Professional Documents
Culture Documents
General Physics - From MR Sai Mun
Uploaded by
Izatul NadiaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
General Physics - From MR Sai Mun
Uploaded by
Izatul NadiaCopyright:
Available Formats
IGCSE Physics : Topic 1 General Physics - mr sai mun
1 of 11
Home
About
http://mrsaimun.blogspot.my/2015/08/igcse-physics-topic-...
Contact
Text to Search...
Home
IGCSE
3:45 PM
IGCSE
IGCSE Physics : Topic 1 General Physics
SI Units
Quantity
Unit
Symbol
Mass
Kilogram
KG
Force
Newton
Weight
Newton
Pressure
Pascal
Pa
Energy
Joules
Work
Joules
Power
Watt
Frequency
Hertz
Hz
PD, EMF
Voltage
Current
Amperes
Resistance
Ohms
(Omega)
Charge
Coulombs
Specific Heat capacity
Joules per kilogram Celsius
J/KgC
Specific Heat Latent
Joules per Kilogram
J/KG
Temperature
Kelvin/ Celsius
K Or C
14/6/2016 12:01 PM
IGCSE Physics : Topic 1 General Physics - mr sai mun
2 of 11
http://mrsaimun.blogspot.my/2015/08/igcse-physics-topic-...
1.1- Measuring Time And Length
Measuring Length-Micrometer ( Use 10 sheets of paper for accuracy)
Measuring Time- E.g. : one swing of pendulum ( Find the times for 25 swings for accurate results)
Example of Scalar qualities-Time, Volume, Speed, temperature
Example of Vector qualities- Velocity, Change in Temperature, acceleration, force, momentum
1.2- Mass, weight, volume and density
Density= Mass/ Volume
Mass: the property of an object that is a measure of its inertia (a resistance to accelerate), the amount of matter it contai
influence in a gravitational field.
Weight is the force of gravity acting on an object, measured in Newtons, and given by the formula: Weight = mass accele
gravity
Measuring volume
Liquid- Level on the scale Regular object(Square box) - Ruler
Irregular Object(Rock)- Lower into a partly filled measuring cylinder, Rise in level on the volume scale gives the volume of
Alternative method - Displacement Can (Fill water to level of spout, insert object, water displaced = volume of object)
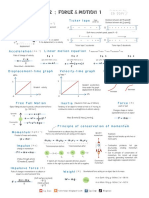
1.3- Speed, velocity, Acceleration
Speed= distance/time
Acceleration= Change in velocity/ time taken
Velocity= Vector ( Magnitude + direction) Speed= Scalar ( Magnitude only)
Distance Time Graph
Constant gradient= constant speed increasing gradient= acceleration
Zero gradient= stopped Gradient= Speed of object
14/6/2016 12:01 PM
IGCSE Physics : Topic 1 General Physics - mr sai mun
3 of 11
http://mrsaimun.blogspot.my/2015/08/igcse-physics-topic-...
Speed Time Graph
Zero gradient= Constant speed Constant gradient= steady acceleration
Gradient of graph= Acceleration Distance= Area under graph
Positive increase of speed= Acceleration Negative increase of speed= Retardation
Acceleration of Free fall= gravitational field strength in Earth = 10
Terminal Velocity
Downward acceleration is caused by Gravitational field strength; Air resistance slow things down. Once air resistance is equ
Gravitational field strength, it is at terminal velocity ( Constant Velocity)
1.4- Forces
Hooke's Law
The extension of an object is proportional to the load beneath its elastic limit.
Load= Spring constant x extension
Limit of proportionality= point at which load and extension are no longer proportional
Elastic limit= Spring will be permanently stretched
Newton's first law of motion= If no external for is acting on it, an object will, if stationary, remain stationary, and if moving
moving at a steady speed in the same straight line
Newtons 2nd law of motion: F = m a -acceleration is proportional to the force, and inversely proportional to mass
Newtons 3rd law of motion: if object A exerts a force on object B, then object B will exert an equal but opposite force on o
Centripetal Force and Centrifugal Force
Circular motions- An object at steady speed in a circular orbit is always accelerating as its direction is changing, but it gets
the centre
Centripetal force- Force acting towards centre of circle
Centrifugal force- Force acting outwards the centre of circle.
