Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Deepawali Flasher
Uploaded by
sankalp89Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Deepawali Flasher
Uploaded by
sankalp89Copyright:
Available Formats
circuit
ideas
Flasher For Deepawali s.c. dwiv
edi
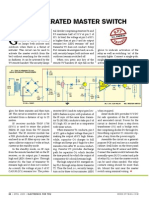
Sunil Kumar The output of IC1 drives transistor T1.
Working of the circuit is simple.
H
ere is the circuit for a port- When output pin 3 of IC1 goes high,
able electric lamp-cum-LED transistor T1 conducts to fire triac1 currents.
flasher. It uses a 25W, 230V and the bulb glows. Bulb L1 turns off In brief, the bulb and the LEDs
AC bulb and nine LEDs. When the when output pin 3 of IC1 goes low. flash alternately depending on the
bulb glows all the LEDs remain ‘off,’ The collector of transistor T1 is con- frequency of IC1. Flashing rates of the
and when the LEDs glow the bulb nected to anodes of all the LEDs (LED1 bulb as well as LEDs can be varied by
remains ‘off.’ through LED9). So when T1 is cut-off adjusting potmeter VR1. Connect the
The circuit is built around timer IC the LEDs glow, and when T1 conducts power supply line (L) of mains to bulb
555 (IC1), which is wired as an astable the LEDs go off. Current-limiting resis- L1 via switch S1 and neutral (N) to
multivibrator generating square wave. tor R4 protects the LEDs from higher MT1 terminal of triac1.
A 12V, 200mA AC adaptor is
used to power the circuit. Using
switch S1, you can switch off the
bulb permanently if you do not
want it to flash.
Assemble the circuit on a
general-purpose PCB and en-
close in a circular plastic cabinet
keeping the bulb at the centre
and LEDs at the circumference.
Drill holes for mounting the
‘on’/‘off’ switch. Use a bulb
holder for bulb L1 and LED
holders for the LEDs. Also use
an IC socket for timer IC 555.
Warning. While assembling,
testing or repairing, take care to
avoid the lethal electric shock.
w w w. e f y m ag . co m e l e c t ro n i c s f o r yo u • N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 0 • 1 1 5
You might also like
- PCS-9830B X Instruction Manual en Domestic General X R1.05Document164 pagesPCS-9830B X Instruction Manual en Domestic General X R1.05Arief Sandy AnggoroNo ratings yet
- Godown Wiring: 19EEE113 - Electrical Engineering PracticeDocument6 pagesGodown Wiring: 19EEE113 - Electrical Engineering PracticeNikhil ReddyNo ratings yet
- Atpg Coverage LossDocument4 pagesAtpg Coverage LossUmesh ParasharNo ratings yet
- Automatic Night Lamp With Morning AlarmDocument17 pagesAutomatic Night Lamp With Morning AlarmAshis karmakar100% (2)
- Automatic Light Controller Using 7806 PDFDocument1 pageAutomatic Light Controller Using 7806 PDFShrivlsi RamNo ratings yet
- Led Flasher: Department of Industrial Engineering, Batangas State UniversityDocument4 pagesLed Flasher: Department of Industrial Engineering, Batangas State UniversitySai VishalNo ratings yet
- Automatic Evening LampDocument4 pagesAutomatic Evening LampRamkrishna ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Smart Phone Light PDFDocument2 pagesSmart Phone Light PDFPavan Kumar ThopaNo ratings yet
- AC Mains Bistable SwitchDocument1 pageAC Mains Bistable SwitchShrivlsi RamNo ratings yet
- Automatic LightDocument2 pagesAutomatic Lightsushant sharmaNo ratings yet
- Staircase LightDocument1 pageStaircase Lightseenu4love100% (1)
- Musical Light Chaser: IdeasDocument2 pagesMusical Light Chaser: IdeasJaveed AhamedNo ratings yet
- Pair Task Activity #03-00-05 555 LED Flasher: ComponentsDocument3 pagesPair Task Activity #03-00-05 555 LED Flasher: ComponentsRissy Kh XhieNo ratings yet
- Led Flasher Final ProjectDocument4 pagesLed Flasher Final ProjectCherrylou Yares Alcantara82% (11)
