Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SAP SD Topics
Uploaded by
chandra_kumarbr0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views11 pagesThis document provides an overview of SAP Sales and Distribution (SD) module. It discusses the core components and functions of SD including master data, sales processes, organizational structures, and process flows. Key areas covered are sales, shipping, billing, pricing, distribution channels, divisions, and integration with other SAP modules.
Original Description:
Original Title
SAP SD topics
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of SAP Sales and Distribution (SD) module. It discusses the core components and functions of SD including master data, sales processes, organizational structures, and process flows. Key areas covered are sales, shipping, billing, pricing, distribution channels, divisions, and integration with other SAP modules.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views11 pagesSAP SD Topics
Uploaded by
chandra_kumarbrThis document provides an overview of SAP Sales and Distribution (SD) module. It discusses the core components and functions of SD including master data, sales processes, organizational structures, and process flows. Key areas covered are sales, shipping, billing, pricing, distribution channels, divisions, and integration with other SAP modules.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
SAP SD -
1. Sales and Distribution (SD) Overview
2. FI SD Financial Sales & Accounting Distribution MM CO Materials Controlling
Mgmt. PP AM R/3 Production Fixed Assets Planning Mgmt. SM EC Service
Enterprise Manage- Controlling Integrated Solution QM ment PS Quality Client /
Server Project Management System PM WF Plant Maintenance Open Systems
Workflow HR IS Human Industry Resources Solutions
3. SD • Mechanisms to execute the business processes used in the selling, shipping and
billing of products and services • Tightly coupled data flow to the other SAP modules
— Integration • Flexible and robust functionality that is tailored through configuration
4. SD Components Master Foreign Data Trade Sales Sales Sales Info Support System
Shipping Billing Transportation
5. SD Overview — Master Data • Detailed information about customers, materials and
business partners • Flexible data structures that support the business environment •
Specialized master data to support sales order processing
6. SD Overview — Sales Support • Provides the functionality to support the staff
involved in business development and customer service processes • Primary functions
– Sales Prospects – Contact Persons – Competitors and Competitive Products – Sales
Activities – Direct Marketing
7. SD Overview — Sales • Sampling of functions • Primary base for – Inquiries &
Quotes customer order – Sales Orders management – Returns Highly customizable • –
Contracts & Scheduling Sophisticated pricing • Agreements – Consignment
Integrated ATP • – Rush Orders & Cash Sales Integrated credit • – Back Orders &
Subsequent management Deliveries – Credit & Debit Memo Requests
8. SD Overview — Shipping • Main functions – Picking, Packing & Inventory
management – Generate Shipping Documents • Transportation Management – Routes
– Transportation Scheduling • Delivery Scheduling, Returns Deliveries & Stock
Transfer
9. SD Overview — Billing • Invoice Generation — automatic or manual Comprehensive
set of billing functions • Linked documents — e.g. invoice & credit • memo Real-time
integration with finance (FI) • Fully integrated and comprehensive • pricing
10. SD Overview — S I S • Flexible tool that allows one to collect, consolidate, and
utilize data from sales and distribution processing • A component of the Logistic
Information System (LIS)
11. Transportation Foreign Trade
12. Sales & Distribution - Process Flow -
13. Supply Chain Process Customer Order Picking Goods Issue Final Payment Accounts
Receivable Billing
14. SAP Process Steps Sales Sales Quotation Order Delivery Post Goods Shipping
Picking Note Issue Billing Billing Post FI Incoming A/R Payment
15. Sales — Inquiry & Quotation • Support pre-sales processes • Are time sensitive •
Automatic availability check • Automatic pricing • No impact to FI • Can be used as
reference documents
16. Sales — Sales Order • Automated standard • Core of customer functions ... order
management – availability check • No impact to G/L – MRP updating • Can reference
– pricing existing documents – credit check • Copies key – delivery scheduling –
information from export control – shipping & route master data determination
17. Shipping — Delivery Note • Initiates the shipping process • Control document for
shipping processes — maintains status of each processing step • Re-confirms:
availability, credit, foreign trade, delivery scheduling • Facilitates transportation
planning
18. Shipping — Picking & Packing • Picking: Physical activity of moving goods from the
warehouse for further processing (packing, loading) • Packing: Determines packing
materials and packing details • Advanced processing includes, e.g. batch mgmt., serial
number control
19. Shipping — Post Goods Issue • Completes the shipping process • Typically
performed when customer takes ownership • Updates inventory • Updates G/L
accounts – Cost of goods sold – Inventory
20. Billing • Generate customer invoice • Updates FI – Customer account – G/L accounts:
revenue, discount, etc. • Applies relevant pricing • Updates customer credit
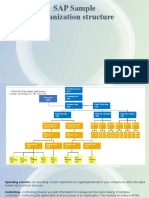
21. Sales & Distribution - Organizational Structures -
22. Sales Organization Client 860 Pastime Corporation Company Code CC00 Domestic
Sales Europe Asia Pacific Sales Organization Sales Organization Sales Organization
So00 EURO APAC Direct Wholesale Retail Wholesale Wholesale Distribution
Channel Distribution Channel Distribution Channel Distribution Channel Distribution
Channel DI WH RE WH WH Baseball Softball Baseball Softball Baseball Softball
Baseball Cricket Baseball Division Division Division Division Division Division
Division Division Division BB SB BB SB BB SB BB SB BB
23. Sales Organization • Sells and distributes products, negotiates terms of sales and is
responsible for these business transactions • Critical organization element to the
definition of business markets • A business transaction is linked to one Sales
Organization
24. Distribution Channel • Identifies how products and services reach the customer • Can
be assigned to one or more Sales Organizations
25. Division • Often times used to define product line distribution • Organization level to
which customer specific information and requirements are maintained — e.g. pricing,
partial delivery • Assigned to one or more Sales Organizations