Magnitude of centripetal and centrifugal is the same but direction is opposite
Centripetal force increase when mass, speed and radius increase
1.5- Turning Effects
Moment of a force= force x perpendicular distance from the point
14/6/2016 12:01 PM
IGCSE Physics : Topic 1 General Physics - mr sai mun
4 of 11
http://mrsaimun.blogspot.my/2015/08/igcse-physics-topic-...
Moments of a force are measured in Newton meters, can be either clockwise or anticlockwise.
Conditions of equilibrium= no net moments, sum of clockwise moment is equal to the sum of anticlockwise moment.
1.6 - Energy, Work and Power
Key terms and formulas: KE- 1/2MV^2 GPE- MGH
Law of conservation of energy- Energy cannot be made or destroyed, but it can change from one form to another.
Types of energy:
Energy Type
What is it?
Example
Kinetic Energy
Energy due to a motion
A moving object
Gravitational Energy
Energy from potential to fall
A book on shelf
Chemical Energy
Energy stored in chemical bonds
Food, Batteries
Strain or elastic Energy
Something stretched has the
Compressed string
potential to do work
Nuclear Energy
Energy released when particles in
Nuclear Power station
atoms are rearranged or when
atom splits
Internal Energy
Kinetic + Potential Energy
Electrical energy
Energy carried by electrons
Bulb
Light
Energy carried in light waves
Light from sun
Sound
Energy carried in sound waves
Sound from loudspeaker
Radiated Energy
Energy Resources
Renewable source- Sources that won't run out
Non-renewable source- Sources that would be extinct in a certain number of time
fuels can be burnt (or nuclear fuel can be forced to decay) in thermal power stations to transform the chemical energy sto
thermal energy which makes steam which turns turbines (kinetic energy) to produce electricity
advantage: cheap, plentiful, low-tech
disadvantage: harmful wastes -produces greenhouse gases and pollutant gases, radiation
hydroelectric dams: river and rain water fill up a lake behind a dam. As water rushes down through the dam, it turns turbi
turn generators
tidal power scheme: a dam is built across a river where it meets the sea. The lake behind the dam fills when the tide com
empties when the tide goes out. The flow of water turns the generator.
advantage: no greenhouse gases are produced
14/6/2016 12:01 PM
IGCSE Physics : Topic 1 General Physics - mr sai mun
5 of 11
http://mrsaimun.blogspot.my/2015/08/igcse-physics-topic-...
disadvantage: expensive, cant be built everywhere
wave energy: generators are driven by the up and down motion of the waves at sea.
advantage: does not produce greenhouse gases
disadvantage: difficult to build
geothermal resources: water is pumped down to hot rocks deep underground and rises as steam.
advantage: no carbon dioxide is produced
disadvantage: deep drilling is difficult and expensive
nuclear fission: uranium atoms are split by shooting neutrons at them.
advantage: produces a lot of energy from using very little resources
disadvantage: producing radioactive waste
solar cells: are made of materials that can deliver an electrical current when they absorb light energy solar panels: absorb
and use it to heat water
advantage: does not produce carbon dioxide
disadvantage: variable amounts of sunshine in some countries
Efficiency, Work and Power Formulas
Efficiency= useful work done/ total energy input
Work done= Force x Distance
Power= Work Done/ Time
1.7 - Pressure
Pressure = Force / area
To reduce pressure- Increase surface area of base
Pressure in liquid
Pressure= density x g(10) x height
Characteristic of pressure in liquids:
-Pressure acts in all directions
14/6/2016 12:01 PM
IGCSE Physics : Topic 1 General Physics - mr sai mun
6 of 11
http://mrsaimun.blogspot.my/2015/08/igcse-physics-topic-...
-Pressure increase with depth
-Pressure depends on the density of liquid
-Pressure doesn't depend on the shape of the container
Pressure from the air
Barometers measure atmospheric pressure, standard atmospheric pressure = pressure that supports a column of 760mm o
(101300 Pa)
Manometer measures pressure difference, height difference in manometer shows extra pressure. Actual pressure of gas s
excess pressure + atmospheric pressure.
