Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module 2 Software Processes
Uploaded by
iedil_din0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
113 views1 pageOriginal Title
Module 2 Software Processes(2)
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
113 views1 pageModule 2 Software Processes
Uploaded by
iedil_dinCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
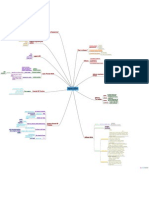
actual work technical work hierarchy activities
work products encompassing actions, populated by
tasks Process Model in Generic
quality assurance filters
milestones
used to identify strengths, weaknesses, and Standard CMMI Assessment
ratings relative to SEI CMMI appraisal Method for Process Improvement
reference model (SCAMPI)
provides a diagnostic technique for assessing
the relative maturity of a software CMM-Based Appraisal for Internal
organization Process Improvement (CBA IPI):
standard that defines a set of Process Assessment and
requirements for software process Improvement
SPICE (ISO/IEC15504): work activities, actions, tasks,
assessment.
performed when software is to be
a generic standard that applies to any software process created
organization that wants to improve the overall
definition these activities, actions, and
quality of the products, systems, or services that
ISO 9001:2000 for Software tasks reside defines their
it provides process model relationship with the process
applicable to all software projects
communication;
linear process flow flow from Framework generic activities
planning;
communication through
V deployment. Waterfall Include modeling,
the development and delivery construction;
is broken down into increments linear and parallel process flows Incremental Process Activities deployment
when requirements are fuzzy Prototyping evolutionary process flow that applied throughout a software projec
Prescriptive Process Models
Each loop/pass consists of risk combines linear and iterative Evolutionary help manage and control
assessment Spiral progress, quality, change, and
exist concurrently but reside in Umbrella complementary activities risk
different states. iterative and parallel process flows Concurrent project tracking and control;
Module 2: Software Processes risk management;
Include software quality assurance (SQA);
technical reviews;
configuration management (CM)
apply when reuse is a
development objective Component based software development (CBSD)
emphasizes the mathematical
specification of requirements Formal methods
defining Linear in sequence.
specifying provides a process and each activity are organized repeats one activities before
methodological approach Aspect-oriented software development (AOSD) with respect to sequence and Iterative proceeding to the next
designing Process Flow time
Evolutionary in a‘circular’ manner.
constructing aspects
executes activities
Unified Process Parallel simultaneously
equirements specification Specialised Process Models
construction An iterative approach Agile Process
deployment,
Emphasizes the need to record
analyze errors each individual Personal Process Model a consistent method for describing problem
practitioner made describes a process-related problem
solutions within the context of the software
Build self-directed teams that Process Patterns process. identifies the environment problem
plan suggests o solutions to the problem.
track their work
Team Process Model
establish goals
own their processes and plans.
You might also like
- Module 10 (Advanced Topics)Document1 pageModule 10 (Advanced Topics)iedil_dinNo ratings yet
- Verification & ValidationDocument1 pageVerification & Validationiedil_dinNo ratings yet
- Software Project ManagementDocument1 pageSoftware Project Managementiedil_dinNo ratings yet
- Module 7 (Software Quality Management)Document1 pageModule 7 (Software Quality Management)iedil_dinNo ratings yet
- Class-Based ModelingDocument1 pageClass-Based Modelingiedil_dinNo ratings yet
- Behavioral ModelingDocument1 pageBehavioral Modelingiedil_dinNo ratings yet
- RE Process (Module 3) Part 3Document1 pageRE Process (Module 3) Part 3iedil_dinNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Requirements Engineering (Part 4)Document1 pageModule 3 Requirements Engineering (Part 4)iedil_dinNo ratings yet
