Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Contet Courses Taken
Uploaded by
api-3178778990 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views2 pagesHis 101 History of Europe to 1648 Classical era to 1648. His 105 The United States to 1877 Continuation of His 105 to the present. His 343 Latin America and The Cold War Political, economic, and cultural developments from Indian settlement through contemporary society.
Original Description:
Original Title
contet courses taken
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHis 101 History of Europe to 1648 Classical era to 1648. His 105 The United States to 1877 Continuation of His 105 to the present. His 343 Latin America and The Cold War Political, economic, and cultural developments from Indian settlement through contemporary society.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views2 pagesContet Courses Taken
Uploaded by
api-317877899His 101 History of Europe to 1648 Classical era to 1648. His 105 The United States to 1877 Continuation of His 105 to the present. His 343 Latin America and The Cold War Political, economic, and cultural developments from Indian settlement through contemporary society.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
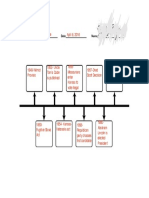
Course #
Course Title
His 101
History of Europe to 1648
Classical era to 1648.
His 102
Course Description
Introduction to European history from the
History of Europe Since 1648
Introduction to European history since 1648.
His 105
The United States to 1877
velopment.
Political, cultural, social, and economic de-
His 106
The United States Since 1877
Continuation of His 105 to the present.
His 307
African American History to 1865 Black American history from West Africa to
1865, emphasizing the role of black leaders and
their struggle against oppression.
His 330
The History of Mississippi
His 343
Latin America and the Cold War
Political, economic, and cultural
developments from Indian settlement through
contemporary society.
This course examines the history of Latin
America's place in the Cold War (1947-1991).
Case studies will be used to understand the
extent of the Communist threat and the logic of
U.S. overt and covert intervention in the region.
His 356 Reformation Europe, 1517-1648
European politics, society, and culture from the
Reformation through the Thirty Years' War.
His 382 The Cold War
Survey of major developments and
consequences of the U.S.-Soviet rivalry from
World War II to the present.
His 397 China and the United States since 1784
History of contacts between the two
peoples since 1784, with focus on the
20th century. Includes all aspects of
cultural, economic, and political relations.
His 450 Undergrad Research: European History
This course is a research based course
where the students will write a 25 page
research essay on a specific topic during `
the Cold War.
Pol 101 Introduction to American Politics
Constitutional principles of U.S.
governmental framework. Political
participation, electoral processes, political
institutions.
Pol 102 Introduction to Comparative Politics
Econ 202 Principles of Microeconomics
Econ 203 Principles of Macroeconomics
Soc 101
Introductory Sociology I
Psy 201
General Psychology
Examination of non-American political
systems, their significant political
institutions, and their political behavior.
The nature of economics, economic
concepts, and institutions; the role of the
price system in directing the production
of goods and services; distribution of
income; and comparative
economic systems.
Resources and goals of the economy;
national income; unemployment; money
and banking; fiscal and monetary policy;
contemporary problems; economic
growth; and international economics.
Concepts and methods necessary for
studying society.
Introduction: individual development,
motivation, emotion, motor function,
sensory and neural functions, intelligence,
learning, perceiving, thinking, social
