Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Motion and acceleration of objects moving along a straight line
Uploaded by
Iqbal A MirOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Motion and acceleration of objects moving along a straight line
Uploaded by
Iqbal A MirCopyright:
Available Formats
32
CHAPTE R 2 M OTION ALONG A STRAIG HT LI N E
give the velocity v(t) for (a) the dropped egg
and (b) the thrown egg? (Curves A and B are
parallel; so are C, D, and E; so are F and G.)
1
8 The following equations give the velocity
v(t) of a particle in four situations: (a) v 3; (b)
v 4t 2 2t 6; (c) v 3t 4; (d) v 5t 2 3.
To which of these situations do the equations of
Table 2-1 apply?
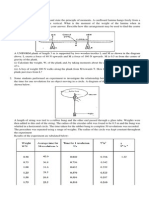
11 Figure 2-23 shows that a particle moving along an x axis undergoes three periods of acceleration. Without written computation, rank the acceleration periods according to the increases
they produce in the particles velocity, greatest first.
3
Acceleration a
9 In Fig. 2-22, a cream tangerine is thrown directly upward past three evenly spaced windows
of equal heights. Rank the windows according
to (a) the average speed of the cream tangerine
while passing them, (b) the time the cream tangerine takes to pass them, (c) the magnitude of
the acceleration of the cream tangerine while
passing them, and (d) the change v in the
speed of the cream tangerine during the passage, greatest first.
apples release, the balloon is accelerating upward with a magnitude of 4.0 m/s2 and has an upward velocity of magnitude 2 m/s.
What are the (a) magnitude and (b) direction of the acceleration of
the apple just after it is released? (c) Just then, is the apple moving
upward or downward, or is it stationary? (d) What is the magnitude of its velocity just then? (e) In the next few moments, does the
speed of the apple increase, decrease, or remain constant?
Figure 2-22
Question 9.
10 Suppose that a passenger intent on lunch
during his first ride in a hot-air balloon accidently drops an apple
over the side during the balloons liftoff. At the moment of the
(3)
(1)
(2)
Time t
Figure 2-23 Question 11.
Problems
Tutoring problem available (at instructors discretion) in WileyPLUS and WebAssign
SSM
Worked-out solution available in Student Solutions Manual
WWW Worked-out solution is at
Number of dots indicates level of problem difficulty
ILW
Interactive solution is at
http://www.wiley.com/college/halliday
Additional information available in The Flying Circus of Physics and at flyingcircusofphysics.com
Module 2-1 Position, Displacement, and Average Velocity
1 While driving a car at 90 km/h, how far do you move while
your eyes shut for 0.50 s during a hard sneeze?
Cogito ergo zoom! (I think, therefore I go fast!). In 2001, Sam
Whittingham beat Hubers record by 19.0 km/h. What was
Whittinghams time through the 200 m?
2 Compute your average velocity in the following two cases:
(a) You walk 73.2 m at a speed of 1.22 m/s and then run 73.2 m at a
speed of 3.05 m/s along a straight track. (b) You walk for 1.00 min
at a speed of 1.22 m/s and then run for 1.00 min at 3.05 m/s along a
straight track. (c) Graph x versus t for both cases and indicate how
the average velocity is found on the graph.
7 Two trains, each having a speed of 30 km/h, are headed at
each other on the same straight track. A bird that can fly 60 km/h
flies off the front of one train when they are 60 km apart and heads
directly for the other train. On reaching the other train, the (crazy)
bird flies directly back to the first train, and so forth. What is the total distance the bird travels before the trains collide?
3 SSM WWW An automobile travels on a straight road for
40 km at 30 km/h. It then continues in the same direction for another 40 km at 60 km/h. (a) What is the average velocity of the car
during the full 80 km trip? (Assume that it moves in the positive x
direction.) (b) What is the average speed? (c) Graph x versus t and
indicate how the average velocity is found on the graph.
8
Panic escape. Figure 2-24 shows a general situation in
which a stream of people attempt to escape through an exit door
that turns out to be locked. The people move toward the door at
speed vs 3.50 m/s, are each d 0.25 m in depth, and are separated by L 1.75 m. The
L
L
L
arrangement in Fig. 2-24
occurs at time t 0. (a) At
what average rate does the
layer of people at the door
d
d
d
increase? (b) At what time
Locked
does the layers depth reach
door
5.0 m? (The answers reveal
Figure 2-24 Problem 8.
how quickly such a situation
becomes dangerous.)