26. Sales Area • Organizational element comprised of: – Sales Organization –
Distribution Channel – Division • Will be used to link together the organizational
aspects of sales to customers • Used for statistical analysis
27. Sales Area Domestic Sales Sales Organization SO00 Direct Wholesale Retail
Distribution Channel Distribution Channel Distribution Channel DI WH RE Baseball
Softball Baseball Softball Baseball Softball Division Division Division Division
Division Division BB SB BB SB BB SB
28. Sales Area Domestic Sales Sales Organization SO00 Direct Wholesale Retail
Distribution Channel Distribution Channel Distribution Channel DI WH RE Baseball
Softball Baseball Softball Baseball Softball Division Division Division Division
Division Division BB SB BB SB BB SB
29. Sales Office • Typically defines a territory or market area • Linked to one or more
Sales Areas • Optional organization structure
30. Internal Sales Organization Domestic Sales Area Western Eastern Sales Office Sales
Office
31. Sales Group • Sales Group – Sub-division of a sales office, territory or market
32. Sales Person • Sales Person – Defined in HR — Personnel Admin. – Specifically
defines an individual rather than a position (sales rep.) in sales processing
33. Internal Sales Organization Domestic Sales Area Western Eastern Sales Office Sales
Office Southwest Northwest Southeast Northeast Sales Group Sales Group Sales
Group Sales Group Sales Sales Sales Sales Sales Person Person Person Person Person
34. Shipping Point & Loading Point • Shipping Point – Location that performs all
delivery related activities – Assigned a factory calendar – A delivery can be processed
from only one shipping point • Loading Point – A subdivision of the shipping point
used for more specialized handling
35. Shipping Organization S io u x F a lls PLANT PT00 F r e ig h t D o c k E x p re s s E
x p o rt S h ip p in g P t S h ip p in g P t S h ip p in g P t SP00 Q U IK EXPT D ock #1
D ock #2 D ock #3 D ock #2 L o a d in g P t L o a d in g P t L o a d in g P t L o a d in
g P t D1 D2 EX XP
36. Sales & Distribution - Master Data -
37. SD Master Data - Core Elements r me M ate sto Master ria Cu l Data Pricing
38. Material Master — Sales: sales org. 1 -General Data Basic Data 1 - 2 Basic Unit of
Measure Classification Sales: sales org. 1 - 2 Division Sales: general/plant Material
Group Purchasing Sales Unit Foreign Trade: Import Data Sales: text Delivering Plant
Purchase order: text Cash discount MRP 1 - 4 -Tax data Forecasting Storage 1 - 2
Country Warehouse Management 1 - 2 Tax category Quality Management Tax
classification Accounting 1 - 2 Costing 1 - 2 -Quantity stipulations Min. order
quantity Min. delivery quantity Delivery unit
39. Material Master — General Data Base Unit of Measure The Base Unit of Measure is
the unit of measure in which stocks are managed within your company. Division You
may enter the Division which your product is in for sales (defaults if entered in the
Basic data screen). Material Group A (freely definable) key that’s used to group
several materials or services for analysis/reporting as well as search by match code.
Sales Unit This is the unit of measure in which the material is sold, if different from
the base unit of measure. Delivering Plant Plant, from which the material is available
for sale. This is a default value only.
40. Material Master — Tax data & Quantity stipulations Tax data Country Country Tax
category Taxes, applicable to this material (e.g. Federal, State taxes in US, VAT in
GB) Tax classification taxable, exempt Quantity stipulations Min. order quantity Min.
quantity a customer can order (in base unit of measure). Min. delivery quantity Min.
delivery quantity to a customer. Delivery unit Only multiples of this number will be
delivered to the customer.
41. Material Master — Sales: sales org. Basic Data 1 - 2 Classification Sales: sales org. 1
- 2 -Grouping terms Sales: general/plant Purchasing Foreign Trade: Import Data Matl
statistics group Sales: text Material pricing grp Purchase order: text Volume rebate
group MRP 1 - 4 Forecasting Acct assignment grp Storage 1 - 2 Commission group
Warehouse Management 1 - 2 Item Category group Quality Management Accounting
1 - 2 Costing 1 - 2
42. Material Master — Grouping terms Matl statistics group Helps to determine which
data the system updates in the Logistics Information System (LIS). Material pricing
grp A way to group materials with similar pricing conditions. Volume rebate group A
material can be assigned to a volume rebate group (e.g. Low Rebate, High Rebate) if
the material qualifies for rebate. Acct assignment grp A grouping of materials with the
same accounting requirements (used to determine revenue and sales deduction
accounts) Commission group Several materials can be assigned to the same
commission group, if the commission sharing between representatives is the same for
these materials (e.g. Rep.A: 6%, Rep.B: 10%, Rep C: 12%). Item Category groupA
grouping of materials, that helps the system determine the Item Category. Item
Category determines how a specific item is processed by system. E.g. a text item is
not relevant for pricing.
43. Material Master — Sales: general/plant Basic Data 1 - 2 Classification General data
Sales: sales org. 1 - 2 Base unit Sales: general/plant Gross weight Purchasing Foreign
Trade: Import Data Net weight Sales text Avail. Check Purchase order: text Shipping
data (times in days) MRP 1 - 4 Trans. Grp Forecasting Storage 1 - 2 LoadingGrp
Warehouse Management 1 - 2 Packaging material data Quality Management Matl grp
ship. matls Accounting 1 - 2 General plant parameters Costing 1 - 2 Negative stock
44. Material Master — General data & Shipping data (times in days) General data Base
unit The Base Unit of Measure is the unit of measure in which stocks are managed
within your company. Gross weight In Base Units of Measure. Net weight In Base
Units of Measure. Avail. Check Tells the system when to do an availability check, as
well as which MRP elements (such as purchase orders, reservations) to include in the
check. Shipping data (times in days) Trans. Grp Transportation groups are groups of
materials that have the same transportation requirements. For example, all goods that
need refrigeration. Loading Grp Loading groups define materials that have the same
loading requirements, such as forklift truck, or crane.
45. Material Master — Packaging material data & General plant parameters Packaging
material data Matl grp ship. matls, or Material group shipping materials Freely
definable group name, which is used to indicate groups of materials with similar
shipping materials, such as liquids or bulk, for example. General plant parameters
Negative stock Check mark indicator, which specifies whether negative stock is
allowed at that plant.
