Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PC Lab 1 Parabolas
Uploaded by
briandmcneillOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PC Lab 1 Parabolas
Uploaded by
briandmcneillCopyright:
Available Formats
Laboratory: Quadratic Functions
Using a graphing calculator we will investigate the quadratic function: y = f(x) = ax2 + bx +c . where a:f.: 0
Set your graphing calculator to the standard window: ~ 1 0 :s; x:s; 10 and -1O:S; Y S 10 with xscl = 1 and yscl = 1.
Calculator directions:
a. Press the key marked WINDOW and enter the data above or press the key ZOOM and then the number 6 (This will set up the standard window automatically)
b. If you want a better view ofa particular function and you can alter these parameters by highlighting the parameter to be changed and typing in the new value.
c. To graph each function press the key Y= and enter the function. Then press GRAPH
d. To view the points on a graph press TRACE and move the right and left arrow keys.
e. If you have more than one graph on the same set of axes and you want to trace, you can move from one graph to another using the up and down arrow keys.
f. Use the 2nd CALC key to find the vertices of the parabolas
Directions: For each of the following questions:
1. Draw and label each graph.
2. List the axis of symmetry and vertex for each function.
3. Answer any questions in sentences.
1. We 'Will first investigate the impact of a on the equation.
Graph the equations y = x2, Y == 3x2, and y = 6x2 on the same set of axes.
Label their axes of symmetry and their vertices. Consider the width of the parabolas. How does changing the value of a appear to affect these graphs?
2, Graph the equations y = x2• Y = .5x2, y::;: .Olx2 on the same set of axes
Label the axes of symmetry and their vertices. Consider the width of the parabolas. How does changing the value of a appear to affect these graphs?
3, Graph the equations y = -x2• y == -2x2, y = -4x2 ,and y = -.5x2 on the same set of axes.
Label their axes of symmetry and their vertices. Consider their width and whether they open up or down. How does changing the sign of a appear to affect these graphs?
> . \
4. We can now generalize about the effect of a on the parabola y = ax2. Using the data obtained above, and the parabola y = x2 as your basis for comparison. describe the parabola y = ax2 if:
1.) a> 1
2.) 0 < a < 1
3.) -1<a<0
4.) a<-1
II. We will now investigate the value of e in the parabola y = ax2 + bx + c.
1. Graph on the same set of axes, y = x2 ,Y = x2 + 3 , and y = x2 - 5 Label the vertices and axes of symmetry.
Describe the differences in the parabolas as the value of c changes?
2. Graph on the same set of axes y = -3x2, Y = -3x2 -6, and y = -3x2 + 4 Label the vertices and axes of symmetry.
Describe the differences in the parabolas as the value of c changes?
3. Graph on the same set of axes, y = 2x2 + 6x, y = 2x2 + 6x -4 and y = 2x2 + 6x + 3.
Label the vertices and axes ofsymrnetry.
Describe the differences in the parabolas as the value of c changes?
4. Given the equations y = ax2 + bx and y = ax2 + bx + c describe the effect that c has on the parabola in general and the effect it has on the vertex of the parabola. What happens if:
c is a positive number?
c is a negative number?
ill. We will now investigate the value of b in the parabola: y" ax~ + bx + C
1. Graph on the same set of axes: y = x2 - 2x, y;= x2 +2x.
Graph on another set of axes: y = x2 + 4x + 2 y == x2 - 4x - 5 Label the vertices and axes of symmetry.
Describe the position of the vertex (left or right of the y-axis) when b is a positive number and when b is a negative number.
2. Graph on the same set of axes: y = "3x2 + 6x and y == -3x2 - 6x Graph on another set of axes: y == -x2'-2x + 8 and y = -x2 + 2x + 8
Label the vertices and the axis of symmetry. ,
Describe the position of the vertex (left or right of the y-axis) when b is a positive number and when b is a negative number.
J. Consider the equation: y = ax2.+ bx + c. Describe the placement of the vertex (left or right) of the y-axis in each of the following conditions. If necessary, draw a few more examples.
a.) a is a positive number where:
b is a positive number
b is a negative number
b.) a is a negative number where:
b is a positive number
b is a negative number
IV. Further investigations in the parabola:
1. The relationship between the discriminant and the parabola:
For each of the following parabolas. determine the discriminant b2 - 4ac, the x-intercepts of the parabola and sketch its graph.
a.) y = x2 + 5",- 2
b.) y = x2 + 6x + 9
c.) y = -2x2 - 6x + 1
d.) y = x2 + 3x+ 5
e.) y = 2x2_7
d.) y = x2 + 3x - 4
_ Using the information provided above, what can you determine about the NUMBER of x-intercepts the parabola has, if the value of the discriminant is:
a positive number?
a negative number?
