Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Essay For Effects of Force
Uploaded by
Cheng NieOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Essay For Effects of Force
Uploaded by
Cheng NieCopyright:
Available Formats
2.
5: The effects of Force (Essay)
1a) i) The shot-put has weigh and the weigh is a force [1]
It is the effect of this force changing the shape of the ground when the shot-put is
landed [1]
ii) The larger mass of the shot-put, the greater diameter of the hole [1]
b) i) Normal Reaction [1]
Weight [1]
ii) The block does not move because the applied force is not greater than the frictional
force between the table and the block [1]
The value of the frictional force is 5N
iii) Constant velocity, acceleration = 0 [1]
F = ma = m (0)
The resultant force is zero [1]
Resultant force = 8- f = 0,
f = frictional force = 8N
c) i) Objective: To find the relationship between force and acceleration of an object [1]
ii) Inference: The acceleration of an object with constant mass depend on the force applied
to the object [1]
iii) Hypothesis: The acceleration of the object is directly proportional to the applied force
[1]
iv) - Manipulated variable: Force
- Responding variable: Acceleration of the trolley
- Fixed variable: Mass of the trolley [2]
v) Definition of variables in operation:
- 1 unit force = the force used to stretch an elastic string by 2cm
- The acceleration of trolley is calculated from the ticker tape [1]
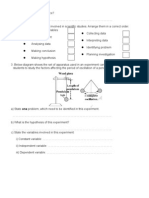
vi) Apparatus: Transformer, ticker-timer, ticker-tape, elastic string, trolley and truck [1]
vii) Procedure:
1. The apparatus is set up as shown in the diagram.
2. Ticker-timer is switched on.
3. The trolley is pulled down by stretching the elastic string to 2cm
4. The experiment is repeated by stretching 2 elastic strings together and then 3
elastic strings with the same extensions.
5. The acceleration, a is calculated from the ticker-tape produced [1]
viii)Analysis of data:
- Tabulate the results as shown - A graph of acceleration against force is plotted
a / cm-2
Force, F/N Acceleration, a
/ cms-2
1 unit force
2 unit force
3 unit force F/N
Conclusion: a α F , The acceleration is directly proportional to the force
You might also like
- Phy 3Document6 pagesPhy 3mathiasshereni243No ratings yet
- G10 Ch03 Test 2024 01 AnsDocument2 pagesG10 Ch03 Test 2024 01 AnsmethaethkNo ratings yet
- 3-Dynamics (Newton's Laws of Motion)Document62 pages3-Dynamics (Newton's Laws of Motion)王玟靖No ratings yet
- Physics MoreDocument5 pagesPhysics Moremathiasshereni243No ratings yet
- Here are the answers to the multiple choice questions:1. c 2. a3. c 4. a5. c6. d7. b8. a9. c10. b11. a12. b13. dDocument23 pagesHere are the answers to the multiple choice questions:1. c 2. a3. c 4. a5. c6. d7. b8. a9. c10. b11. a12. b13. dAkash GuptaNo ratings yet
- 11 Holiday HomeworkDocument199 pages11 Holiday Homeworksupriyarama413No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes For Section 15-1Document24 pagesLecture Notes For Section 15-1Daniel HaiqalNo ratings yet
- Revision Test 1 Set 2Document7 pagesRevision Test 1 Set 2hadassahhadidNo ratings yet
- PHY 111 Lecture Note 21-11-2023Document54 pagesPHY 111 Lecture Note 21-11-2023TimmyNo ratings yet
- Ch15 - 1 - Impulse&MomentumDocument19 pagesCh15 - 1 - Impulse&MomentumJacinta SamalengiNo ratings yet
- 5 Forces: Pages 69-72 Exam Practice QuestionsDocument5 pages5 Forces: Pages 69-72 Exam Practice QuestionsKoe ChoNo ratings yet