behavior, and personality.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Screen Shot 2016-05-10 at 10 47 13 AmDocument1 pageScreen Shot 2016-05-10 at 10 47 13 Amapi-317877899No ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Screen Shot 2016-05-10 at 10 46 21 AmDocument1 pageScreen Shot 2016-05-10 at 10 46 21 Amapi-317877899No ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Screen Shot 2016-05-10 at 10 08 28 AmDocument1 pageScreen Shot 2016-05-10 at 10 08 28 Amapi-317877899No ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Screen Shot 2016-05-10 at 10 11 41 AmDocument1 pageScreen Shot 2016-05-10 at 10 11 41 Amapi-317877899No ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Screen Shot 2016-05-10 at 10 46 48 AmDocument1 pageScreen Shot 2016-05-10 at 10 46 48 Amapi-317877899No ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Screen Shot 2016-05-10 at 10 11 29 AmDocument1 pageScreen Shot 2016-05-10 at 10 11 29 Amapi-317877899No ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Screen Shot 2016-05-10 at 10 09 15 AmDocument1 pageScreen Shot 2016-05-10 at 10 09 15 Amapi-317877899No ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Screen Shot 2016-05-10 at 10 46 58 AmDocument1 pageScreen Shot 2016-05-10 at 10 46 58 Amapi-317877899No ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Screen Shot 2016-05-10 at 10 09 24 AmDocument1 pageScreen Shot 2016-05-10 at 10 09 24 Amapi-317877899No ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- Screen Shot 2016-05-10 at 10 08 14 AmDocument1 pageScreen Shot 2016-05-10 at 10 08 14 Amapi-317877899No ratings yet
- Screen Shot 2016-05-10 at 10 12 26 AmDocument1 pageScreen Shot 2016-05-10 at 10 12 26 Amapi-317877899No ratings yet
- Screen Shot 2016-05-10 at 10 12 37 AmDocument1 pageScreen Shot 2016-05-10 at 10 12 37 Amapi-317877899No ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Screen Shot 2016-05-10 at 10 05 43 AmDocument1 pageScreen Shot 2016-05-10 at 10 05 43 Amapi-317877899No ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Screen Shot 2016-05-10 at 10 05 04 AmDocument1 pageScreen Shot 2016-05-10 at 10 05 04 Amapi-317877899No ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Chapter 11-The North and South Take Different Paths and Chapter 12-An Age of ReformsDocument6 pagesChapter 11-The North and South Take Different Paths and Chapter 12-An Age of Reformsapi-317877899100% (1)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Create A Political PartyDocument1 pageCreate A Political Partyapi-317877899No ratings yet
- 2016 Chapter 10 Study Guide 1Document2 pages2016 Chapter 10 Study Guide 1api-317877899No ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Timeline Template 1Document1 pageChapter 14 Timeline Template 1api-317877899No ratings yet
- Mississippi Ordinance of SecessionDocument2 pagesMississippi Ordinance of Secessionapi-317877899No ratings yet
- Rogers Donald Texasmexico MapDocument1 pageRogers Donald Texasmexico Mapapi-317877899No ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Essay 2Document4 pagesEssay 2api-317877899No ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Classroom ManagmentDocument2 pagesClassroom Managmentapi-317877899No ratings yet
- Book Essay 1Document5 pagesBook Essay 1api-317877899No ratings yet
- Soviet-Afghan War DraftDocument25 pagesSoviet-Afghan War Draftapi-317877899No ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Color of Water PaperDocument5 pagesColor of Water Paperapi-317877899No ratings yet
- Eportfolio ResumeDocument1 pageEportfolio Resumeapi-317877899No ratings yet
- Second Book Essay For His 343 Final DraftDocument5 pagesSecond Book Essay For His 343 Final Draftapi-317877899No ratings yet
- Aas PaperDocument5 pagesAas Paperapi-317877899No ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Standard Costing MdiDocument4 pagesStandard Costing MdiAbhineet Kumar0% (1)
- Guc 57 59 28240 2023-02-12T11 44 58Document33 pagesGuc 57 59 28240 2023-02-12T11 44 58Yomna ElmassryNo ratings yet
- Micro Economics Case Study 2: SolvedDocument1 pageMicro Economics Case Study 2: SolvedSayed HashimiNo ratings yet
- Tanay Pansari's Resume - Demand Forecasting, Pricing Analysis, Operations ResearchDocument1 pageTanay Pansari's Resume - Demand Forecasting, Pricing Analysis, Operations ResearchKeshav KumarNo ratings yet
- USTmacro2022b ps2Document2 pagesUSTmacro2022b ps2Jasmine LeeNo ratings yet
- Strategic Bidding in Electricity Spot Markets Under Uncertainty: A RoadmapDocument8 pagesStrategic Bidding in Electricity Spot Markets Under Uncertainty: A RoadmapsunitharajababuNo ratings yet
- H. V. Emy - Liberals, Radicals and Social Politics 1892-1914 (1973, CUP Archive) PDFDocument333 pagesH. V. Emy - Liberals, Radicals and Social Politics 1892-1914 (1973, CUP Archive) PDFDanang Candra Bayuaji100% (1)