Gas Pressure and Volume
For a fed mass of gas at a constant temperature, the pressure is inversely proportional to the volume. (Boyle's Law
Pressure and Volume are inversely proportional ( volume halves = pressure double)
P1V1=P2V2
Pressure x volume always has the same value
--Next Topic
Topic 1 General Physics
Topic 2 Thermal Physics
Topic 3 Properties of Waves, Including Sound and Light
Topic 4 Electricity and Magnetism
Topic 5 Atomic Physics
--Related Post
IGCSE Past 10 Years Series
IGCSE Results Says It All
Top 9 Things You Must Know About IGCSE
Top 10 Reasons To Study In An International School
--
Share on Facebook
Share on Twitter
Share on Google Plus
14/6/2016 12:01 PM
IGCSE Physics : Topic 1 General Physics - mr sai mun
7 of 11
http://mrsaimun.blogspot.my/2015/08/igcse-physics-topic-...
RELATED POSTS
0 comments:
Comment as:
Publish
Newer Post
Home
1,681,812
14/6/2016 12:01 PM
IGCSE Physics : Topic 1 General Physics - mr sai mun
8 of 11
http://mrsaimun.blogspot.my/2015/08/igcse-physics-topic-...
14/6/2016 12:01 PM
IGCSE Physics : Topic 1 General Physics - mr sai mun
9 of 11
http://mrsaimun.blogspot.my/2015/08/igcse-physics-topic-...
Teacher's Profile on V I P
Website
in ASTRO Top Tutor TV
in Radio BFM 89.9
in ASTRO
in NTV 7
in The STAR Newspaper
in New Straits Times I
in New Straits Times II
in New Straits Times III
in The STAR Online
in R.AGE The STAR
in China Press
in Sin Chew Daily
in AYA Awards
14/6/2016 12:01 PM
IGCSE Physics : Topic 1 General Physics - mr sai mun
10 of 11
Copyright 2015 mr sai mun
http://mrsaimun.blogspot.my/2015/08/igcse-physics-topic-...
Tweets
Created By Sora Templates and
Blogger Themes
by My
@mrsaimun
Distributed By Gooyaabi Templates
mr sai mun @mr
14/6/2016 12:01 PM
IGCSE Physics : Topic 1 General Physics - mr sai mun
11 of 11
http://mrsaimun.blogspot.my/2015/08/igcse-physics-topic-...
14/6/2016 12:01 PM
You might also like
- Physics 1010-401: Signature Assignment & Reflective EssayDocument12 pagesPhysics 1010-401: Signature Assignment & Reflective Essayapi-272566492No ratings yet
- Amrit Lab 4Document10 pagesAmrit Lab 4amritsingh292004No ratings yet
- Conservation of EnergyDocument8 pagesConservation of EnergyKarl HendrixNo ratings yet
- 2 Phys 2 Task 2023Document12 pages2 Phys 2 Task 2023lizardsquad0705No ratings yet
- Thermal Physics 6: Last TimeDocument6 pagesThermal Physics 6: Last TimekewancamNo ratings yet
- Hacking The Universe: Deepak Soman. Dinoop P.Malayil, Achu BDocument14 pagesHacking The Universe: Deepak Soman. Dinoop P.Malayil, Achu BDeepak Soman100% (1)
- Physics Ss2 2nd Term e NotesDocument73 pagesPhysics Ss2 2nd Term e NotesAdio Babatunde Abiodun CabaxNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy and Power Physics ChapterDocument9 pagesWork, Energy and Power Physics ChapterAnthony HugillNo ratings yet
- CCCCC CC CCCCCCCCCCCCCCC C!"CC# "#"CCDocument27 pagesCCCCC CC CCCCCCCCCCCCCCC C!"CC# "#"CCDeepak SomanNo ratings yet
- Topic 2.4 - Momentum and ImpulseDocument49 pagesTopic 2.4 - Momentum and ImpulsePaul Amezquita100% (1)
- General Physics - Thermodynamics I Work & First LawDocument92 pagesGeneral Physics - Thermodynamics I Work & First LawPé Nấm ĐộcNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document14 pagesChapter 1Camella Shuriken CataluñaNo ratings yet
- 11P01 Physical World (V1.3)Document6 pages11P01 Physical World (V1.3)Pukhraj Singh RajguruNo ratings yet
- Sci Revision NotesDocument6 pagesSci Revision NotesMysha OngNo ratings yet
- Physicsproject 1Document7 pagesPhysicsproject 1api-232800390No ratings yet
