Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Concrete Shell Element
Uploaded by
Rudranath BhattacharyaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Concrete Shell Element
Uploaded by
Rudranath BhattacharyaCopyright:
Available Formats
WORKSHOP ON
ING-IABSE
CODE OF PRACTICE FOR CONCRETE ROAD
BRIDGES IRC:112
WORKSHOP ON CODE OF PRACTICE FOR CONCRETE ROAD BRIDGES IRC:112 2011, ORGANISED BY ING-IABSE, 11-12 JULY 2014, KOLKATA
Session -2
CONCRETE SHELL ELEMENTS
Umesh Rajeshirke
Managing Director
SPECTRUM Techno Consultants Pvt Ltd, Navi Mumbai
Mr. Umesh Rajeshirke has completed his BE Civil form VJTI (Univ. of
Bombay) and M.S. from IIT, Madras. He has over 27 years of
experience in planning & designing of long span bridges, precast
segmental & cable stayed bridges. He has also involved in design of
number Nuclear Containments, tall chimneys, Natural Draught Cooling
Towers and maritime structures. Actively involved in various code
committees
CONCRETE SHELL ELEMENTS
ING-IABSE
WORKSHOP ON CODE OF PRACTICE FOR CONCRETE ROAD BRIDGES IRC:112 2011, ORGANISED BY ING-IABSE, 11-12 JULY 2014, KOLKATA
Method for design of shell element
is given in annexure B1 of the
code.
This method is generally used
when the analysis is performed
using finite element method for
structures like fish belly or curved
box girders.
Verification at ULS is to be
performed adopting the sandwich
model for shell elements
Force Resultants of Shell Element.
Out-of-plane moments and twisting moments are converted into stress
resultants acting planes of the top and bottom layers.
The core/middle layer is designed to carry the out of plane shear force.
CONCRETE SHELL ELEMENTS
ING-IABSE
WORKSHOP ON CODE OF PRACTICE FOR CONCRETE ROAD BRIDGES IRC:112 2011, ORGANISED BY ING-IABSE, 11-12 JULY 2014, KOLKATA
The method is broadly described in following three steps:
1.
Carry out FEM analysis (generally elastic, linear) of structure with
geometry assumed initially, for all applicable loads and load
combinations and get the results (i.e. nEdx, nEdy, nEdxy, mEdx, mEdy, mEdxy,
vEdx, vEdy, and principal stresses s1, s2, s3) at required locations.
2.
Find out whether the element is cracked or not, using Eqn. B-1-1 of
the code. If the element is un-cracked, the only verification required is
to check that minimum principal stress, s3 (i.e. maximum compressive
stress) does not exceed the design compressive strength, fcd.
3.
If the element is cracked, follow the method using sandwich model to
find out the required reinforcement.
CONCRETE SHELL ELEMENTS
ING-IABSE
WORKSHOP ON CODE OF PRACTICE FOR CONCRETE ROAD BRIDGES IRC:112 2011, ORGANISED BY ING-IABSE, 11-12 JULY 2014, KOLKATA
Check for cracking
Where
CONCRETE SHELL ELEMENTS
ING-IABSE
WORKSHOP ON CODE OF PRACTICE FOR CONCRETE ROAD BRIDGES IRC:112 2011, ORGANISED BY ING-IABSE, 11-12 JULY 2014, KOLKATA
Calculation of reinforcement using sandwich model:
Steps involved in this method are given below:
1. Split the shell element in three layers as shown in figure below:
Two outer layers resist the
membrane actions arising from nEdx,
nEdy, nEdxy, mEdx, mEdy, mEdxy,
Inner layer carries the shear forces
vEdx, vEdy.
The thickness of the different layers
should be established by means of
an iterative procedure
The Sandwich Model
CONCRETE SHELL ELEMENTS
ING-IABSE
WORKSHOP ON CODE OF PRACTICE FOR CONCRETE ROAD BRIDGES IRC:112 2011, ORGANISED BY ING-IABSE, 11-12 JULY 2014, KOLKATA
2. Design of outer layers for membrane action:
Determine the forces in outer layers of sandwich model using
equation B1-13 to B1-20 of the code or by using simplified approach
in section B1-13 & 14.