46. Material Master — Sales texts Basic Data 1 - 2 Classification Sales: sales org. 1 - 2
Sales: general/plant - Sales texts Text Purchasing specific to Foreign Trade: Import
Data the material Sales text Purchase order: text and in an MRP 1 - 4 appropriate
Forecasting language. Storage 1 - 2 Warehouse Management 1 - 2 Quality
Management Accounting 1 - 2 Costing 1 - 2
47. Account Groups • Account group determines which fields are to be used in defining
customer master data
48. Field Status Field status controls the use of each field within the customer master
determining whether a field is required, optional, suppressed or display only Field
status controls are also relevant to a specific activity — create, change, or display
49. Sales & Distribution - Customer Master -
50. Customer Master G e n e ra l D a ta S a le s & D is tr ib u tio n Com pany Code D a ta
D a ta
51. Customer Master • Centralized data for both SD & FI • Segmented into three sections
– General data - address & communication – Company code data (FI) - banking and
payment information related to FI – Sales data (SD) - pricing, delivery, output • The
sales data is specific to one sales area and is therefore dependent on the sales
organization
52. Customer Master by Sales Area Customer • Sales Organization • Distribution Channel
• Division
53. Customer Master — Address & Communication General Data — Address Customer
Name Search Term Street address, City, Postal code, Country Language General Data
— Communication Telephone, Fax, Data numbers
54. Customer Master — Control Data General data — Control data Account control :
Vendor, Authorization Trading partner, Group key Tax information : Tax codes,
Fiscal address Country code, City code VAT N, Tax jurisdiction code Equalization
tax, Sole proprietor Tax on sls/pur. Reference data / area : International Locator No.
Industry: Transport Zone Express station Train station Location code
55. Customer Master — Marketing General Data — Marketing Classification : Nielsen
ID Customer classification Industry Industry codes Operating figures : Annual sales
Number of employees Fiscal year variant Sales prospecting : Legal status
56. Customer Master — Payment Transactions General Data — Payment Transactions
Bank details Country Bank Key Account holder Bank Account Control Key
Collection
57. Customer Master — Unloading Point General Data — Unloading points Unloading
point Customer factory calendar Default Unloading Point Goods receiving hours
58. Customer Master — Foreign Trade General Data — Foreign trade Country key for
export control of customer Table of Denial Orders list (TDO) Special Designated
Nationals list (SDN) Diversion High Risk Profile list (DHRP) Usage and
Classification
59. Customer Master — Contact Persons General Data — Contact persons Name
Telephone number Department First name Form of address (e.g. Mr., Ms.) Function
60. Customer Master — Accounting Information Company Code Data Accounting
Information Accounting info Reconciliation Account Sort key Head office Interest
calculation Interest indicator Interest calculation frequency Last key date Reference
data Buying group
61. Customer Master — Payment Transactions Company Code Data Payment
Transactions Payment data: Payment terms Tolerance group Automatic Payment
Transactions: Payment methods Alternative payer Lockbox
62. Customer Master — Correspondence Company Code Data Correspondence Dunning
data : Dunning procedure Dunning recipient Correspondence : Account number at
customer Customer user Payment notices to : Customer Sales Accounting Legal
63. Customer Master — Insurance Company Code Data Insurance Export credit
insurance : Policy number Institution number Amount insured Valid until Lead
months Deductible
64. Customer Master — Sales Sales Data — Sales area Sales order : Sales district Sales
office Sales group Order probability Item proposal Account at customer Pricing /
Statistics: Price group Customer pricing procedure Price list type Customer statistical
group
65. Customer Master — Shipping S & D Data — Shipping Shipping : Delivery priority
Shipping conditions Delivering plant Order combination Batch split allowed Partial
Delivery: Complete delivery Partial delivery of item Maximum part deliveries
66. Customer Master — Billing S&D Data — Billing Billing section : Manual invoice
maint. Rebate Pricing Billing schedule Invoice list schedule Delivery and payment
terms : Incoterms Payment terms Accounting : Account assignment group Taxes: Tax
requirements for the customer
67. Customer Master — Partner Functions S&D Data — Partner functions The different
partners are assigned • SP Sold-to-party • BP Bill-to-party • PY Payer • SH Ship-to-
party • … additional Partner function(s)
68. Assigning Additional Partners — Siesta Baseball League - Vera Cruz, NM — Sold-to
: 10018 Sold-to Bill-to : 10018 Payer : 10018 Bill-to Payer Ship-to Ship-to : 10018 —
Siesta Baseball League - Vera Cruz, NM — Sold-to : 10018 Sold-to Bill-to : 10018
Payer : 10018 Ship-to : 10018 Bill-to Payer Ship-to Ship-to Ship-to : 10249 -
Bakersfield, CA
69. Sales & Distribution - Business Partners -
70. Business Partners • Defines all of the parties involved in a business transaction and
differentiates between their roles — customer, carrier, employees, customer contact,
etc. • Through customizing the system automatically assigns partners to the customer
master and to transactions Sold-to Ship-to Bill-to Payer