4 A car moves uphill at 40 km/h and then back downhill at 60
km/h. What is the average speed for the round trip?
5 SSM The position of an object moving along an x axis is given
by x 3t 4t 2 t 3, where x is in meters and t in seconds. Find the
position of the object at the following values of t: (a) 1 s, (b) 2 s,
(c) 3 s, and (d) 4 s. (e) What is the objects displacement between t 0
and t 4 s? (f) What is its average velocity for the time interval
from t 2 s to t 4 s? (g) Graph x versus t for 0 t 4 s and indicate how the answer for (f) can be found on the graph.
6 The 1992 world speed record for a bicycle (human-powered
vehicle) was set by Chris Huber. His time through the measured
200 m stretch was a sizzling 6.509 s, at which he commented,
9 ILW In 1 km races, runner 1 on track 1 (with time 2 min, 27.95 s)
appears to be faster than runner 2 on track 2 (2 min, 28.15 s).
However, length L2 of track 2 might be slightly greater than length
L1 of track 1. How large can L2 L1 be for us still to conclude that
runner 1 is faster?
You might also like
- Questions CH-1 To 7Document10 pagesQuestions CH-1 To 7ajaysahu1441No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Assignment For IitjeeDocument25 pagesChapter 2 Assignment For IitjeeShashank ShekharNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter on Kinematics Formulas and ConceptsDocument22 pagesPhysics Chapter on Kinematics Formulas and ConceptsSubho Bhattacharya0% (1)
- University Physics Chapter2Document9 pagesUniversity Physics Chapter2Karlo OrnietaNo ratings yet
- Motion in 1 D QuestionsDocument2 pagesMotion in 1 D QuestionsIqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- Tutorials 3 - Motion in One Dimension and Two DimensionsDocument6 pagesTutorials 3 - Motion in One Dimension and Two DimensionsSamson ManyanyeNo ratings yet
- Kinematics MC PracticeDocument17 pagesKinematics MC Practicescientific1576No ratings yet
- QPDocument5 pagesQPSamuelNo ratings yet
- Extra Solved Physics ProblemsDocument7 pagesExtra Solved Physics ProblemsAhmed AttallaNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document9 pagesSheet 1Tony AtefNo ratings yet
- 2010 Physiscs SolutionsDocument21 pages2010 Physiscs Solutionsjoebloggs_com100% (1)
- Monday Test 1 Xi 21-22Document5 pagesMonday Test 1 Xi 21-22Yash MorjhawalNo ratings yet
- 04 KinematicsDocument17 pages04 KinematicsMilan LawNo ratings yet
- Sem 2015-16Document5 pagesSem 2015-16Samya QureshiNo ratings yet
- Tut 1Document2 pagesTut 1muhammadmusakhanNo ratings yet
- Ch3 ExerciseDocument14 pagesCh3 ExerciseAldrin taduranNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper +1 Physics September 2022Document7 pagesSample Paper +1 Physics September 2022Sukhwinder KumarNo ratings yet
- Ch2 ExerciseDocument14 pagesCh2 ExerciseAldrin taduranNo ratings yet
- 11 Phy ln3 Problems 1629708307Document15 pages11 Phy ln3 Problems 1629708307Sathiya RNo ratings yet
- Exampler CH 8 Motion QuestionsDocument8 pagesExampler CH 8 Motion QuestionsCrackneet SuratNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight Line WorksheetDocument2 pagesMotion in A Straight Line WorksheetSajjan BalasubramanyanNo ratings yet
- CP S HW CH 2Document5 pagesCP S HW CH 2Steve Julius100% (1)
- PPA6 EOC CH 02 MacDocument13 pagesPPA6 EOC CH 02 Macdevonna.wolfeNo ratings yet
- VI To VII Physics3!1!15 LDocument4 pagesVI To VII Physics3!1!15 LiitsivaiahNo ratings yet
- 9 Science Exemplar Chapter 8Document4 pages9 Science Exemplar Chapter 8AnujMauryaNo ratings yet
- JHL RNRX QPX AMVzpwd 4 U4Document50 pagesJHL RNRX QPX AMVzpwd 4 U4Soujany Agnihotri 9th ENo ratings yet
- Kinematicsschool 2009Document7 pagesKinematicsschool 2009EzhilarasiPazhanivelNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Xi See Physics 2023-24Document6 pagesSample Paper Xi See Physics 2023-24jethvadevashyaNo ratings yet
- PHY5113 TUTORIAL N0 2 Questionss-1Document3 pagesPHY5113 TUTORIAL N0 2 Questionss-1AlbertNo ratings yet