Basically, the membrane forces, nEdx, nEdy, nEdxy are divided between
the two layers and the bending moments, mEdx, mEdy, mEdxy are
converted into ( +- m/z ) forces in top and bottom layers.
These forces are depicted here in figures on next slide
CONCRETE SHELL ELEMENTS
ING-IABSE
WORKSHOP ON CODE OF PRACTICE FOR CONCRETE ROAD BRIDGES IRC:112 2011, ORGANISED BY ING-IABSE, 11-12 JULY 2014, KOLKATA
2. Design of outer layers for membrane action (Cont)
Axial Forces & Bending
Moments in Outer layers
Membrane Shear forces and
Twisting Bending Moments in
the Outer Layers
CONCRETE SHELL ELEMENTS
ING-IABSE
WORKSHOP ON CODE OF PRACTICE FOR CONCRETE ROAD BRIDGES IRC:112 2011, ORGANISED BY ING-IABSE, 11-12 JULY 2014, KOLKATA
2. Design of outer layers for membrane action (Cont )
Design the outer layers as membrane element using method
given in section 9 of the code.
If it is not possible to satisfy the design rules given in section 9,
then as suggested in clause B1.15 of the code, either
increase the concrete cover and consequently reduce the
internal lever arm or
use different values for lever arms, zn and zt with zn > zt ;
internal concrete stresses should then be added vectorially
or
Increase the layer thickness to satisfy the concrete
CONCRETE SHELL ELEMENTS
ING-IABSE
WORKSHOP ON CODE OF PRACTICE FOR CONCRETE ROAD BRIDGES IRC:112 2011, ORGANISED BY ING-IABSE, 11-12 JULY 2014, KOLKATA
3. Design of inner layer for out of plane shear:
Out of plane shear forces vEdx and vEdy are applied to the inner layer with the laver arm
zc , determined with reference to the centroid of the appropriate layers of
reinforcement
For the design of the inner layer the principal shear vEdo and its direction o should
be evaluated as follows:
In the direction of principal shear the shell element behaves like a beam and the
appropriate design rules should therefore be applied. In particular clause 6.2.2 of
the code should be applied for members not requiring shear reinforcement and
clause 6.2.3 should be applied for members requiring shear reinforcement. In
expression 6.2a, 1 should be taken as
CONCRETE SHELL ELEMENTS
ING-IABSE
WORKSHOP ON CODE OF PRACTICE FOR CONCRETE ROAD BRIDGES IRC:112 2011, ORGANISED BY ING-IABSE, 11-12 JULY 2014, KOLKATA
When shear reinforcement is necessary, the longitudinal force resulting from the
truss model vEdo cotq gives rise to the following membrane forces in x and y
directions and shall be added to the forces obtained in outer layers:
CONCRETE SHELL ELEMENTS
ING-IABSE
WORKSHOP ON CODE OF PRACTICE FOR CONCRETE ROAD BRIDGES IRC:112 2011, ORGANISED BY ING-IABSE, 11-12 JULY 2014, KOLKATA
Worked Examples:
CONCRETE SHELL ELEMENTS
ING-IABSE
WORKSHOP ON CODE OF PRACTICE FOR CONCRETE ROAD BRIDGES IRC:112 2011, ORGANISED BY ING-IABSE, 11-12 JULY 2014, KOLKATA
CONCRETE SHELL ELEMENTS
ING-IABSE
WORKSHOP ON CODE OF PRACTICE FOR CONCRETE ROAD BRIDGES IRC:112 2011, ORGANISED BY ING-IABSE, 11-12 JULY 2014, KOLKATA
CONCRETE SHELL ELEMENTS
ING-IABSE
WORKSHOP ON CODE OF PRACTICE FOR CONCRETE ROAD BRIDGES IRC:112 2011, ORGANISED BY ING-IABSE, 11-12 JULY 2014, KOLKATA
CONCRETE SHELL ELEMENTS
ING-IABSE