71. Business Partners • The system creates these four business partners by default. All
four are required. • All four may be the same or may be different. • Since these are
automatically assigned partners you may need to add additional partners to carry out
your business transactions. Sold-to Ship-to Bill-to Payer
72. Business partners — Sold-to • Customer that orders the goods Sold-to • Can perform
all primary partner Ship-to functions — sold-to, Bill-to ship-to, payer, bill-to •
Primary type of Payer business partner • Cannot be linked to other sold-to partners
73. Business partners — Ship-to • Party that receives the goods Sold-to • Can be created
as an Ship-to independent partner and linked to one or Bill-to more sold-to partners
Payer
74. Business partners — Bill-to • Party that receives the invoice Sold-to • Can be created
as an Ship-to independent partner and linked to one or Bill-to more sold-to partners
Payer
75. Business partners — Payer • Party that sends the payment Sold-to • Can be created as
an Ship-to independent partner and linked to one or Bill-to more sold-to partners
Payer
76. Business Partners — Example Sold-to Sold-to Ship-to Bill-to Ship-to Ship-to Payer
Ship-to Ship-to Ship-to
77. Sales & Distribution - Pricing -
78. Pricing • “World-class” functionality • Highly customizable & extendible • One of the
most complex features of SAP • Used to determine the net price for a material or an
order
79. Pricing Process • Standard pricing calculates the gross price, then applies discounts,
surcharges and applicable taxes to arrive at the final price final price = gross price -
discounts + surcharges + taxes • Cost-plus pricing determines the base cost and
applies the appropriate discounts, surcharges and taxes final price = cost - discounts +
surcharges + taxes
80. Pricing Components • Pricing is based on a matrix of predefined and custom elements
• Delivered element groups (a.k.a. conditions) – Prices – Discounts & Surcharges –
Freight – Taxes
81. Pricing Procedure • In short, the mechanism used to arrive at the final price •
Considers all of the applicable pricing conditions, e.g. material price, customer
discount • Is assigned by: sales area, sold-to party and sales document type (e.g. sales
order)
82. Pricing Procedure • The pricing procedure uses what SAP calls “the condition
technique”. • The pricing condition technique starts with the: – Pricing Procedure
which looks at – Conditions which use – Access Sequences which accesses –
Condition tables which point to – A price, discount or other condition ($)
83. R/3 Pricing Process DETERMINE ACCESS SALES DOC. DETERMINE PRICING
ACCESS THE CONDITION PRICE THE SEQUENCE FOR EVERY ITEM
PROCEDURE RECORDS AND ITEM CONDITION TYPE IN FOR ITEM
DETERMINE PRICE PRICING PROCEDURE CONDITION TYPE AND ---
SALES AREA & CUSTOMER/MAT’L OR ACCESS SEQUENCE $9.25
UNIFORM DOCUMENT TYPE & PRICE LIST/MAT’L OR ARE LINKED IN
SOLD-TO MATERIAL N/A TABLE CONDITION ACCESS STOPS LOOKING
AFTER SALES DOC. SOLD PRICING TYPE SEQUENCE FINDING FIRST
VALUE AREA TYPE TO PROCEDURE KEY PR00 PR00 US01 A 1 USSTD KI00
KI00 TX00 TX00 LOOK FOR CONDITION US01 B 1 USALT ACCESS OR
RECORDS IN THIS ORDER FR00 FR00 SEQUENCE DER UK01 A 1 UKSTD OF
CONDITION TABLES UK02 A 1 UKSTD PR00 01 CUSTOMER/MATERIAL
PRICING CONDITION CONDITION PROCEDURE TYPE 02 PRICE LIST
TYPE/MAT’L USSTD PR00 PRICE 03 MATERIAL KI00 DISCOUNT KI00 01
CUSTOMER/MATERIAL TX00 TAXES 02 PRICE LIST TYPE/MAT’L FR00
FREIGHT PRICE ELEMENT 03 MATERIAL CONTROL PARAMETERS USALT
PR00 PRICE UPPER/LOWER LIMITS ETC. ETC. KI01 DISCOUNT
84. Price Agreements • Simple price • Detailed price agreements agreements – – pricing
scales product – – rebates customer – – customer expected customer & material price
– customer group & material
85. Specialized Master Data • Customer Material Info. Record • Item Proposal • Listing &
Exclusion • Product Substitution
86. Customer/Material Info. Record • Defines a customer alias for a material &
description, for example: Material # : Glove Customer # : Pastime Glove • Can further
define attributes of the material, shipping and partial delivery information specific to
the product and customer • Referenced in the sales order using the Ordering Party
overview
87. Item Proposal • Used to define frequently ordered combinations or special
assortments of products and quantities • Either products or products with quantities
can be selected during order entry • An item proposal can be defined for a customer
via the customer master record
88. Material Listing & Exclusion • Used to control what products are available for a
customer or group • Material Listing — defines products that can be sold to a
customer • Material Exclusion — defines products that cannot be sold to a customer
89. Product Substitution Material Determination • Enables automatic or manual
substitution of materials during sales order processing • Examples: – substitute a
standard product with a promotional material – substitute based on a customer
preference – substitute based on selection list (manual)
90. Customizing For Transactions Shipping Functions • Shipping Point Determination –
The shipping point is determined for each line item based on the shipping point
determination – shipping point = shipping condition + loading group + delivering
plant
91. Customizing For Transactions Shipping Functions • Route Definition – Route to be
traveled and the transit time – Generic routes can be used to simply define transit time