- W5 Kinetics of Particle Impulse Momentum (Ch15)Document74 pagesW5 Kinetics of Particle Impulse Momentum (Ch15)Shah KhanNo ratings yet
- Revision For Test 1 (SET 2) Answer All Question Within 1 Hour. Total Marks Is 40 MarksDocument4 pagesRevision For Test 1 (SET 2) Answer All Question Within 1 Hour. Total Marks Is 40 MarkshadassahhadidNo ratings yet
- 3 - 6. Forces and DynamicsDocument6 pages3 - 6. Forces and Dynamicshavertz291aNo ratings yet
- Physics Concepts and CalculationsDocument10 pagesPhysics Concepts and CalculationsannahiazNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Kinetics of A Particle-Impulse and MomentumDocument72 pagesModule 4 Kinetics of A Particle-Impulse and MomentumHuy VũNo ratings yet
- PRINCIPLE OF LINEAR IMPULSE AND MOMENTUM EXPLAINEDDocument21 pagesPRINCIPLE OF LINEAR IMPULSE AND MOMENTUM EXPLAINEDNikkei Pfeiffer TadiliNo ratings yet
- 17. RM 09 - Physics for Engineers (Part 02)Document2 pages17. RM 09 - Physics for Engineers (Part 02)usueNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 APHY 111: DynamicsDocument23 pagesGeneral Physics 1 APHY 111: DynamicsJoanna PanayiNo ratings yet
- Physics 111Document59 pagesPhysics 111rolandmichael461No ratings yet
- 4003 Physics Section Revision Guide-1Document31 pages4003 Physics Section Revision Guide-1Noel MakambaNo ratings yet
- FORCES OF FRICTION: The Static and Kinetic: Laboratory No. 3Document12 pagesFORCES OF FRICTION: The Static and Kinetic: Laboratory No. 3Random JaiNo ratings yet
- Engineering Dynamics BEM2013/EM210 Chapter 15 Kinetics of A ParticleDocument21 pagesEngineering Dynamics BEM2013/EM210 Chapter 15 Kinetics of A ParticlemahrusNo ratings yet
- Dynamics: Type of ForcesDocument18 pagesDynamics: Type of ForcesheheheNo ratings yet
- Principle of Linear Impulse and MomentumDocument19 pagesPrinciple of Linear Impulse and MomentumCARLUCASPANNo ratings yet
- AP Physics Test ReviewDocument21 pagesAP Physics Test ReviewAnish KalappaNo ratings yet
- G10 Ch05 Test 2024 01 AnsDocument2 pagesG10 Ch05 Test 2024 01 AnsmethaethkNo ratings yet
- Section 15-1 Dynamics HibbelerDocument17 pagesSection 15-1 Dynamics Hibbelershamik1978No ratings yet
- 2.5 Effects of A ForceDocument30 pages2.5 Effects of A ForcekhodijahaminNo ratings yet
- Physics Forces Secondary3Document23 pagesPhysics Forces Secondary3SoniaAlexNo ratings yet
- Force, Mass and MomentumDocument16 pagesForce, Mass and MomentumAlberto BenitoNo ratings yet
- Chap 05Document152 pagesChap 05noscribdyoucantNo ratings yet
- OH - DSE - 2025-PHY X1 PHY - EnergyDocument16 pagesOH - DSE - 2025-PHY X1 PHY - EnergySeanNo ratings yet
- Force AnalysisDocument152 pagesForce AnalysisWang Han Zhu100% (1)
- Speed, Velocity and Acceleration - 1Document114 pagesSpeed, Velocity and Acceleration - 1qussai salahNo ratings yet
- Impulse Momentum AnalysisDocument56 pagesImpulse Momentum Analysisiwhy_No ratings yet
- Particle Dynamics (11th JK) WADocument48 pagesParticle Dynamics (11th JK) WAParijat SutradharNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes For Section 15-1Document19 pagesLecture Notes For Section 15-1JersonFerrerasPuaNo ratings yet
- 6B Circular Motion & Gravitation 2020-2021Document46 pages6B Circular Motion & Gravitation 2020-2021RandominicNo ratings yet
- Forces and Motion II: 5.1 The Important StuffDocument28 pagesForces and Motion II: 5.1 The Important StuffSclaffenNo ratings yet