WORKSHOP ON CODE OF PRACTICE FOR CONCRETE ROAD BRIDGES IRC:112 2011, ORGANISED BY ING-IABSE, 11-12 JULY 2014, KOLKATA
ICI Workshop, New Delhi, May
2013
CONCRETE SHELL ELEMENTS
ING-IABSE
WORKSHOP ON CODE OF PRACTICE FOR CONCRETE ROAD BRIDGES IRC:112 2011, ORGANISED BY ING-IABSE, 11-12 JULY 2014, KOLKATA
CONCRETE SHELL ELEMENTS
ING-IABSE
WORKSHOP ON CODE OF PRACTICE FOR CONCRETE ROAD BRIDGES IRC:112 2011, ORGANISED BY ING-IABSE, 11-12 JULY 2014, KOLKATA
CONCRETE SHELL ELEMENTS
ING-IABSE
WORKSHOP ON CODE OF PRACTICE FOR CONCRETE ROAD BRIDGES IRC:112 2011, ORGANISED BY ING-IABSE, 11-12 JULY 2014, KOLKATA
CONCRETE SHELL ELEMENTS
ING-IABSE
WORKSHOP ON CODE OF PRACTICE FOR CONCRETE ROAD BRIDGES IRC:112 2011, ORGANISED BY ING-IABSE, 11-12 JULY 2014, KOLKATA
CONCRETE SHELL ELEMENTS
ING-IABSE
WORKSHOP ON CODE OF PRACTICE FOR CONCRETE ROAD BRIDGES IRC:112 2011, ORGANISED BY ING-IABSE, 11-12 JULY 2014, KOLKATA
, Reinforcement provided in Y-dirn is sufficient.
CONCRETE SHELL ELEMENTS
ING-IABSE
WORKSHOP ON CODE OF PRACTICE FOR CONCRETE ROAD BRIDGES IRC:112 2011, ORGANISED BY ING-IABSE, 11-12 JULY 2014, KOLKATA
CONCRETE SHELL ELEMENTS
ING-IABSE
WORKSHOP ON CODE OF PRACTICE FOR CONCRETE ROAD BRIDGES IRC:112 2011, ORGANISED BY ING-IABSE, 11-12 JULY 2014, KOLKATA
CONCRETE SHELL ELEMENTS
ING-IABSE
WORKSHOP ON CODE OF PRACTICE FOR CONCRETE ROAD BRIDGES IRC:112 2011, ORGANISED BY ING-IABSE, 11-12 JULY 2014, KOLKATA
CONCRETE SHELL ELEMENTS
ING-IABSE
WORKSHOP ON CODE OF PRACTICE FOR CONCRETE ROAD BRIDGES IRC:112 2011, ORGANISED BY ING-IABSE, 11-12 JULY 2014, KOLKATA
* fcd = 0.541 * 13.4 = 7.262
MPa
CONCRETE SHELL ELEMENTS
ING-IABSE
WORKSHOP ON CODE OF PRACTICE FOR CONCRETE ROAD BRIDGES IRC:112 2011, ORGANISED BY ING-IABSE, 11-12 JULY 2014, KOLKATA
Thank you
You might also like
- Existing Bridge: Code of Practice For Concrete Road Bridges IRC:112Document5 pagesExisting Bridge: Code of Practice For Concrete Road Bridges IRC:112Sony JsdNo ratings yet
- Code of Practice For Concrete Road Bridges Irc:112: ULS For Linear ElementsDocument6 pagesCode of Practice For Concrete Road Bridges Irc:112: ULS For Linear ElementsSony JsdNo ratings yet
- Mahesh Tandon PDFDocument57 pagesMahesh Tandon PDFhavmanyfriendsNo ratings yet
- IMPLICATION OF IRC 112 ON RCC BRIDGE DESIGNDocument8 pagesIMPLICATION OF IRC 112 ON RCC BRIDGE DESIGNkrunalNo ratings yet
- Advanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionFrom EverandAdvanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionNo ratings yet
- Calculating design tensile forces in external tendons of Vietnam's extradosed bridgesDocument6 pagesCalculating design tensile forces in external tendons of Vietnam's extradosed bridgestungch46No ratings yet
- 11 DR Harshawaradan Subba CASE STUDIES ON EXTRADOSED BRIDGES WORLDWIDE - For PendriveDocument26 pages11 DR Harshawaradan Subba CASE STUDIES ON EXTRADOSED BRIDGES WORLDWIDE - For PendriveKedarNo ratings yet
- Consultant Expert DR Mohamed Seif Al Den TahaDocument228 pagesConsultant Expert DR Mohamed Seif Al Den Tahaconsultant expert dr mohamed seif al den tahaNo ratings yet
- Umesh Rajshirke Material Properties and Their Design Value PDFDocument53 pagesUmesh Rajshirke Material Properties and Their Design Value PDFVarun VermaNo ratings yet
