Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unitportfoliojamesohara
Uploaded by
api-305332613Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unitportfoliojamesohara
Uploaded by
api-305332613Copyright:
Available Formats
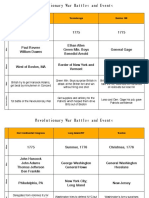
Fall Honors United States History
Honors US History 2015 Fall Semester
James OHara
Allatoona High School
Fall Honors United States History
1A
Political
Standards
a. Explain Virginias development; include the Virginia Company, tobacco cultivation,
relationships with Native Americans such as Powhatan, development of the House of Burgesses,
Bacons Rebellion, and the development of slavery. b. Describe the settlement of New England;
include religious reasons, relations with Native Americans (e.g., King Phillips War), the
establishment of town meetings and development of a legislature, religious tensions that led to
the founding of Rhode Island, the half-way covenant, Salem Witch Trials, and the loss of the
Massachusetts charter and the transition to a royal colony. c. Explain the development of the
mid-Atlantic colonies; include the Dutch settlement of New Amsterdam and subsequent English
takeover, and the settlement of Pennsylvania. d. Explain the reasons for French settlement of
Quebec. e. Analyze the impact of location and place on colonial settlement, transportation, and
economic development; include the southern, middle, and New England colonies.
NarrativeFrom the beginning, the people living in America had forms of representative democracy,
which would set the precedent for the eventual founding of the United States as a democratic
nation. While the first true governments such as the House of Burgesses in Virginia, there were
also many smaller town hall governments like the one at Plymouth. Eventually, there would be
rebellions as in the case of Bacons Rebellion, in which Nathaniel Bacon and other farmers
Fall Honors United States History
against the governors that were brought in by the British to replace the representative
democracies that the colonies had founded. British appeasement of the rebels would lead to more
and more demands by them until the British were giving way to everything the rebels wanted
until it got to the point where there was next to no British interference in the colonies
governments up until the French and Indian war. This would set the stage for the American
Revolution in the late 1700s. The revolution was started due to many factors, most of which
revolved around the high taxes and oppressive laws levied on the colonists by the Crown after
the French and Indian war, such as the Townshend acts and the Intolerable acts.
Terms-
Roanoke- The first colony in North America, it failed and the people living there were never
heard from again.
Jamestown- The first successful colony in North America, it had a rough start but ended up very
successful when tobacco seeds were smuggled in.
House of Burgesses- The first representative democracy in colonial America. To vote, you had
to be a white, land-owning male over 17.
Bacons Rebellion- Nathaniel Bacon led a group of more than a thousand rebels into Jamestown
and burned it to the ground after the government refused to help them.
Mayflower Compact- The Mayflower colonists, realizing that they were far off course and were
going to land in an entirely separate area, decided to form their own representative government.
Navigation Acts- Limited trade in the Colonies to only British ships.
Proprietary Colony- A colony controlled by a corporation, not an official part of the empire.
Fall Honors United States History
Royal Colony- A colony that has been declared part of the empire by the government, has a
colonial governor and a charter.
Salutary Neglect- The process where the government lets certain rules go unenforced in a given
colony on condition that the colony continues to be part of the empire.
First Continental Congress- The first government of the United States, eventually replaced
when the Constitution was drafted.
French and Indian War- Removed the French from North America, left Britain with a massive
war debt.
Treaty of Paris 1763- Ended the French and Indian War
Proclamation of 1763- British crown levied heavy taxes on the colonists, decided they should
pay for the war.
Stamp Act- Made a tax on every printed object
Intolerable Acts- Acts which finally caused the revolution
Pontiacs Rebellion- Attempt by Native Americans to secure their borders against the colonists,
failed.
Albany Plan of Union- Attempt to bring the colonies together, failed.
New Amsterdam- Would become New York, was a Dutch colony until the British captured it.
Sons of Liberty- Opposed the high taxes, violent protesters that tarred and feathered tax
collectors.