- Physics: Chapter 2 (F4) Linear MotionDocument4 pagesPhysics: Chapter 2 (F4) Linear MotionKai YuanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document9 pagesChapter 5Keith Alfred GargarNo ratings yet
- Practice Test-1 Class: Xi Subject: Physics Physical World (Chapter-1) Units & Measurement (Chapter-2)Document21 pagesPractice Test-1 Class: Xi Subject: Physics Physical World (Chapter-1) Units & Measurement (Chapter-2)Sunil KumarNo ratings yet
- Friction Lab ReportDocument51 pagesFriction Lab ReportFang Ying Tee78% (23)
- 2nd Assess Y9 2023 KSSDocument7 pages2nd Assess Y9 2023 KSSAhsan AhmedNo ratings yet
- IplanelabDocument9 pagesIplanelabromwamaNo ratings yet
- Linear Momentum & Impulse ConservationDocument17 pagesLinear Momentum & Impulse ConservationChrise RajNo ratings yet
- Serway_ISM_V1_Chapter_4_AnswersDocument10 pagesSerway_ISM_V1_Chapter_4_AnswersShilpi Sandeep TripsNo ratings yet
- ProblemSet 2 SolutionsDocument6 pagesProblemSet 2 SolutionsnormanNo ratings yet
- Kinetics of Particle Impulse and Momentum Edited - ClassDocument35 pagesKinetics of Particle Impulse and Momentum Edited - ClassLebogang TlhagwaneNo ratings yet
- Scee 271 15 Sec 2 4 PDFDocument38 pagesScee 271 15 Sec 2 4 PDFSyah ReelNo ratings yet
- A Level PhysicsDocument7 pagesA Level PhysicsshmaNo ratings yet
- Newton's First LawDocument18 pagesNewton's First LawjoeNo ratings yet
- PHY 101 Quiz #16 SolutionsDocument8 pagesPHY 101 Quiz #16 SolutionsKhalila KhalishaNo ratings yet
- January 2008 QP - M1 OCRDocument4 pagesJanuary 2008 QP - M1 OCRMohammad Abdul OhabNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Newton's Laws and Motion: I. History of Explaining MotionDocument16 pagesChapter 4 Newton's Laws and Motion: I. History of Explaining Motionapi-19790880No ratings yet
- Impulse-Momentum TheoremDocument24 pagesImpulse-Momentum TheoremMary Joy RosarioNo ratings yet
- SLG 13.3.2 Simple Machines, Mechanical Advantage and EfficiencyDocument6 pagesSLG 13.3.2 Simple Machines, Mechanical Advantage and EfficiencyKifrannwNo ratings yet
- Final Exam - Segamat Paper 1Document6 pagesFinal Exam - Segamat Paper 1Cheng NieNo ratings yet
- Science concepts explainedDocument8 pagesScience concepts explainedCheng NieNo ratings yet
- Form 1 ScienceDocument4 pagesForm 1 ScienceCheng NieNo ratings yet
- Form 1 ScienceDocument7 pagesForm 1 ScienceCheng NieNo ratings yet
- Form 1 ScienceDocument4 pagesForm 1 ScienceCheng NieNo ratings yet
- Form 1 ScienceDocument2 pagesForm 1 ScienceCheng NieNo ratings yet
- Form 1 ScienceDocument4 pagesForm 1 ScienceCheng NieNo ratings yet
- Measure Volume Irregular ObjectsDocument4 pagesMeasure Volume Irregular ObjectsCheng NieNo ratings yet
- Review VocabularyDocument4 pagesReview VocabularyCheng NieNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Chapter 1Document17 pagesForm 5 Chapter 1Satya ViknesrajNo ratings yet
- Impact of Bap and Iaa in Various Media Concentrations and Growth Analysis of Eucalyptus CamaldulensisDocument5 pagesImpact of Bap and Iaa in Various Media Concentrations and Growth Analysis of Eucalyptus CamaldulensisInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document25 pagesLecture 4ptnyagortey91No ratings yet
- Clogging in Permeable (A Review)Document13 pagesClogging in Permeable (A Review)Chong Ting ShengNo ratings yet
- Employee Engagement A Case Study at IVRCL-1Document7 pagesEmployee Engagement A Case Study at IVRCL-1Anonymous dozzql7znKNo ratings yet