- Seismic Protection of Bridges with LRB DevicesDocument15 pagesSeismic Protection of Bridges with LRB DevicesBanafsheh AsgariNo ratings yet
- Extradosed Bridge PDFDocument2 pagesExtradosed Bridge PDFMelNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistant Design of Bridges-1Document42 pagesEarthquake Resistant Design of Bridges-1sanilNo ratings yet
- IASE SED Journal - April-June, 2023Document107 pagesIASE SED Journal - April-June, 2023S DuttaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Balance Cantilever Bridge and Extradosed BridgeDocument13 pagesComparative Study of Balance Cantilever Bridge and Extradosed BridgeIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- P15 Harpreet Singh 2nd Presentation - PSC Segmental Box Girder PDFDocument16 pagesP15 Harpreet Singh 2nd Presentation - PSC Segmental Box Girder PDFRajat Baghel100% (1)
- Balanced Cantilever StabilityDocument12 pagesBalanced Cantilever StabilityTeo Peng KeatNo ratings yet
- Second Vivekananda BridgeDocument2 pagesSecond Vivekananda BridgedarmumbaiNo ratings yet
- Bowstring Steel Bridge - ModifiedDocument44 pagesBowstring Steel Bridge - Modifiedpratap jadhavNo ratings yet
- Erection techniques for steel bridgesDocument10 pagesErection techniques for steel bridgeswim hoeckmanNo ratings yet
- FCM TrainingDocument58 pagesFCM TrainingLeonardo RojasNo ratings yet
- Proportioning Guidelines for Extradosed Prestressed BridgesDocument14 pagesProportioning Guidelines for Extradosed Prestressed BridgesRadek SekNo ratings yet
- Extradosed Bridges in Poland-Design and Constructi PDFDocument10 pagesExtradosed Bridges in Poland-Design and Constructi PDFFitsum AbebeNo ratings yet
- DN002 RA AMR Detailed DesignDocument37 pagesDN002 RA AMR Detailed DesignAbhishek SinghalNo ratings yet
- GRP5 Design of Free Pier & Pile P3RDocument76 pagesGRP5 Design of Free Pier & Pile P3Rsantosh yevvariNo ratings yet
- AdSec Theory PDFDocument72 pagesAdSec Theory PDFPhan Anh NhậtNo ratings yet
- MB Concrete Footbridges July2012Document8 pagesMB Concrete Footbridges July2012Yasonsky CaptainNo ratings yet
- Jennifer Dietrich MSC DissertationAnalysis and Design of PDFDocument238 pagesJennifer Dietrich MSC DissertationAnalysis and Design of PDFopulitheNo ratings yet
- REFRESHER COURSE ON APPLICATION OF NEW SEISMIC CODE FOR HIGHWAY BRIDGESDocument69 pagesREFRESHER COURSE ON APPLICATION OF NEW SEISMIC CODE FOR HIGHWAY BRIDGESNeeraj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Selection of erection technologies for cable stayed bridgesDocument4 pagesSelection of erection technologies for cable stayed bridgesHarpreet SandhuNo ratings yet
- Slide Cable Stayed PDFDocument117 pagesSlide Cable Stayed PDFpu3bsdNo ratings yet
- Nit WBHDCLDocument194 pagesNit WBHDCLManish Choudhary100% (1)
- Design of Pier Segments in Segmental Hollow Box Girder Bridges 3898739929 PDFDocument1 pageDesign of Pier Segments in Segmental Hollow Box Girder Bridges 3898739929 PDFVarun VermaNo ratings yet
- IBIG20623wpb3 PDFDocument82 pagesIBIG20623wpb3 PDFVenkatesh VarmaNo ratings yet
- DBR Rev.G 26th SeptDocument51 pagesDBR Rev.G 26th Septsudhir12345No ratings yet