- The Basics of ThermodynamicsDocument11 pagesThe Basics of Thermodynamicsの雪No ratings yet
- Physics Basics, Part I: Units Laws of MotionDocument20 pagesPhysics Basics, Part I: Units Laws of MotionpmnvmgpmnvmgNo ratings yet
- Initial DesignDocument66 pagesInitial DesignDinoop Philip MalayilNo ratings yet
- 211Document7 pages211Anonymous Qr763VNo ratings yet
- Signature AssignmentDocument7 pagesSignature Assignmentapi-272675381No ratings yet
- E MC2Document12 pagesE MC2jiljil1980100% (2)
- Biological Physics: NelsonDocument23 pagesBiological Physics: NelsonShoniqua JohnsonNo ratings yet
- 7th Grade Physical Science-EnergyDocument20 pages7th Grade Physical Science-Energyleojohn2100% (1)
- Co777Document10 pagesCo777Rafi HossainNo ratings yet
- HSC Physics Notes KISSDocument45 pagesHSC Physics Notes KISSAnita James100% (2)
- Term ProjectDocument9 pagesTerm Projectapi-227668688No ratings yet
- Lecture 1-Part 1-Energy and The EnvironmentDocument8 pagesLecture 1-Part 1-Energy and The EnvironmentShahid AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To PhysicsDocument3 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To PhysicsDin AhmadNo ratings yet
- Impulse - MomentumDocument5 pagesImpulse - MomentumMichael CaingletNo ratings yet
- FR 8 - CollisionsDocument5 pagesFR 8 - CollisionsAngelica UyNo ratings yet
- GENERAL PHYSICS 1 Quarter 2 Activity SheetDocument26 pagesGENERAL PHYSICS 1 Quarter 2 Activity SheetSeverus S Potter100% (1)
- Work, Energy and Power: Key Concepts ExplainedDocument8 pagesWork, Energy and Power: Key Concepts ExplainedShoryamann SharmaNo ratings yet
- MD - Mahtabul Islam ID-192200011Document16 pagesMD - Mahtabul Islam ID-192200011Mahtab IslamNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy, Power, Momentum: Measures of Effort & Motion Conservation LawsDocument32 pagesWork, Energy, Power, Momentum: Measures of Effort & Motion Conservation Lawsraj78678No ratings yet
- LTseung PDFDocument71 pagesLTseung PDFMAGUS43No ratings yet
- Space: What Is This Topic About?Document34 pagesSpace: What Is This Topic About?CyberbullyNo ratings yet
- Work-Power-Energy Physsics 12 LectureDocument12 pagesWork-Power-Energy Physsics 12 LecturefilchibuffNo ratings yet
- Basics of Physics: Physics Is Branch of Science Which Deals With Properties and Interaction of Matter andDocument28 pagesBasics of Physics: Physics Is Branch of Science Which Deals With Properties and Interaction of Matter andSalman Bhatti0% (1)
- Natsci 101.1: Physical Science: O O O ODocument5 pagesNatsci 101.1: Physical Science: O O O OMatthew Alison ApostolNo ratings yet
- Nuclear FusionDocument6 pagesNuclear FusionmokshNo ratings yet
- G9d - Semester Exam Revision HelpDocument3 pagesG9d - Semester Exam Revision HelpSimonNo ratings yet
- ASTR1020: Reminder - WebsiteDocument9 pagesASTR1020: Reminder - Websitemaokly10No ratings yet
- Physics 1010 ProjectDocument9 pagesPhysics 1010 Projectapi-242211470No ratings yet
- 22 Physics Semester Final Exam ReviewDocument7 pages22 Physics Semester Final Exam ReviewDemetrius HughesNo ratings yet
- Physics: PressureDocument7 pagesPhysics: PressureJason TehNo ratings yet
- Checkpoint Physics Notes Chapter 1-5Document5 pagesCheckpoint Physics Notes Chapter 1-5Siddhant Srivastava50% (2)
- O Level Physics CheatsheetDocument11 pagesO Level Physics Cheatsheetkoh_tian_2No ratings yet
- KOE043Document15 pagesKOE043Utkarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy, Power, Momentum: Measures of Effort & Motion Conservation LawsDocument32 pagesWork, Energy, Power, Momentum: Measures of Effort & Motion Conservation Lawskur8cobainNo ratings yet