• Route Determination Proposed route = shipping point + destination country +
transportation zone + shipping condition
92. Sales & Distribution - Transactions -
93. Business Document Types Returns Inquiry Quotation Contract Sales Order
Consignment Scheduling Cash Sale Agreement Returnable Rush Order Packaging
Debit Memo Credit Memo
94. Order Processing Functionality • Delivery scheduling • Availability check • Transfer
of requirements to MRP • Pricing • Credit check • Shipping point & route
determination • Foreign trade & license processing • Document flow
95. Delivery Scheduling • Automatic scheduling of essential shipping activities ...
Calculated using defined activity times ... Resulting in scheduled activity dates •
Determined using backward and forward scheduling rules
96. Delivery Scheduling • Structure of sales documents Header Line item # 1 Schedule
line # 1 Schedule line # 2 Line Item # 2 Schedule line # 1
97. Delivery Scheduling — Terminology • Transportation lead time — time required to
schedule transportation • Pick/Pack time — time required for picking and packing •
Load time — time required to load • Transit time — time required to transport goods
from shipping point to ship-to
98. Backward Scheduling 25 Order Material Transp. Loading Goods Requested Date
Issue Availability Delv. Date Sched. 25th 26th 27th 28th 29th 31st Transp Loading
Transit . Time Time Sched. (1 day) (2 days) Time (1 day) Pick & Pack Time (2 days)
99. Forward Scheduling 27 Material Order Transp. Goods Requested Availability Date
Sched. Loading Issue Delv. Date 26th 27th 27th 28th 29th 31st Transp. Loading
Transit Sched. Time Time 1 Time (1 day) (2 days) (1 day) New Delv. Date Pick &
Pack Time (2 days)
100. Availability Check • Determines the material availability date • Considers
inward and outward movement of inventory — customizable • Influences partial
deliveries by – proposing a quantity that can be delivered on the requested date
(complete delivery) – determines the earliest date for full delivery – determines the
number and dates for partial deliveries to fulfill the order
101. Availability Check • In determining the material availability date the system
can include specific stocks if selected, such as: – Safety stock – Stock in transfer –
Quality inspection stock – Blocked stock – Restricted use stock
102. Transfer of Requirements to MRP • Ordered quantities are passed to MRP
(MM) • Controlled by the schedule line category • Blocking of documents can affect
requirements passing — delivery block
103. Credit Check • Efficient means to implement credit management • Integrated
with FI — via credit control area • Automatically alerts when a credit check fails •
Comprehensive credit management reporting
104. Shipping Point & Route Determination • A shipping point is determined for
each line item — shipping point determination • A delivery can only be processed
from one shipping point • Routes - route to be traveled & transit time are determined
using customized rules • Routes can be used to simply define transit time
105. Foreign Trade & License Processing • Predefined trade areas — NAFTA, EU
• Automated reporting for trade areas • Automated controls – license management –
embargo lists – control by customer, country, product, point in time
106. Shipping
107. Shipping Overview • Comprehensive functionality to support picking, packing
and loading functions • Work list and deadline monitoring • Functions with backorder
processing • Tightly coupled to the MM and FI modules • Facility for transportation
management
108. Shipping Overview Order Order Order Order Delivery Order Delivery
Delivery Delivery Delivery Order Partial Complete Combination Delivery Delivery
109. Shipping Overview • Delivery creation activities – checks order and materials
to determine if a delivery is possible — delivery block, incompleteness – confirms
availability – confirms export/foreign trade requirements – determines total weight &
volume
110. Shipping Overview • Delivery creation activities – generates packing proposal
– considers partial deliveries – updates route assignment – assigns picking location –
determines batches – updates sales order — status, delivery qty
111. Deliveries & Delivery Notes • The Delivery Note – Initiates the delivery
process – Control mechanism for the process – Changes to delivery are allowable -
products, quantities Picking Packing Delivery Status Note Loading Post Goods Issue
112. Delivery Due List • Produces a work-list of deliveries • Encompasses
deliveries and transfers • Can be scheduled to run in batch • Automatically combines
deliveries
113. Picking • Quantities based on delivery • Assigned date when picking should
begin • Automated storage location assignment • Supports serial number tracking and
batch management • Integrated with Warehouse Management (WM)
114. Packing • Identifies which packaging is to be used for specified products •
Identifies and updates accounts associated with returnable packaging • Tracks the
packed product by container • Insures weight/volume restrictions are enforced
115. Goods Issue • Event that indicates the change in ownership of the products •
Reduces inventory • Automatically updates the G/L accounts • Ends the shipping
process and prevents changes to the shipping documents
116. Goods Issue Inventory Cost of goods sold General 750 750 ledger
117. Billing Overview • Automated invoicing based on sales orders and/or
deliveries • Functionality for processing credit/debit memos and rebates • Integration
with FI & CO-PA • Updates customer’s credit data • Can create pro forma invoices
118. Automatic Account Assignment • Defines the G/L accounts that billing entries
are posted to — revenue, deduction, freight charges Applicati Conditi Chart Sale Cust
Accou G/L on on Type of s Acct nt Key Accou Accoun Org. . nt ts Grp. V KOFI 01
6100 CHRT S ERL 00 Oxx From From From From From From From Sales Table
Sales Sales Customer Pricing Table Doc. Doc. Doc. Master Proc
119. Billing Methods Delivery Invoice Separate invoice Order per delivery
