFJohn Carlo LEBRILLANo ratings yet
- Piping Engineering Questions - Piping Courses - Piping Design InstituteDocument4 pagesPiping Engineering Questions - Piping Courses - Piping Design InstituteGemailNo ratings yet
- Assignment For Day 2Document7 pagesAssignment For Day 2Aldrin Marc DaquizNo ratings yet
- Material Chap 7Document24 pagesMaterial Chap 7chemicaly12No ratings yet
- SurgeryDocument93 pagesSurgerysalah subbahNo ratings yet
- PRESSURE Relief Valve EXCEL SHEETSDocument9 pagesPRESSURE Relief Valve EXCEL SHEETSsathishNo ratings yet
- 2501-General Instructions For Thermal DesignDocument12 pages2501-General Instructions For Thermal DesignfarooqkhanerNo ratings yet
- Enhancement Method'S On Boiler EfficiencyDocument16 pagesEnhancement Method'S On Boiler Efficiencysidan magnaNo ratings yet
- Flyer Int Steam Tables Iphone Ipad IpodDocument6 pagesFlyer Int Steam Tables Iphone Ipad IpodNguyen Duc DungNo ratings yet
- Vijay Resume QECDocument6 pagesVijay Resume QECeimanoNo ratings yet
- SOP of Sanitation of PW SystemDocument6 pagesSOP of Sanitation of PW Systemanon_350461302100% (1)
- Causes of Vibration For Steam TurbineDocument21 pagesCauses of Vibration For Steam TurbineAugustine Owo Ukpong100% (6)