- Led Flasher Final Project PDF FreeDocument4 pagesLed Flasher Final Project PDF FreeMortal ShooterNo ratings yet
- 06 So6205-4f Alumbrado 2 LNDocument4 pages06 So6205-4f Alumbrado 2 LNJionni DlzmaNo ratings yet
- Leakage and Continuity Tester: IdeasDocument1 pageLeakage and Continuity Tester: Ideassoumen1963100% (1)
- Smart Emergency LightDocument1 pageSmart Emergency LightaassaanmkNo ratings yet
- EL005 Electronic Projects New Collections Vol 5NDocument273 pagesEL005 Electronic Projects New Collections Vol 5NSoeThihaLwin100% (1)
- LED Flasher Circuit PPT PresentationDocument6 pagesLED Flasher Circuit PPT PresentationBharath100% (1)
- Tiny DevicesDocument1 pageTiny DevicesHari SjjhNo ratings yet
- Highway Alert Signal Lamp PDFDocument1 pageHighway Alert Signal Lamp PDFShrivlsi Ram100% (1)
- Staircase Light WithDocument1 pageStaircase Light WithmartinNo ratings yet
- Light Sensitive SwitchDocument2 pagesLight Sensitive Switchvaibhav9428No ratings yet
- "Chip Card" As Security Key (Digital Ic's)Document1 page"Chip Card" As Security Key (Digital Ic's)Peeters GuyNo ratings yet
- Kumpulan Skematik Elektronika 2Document77 pagesKumpulan Skematik Elektronika 2rizal tri susiloNo ratings yet
- Automatic Bathroom Light PDFDocument1 pageAutomatic Bathroom Light PDFJan Ahmed0% (1)
- Pplyphonic Doorbell Description: Led Torch Light DescriptionDocument2 pagesPplyphonic Doorbell Description: Led Torch Light DescriptionÑéél ShármáNo ratings yet
- Front Door GuardDocument2 pagesFront Door GuardmozammilNo ratings yet
- SjhaDocument40 pagesSjhamohit meshramNo ratings yet
- 4060 CircuitsDocument4 pages4060 CircuitsmatkopNo ratings yet
- Introduction To: CircuitsDocument12 pagesIntroduction To: Circuitsexia breakNo ratings yet
- Lm3909 ApplicationsDocument16 pagesLm3909 Applicationspre freedaNo ratings yet
- ZoyaDocument15 pagesZoyaNaveen ParmarNo ratings yet
- CI-1 Sep11 Hot-1Document1 pageCI-1 Sep11 Hot-1svinduchoodan8614No ratings yet
- Light Dependent Resistor LM339 Automatic Lightdark Indicator BC 547Document3 pagesLight Dependent Resistor LM339 Automatic Lightdark Indicator BC 547yeateshwarriorNo ratings yet
- LED Flasher. Design Note 34 - Hobby ProjectsDocument2 pagesLED Flasher. Design Note 34 - Hobby Projectsajithmanohar1221No ratings yet
- Electronic Bicycle Lock - OptDocument1 pageElectronic Bicycle Lock - OptAbisheik RishiNo ratings yet
- Ica ProjectDocument5 pagesIca ProjectDushyant DabhiNo ratings yet
- FlasherDocument6 pagesFlasheriwanbossemeNo ratings yet
- 555 DC Boost Converter CircuitsDocument5 pages555 DC Boost Converter CircuitsFelipe VargasNo ratings yet
- Mini Project Report 2010-11 GPTC MeppadiDocument18 pagesMini Project Report 2010-11 GPTC MeppadiAkhil V MohanNo ratings yet
- E 01 CH 02Document2 pagesE 01 CH 02Tariq Zuhluf100% (1)
- CH 6 Slides 6 PDFDocument3 pagesCH 6 Slides 6 PDFrakshit dadhichNo ratings yet
- Digital Logic DesignDocument9 pagesDigital Logic DesignLaiba AfzalNo ratings yet
- BEEE (Experiment 7 and 8)Document5 pagesBEEE (Experiment 7 and 8)Surjosnath Guha ThakurtaNo ratings yet
- Project Report 555Document14 pagesProject Report 555بنیاد پرست100% (1)
- 555 Holiday Fun - WorkshopDocument14 pages555 Holiday Fun - WorkshopSamy KaruppuNo ratings yet
- 4N25 Optocoupler - A Simple Application Circuit (With Example)Document5 pages4N25 Optocoupler - A Simple Application Circuit (With Example)Fidaa JaafrahNo ratings yet
- Pneumatics Activity 2Document2 pagesPneumatics Activity 2Jay Mark BalaneNo ratings yet
- Pneumatics Activity 2Document2 pagesPneumatics Activity 2Jay Mark BalaneNo ratings yet
- A Dimmer Circuit For Various Lighting Devices: R. Bar Dai, Mert Turhan, Deniz Yldrm, and Canbolat UçakDocument5 pagesA Dimmer Circuit For Various Lighting Devices: R. Bar Dai, Mert Turhan, Deniz Yldrm, and Canbolat UçakRichu UhcirNo ratings yet