- Seismic Design of BridgesDocument10 pagesSeismic Design of BridgesnfaayedNo ratings yet
- Shear Capacity of Circular Concrete SectionsDocument14 pagesShear Capacity of Circular Concrete Sectionspatricklim1982No ratings yet
- Railway & Bridge EngineeringDocument94 pagesRailway & Bridge EngineeringVishwajit ShindeNo ratings yet
- Stakeholder Engagement in PPP Projects - Causes of Precast Segmental Bridge Failures and RemediesDocument7 pagesStakeholder Engagement in PPP Projects - Causes of Precast Segmental Bridge Failures and RemediesPremnath YadavNo ratings yet
- 24-Design and Construction Techniques of Daning River BridgeDocument6 pages24-Design and Construction Techniques of Daning River Bridgeatac101No ratings yet
- Design of Pier Segments in Segmental Hollow Box Girder Bridges 3898739929Document1 pageDesign of Pier Segments in Segmental Hollow Box Girder Bridges 3898739929Varun VermaNo ratings yet
- FRP Traffic Signs Steel Joint Retrofit BridgesDocument185 pagesFRP Traffic Signs Steel Joint Retrofit Bridgesaygunbayram100% (1)
- Kali Khola FinalDocument15 pagesKali Khola FinalsurendramaharjanNo ratings yet
- Pre-tensioned Sutlej Bridge DesignDocument16 pagesPre-tensioned Sutlej Bridge DesignYogesh GhuleNo ratings yet
- Design Basis Report-Main Bridge-CommentsDocument19 pagesDesign Basis Report-Main Bridge-Commentsvenkatd123603No ratings yet
- Analysis and Behavior Investigations of Box Girder Bridges PDFDocument126 pagesAnalysis and Behavior Investigations of Box Girder Bridges PDFAravind BhashyamNo ratings yet
- CSIR-CRRI Guide to Wind Loads on BridgesDocument94 pagesCSIR-CRRI Guide to Wind Loads on BridgesRashid Irshad AliNo ratings yet
- GRP1 Design of Fixed Pier & Pile P2RDocument73 pagesGRP1 Design of Fixed Pier & Pile P2Rsantosh yevvariNo ratings yet
- Midas/Civil prestress verification reportDocument6 pagesMidas/Civil prestress verification reportBodhi RudraNo ratings yet
- Second Narmada BridgeDocument1 pageSecond Narmada BridgedarmumbaiNo ratings yet
- Differential Shrinkage PrestressedDocument7 pagesDifferential Shrinkage PrestressedJayapaul ViyagulamNo ratings yet
- Stefania Palaoro Arch Bridges, Design-Construction-PerceptionDocument270 pagesStefania Palaoro Arch Bridges, Design-Construction-PerceptionFeliciano Esteban Dominguez50% (2)
- Pre-Cast Segment Fabrication Box Girder For Span CP03-CP04 PDFDocument127 pagesPre-Cast Segment Fabrication Box Girder For Span CP03-CP04 PDFnyssa7890No ratings yet
- CVH CFST Arch BridgeDocument71 pagesCVH CFST Arch BridgeTùng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Prologue To Presentation: Code of Practice For Concrete Road Bridges IRC:112Document9 pagesPrologue To Presentation: Code of Practice For Concrete Road Bridges IRC:112Sony JsdNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Prestressed Concrete Box Girder BridgeDocument14 pagesAnalysis and Design of Prestressed Concrete Box Girder BridgeCETNo ratings yet
- Condition Survey and Rehabilitation of BridgeDocument11 pagesCondition Survey and Rehabilitation of BridgeManvendra NigamNo ratings yet
- Design Balanced Cantilever BridgesDocument26 pagesDesign Balanced Cantilever BridgesShijo AntonyNo ratings yet