- The Gravitational Force Quantum and Its ValueDocument4 pagesThe Gravitational Force Quantum and Its ValueВасилена ГеоргиеваNo ratings yet
- General Physics (PHY 2140) : Modern Physics Nuclear and Particle Physics Nuclear Energy Elementary ParticlesDocument38 pagesGeneral Physics (PHY 2140) : Modern Physics Nuclear and Particle Physics Nuclear Energy Elementary ParticlesmehrsaNo ratings yet
- O Level Physics Revision NotesDocument28 pagesO Level Physics Revision NotesRegie Sacil EspiñaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Energy.Document5 pagesElectrical Energy.ShehbazShoukatNo ratings yet
- GCSE Physics guide to energy stores and transfersDocument4 pagesGCSE Physics guide to energy stores and transferssuperpooh-1No ratings yet
- Power Plants Lecture 10thDocument26 pagesPower Plants Lecture 10thharis shahNo ratings yet
- EME E-Note 02032016 091807AMDocument207 pagesEME E-Note 02032016 091807AMDHAVAL PANCHALNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5: Elastic and Inelastic Collisions: MicroscopicDocument3 pagesLesson 5: Elastic and Inelastic Collisions: Microscopicjayson bullenaNo ratings yet
- Negative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 4: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #4From EverandNegative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 4: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #4No ratings yet
- Past Physics exam questions on Forces, Motion and EnergyDocument9 pagesPast Physics exam questions on Forces, Motion and EnergyIzatul NadiaNo ratings yet
- Force and Motion Ex1Document16 pagesForce and Motion Ex1Izatul NadiaNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion and Turning EffectDocument10 pagesCircular Motion and Turning EffectIzatul NadiaNo ratings yet
- CP WS Tuning ForkDocument1 pageCP WS Tuning ForkIzatul NadiaNo ratings yet
- Phyiscs Paper 6 CardsDocument19 pagesPhyiscs Paper 6 CardsSiddique ShahidNo ratings yet
- Measuring Motion Worksheet - 1.1Document7 pagesMeasuring Motion Worksheet - 1.1Izatul Nadia0% (1)
- PREP Moon Choir and GolfersDocument1 pagePREP Moon Choir and GolfersIzatul NadiaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Revision Guide Chapter 1Document18 pagesIGCSE Physics Revision Guide Chapter 1Izatul NadiaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE Physics Practice Book AnswersDocument22 pagesCambridge IGCSE Physics Practice Book AnswersRonnie Quek50% (2)
- 0625 Scheme of WorkDocument64 pages0625 Scheme of WorkIzatul NadiaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Physics 167041-2016-2018-Syllabus PDFDocument45 pagesSyllabus Physics 167041-2016-2018-Syllabus PDFjanpath3834No ratings yet
- ISO 9001Document40 pagesISO 9001Izatul NadiaNo ratings yet
- Notes and WS - 8Lb - Sound Travelling in SpaceDocument5 pagesNotes and WS - 8Lb - Sound Travelling in SpaceIzatul NadiaNo ratings yet
- Acoustics PosterDocument1 pageAcoustics PosterIzatul NadiaNo ratings yet
- UMIES Paper Nadia 2Document6 pagesUMIES Paper Nadia 2Izatul NadiaNo ratings yet
- 5s ConceptDocument28 pages5s ConceptIzatul NadiaNo ratings yet
- Examples of Physics Homework Help: Solved Mechanical Energy Conservation ProblemsDocument4 pagesExamples of Physics Homework Help: Solved Mechanical Energy Conservation ProblemsJeff HardyNo ratings yet
- AP Physics Semester 1 Final Exam ReviewDocument42 pagesAP Physics Semester 1 Final Exam ReviewLynn Hollenbeck BreindelNo ratings yet