Delivery Invoice Delivery Order Collective Delivery Invoice Invoice Order Delivery
Invoice Invoice Order Delivery Split Invoice
120. Billing Documents • Explicitly specify documents • Billing due list — builds a
worklist of invoices that should be generated • Automatic posting to FI
121. Billing Documents Revenue Customer A/R recon. General 2000 2000 2000
ledger
122. Billing Plans • Periodic — total amount for a planned billing period •
Milestone — distributing the total amount over multiple billing dates - typically used
with the project system (PS) • Installment — evenly proportioned amounts and
defined payment dates • Resource related — consumed resources such as service or
consulting
123. SD Milestone Billing Sales Sold-to : QAZ Industries Delivery Date : 06/20/97
Material : 546-dk1 Generator Price : $300,000 Order Billing Description % Value
Billing Milestone Billing date block status 11/20/96 Contract 10 30,000 - x x Billing
01/20/97 Assembly 40 120,000 - x x Plan 04/20/97 Operational 40 120,000 x x
05/20/97 Acceptance 10 30,000 x x 06/20/97 Final invoice -- -- x
124. Outline Agreements • Contracts • Schedule Agreements
125. Contracts • Defined quantities and validity period for a customer • The
contract is fulfilled by orders placed against the contract - release orders • Contracts
are automatically updated through release order processing • Pricing can be assigned
to a contract
126. Contracts Contract Target Qty: 900 Release Order Order Qty: 700 Order Qty:
200 . . . Contract Target Qty: 900 Release Order Order Qty: 750 Order Qty: 150
127. Scheduling Agreements • Defines specific product quantities and delivery
dates for a customer • Schedule lines and processed through standard delivery
processing • Availability check is performed during creation and quantities are passed
to MRP • System automatically updates delivered quantities
128. Scheduling Agreements Scheduling Delivery Agreement 5/10 100 Date Qty
Delivery 05/15 100 6/10 100 06/15 100 Delivery 07/15 200 7/10 200 08/15 300
Delivery 8/10 300
129. Backorders Backorder Processing Rescheduling
130. Backorders • Backorder processing – determines which orders have
unconfirmed quantities by customer or material – sort the orders according to priority
– assign available stock to outstanding orders or reassign confirmed quantities to
high- profile orders
131. Backorders • Rescheduling – updates the orders with the results of the
availability check – can be used to manage the distribution of available inventory
when demand is greater than supply • Best if run in batch mode, rescheduling can be
very time consuming
132. Customer Returns Return Order Goods Receipt Quality Inspection Credit
Memo
133. Customer Returns Order Delivery Invoice 1 Returns Return to Return 2
Inventory Delivery Credit 3 Memo
134. Customer Returns • Returns document – Billing block can be proposed – Use
the Order reason field to identify the reason for the return – Full access to pricing and
ability to re-price • Return delivery – Issues a goods receipt to place material into
inventory
135. Customer Returns • Credit memo – Billing block must be cleared from Return
– Posts to FI – Can be processed in batch (background) – Can be processed
collectively (grouped)
136. Output & Text
137. Communication — Output Printed Documents Bar Coded Documents FAX
SAP Email Document EDI Workflow
138. Communication — Output • Output — traditional forms or electronic
communications produced for internal or external partners • Assigned to business
partners & sales documents • Definable media — EDI, fax, print • Highly
customizable — Sapscript
139. Communication — Text • Texts are used for internal and external
communication • Created for business partners, materials, header or item level of
sales documents — order, delivery, billing, picking lists
140. SIS Overview • Flexible information system designed to support business
planning, forecasting and reporting • Pre-defined catalog of performance measures
and reports • On-demand access to reports and exceptions • Data maintained in a
separate database
141. Logistics Information System • Inventory Management • Purchasing • Sales
and Distribution • Production • Plant Maintenance • Quality Management
142. Inventory Information System Standard Analysis • Material • Plant • Storage
Location • MRP Controller • Material Groupings
143. Purchasing Information System Standard Analysis • Material • Vendor •
Material Group • Purchasing Group • Purchasing Documents
144. Sales Information System Standard Analysis • 5 Pre-defined drill-down
reports – Customer – Material – Sales Organization – Shipping Point – SD
Documents
145. Production Information System Standard Analysis • Product Group • Material
• Work Center • Production Resources and Tools
146. Reporting Tools • Value display - absolute or percentage • Top N - top 10, top
100, etc. • Sorted - ascending or descending • ABC • Classification • Graphics - 2D,
3D
You might also like
- SAP PR Release Strategy Concept and Configuration Guide: A Case StudyFrom EverandSAP PR Release Strategy Concept and Configuration Guide: A Case StudyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- SAP Sales & DistributionDocument31 pagesSAP Sales & Distributionsaif_r_khan9409100% (2)
- Sales & DistributionDocument30 pagesSales & Distributionsaif_r_khan9409No ratings yet
- Sales and Distribution (SD)Document30 pagesSales and Distribution (SD)Vaibhav BatuaNo ratings yet
- SD OverviewDocument85 pagesSD OverviewSamatha GantaNo ratings yet
- SD PresentationDocument43 pagesSD Presentationesameer7837No ratings yet
- SD Process FlowDocument54 pagesSD Process Flowshravanz252100% (1)
- Sales and Distribution OverviewDocument29 pagesSales and Distribution OverviewNitesh NigamNo ratings yet
- Configuration PDFDocument43 pagesConfiguration PDFPedro Afán BalseraNo ratings yet
- Sales & Distribution: BPI - OverviewDocument47 pagesSales & Distribution: BPI - Overviewlvlnpraju100% (1)
- Sales & DistributionDocument47 pagesSales & Distributionemail2srcNo ratings yet