Zero?
VI. Further investigations in the parabola:
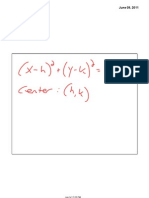
1. The general form y = a(x-h)2 + k
Graph each parabola and completethe table below:
IParabola a h k Axis of Symmetry Vertex (h, k)
y=x2-5
y=-2(x-I/-5
y = 4(x + 3/ - 2
ly=·5(x-4/+1
y = -(2/3)(x + Ii - 3 Using the information provided above, given the equationofa parabola in the form y =a(x-h/ + k what is the vertex and the axis of symmetry?
Vertex _
.Axis of Symmetry _
The variable a serves the sam~ purpose in a11 forms of a parabola.
What happens in the parabola if a is positive _
if a is negative, _
Is the parabola wide or narrow in comparison to a parabola where a = 1
if la! is a large number
if lal is a small number
Write an equation of a parabola satisfying the following conditions:
a.) Axis of symmetry, x=-2 Vertex (-2,7) Opens up a.) _
b) Axis of symmetry x=5 Vertex (5,-3) Opensdown b.) _
C,) Axis of symmetry x = 0
Vertex (0, -3)
Opens upand is wide
c.) _
d.) Axis of symmetry x = -3
Vertex (-3, 4)
Opens down and is narrow
d.) _
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- AP Statistics Syllabus 2015-16Document7 pagesAP Statistics Syllabus 2015-16briandmcneillNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- AP Statistics Syllabus 2015-16Document7 pagesAP Statistics Syllabus 2015-16briandmcneillNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Pre Calculus Syllabus 2013-14Document3 pagesPre Calculus Syllabus 2013-14briandmcneillNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- AP Statistics Syllabus 2014-15Document6 pagesAP Statistics Syllabus 2014-15briandmcneillNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- AP Calculus AB Syllabus 2013-14Document5 pagesAP Calculus AB Syllabus 2013-14briandmcneillNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Calculus I Course ExpectationsDocument3 pagesCalculus I Course ExpectationsbriandmcneillNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Burlington High School - Department of Mathematics: Trigonometry (260) - Course Syllabus 2016-2017Document3 pagesBurlington High School - Department of Mathematics: Trigonometry (260) - Course Syllabus 2016-2017briandmcneillNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- AP Statistics Syllabus 2013-14Document6 pagesAP Statistics Syllabus 2013-14briandmcneillNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- AP Statistics Syllabus 2013-14Document6 pagesAP Statistics Syllabus 2013-14briandmcneillNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- AP Statistics Syllabus 2011-12Document6 pagesAP Statistics Syllabus 2011-12briandmcneillNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus AB Syllabus 2013-14Document5 pagesAP Calculus AB Syllabus 2013-14briandmcneillNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Pre Calculus SyllabusDocument3 pagesPre Calculus SyllabusbriandmcneillNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus AB Syllabus 2013-14Document5 pagesAP Calculus AB Syllabus 2013-14briandmcneillNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Pre Calculus SyllabusDocument3 pagesPre Calculus SyllabusbriandmcneillNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- 6-9-11 at 6Document5 pages6-9-11 at 6briandmcneillNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- AP Statistics Syllabus 2011-12Document4 pagesAP Statistics Syllabus 2011-12briandmcneillNo ratings yet
- 6-13-11 PC 3Document11 pages6-13-11 PC 3briandmcneillNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- 6-13-11 PC 2Document10 pages6-13-11 PC 2briandmcneillNo ratings yet
- 6-9-11 PC 2Document5 pages6-9-11 PC 2briandmcneillNo ratings yet
- 6-13-11 atDocument1 page6-13-11 atbriandmcneillNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- 6-10-11 PC 3Document6 pages6-10-11 PC 3briandmcneillNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- 6-9-11 at 5Document6 pages6-9-11 at 5briandmcneillNo ratings yet
- 6-10-11 PC 2Document6 pages6-10-11 PC 2briandmcneillNo ratings yet
- 6-9-11 PC 3Document6 pages6-9-11 PC 3briandmcneillNo ratings yet