- ABS-G-Guidance On Spectral-Based Fatigue Analysis For Vessels-Jan-2012Document38 pagesABS-G-Guidance On Spectral-Based Fatigue Analysis For Vessels-Jan-2012Alicia JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Boardworks - GravitationDocument36 pagesBoardworks - Gravitationdiane hoylesNo ratings yet
- H9C Mnu eDocument238 pagesH9C Mnu es_barriosNo ratings yet
- 04 Scalar and VectorsDocument26 pages04 Scalar and VectorsMohamed Siyad HassanNo ratings yet
- Dictionary of Automotive Terms Vol IDocument922 pagesDictionary of Automotive Terms Vol IMakNo ratings yet
- SHORT NOTES Force and Motion 1Document1 pageSHORT NOTES Force and Motion 1YARSHANA A/P SIVAM MoeNo ratings yet
- Science 5124 - G 10 - 12Document108 pagesScience 5124 - G 10 - 12Andrew Jr Tembo83% (6)
- Motion Along A Straight LineDocument9 pagesMotion Along A Straight Lineahmednalla50% (2)
- A Differential Equation Is A Mathematical Equation For An Unknown Function of One or Several Variables That Relates The Values of The Function Itself and Its Derivatives of Various OrdersDocument1 pageA Differential Equation Is A Mathematical Equation For An Unknown Function of One or Several Variables That Relates The Values of The Function Itself and Its Derivatives of Various OrderschrajnaagNo ratings yet
- A1 C2 L8 Solution Key Worked OutDocument27 pagesA1 C2 L8 Solution Key Worked OutVhenSerdanNo ratings yet
- 2D Acceleration ExamplesDocument3 pages2D Acceleration ExamplesEvalineNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 4 - Terminal VelocityDocument3 pagesLesson Plan 4 - Terminal Velocityapi-300725936No ratings yet
- Choi, J., and Curry, RDocument9 pagesChoi, J., and Curry, RRajdeep PawarNo ratings yet
- Edexel GCSE (9-1) Science CP1 Motion and CP2 Forces and Motion Test 15 - 16 With Mark SchemeDocument16 pagesEdexel GCSE (9-1) Science CP1 Motion and CP2 Forces and Motion Test 15 - 16 With Mark SchemePaul Burgess91% (11)
- As Level Physics Revision NotesDocument13 pagesAs Level Physics Revision NotesZulaa JargalsaikhanNo ratings yet
- Calculating velocities, accelerations and forces for moving objectsDocument3 pagesCalculating velocities, accelerations and forces for moving objectssara MartinezNo ratings yet
- Science-8-Q1-Mod1-Force, Motion - EnergyDocument27 pagesScience-8-Q1-Mod1-Force, Motion - EnergyAngelica BuquiranNo ratings yet
- 513 Momentum and Impulse ProblemsDocument2 pages513 Momentum and Impulse ProblemsNick PolitiNo ratings yet
- Phys CH2Document37 pagesPhys CH2dockmom4100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Kinematics - 2022 NotesDocument22 pagesChapter 3 Kinematics - 2022 NotesLazy BanditNo ratings yet
- Quake II PhysicsDocument15 pagesQuake II PhysicsjshdflsieoijfsdNo ratings yet
- Second Edition: by Ken Burnside, Eric Finley & Tony ValleDocument24 pagesSecond Edition: by Ken Burnside, Eric Finley & Tony ValleILuvLA100% (1)
- SUVAT Support SheetDocument10 pagesSUVAT Support SheetAdam ChiangNo ratings yet
- Physics BSC QuestionDocument31 pagesPhysics BSC QuestionIsha MohadikarNo ratings yet
- 141 Lab+manualDocument138 pages141 Lab+manualMiles HarberNo ratings yet
- 1 - Intro and Rectilinear Motion With ProblemsDocument29 pages1 - Intro and Rectilinear Motion With ProblemsSuhaib IntezarNo ratings yet
- Scope and Sequence - PhysicsDocument2 pagesScope and Sequence - Physicsapi-232424041No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Curvilinear MotionDocument87 pagesLecture 2 Curvilinear MotionDave CruzNo ratings yet