- Sales Order ProcessDocument42 pagesSales Order ProcessManny AR100% (2)
- Organizational Structure & Master DataDocument35 pagesOrganizational Structure & Master Datazs_sapNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Level 2 Training: by LGS TeamDocument31 pagesWelcome To Level 2 Training: by LGS Teamkrishna_1238No ratings yet
- SAP Order To Cash Business ProcessDocument75 pagesSAP Order To Cash Business Processrk_solomon100% (2)
- w3 ISS3205 ERP EnterpriseSistemDocument60 pagesw3 ISS3205 ERP EnterpriseSistemElsaday SimamoraNo ratings yet
- 1.SD - Sales & DistributionDocument140 pages1.SD - Sales & DistributionPuji MargariyantoNo ratings yet
- SAP SD OverviewDocument13 pagesSAP SD OverviewtupacshakrNo ratings yet
- SAP SD - OverviewDocument32 pagesSAP SD - OverviewMarieTee100% (1)
- SAP MM Presentstion-FinalDocument80 pagesSAP MM Presentstion-Finalsamirjoshi73100% (2)
- SAP SD End To EndDocument42 pagesSAP SD End To Endramesh B67% (3)
- Sales and Distribution and SAP2Document4 pagesSales and Distribution and SAP2Mohamed NazimNo ratings yet
- Lesson SAP SD FullDocument68 pagesLesson SAP SD FullGlender AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Sap SDDocument29 pagesSap SDneelakantaNo ratings yet
- Sales & Distribution (SD) : INFS 5024 - Enterprise SystemsDocument33 pagesSales & Distribution (SD) : INFS 5024 - Enterprise SystemsPhuoc HuynhNo ratings yet
- Business Functions and BusinesDocument44 pagesBusiness Functions and BusinesMuddaser NawazNo ratings yet
- Sap (TSCM60)Document12 pagesSap (TSCM60)Raj Kumar0% (1)
- SAPDocument18 pagesSAPRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Sales Order Processing : Right Solution, Right Time, Right PriceDocument110 pagesSales Order Processing : Right Solution, Right Time, Right Pricesunildashsapsd0% (1)
- Chapter One DBDocument44 pagesChapter One DBAlanoud AlmhlbdiNo ratings yet
- Introduction SAP R/3 - MM: Dr. Djamal Ziani King Saud UniversityDocument67 pagesIntroduction SAP R/3 - MM: Dr. Djamal Ziani King Saud UniversityBaalu KathirveluNo ratings yet
- Introduction SAP R/3 - MM: Dr. Djamal Ziani King Saud UniversityDocument67 pagesIntroduction SAP R/3 - MM: Dr. Djamal Ziani King Saud UniversitySachin RachanaikarNo ratings yet
- Pert 2 CH 1Document15 pagesPert 2 CH 1Christian LinNo ratings yet
- Master Data: INFS 5024 - Enterprise Systems Module 3bDocument30 pagesMaster Data: INFS 5024 - Enterprise Systems Module 3bPhuoc HuynhNo ratings yet
- Sap SD NoteDocument14 pagesSap SD NoteNarayana100% (1)
- Organizational StructureDocument7 pagesOrganizational StructureSiva Prasad KantipudiNo ratings yet
- 2 - m1 Sap OverviewDocument64 pages2 - m1 Sap OverviewOscar Edgar BarreraNo ratings yet
- Sap MM OverviewDocument26 pagesSap MM OverviewrameshbabualluriNo ratings yet
- IS-344 Computing Applications in Business Spring 2015 Week 5Document70 pagesIS-344 Computing Applications in Business Spring 2015 Week 5Faded RianbowNo ratings yet
- SAP Org StructureDocument7 pagesSAP Org StructureBhanu ChanderNo ratings yet
- Logistics ExecutionDocument53 pagesLogistics Executionvenkatanaidu12388% (8)
- SAP Materials Management OverViewDocument243 pagesSAP Materials Management OverViewMihai Toma75% (4)
- Outbound Logistics: Class 2: by Rebecca SpagnoloDocument42 pagesOutbound Logistics: Class 2: by Rebecca SpagnoloLlanraeyNo ratings yet
- Sales Order ProcessDocument32 pagesSales Order ProcessRalph LesterNo ratings yet
- Sales Order ProcessDocument42 pagesSales Order Processjorge_r_souza100% (3)
- AACS1304 01 - Introduction To Is 202005Document49 pagesAACS1304 01 - Introduction To Is 202005WIN YE KUANNo ratings yet
- Sap PresentationDocument37 pagesSap PresentationAshutosh VikramNo ratings yet
- Configuring SAP: Enterprise Wide Information SystemsDocument43 pagesConfiguring SAP: Enterprise Wide Information Systemsyashkr2010No ratings yet
- Amity School of Business: Module-2 Sales OrganizationDocument29 pagesAmity School of Business: Module-2 Sales OrganizationGeetanshi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- SAP SD DefinitionsDocument11 pagesSAP SD DefinitionsSridharan RajagopalanNo ratings yet
- Marketing Information Systems and The Sales Order ProcessDocument17 pagesMarketing Information Systems and The Sales Order ProcessBella BrymoraNo ratings yet
- Sd4 Sales Order ProcessingDocument110 pagesSd4 Sales Order Processingdbedada100% (1)
- ASAP Methodology SAPDocument50 pagesASAP Methodology SAPshivdeepb50% (2)
- ERP - Business Functions & ProcessDocument44 pagesERP - Business Functions & Processsarvjeet_kaushalNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Erp AND Its UsageDocument31 pagesIntroduction of Erp AND Its UsageRakesh VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Basic Rules in SD Configuration - ERP Operations - SCN WikiDocument7 pagesBasic Rules in SD Configuration - ERP Operations - SCN Wikisalmanak18No ratings yet
- Syllabus For Sap SD TrainingDocument11 pagesSyllabus For Sap SD TrainingragunathenNo ratings yet
- SAP IS-Retail Interview Questions, Answers, and ExplanationsFrom EverandSAP IS-Retail Interview Questions, Answers, and ExplanationsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (11)
- Batch Tool DO To CheckDocument2 pagesBatch Tool DO To Checkchandra_kumarbrNo ratings yet
- Screenshot - 1.0Document1 pageScreenshot - 1.0chandra_kumarbrNo ratings yet
- Batch Print Arla ScreenshotsDocument5 pagesBatch Print Arla Screenshotschandra_kumarbrNo ratings yet
- ARLA - Batch Info Not Getting Printed in The PicklistDocument3 pagesARLA - Batch Info Not Getting Printed in The Picklistchandra_kumarbrNo ratings yet
- Ticket # 5000001236 COGS ZPRM Calculalations 28may2015Document2 pagesTicket # 5000001236 COGS ZPRM Calculalations 28may2015chandra_kumarbrNo ratings yet
- Slab CalculationsDocument6 pagesSlab Calculationschandra_kumarbrNo ratings yet
- Customer Block Changes Report - 1.0Document2 pagesCustomer Block Changes Report - 1.0chandra_kumarbrNo ratings yet