- Scenario-Based ModelingDocument1 pageScenario-Based Modelingiedil_dinNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Requirements Engineering (Part1)Document1 pageModule 3 Requirements Engineering (Part1)iedil_dinNo ratings yet
- RE Process (Module 3) Part 2Document1 pageRE Process (Module 3) Part 2iedil_dinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Software Engineering (Module 1)Document1 pageIntroduction To Software Engineering (Module 1)iedil_dinNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Software Processes Part 2Document1 pageModule 2 Software Processes Part 2iedil_dinNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Davinci Configures Vlinkgen - Programmer Sought PDFDocument4 pagesDavinci Configures Vlinkgen - Programmer Sought PDFChittaranjan BaralNo ratings yet
- Questions Second 10 Pages Ch2Document4 pagesQuestions Second 10 Pages Ch2Raneen ForsanNo ratings yet
- X Is The Inputted Name) .: Csuk:Teacher Csuk Csuk:RevisecsDocument2 pagesX Is The Inputted Name) .: Csuk:Teacher Csuk Csuk:RevisecshadibenmansourNo ratings yet
- 017 Domestic Violence PPT PresentationDocument26 pages017 Domestic Violence PPT PresentationNguyễn Thị Trà MyNo ratings yet
- D 415Document49 pagesD 415Alyssa LNo ratings yet
- Easily Edit and Modify Your PDF Files: DownloadDocument8 pagesEasily Edit and Modify Your PDF Files: Downloadp tjcNo ratings yet
- Subham Chakraborty ResumeDocument1 pageSubham Chakraborty ResumetankuliNo ratings yet
- Cs201 Solved Mcqs Final Term by JunaidDocument44 pagesCs201 Solved Mcqs Final Term by JunaidDaniyal PervaizNo ratings yet
- Solution of ProgramsDocument17 pagesSolution of ProgramsujjwalmittalNo ratings yet
- Social Media MarketingDocument63 pagesSocial Media MarketingPriyank MalikNo ratings yet
- Group Project: 45% of The Total Mark For The Class : Title: Network Administration ProjectDocument5 pagesGroup Project: 45% of The Total Mark For The Class : Title: Network Administration ProjectSeprah KNo ratings yet
- Stack: Basic Operation On StackDocument107 pagesStack: Basic Operation On StackSanchit RkNo ratings yet
- PLSQL Semester 1 Final ReviewDocument12 pagesPLSQL Semester 1 Final Reviewfleur d'automne clairNo ratings yet
- Slides PDF - Scrumble enDocument17 pagesSlides PDF - Scrumble enRide TeamNo ratings yet
- Inheritance and Operator OverloadingDocument33 pagesInheritance and Operator OverloadingAsasAsasNo ratings yet
- C01 OverviewDocument33 pagesC01 OverviewburthoNo ratings yet
- PHP P4Document41 pagesPHP P4ChellamNo ratings yet
- CP Viva Questions With AnswersDocument18 pagesCP Viva Questions With AnswersPawanAgarwalNo ratings yet
- A11yprovider LogDocument169 pagesA11yprovider LogMadrYxNo ratings yet
- Conditional SolutionsDocument3 pagesConditional SolutionsHARSHNo ratings yet
- Research of Fine Grit Access Control Based On Time in Cloud Computing 1Document77 pagesResearch of Fine Grit Access Control Based On Time in Cloud Computing 1vikkinikkiNo ratings yet
- AverageDocument8 pagesAverageFirst EntertrainmentNo ratings yet
- Online Admission Management SystemDocument4 pagesOnline Admission Management SystemEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Computer Science 9618/41Document12 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Computer Science 9618/41abdullahhumayoun7No ratings yet
- Avaya WFO - 15.1 - February 2016 - Interactions and Analytics Administration GuideDocument155 pagesAvaya WFO - 15.1 - February 2016 - Interactions and Analytics Administration GuideSagar NaiduNo ratings yet
- Redux: #React NotesDocument24 pagesRedux: #React NotesMeet MunjaparaNo ratings yet
- Python Class 11 Ip NotesDocument5 pagesPython Class 11 Ip NotesAishahNo ratings yet
- 1670-Gcs210314 HoangQuangQuyen Assignment 1Document21 pages1670-Gcs210314 HoangQuangQuyen Assignment 1hqq.7.12.03No ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer ProgrammingDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Computer ProgrammingDinesh LasanthaNo ratings yet
- C Fioridev 21Document29 pagesC Fioridev 21Praveen KumarNo ratings yet