- Inematics: Section (A) : Distance and DisplacementDocument10 pagesInematics: Section (A) : Distance and DisplacementIshu FuliyaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Energy Central School mid-term exam physics questionsDocument3 pagesAtomic Energy Central School mid-term exam physics questions39 Yogendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Xi Hy Phy 2023-24Document2 pagesXi Hy Phy 2023-24Guru PrasathNo ratings yet
- Tipler - Chapter03 (Compatibility Mode)Document91 pagesTipler - Chapter03 (Compatibility Mode)Richard Rayner MulyadiNo ratings yet
- Analysis of MotionDocument5 pagesAnalysis of MotionDong Chooi YingNo ratings yet
- Newtonian Mechanics-2D KinematicsDocument68 pagesNewtonian Mechanics-2D KinematicsSuman K ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- PH1011 Tut 1 With Ans BehindDocument5 pagesPH1011 Tut 1 With Ans BehindDayne JongNo ratings yet
- 2: Kinematics (Exercises) : Conceptual QuestionsDocument19 pages2: Kinematics (Exercises) : Conceptual Questions01-Abhinandan Sankar Sadhukhan-12SC2No ratings yet
- Section A and B MechanicsDocument7 pagesSection A and B MechanicsJerrord ThomasNo ratings yet
- 11ap T1 Sec BDocument3 pages11ap T1 Sec Bmahsan abbasNo ratings yet
- Kinema TicsDocument7 pagesKinema Ticsapcc1No ratings yet
- Physics Exam ReviewDocument77 pagesPhysics Exam ReviewJarrett LindseyNo ratings yet
- SS 1 Physics First Term Exam (Hidden Treasure) 2Document5 pagesSS 1 Physics First Term Exam (Hidden Treasure) 2diamondannie90No ratings yet
- Motion WorksheetDocument8 pagesMotion Worksheetstreetdiary.blogNo ratings yet
- Motion in One and Two Dimensions PDFDocument4 pagesMotion in One and Two Dimensions PDFTarun GuptaNo ratings yet
- ch-8 MotionDocument5 pagesch-8 MotionLohith Chary100% (1)
- Physics 1401 (Chapters 1-5) Review - Chapter 1,2Document33 pagesPhysics 1401 (Chapters 1-5) Review - Chapter 1,2FRANCISCO JERHYL KEITH G.No ratings yet
- Motion in 1 Dimension TestDocument11 pagesMotion in 1 Dimension TestKRISHNA KUTADINo ratings yet
- 2.1 Practice QDocument3 pages2.1 Practice QLanTsyNo ratings yet
- Ex3mech 2019Document8 pagesEx3mech 2019Nasim RazaviNo ratings yet
- C - Mock Test 1Document14 pagesC - Mock Test 1RubyBull 18No ratings yet
- Question MVMDocument7 pagesQuestion MVMTusharkanti Sinha RoyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 01 Rectillinear Motion AJN Sir-2921Document3 pagesAssignment 01 Rectillinear Motion AJN Sir-2921iitforumNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Physics SoloutionDocument9 pagesFundamentals of Physics Soloution8310032914No ratings yet
- MCQs on Displacement, Velocity and AccelerationDocument8 pagesMCQs on Displacement, Velocity and AccelerationAdliNo ratings yet
- 71EEE 1stLE MC1Document12 pages71EEE 1stLE MC1Gabriel LizaresNo ratings yet
- Chanakya Vidyalaya STD 11: Physics Unit TestDocument51 pagesChanakya Vidyalaya STD 11: Physics Unit TestANUBHAV ThakurNo ratings yet
- Physics: Kinematics: Motion Along Straight Line: Learning Activity Sheets (Las)Document5 pagesPhysics: Kinematics: Motion Along Straight Line: Learning Activity Sheets (Las)Jhullian Frederick Val VergaraNo ratings yet
- Sph3u Exam ReviewDocument8 pagesSph3u Exam ReviewchelseaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Practice Test-1: Read The Following Instructions Very Carefully Before You ProceedDocument11 pagesAdvanced Practice Test-1: Read The Following Instructions Very Carefully Before You ProceedIqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- 1 Living WorldDocument1 page1 Living WorldIqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- Olympiad GeometryDocument17 pagesOlympiad GeometryIqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- Page PrintDocument1 pagePage PrintIqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- 1 Living WorldDocument1 page1 Living WorldIqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- Dwarf Song Misty MountainDocument1 pageDwarf Song Misty MountainIqbal A Mir0% (1)