Daughters of Liberty- Refused to use English cloth.
Committees of Correspondence- Shadow governments created by the Colonial leaders that
were in place until the Articles of Confederation could be ratified.
Fall Honors United States History
Quartering Act- Allowed British soldiers to stay in any home they wanted and expect free food
from the owners.
Townshend Acts- Acts that created harsh consequences for not following the previous acts.
Social
Standards
a. Explain Virginias development; include the Virginia Company, tobacco cultivation,
relationships with Native Americans such as Powhatan, development of the House of Burgesses,
Bacons Rebellion, and the development of slavery. b. Describe the settlement of New England;
include religious reasons, relations with Native Americans (e.g., King Phillips War), the
establishment of town meetings and development of a legislature, religious tensions that led to
the founding of Rhode Island, the half-way covenant, Salem Witch Trials, and the loss of the
Massachusetts charter and the transition to a royal colony. c. Explain the development of the
mid-Atlantic colonies; include the Dutch settlement of New Amsterdam and subsequent English
takeover, and the settlement of Pennsylvania. d. Explain the reasons for French settlement of
Quebec. e. Analyze the impact of location and place on colonial settlement, transportation, and
economic development; include the southern, middle, and New England colonies.
Narrative-
The early colonists had to work together in the face of hardship until they had finally
created a safe place for themselves to live. These colonies created their own representative
governments, which grew into a general attitude of self government among the colonists. After
the colony was changed from a proprietary colony to a royal colony, the colonists grew frustrated
Fall Honors United States History
at the fact that their representative governments were taken away. This began a trend of distrust
towards the British government which would lead to numerous rebellions. Up until the French
and Indian War, the colonists were very opposed to the French, however when the Revolution
occurred, they became the Patriots best ally against the British. After the French and Indian war,
the colonists had to deal with heavy taxes from the British, and in response to their outcries the
government put harsher and harsher acts into place. Eventually, the colonists organized a
revolution, and with French backing, they successfully overthrew the British and became their
own independent state.
Terms
Great Awakening- A religious revival that occurred in mid to late 1700s that saw the rise of
large Puritan and Protestant movements.
Half-way Covenant- The Puritan government of Plymouth allowed descendants of those who
had declared their faith to vote.
Puritans- Fundamentalist Christians that founded the Plymouth colony and controlled New
England.
Quakers- Baptist Christians that controlled the Middle Colonies.
Pilgrims/Separatists- Wanted to separate from the British in order to gain religious freedom.
Salem Witch Trials- A series of false trials that condemned numerous people to death on the
grounds of being witches.
Common Sense- A manuscript written by Thomas Paine calling for a revolution on the part of
the colonists to overthrow the British.
Boston Massacre- The massacre of colonists by British soldiers, this was one of the key factors
in the start of the revolution.
Fall Honors United States History
Boston Tea Party- This was a response to the Intolerable Acts, which prompted the closing of
Boston Harbor until the colonists paid for the tea.
Economic
Standards
a. Explain Virginias development; include the Virginia Company, tobacco cultivation,
relationships with Native Americans such as Powhatan, development of the House of Burgesses,
Bacons Rebellion, and the development of slavery. b. Describe the settlement of New England;
include religious reasons, relations with Native Americans (e.g., King Phillips War), the
establishment of town meetings and development of a legislature, religious tensions that led to
the founding of Rhode Island, the half-way covenant, Salem Witch Trials, and the loss of the
Massachusetts charter and the transition to a royal colony. c. Explain the development of the
mid-Atlantic colonies; include the Dutch settlement of New Amsterdam and subsequent English
takeover, and the settlement of Pennsylvania. d. Explain the reasons for French settlement of
Quebec. e. Analyze the impact of location and place on colonial settlement, transportation, and
economic development; include the southern, middle, and New England colonies.