- Cable Supported Bridges: Concept and DesignFrom EverandCable Supported Bridges: Concept and DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Moody's ChartDocument100 pagesMoody's Chartbsk109100% (3)
- RCC Bridge Elastomeric Bearing DesignDocument3 pagesRCC Bridge Elastomeric Bearing DesignRudranath BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- OrderDocument20 pagesOrderRudranath BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Irc 107 - 2013 PDFDocument24 pagesIrc 107 - 2013 PDFRudranath BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Seismic DesignDocument144 pagesGuidelines For Seismic DesignRudranath BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- 2015.453410.sri Chaitanyer Antardhan Rahasya Vol 1 2 Ed 3rdDocument377 pages2015.453410.sri Chaitanyer Antardhan Rahasya Vol 1 2 Ed 3rdRudranath BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- IWAI ActDocument15 pagesIWAI ActPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- IRC-64 - (Capacity of Road in Rural Areas) PDFDocument11 pagesIRC-64 - (Capacity of Road in Rural Areas) PDFRudranath Bhattacharya50% (2)
- Bridge Deck Construction GuideDocument21 pagesBridge Deck Construction Guide4chi11esNo ratings yet
- Roads & BridgesDocument66 pagesRoads & BridgesvivekranjanjamNo ratings yet
- Amendment No. 1 To IRC 112 - 2014 PDFDocument3 pagesAmendment No. 1 To IRC 112 - 2014 PDFmrraee4729100% (3)
- Influence Lines in Continuous BeamsDocument10 pagesInfluence Lines in Continuous BeamsRudranath BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- WB Treasury RulesDocument498 pagesWB Treasury Rulesnandi_scr100% (1)
- Is 458 2003Document39 pagesIs 458 2003somnathjoyNo ratings yet
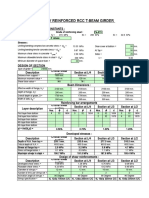
- Design of Singly Reinforced RCC T-Beam Girder: M Value 10.0Document3 pagesDesign of Singly Reinforced RCC T-Beam Girder: M Value 10.0Rudranath BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Solution: Sum of Rows: Sum of Columns: Sum of Blocks: Calculation ProgressDocument1 pageSolution: Sum of Rows: Sum of Columns: Sum of Blocks: Calculation ProgressRudranath BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- 1 Well QuantitiesDocument1 page1 Well QuantitiesRudranath BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Design of Main Girder (Compatibility Mode)Document58 pagesDesign of Main Girder (Compatibility Mode)Mohamed Azazy100% (1)
- IRC-64 - (Capacity of Road in Rural Areas)Document11 pagesIRC-64 - (Capacity of Road in Rural Areas)Rudranath BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Flat Slab ExampleDocument103 pagesFlat Slab ExampleShishir Kumar Nayak100% (3)
- 1 - Tri-Axial TestDocument1 page1 - Tri-Axial TestRudranath BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- 1 Well QuantitiesDocument1 page1 Well QuantitiesRudranath BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Amendment No. 1 To IRC 112 - 2014 PDFDocument3 pagesAmendment No. 1 To IRC 112 - 2014 PDFmrraee4729100% (3)
- High Yield Pics For STEP 2 CKDocument24 pagesHigh Yield Pics For STEP 2 CKKinan Alhalabi96% (28)
- Literature Review Marketing StrategyDocument4 pagesLiterature Review Marketing Strategyc5td1cmc100% (1)