- Transistorred Code Lock With TorchDocument1 pageTransistorred Code Lock With TorchFadli Fatur RahmatNo ratings yet
- Slide No. Slide Content Voice Over: ( (VIDEO:13018) ) + P.15.3.2Document4 pagesSlide No. Slide Content Voice Over: ( (VIDEO:13018) ) + P.15.3.2Gaurav JainNo ratings yet
- Current Balance Relays: InstructionsDocument12 pagesCurrent Balance Relays: InstructionsEvglazNo ratings yet
- Industrial Electric RelayDocument26 pagesIndustrial Electric Relaysyed muazzam shah putraNo ratings yet
- Twilight SwitchDocument6 pagesTwilight SwitchRashid50% (2)
- Automatic Street LightDocument3 pagesAutomatic Street LightShilpa MohanNo ratings yet
- CI-02 Apr09Document1 pageCI-02 Apr09bhalaji1991100% (1)
- Simple Two-Transistor Motorcycle AlarmDocument6 pagesSimple Two-Transistor Motorcycle AlarmvladmileaNo ratings yet
- Icom IC 718 Instruction ManualDocument62 pagesIcom IC 718 Instruction ManualYayok S. Anggoro100% (1)
- System and Standard Functions Reference Manual.: Technical SpecificationsDocument2 pagesSystem and Standard Functions Reference Manual.: Technical SpecificationspandukrishnaNo ratings yet
- PGTR - Trafos SecosDocument2 pagesPGTR - Trafos Secosjotaruiz30No ratings yet
- IO Bus 2 PDFDocument30 pagesIO Bus 2 PDFbalaji224No ratings yet
- MT87Document2 pagesMT87Jenalyn Orbasido EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- CodanDocument2 pagesCodaninsinyurNo ratings yet
- Computer DefinitionDocument5 pagesComputer DefinitionPastidyuso C. NinzNo ratings yet
- Rta Fousb Mon Users ManualDocument28 pagesRta Fousb Mon Users ManualConduraru Alina100% (1)
- STW 5-10kva KWDocument4 pagesSTW 5-10kva KWPauloSempiternoNo ratings yet
- Magelis GTO - HMIGTO4310Document8 pagesMagelis GTO - HMIGTO4310CckqtNo ratings yet
- CI 980 Multi-Channel Amplifier Data SheetDocument2 pagesCI 980 Multi-Channel Amplifier Data SheetNatanael BetancesNo ratings yet
- IndtsDocument5 pagesIndtsSrinivas NiceNo ratings yet
- CDX mp30Document48 pagesCDX mp30sonicman23No ratings yet
- TheveninDocument5 pagesTheveninErnesto FrancoNo ratings yet
- 12th Practical Booklet With Readings (Paper-1)Document20 pages12th Practical Booklet With Readings (Paper-1)Vasudevanand KherNo ratings yet
- Feedback AmplifiersDocument4 pagesFeedback Amplifiersbetoy00No ratings yet
- Circuit Diagrams: 1. Smps - Power #1 Circuit DiagramDocument2 pagesCircuit Diagrams: 1. Smps - Power #1 Circuit DiagramOrlando BurgosNo ratings yet
- EAW MK5326 - Specs - Rev1Document2 pagesEAW MK5326 - Specs - Rev1Noah WestonNo ratings yet
- Cmos Vlsi Design: A Systems & Circuits PerspectiveDocument44 pagesCmos Vlsi Design: A Systems & Circuits PerspectiveNoman RathoreNo ratings yet
- EGRZV4-65D-R8N43 Product Specifications (Comprehensive)Document6 pagesEGRZV4-65D-R8N43 Product Specifications (Comprehensive)CristiNo ratings yet
- History of TelevisionDocument18 pagesHistory of TelevisionMyou ChoNo ratings yet
- Bucky C-TS PDFDocument33 pagesBucky C-TS PDFJojo KawayNo ratings yet
- HyppTV Set Top BoxDocument28 pagesHyppTV Set Top BoxMirza ArshadNo ratings yet
- Systems Theory and Management Information SystemsDocument393 pagesSystems Theory and Management Information SystemsWycliffNo ratings yet
- KTS-440 Data Transfer 2012-6Document27 pagesKTS-440 Data Transfer 2012-6nekive100% (1)
- Daftar Set Top Box Bersertifikat Perangkat Dari Kominfo: No Kategori Merek Model/tipe Official Shop/Tutorial InstallationDocument3 pagesDaftar Set Top Box Bersertifikat Perangkat Dari Kominfo: No Kategori Merek Model/tipe Official Shop/Tutorial InstallationOejank 08No ratings yet
- Tle 6220 GPDocument17 pagesTle 6220 GPArmando UsedaNo ratings yet