- 6-8-11 at 6Document5 pages6-8-11 at 6briandmcneillNo ratings yet
- 6-8-11 PC 3Document6 pages6-8-11 PC 3briandmcneillNo ratings yet
- BHS Strength and Conditioning 2011Document2 pagesBHS Strength and Conditioning 2011briandmcneillNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- At Circle ReviewDocument1 pageAt Circle ReviewbriandmcneillNo ratings yet
- 6-8-11 at 5Document5 pages6-8-11 at 5briandmcneillNo ratings yet
- 6-8-11 PC 2Document5 pages6-8-11 PC 2briandmcneillNo ratings yet
- 07 Indian WeddingDocument2 pages07 Indian WeddingNailah Al-FarafishahNo ratings yet
- DapusDocument2 pagesDapusIneke PutriNo ratings yet
- Devi Strotam PDFDocument9 pagesDevi Strotam PDFDiary Of A Wise ManNo ratings yet
- Christify LyricsDocument1 pageChristify LyricsJomel GarciaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Form Day 2 / 3 (4) Webquest Data GatheringDocument1 pageLesson Plan Form Day 2 / 3 (4) Webquest Data GatheringMarkJLanzaNo ratings yet
- RCBC Capital Corporation Vs Banco de OroDocument18 pagesRCBC Capital Corporation Vs Banco de OroLove HatredNo ratings yet
- Odisha State Museum-1Document26 pagesOdisha State Museum-1ajitkpatnaikNo ratings yet
- Tutorial-Midterm - CHEM 1020 General Chemistry - IB - AnsDocument71 pagesTutorial-Midterm - CHEM 1020 General Chemistry - IB - AnsWing Chi Rainbow TamNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Mediated Read Aloud Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesMediated Read Aloud Lesson PlanMandy KapellNo ratings yet
- Graph Theory and ApplicationsDocument45 pagesGraph Theory and Applicationssubramanyam62No ratings yet
- Degenesis Rebirth Edition - Interview With Marko DjurdjevicDocument5 pagesDegenesis Rebirth Edition - Interview With Marko DjurdjevicfoxtroutNo ratings yet
- A Translation Quality Assessment of Two English Translations of Nazım HikmetDocument14 pagesA Translation Quality Assessment of Two English Translations of Nazım HikmetIntzarEltlNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis Cheat SheetDocument5 pagesStructural Analysis Cheat SheetByram Jennings100% (1)
- Cost ContingenciesDocument14 pagesCost ContingenciesbokocinoNo ratings yet
- Jestine Seva - PEModuleWeek5&6Document5 pagesJestine Seva - PEModuleWeek5&6Mike AlbaNo ratings yet
- Conflict of Laws Bar OutlineDocument4 pagesConflict of Laws Bar OutlineJohn Risvold50% (2)
- Orpiano Vs TomasDocument2 pagesOrpiano Vs TomasDotsNo ratings yet
- Power Semiconductor DevicesDocument11 pagesPower Semiconductor DevicesBhavesh Kaushal100% (1)
- Yangkam WordlistDocument19 pagesYangkam Wordlistxdboy2006No ratings yet
- River: A Boon or A BaneDocument3 pagesRiver: A Boon or A BaneIJELS Research JournalNo ratings yet
- How Cooking The Books WorksDocument27 pagesHow Cooking The Books WorksShawn PowersNo ratings yet
- Kashida Embroidery: KashmirDocument22 pagesKashida Embroidery: KashmirRohit kumarNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Marketing 12th Edition LambDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Marketing 12th Edition Lambangelascottaxgeqwcnmy100% (39)
- Microbiology KROK-1 PDFDocument121 pagesMicrobiology KROK-1 PDFHimanshu RanaNo ratings yet
- Vampire Lord Strategy - FinalDocument8 pagesVampire Lord Strategy - FinalMarco RadiciNo ratings yet
- Oracle Partitioned TablesDocument38 pagesOracle Partitioned TablesshahbazbNo ratings yet
- Lantus SoloStar Pen Guide PDFDocument7 pagesLantus SoloStar Pen Guide PDFKai HarukaNo ratings yet
- Family Coping IndexDocument5 pagesFamily Coping IndexDarcey NicholeNo ratings yet
- Impulse: Operation ManualDocument8 pagesImpulse: Operation ManualRonggo SukmoNo ratings yet
- Developmental Stages WritingDocument2 pagesDevelopmental Stages WritingEva Wong AlindayuNo ratings yet
- Calculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandCalculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsFrom EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingFrom EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)