- Project Cost ForecastDocument11 pagesProject Cost ForecastJames MendesNo ratings yet
- Open MPDocument30 pagesOpen MPmacngocthanNo ratings yet
- TiONA 592 PDS - ENDocument1 pageTiONA 592 PDS - ENQuang VANo ratings yet
- Ethics Book of TAMIL NADU HSC 11th Standard Tamil MediumDocument140 pagesEthics Book of TAMIL NADU HSC 11th Standard Tamil MediumkumardjayaNo ratings yet
- Pankaj Screener 10 Oct 2014Document127 pagesPankaj Screener 10 Oct 2014Sadul Singh Naruka100% (1)
- Defender 90 110 Workshop Manual 5 WiringDocument112 pagesDefender 90 110 Workshop Manual 5 WiringChris Woodhouse50% (2)
- Philippine Politics and Constitution SyllabusDocument7 pagesPhilippine Politics and Constitution SyllabusIvy Karen C. Prado100% (1)
- Informed Consent: Ghaiath M. A. HusseinDocument26 pagesInformed Consent: Ghaiath M. A. HusseinDocAxi Maximo Jr AxibalNo ratings yet
- Explore Spanish Lesson Plan - AnimalsDocument8 pagesExplore Spanish Lesson Plan - Animalsapi-257582917No ratings yet
- Linear Programming Models: Graphical and Computer MethodsDocument91 pagesLinear Programming Models: Graphical and Computer MethodsFaith Reyna TanNo ratings yet
- As 2710-1984 Screw Gauges - VerificationDocument7 pagesAs 2710-1984 Screw Gauges - VerificationSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- معامل الاسفلتDocument32 pagesمعامل الاسفلتMohammed AbbasNo ratings yet
- Balajit Nath Pandita-Specific Principles of Kashmir Saivism-Munshiram Manoharlal Publishers (1998) PDFDocument228 pagesBalajit Nath Pandita-Specific Principles of Kashmir Saivism-Munshiram Manoharlal Publishers (1998) PDFvramaniitkNo ratings yet
- Unit 01 Family Life Lesson 1 Getting Started - 2Document39 pagesUnit 01 Family Life Lesson 1 Getting Started - 2Minh Đức NghiêmNo ratings yet
- Chicago TemplateDocument4 pagesChicago TemplateJt MetcalfNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Tech-1Document6 pagesManufacturing Tech-1Vikram Rao0% (1)
- 2018 Diesel TOYOTA Jun11Document90 pages2018 Diesel TOYOTA Jun11eko sulistyo75% (4)
- Exploratory Data Analysis: M. SrinathDocument19 pagesExploratory Data Analysis: M. SrinathromaNo ratings yet
- Catalogue MinicenterDocument36 pagesCatalogue Minicentermohamed mahdiNo ratings yet
- Optitex Com Products 2d and 3d Cad SoftwareDocument12 pagesOptitex Com Products 2d and 3d Cad SoftwareFaathir Reza AvicenaNo ratings yet
- Kashmira Karim Charaniya's ResumeDocument3 pagesKashmira Karim Charaniya's ResumeMegha JainNo ratings yet
- CPS Layoffs BreakdownDocument21 pagesCPS Layoffs BreakdownjroneillNo ratings yet
- AWS S3 Interview QuestionsDocument4 pagesAWS S3 Interview QuestionsHarsha KasireddyNo ratings yet
- Hmdu - EnglishDocument20 pagesHmdu - EnglishAbdulaziz SeikoNo ratings yet
- Rock ClimbingDocument11 pagesRock ClimbingDaria TurdalievaNo ratings yet
- Ips 350:400:450:500:600 07:05 PDFDocument124 pagesIps 350:400:450:500:600 07:05 PDFRandall PettersonNo ratings yet
- CP R77.30 ReleaseNotesDocument18 pagesCP R77.30 ReleaseNotesnenjamsNo ratings yet
- Otis Brochure Gen2life 191001-BELGIUM SmallDocument20 pagesOtis Brochure Gen2life 191001-BELGIUM SmallveersainikNo ratings yet