- GL Settings - Invoice Accounting DocumentDocument6 pagesGL Settings - Invoice Accounting Documentchandra_kumarbrNo ratings yet
- Introducing A New VAT System: Everything You Always Wanted To Know About VAT in SAP But Were Not Aware To AskDocument7 pagesIntroducing A New VAT System: Everything You Always Wanted To Know About VAT in SAP But Were Not Aware To Askchandra_kumarbrNo ratings yet
- JAWS TruckInfo 26may2015Document166 pagesJAWS TruckInfo 26may2015chandra_kumarbrNo ratings yet
- ABAP Code - ZSD Sminv Pad CheckDocument4 pagesABAP Code - ZSD Sminv Pad Checkchandra_kumarbrNo ratings yet
- Dear Sir, Below Is The Required ScreenshotsDocument4 pagesDear Sir, Below Is The Required Screenshotschandra_kumarbrNo ratings yet
- AlSafi Programs 1.0Document70 pagesAlSafi Programs 1.0chandra_kumarbrNo ratings yet
- Billing Output InfoDocument2 pagesBilling Output Infochandra_kumarbrNo ratings yet
- Cfo CalculatorDocument16 pagesCfo Calculatorghazi4uNo ratings yet
- SAP Stock Inconsistency AnalysisDocument9 pagesSAP Stock Inconsistency Analysischandra_kumarbrNo ratings yet
- Pricing Field Catalogue InfoDocument5 pagesPricing Field Catalogue Infochandra_kumarbrNo ratings yet
- Al Safi Cost Sheet SampleDocument1 pageAl Safi Cost Sheet Samplechandra_kumarbrNo ratings yet
- Credit FlowDocument13 pagesCredit Flowchandra_kumarbrNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting Comprehensive Exercise (With Cost of Capital) - SOLUTIONDocument4 pagesCapital Budgeting Comprehensive Exercise (With Cost of Capital) - SOLUTIONchandra_kumarbrNo ratings yet
- SAP Material Management Standard ReportsDocument1 pageSAP Material Management Standard Reportschandra_kumarbrNo ratings yet
- Brands 1.0Document174 pagesBrands 1.0chandra_kumarbrNo ratings yet
- Netsales Report 1.0Document6 pagesNetsales Report 1.0chandra_kumarbrNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1. Input Information: Schedule F Data Taxable YearDocument5 pagesWorksheet 1. Input Information: Schedule F Data Taxable Yearchandra_kumarbrNo ratings yet
- SAP Production Planning LessonsDocument2 pagesSAP Production Planning LessonsNandha KumarNo ratings yet
- Bloomberg FunctionsDocument1 pageBloomberg Functionschandra_kumarbrNo ratings yet
- Sap TablesDocument29 pagesSap Tableslucaslu100% (14)
- Independent Contractor Employer Statutory Approaches To Worker ClassificationDocument17 pagesIndependent Contractor Employer Statutory Approaches To Worker ClassificationNational Association of REALTORS®No ratings yet
- Script BookDocument95 pagesScript BookCorben Dallas100% (1)
- BSBOPS502: Manage Business Operational PlansDocument7 pagesBSBOPS502: Manage Business Operational Plansstar trendzNo ratings yet
- Sales Forecasting: Presentation Given By: Mohsen & AbbasDocument23 pagesSales Forecasting: Presentation Given By: Mohsen & AbbasMohsen RazaNo ratings yet
- Ellen Industries Private LimitedDocument29 pagesEllen Industries Private LimitedEvergreen KejayNo ratings yet
- Minicases and Applications - 2Document4 pagesMinicases and Applications - 2Inês FerrazNo ratings yet
- Operations ManagementDocument30 pagesOperations ManagementAbhishek Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Statement of Purpose: Management and The Procedure To Implement The Strategies and Other Methodologies To Run TheDocument2 pagesStatement of Purpose: Management and The Procedure To Implement The Strategies and Other Methodologies To Run Thedapinder singhNo ratings yet
- Interpret Market Trends and DevelopmentsDocument20 pagesInterpret Market Trends and DevelopmentsMohinderSingh100% (2)
- ToyotaDocument27 pagesToyotaEeshal Mirza0% (1)
- Chapter 05Document10 pagesChapter 05Bashar Abu Hijleh50% (2)
- Opportunity in Soft Drink IndustryDocument58 pagesOpportunity in Soft Drink Industrymaddy205075% (4)
- Frosty Tint Business PlanDocument39 pagesFrosty Tint Business PlanCentral VaporsNo ratings yet
- Herring - 2009 - Does Diversity Pay Race, Gender, and The BusinesDocument17 pagesHerring - 2009 - Does Diversity Pay Race, Gender, and The BusinesRMADVNo ratings yet
- Panache TravelDocument33 pagesPanache TravelDevon Vernon100% (1)
- Answer 2023 2 UNIT03!07!04Document12 pagesAnswer 2023 2 UNIT03!07!04gmlwodldhNo ratings yet
- Organisational Change UNIQLODocument36 pagesOrganisational Change UNIQLOpalejarm100% (1)
- Handmade Sunglass Strap Multicolor Sunglass Holder Sunglass EtsyDocument1 pageHandmade Sunglass Strap Multicolor Sunglass Holder Sunglass Etsyİzmirde Özel Piyano DersiNo ratings yet
- SBI PO (Quantitative Aptitude) Memory Based Held On 04-06-17 (QUESTION PAPER) BankersaddaDocument7 pagesSBI PO (Quantitative Aptitude) Memory Based Held On 04-06-17 (QUESTION PAPER) BankersaddaBavya MohanNo ratings yet
- Case-4 KAR FoodsDocument2 pagesCase-4 KAR FoodsHimanshu GargNo ratings yet
- Ibo 2 em PDFDocument8 pagesIbo 2 em PDFFirdosh Khan86% (7)
- De Jager Plot Seeis Business Plan1Document31 pagesDe Jager Plot Seeis Business Plan1Tully HamutenyaNo ratings yet
- Marisol Lopezs ResumeDocument3 pagesMarisol Lopezs Resumeapi-268914089No ratings yet
- An Analysis of Factors Influencing Use of Digital Opinion Leaders (DOL) in Marketing An Indian PerspectiveDocument6 pagesAn Analysis of Factors Influencing Use of Digital Opinion Leaders (DOL) in Marketing An Indian PerspectiveInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- SCM of Samsung ElectronicsDocument20 pagesSCM of Samsung ElectronicsĐinh Công Thành100% (1)
- (H) Sem-6 Project GKJ PDFDocument216 pages(H) Sem-6 Project GKJ PDFsingh somyadeepNo ratings yet
- Introduce Sales and Operations Execution (S&OE)Document14 pagesIntroduce Sales and Operations Execution (S&OE)Silvia Castillo100% (1)
- Girisha N Aradhya: No. 81, Swamy Vivekananda Road, Hebbagodi, Bengaluru - 560099, KA, IndiaDocument4 pagesGirisha N Aradhya: No. 81, Swamy Vivekananda Road, Hebbagodi, Bengaluru - 560099, KA, Indiagiri_loveNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Module 1 5Document15 pagesEntrepreneurship Module 1 5Mariel GaanNo ratings yet
- Staffing The SalesforceDocument27 pagesStaffing The SalesforceSourav SinhaNo ratings yet