- Case Study On ITC E-ChoupalDocument3 pagesCase Study On ITC E-ChoupalRaafia RizwanNo ratings yet
- Oligopoly Market Structure ExplainedDocument38 pagesOligopoly Market Structure Explainedharsh guptaNo ratings yet
- PGDBM Program Business Environment AnalysisDocument11 pagesPGDBM Program Business Environment AnalysisAnubha Bhatnagar100% (1)
- Sarkar-Singer Hypothesis AssessmentDocument8 pagesSarkar-Singer Hypothesis AssessmentArjun Garg100% (1)
- Biology Unit Test and Half Yearly Exam DetailsDocument3 pagesBiology Unit Test and Half Yearly Exam DetailsPriyam SahaNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Riba, Its Types and ImplicationsDocument37 pagesRiba, Its Types and Implicationsmahamamir012No ratings yet
- Managerial EconomicsDocument10 pagesManagerial EconomicsDipali DeoreNo ratings yet
- Inflation Chapter SummaryDocument14 pagesInflation Chapter SummaryMuhammed Ali ÜlkerNo ratings yet
- 2021 PHC General Report Vol 3E - Economic ActivityDocument180 pages2021 PHC General Report Vol 3E - Economic ActivityMartin AnsongNo ratings yet
- Marketing vs Sales: Why Combining The Two Is A Strategic MistakeDocument12 pagesMarketing vs Sales: Why Combining The Two Is A Strategic Mistake'Tareque SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Vocabularies Units 1-4Document3 pagesVocabularies Units 1-4HaloWingsNo ratings yet
- Multinational Capital Budgeting AnalysisDocument17 pagesMultinational Capital Budgeting AnalysisAguntuk Shawon100% (1)
- Pump-Dump Manipulation AnalysiDocument15 pagesPump-Dump Manipulation Analysihedrywan8No ratings yet
- Most Expected Questions Economics Section A MicroDocument3 pagesMost Expected Questions Economics Section A MicroRaju RanjanNo ratings yet
- Chartered UniversityCollege FMA Management Accounting EXAMDocument12 pagesChartered UniversityCollege FMA Management Accounting EXAMMohsena MunnaNo ratings yet
- Nudge Theory in Transport Economics-Anik MaityDocument17 pagesNudge Theory in Transport Economics-Anik MaityAnik MaityNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in Applied Economics Date:, 2016 Track: Academic Time: 2:20 - 3:20 P.M. Grade 11 Strand: ABM Code: ABM - AE12-Ia-d-1Document2 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson Plan in Applied Economics Date:, 2016 Track: Academic Time: 2:20 - 3:20 P.M. Grade 11 Strand: ABM Code: ABM - AE12-Ia-d-1Myla Ebillo67% (3)
- Roadmap of MSCCPM and MScRE 2015 16Document2 pagesRoadmap of MSCCPM and MScRE 2015 16Jasmine TsoNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Demand and Real GDP OutputDocument6 pagesAggregate Demand and Real GDP OutputHarry zhangNo ratings yet
- HAFALAN AKUNTANSI HUMPB (HARTA UTANG MODAL PENDAPATAN BEBAN) (English)Document3 pagesHAFALAN AKUNTANSI HUMPB (HARTA UTANG MODAL PENDAPATAN BEBAN) (English)Ilham SukronNo ratings yet
- Case 4 - Victoria ChemicalsDocument18 pagesCase 4 - Victoria ChemicalsYale Brendan CatabayNo ratings yet
- Exercise A.1.1 - GlobalizationDocument3 pagesExercise A.1.1 - GlobalizationShailani HossainNo ratings yet
- Board Question Paper - July 2023 - 64d0d24ee7f31Document3 pagesBoard Question Paper - July 2023 - 64d0d24ee7f31Sadab raeenNo ratings yet
- Bound for Canaan: The Epic Story of the Underground Railroad, America's First Civil Rights Movement,From EverandBound for Canaan: The Epic Story of the Underground Railroad, America's First Civil Rights Movement,Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (69)
- The Warmth of Other Suns: The Epic Story of America's Great MigrationFrom EverandThe Warmth of Other Suns: The Epic Story of America's Great MigrationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1569)
- Pulling the Chariot of the Sun: A Memoir of a KidnappingFrom EverandPulling the Chariot of the Sun: A Memoir of a KidnappingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- The Devil You Know: A Black Power ManifestoFrom EverandThe Devil You Know: A Black Power ManifestoRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- White Guilt: How Blacks and Whites Together Destroyed the Promise of the Civil Rights EraFrom EverandWhite Guilt: How Blacks and Whites Together Destroyed the Promise of the Civil Rights EraRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (43)
- The Pursuit of Happyness: The Life Story That Inspired the Major Motion PictureFrom EverandThe Pursuit of Happyness: The Life Story That Inspired the Major Motion PictureNo ratings yet