- Afu 08504 - International Capital Bdgeting - Tutorial QuestionsDocument4 pagesAfu 08504 - International Capital Bdgeting - Tutorial QuestionsHashim SaidNo ratings yet
- Standard Deviation IntroductionDocument3 pagesStandard Deviation IntroductionShyam ShresthaNo ratings yet
- 2019 May Chronicle AICFDocument27 pages2019 May Chronicle AICFRam KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Liber Chao (Final - Eng)Document27 pagesLiber Chao (Final - Eng)solgrae8409100% (2)
- Cinema 4D ShortcutsDocument8 pagesCinema 4D ShortcutsAnonymous 0lRguGNo ratings yet
- Basf Masterseal 725hc TdsDocument2 pagesBasf Masterseal 725hc TdsshashiNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication Quantization OverviewDocument5 pagesDigital Communication Quantization OverviewNiharika KorukondaNo ratings yet
- Yanmar America publication listing for engine parts, service, and operation manualsDocument602 pagesYanmar America publication listing for engine parts, service, and operation manualsEnrique Murgia50% (2)
- Cells in The Urine SedimentDocument3 pagesCells in The Urine SedimentTaufan LutfiNo ratings yet
- Postnatal Assessment: Name Date: Age: D.O.A: Sex: Hospital: Marital Status: IP .NoDocument11 pagesPostnatal Assessment: Name Date: Age: D.O.A: Sex: Hospital: Marital Status: IP .NoRadha SriNo ratings yet
- Development of Rsto-01 For Designing The Asphalt Pavements in Usa and Compare With Aashto 1993Document14 pagesDevelopment of Rsto-01 For Designing The Asphalt Pavements in Usa and Compare With Aashto 1993pghasaeiNo ratings yet
- C Exam13Document4 pagesC Exam13gauravsoni1991No ratings yet
- Give Five Examples Each of Nature Having Reflection Symmetry and Radial Symmetry Reflection Symmetry Radial Symmetry Butterfly StarfishDocument12 pagesGive Five Examples Each of Nature Having Reflection Symmetry and Radial Symmetry Reflection Symmetry Radial Symmetry Butterfly StarfishANNA MARY GINTORONo ratings yet
- Distinguish Between Tax and FeeDocument2 pagesDistinguish Between Tax and FeeRishi Agarwal100% (1)
- Overview of Quality Gurus Deming, Juran, Crosby, Imai, Feigenbaum & Their ContributionsDocument11 pagesOverview of Quality Gurus Deming, Juran, Crosby, Imai, Feigenbaum & Their ContributionsVenkatesh RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Land Measurement in PunjabDocument3 pagesLand Measurement in PunjabJunaid Iqbal33% (3)
- Environmental Technology Syllabus-2019Document2 pagesEnvironmental Technology Syllabus-2019Kxsns sjidNo ratings yet
- Elmeasure Solenoid Ates CatalogDocument12 pagesElmeasure Solenoid Ates CatalogSEO BDMNo ratings yet
- Rhodes Motion For Judicial NoticeDocument493 pagesRhodes Motion For Judicial Noticewolf woodNo ratings yet
- WhatsoldDocument141 pagesWhatsoldLuciana KarajalloNo ratings yet
- Amul ReportDocument48 pagesAmul ReportUjwal JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Ground Water Resources of Chennai DistrictDocument29 pagesGround Water Resources of Chennai Districtgireesh NivethanNo ratings yet
- DSE61xx Configuration Suite Software Manual PDFDocument60 pagesDSE61xx Configuration Suite Software Manual PDFluisNo ratings yet
- PC November 2012Document50 pagesPC November 2012bartekdidNo ratings yet
- Restructuring Egypt's Railways - Augst 05 PDFDocument28 pagesRestructuring Egypt's Railways - Augst 05 PDFMahmoud Abo-hashemNo ratings yet
- BMS Technical ManualDocument266 pagesBMS Technical Manualiago manziNo ratings yet