- 1 Living World 12Document3 pages1 Living World 12Iqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- IIT Target Course PlannerDocument4 pagesIIT Target Course PlannerIqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- Introduction Geometry PosttestDocument3 pagesIntroduction Geometry PosttestIqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- 1 Living World 9Document1 page1 Living World 9Iqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- Biology (Unity & Diversity of Life) Living World: 2.2.5 ProtozoansDocument4 pagesBiology (Unity & Diversity of Life) Living World: 2.2.5 ProtozoansIqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- 1 Living WorldDocument2 pages1 Living WorldIqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- Biology (Unity & Diversity of Life) Living World: 2.4 Kingdom PlantaeDocument2 pagesBiology (Unity & Diversity of Life) Living World: 2.4 Kingdom PlantaeIqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- Biology (Unity & Diversity of Life) Living World: 2.2.5 ProtozoansDocument4 pagesBiology (Unity & Diversity of Life) Living World: 2.2.5 ProtozoansIqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- 1 Living World 8Document2 pages1 Living World 8Iqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- 1 Living World - 7Document1 page1 Living World - 7Iqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- Neet Biology/Biological Classif. (Dated 06.09.2016)Document2 pagesNeet Biology/Biological Classif. (Dated 06.09.2016)Iqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- Biology (Unity & Diversity of Life) Living World: 1.1 Taxonomical AidsDocument1 pageBiology (Unity & Diversity of Life) Living World: 1.1 Taxonomical AidsIqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- 03.10.2016-NEET 2017 Edge - PCBDocument1 page03.10.2016-NEET 2017 Edge - PCBIqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- Neet Biology/Biological Classif. (Dated 06.09.2016)Document2 pagesNeet Biology/Biological Classif. (Dated 06.09.2016)Iqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- Phasors' Biology/Biological Classif. Forum ProgramDocument1 pagePhasors' Biology/Biological Classif. Forum ProgramIqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- 1 Living WorldDocument1 page1 Living WorldIqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- 03.10.2016-NEET 2017 Edge - PCBDocument1 page03.10.2016-NEET 2017 Edge - PCBIqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- Neet/Jee Physics / Early Steps / Laws of Motion: Fill in The Blanks, True/False (With Reason) EtcDocument2 pagesNeet/Jee Physics / Early Steps / Laws of Motion: Fill in The Blanks, True/False (With Reason) EtcIqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- Phasors NEET/JEE Physics guide for motion in 2DDocument1 pagePhasors NEET/JEE Physics guide for motion in 2DIqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- Phasors NEET/JEE Physics guide for motion in 2DDocument1 pagePhasors NEET/JEE Physics guide for motion in 2DIqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- Neet/Jee Physics / Early Steps / Motion in 1 DDocument1 pageNeet/Jee Physics / Early Steps / Motion in 1 DIqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- Contents IDocument1 pageContents IIqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- 02 Units & DimensionsDocument2 pages02 Units & DimensionsIqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- Assignment HeirarchyDocument1 pageAssignment HeirarchyIqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- DLL SHS STEM Grade 12 - General Physics1 Quarter1 Week3 (Palawan Division) .DocxDocument9 pagesDLL SHS STEM Grade 12 - General Physics1 Quarter1 Week3 (Palawan Division) .Docxjp rotsan100% (4)
- Lecture-4 Moher CircleDocument37 pagesLecture-4 Moher CircleAbhishek BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Modul SBP SPM 2014 Perfect Score Add MathDocument83 pagesModul SBP SPM 2014 Perfect Score Add MathCikgu Faizal67% (3)
- SULIT 3472/1 Matematik Tambahan Kertas 1 Mei 2007Document13 pagesSULIT 3472/1 Matematik Tambahan Kertas 1 Mei 2007ksganNo ratings yet
- Oct 13 2022 CH 13 (6-7) Kinetics of Particles R-Theta Coordinat SystemDocument22 pagesOct 13 2022 CH 13 (6-7) Kinetics of Particles R-Theta Coordinat SystemArtEEzNo ratings yet
- MHT Cet Physics PDFDocument50 pagesMHT Cet Physics PDFPrathamesh Rumde100% (3)
- Introduction To The Agile Systems Engineering Life Cycle MBSE PatternDocument19 pagesIntroduction To The Agile Systems Engineering Life Cycle MBSE PatternsgNo ratings yet
- Sustainability 11 06241Document15 pagesSustainability 11 06241Nguyen Le Tuan KietNo ratings yet
- Science 7 - Module 1 - Version 3Document16 pagesScience 7 - Module 1 - Version 3El Comedor BenedictNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra With SAGEDocument422 pagesLinear Algebra With SAGEKumar BhattathiriNo ratings yet
- ME401T CAD Circle Algorithm - 4Document22 pagesME401T CAD Circle Algorithm - 4AnuragShrivastavNo ratings yet
- Basic Trigonometriy Formulas For Class 10Document3 pagesBasic Trigonometriy Formulas For Class 10LearningScienceNo ratings yet
- Work Immersion Narrative Report SAMPLEDocument38 pagesWork Immersion Narrative Report SAMPLEBaroxx Diaz0% (1)
- @iitandneetwale On Telegram: Jee Main-New Pattern Mathematics Numerical Value & Integer Answer Type QuestionsDocument70 pages@iitandneetwale On Telegram: Jee Main-New Pattern Mathematics Numerical Value & Integer Answer Type QuestionsPranati JenaNo ratings yet
- Measure Theory FundamentalsDocument8 pagesMeasure Theory FundamentalsKaushik JangaNo ratings yet
- Intro 2 AdcsDocument22 pagesIntro 2 AdcsSachin ShendeNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Sample Paper For Class 10Document5 pagesMathematics Sample Paper For Class 10Aman GhastiNo ratings yet
- Distance and DisplacementDocument5 pagesDistance and Displacementvishal_kalraNo ratings yet
- Calculus II: Vector Calculus, Multivariable Functions and SeriesDocument53 pagesCalculus II: Vector Calculus, Multivariable Functions and SeriesWahyu HidayatNo ratings yet
- Formula Matematik Dan Nota RingkasDocument9 pagesFormula Matematik Dan Nota RingkasPurawin Subramaniam100% (11)
- Triangle Congruence for Structure StabilityDocument28 pagesTriangle Congruence for Structure StabilityKimverly Ledda GanadenNo ratings yet
- In Order To Determine The Motion of A Rigid Body, Under The Action of External Forces, It Is Convenient To Replace The Rigid Body by Two Masses Placed at Fixed Distance ApartDocument7 pagesIn Order To Determine The Motion of A Rigid Body, Under The Action of External Forces, It Is Convenient To Replace The Rigid Body by Two Masses Placed at Fixed Distance ApartamdevaNo ratings yet
- G.B.H.S. NYALLA March 2019 Math Practice ExamDocument4 pagesG.B.H.S. NYALLA March 2019 Math Practice ExamAlphonsius WongNo ratings yet
- Phy 11 CH 5Document48 pagesPhy 11 CH 5samyakNo ratings yet
- Workshop CalculationDocument64 pagesWorkshop Calculationbentapada100% (1)
- Articulating Space:: Geometric Algebra For Parametric Design - Symmetry, Kinematics, and CurvatureDocument222 pagesArticulating Space:: Geometric Algebra For Parametric Design - Symmetry, Kinematics, and CurvatureSanjay DuraiNo ratings yet
- 5 - Length, Area, Surface Area and Volume PDFDocument54 pages5 - Length, Area, Surface Area and Volume PDFJeff SnyderNo ratings yet
- ARC101 Theory of ArchitectureDocument4 pagesARC101 Theory of ArchitectureFatima Joy JudayaNo ratings yet
- Question Bank-Static and Strength of Material - Module 3 - B.archDocument8 pagesQuestion Bank-Static and Strength of Material - Module 3 - B.archIrfan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- BT 105 Engineering Graphics Jun 2020Document3 pagesBT 105 Engineering Graphics Jun 2020khanak patleNo ratings yet