Narrative-
The original colonies at Jamestown and Roanoke hoped to find gold, however when there
was none to be found they struggled to find a way to make a profit until tobacco seeds were
smuggled in. When this happened, the population of the Jamestown colony exploded. These
Fall Honors United States History
colonies became profitable enough that the British declared them a Royal colony and began to
collect taxes. As time went on, the colonists began to diversify their income, beginning to grow
other cash crops like cotton or indigo. New England did not have the proper soil for growing
food or cash crops, so they turned to fishing along their rich coastlines. Since New England
never had much agriculture, this would lead to them being one of the first areas of the United
States to industrialize. When the British began to levy taxes after the French and Indian War, the
colonies struggled to remain profitable. When the British closed Boston Harbor it caused the
entire economy of Boston to crash, due to the fact that the entire city depended on the harbor for
income. When the United States declared independence, they were able to trade with other
nations again, something that was not possible under the Navigation Acts.
Terms-
Cash Crop/Staple Crop- A crop that provided large amounts of money or was a main crop for a
given area in the colonies.
Virginia Company- The join-stock company that controlled the Virginia colony until it became
a Royal Colony.
Indentured Servant- Not necessarily a slave, an indentured servant was bound to serve their
master until they had repaid their debts to them.
Joint Stock Company- A group of investors trying to make a profit off of different ventures
Mercantilism- A system where the colonies provide unrefined goods to the mother colony,
which refines them and turns them into finished products and sells them back to the colonies at a
higher price.
Fall Honors United States History
Middle Passage/Triangle Slave Trade- Slaves go to the Americas, which sends unrefined goods
to Europe, which sends refined goods to Africa, which sends slaves to the Americas.
Proprietary Colony- A colony controlled by a Joint Stock company.
Royal Colony- A colony controlled by the British crown.
1B
Political
Standards
SSUSH4 The student will identify the ideological, military, and diplomatic aspects of the
American Revolution.
a. Explain the language, organization, and intellectual sources of the Declaration of
Independence; include the writing of John Locke and the role of Thomas Jefferson.
b. Explain the reason for and significance of the French alliance and foreign assistance
and the roles of Benjamin Franklin and the Marquis de Lafayette.
c. Analyze George Washington as a military leader; include the creation of a professional
military and the life of a common soldier, and describe the significance of the crossing of the
Delaware River and Valley Forge.
d. Explain the role of geography at the Battle of Yorktown, the role of Lord Cornwallis,
and the Treaty of Paris, 1783.
SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption
and implementation of the United States Constitution.
a. Explain how weaknesses in the Articles of Confederation and Daniel Shays Rebellion
led to a call for a stronger central government.
b. Evaluate the major arguments of the anti-Federalists and Federalists during the debate
on ratification of the Constitution as put forth in The Federalist concerning form of government,
factions, checks and balances, and the power of the executive, including the roles of Alexander
Hamilton and James Madison.
c. Explain the key features of the Constitution, specifically the Great Compromise,
separation of powers (influence of Montesquieu), limited government, and the issue of slavery.
d. Analyze how the Bill of Rights serves as a protector of individual and states rights.
Fall Honors United States History
10
e. Explain the importance of the Presidencies of George Washington and John Adams;
include the Whiskey Rebellion, non-intervention in Europe, and the development of political
parties (Alexander Hamilton).
SSUSH6 The student will analyze the impact of territorial expansion and population growth and
the impact of this growth in the early decades of the new nation.
a. Explain the Northwest Ordinances importance in the westward migration of
Americans, and on slavery, public education, and the addition of new states.
b. Describe Jeffersons diplomacy in obtaining the Louisiana Purchase from France and
the territorys exploration by Lewis and Clark.
c. Explain major reasons for the War of 1812 and the wars significance on the
development of a national identity.
d. Describe the construction of the Erie Canal, the rise of New York City, and the
development of the nations infrastructure.
e. Describe the reasons for and importance of the Monroe Doctrine.
Vocabulary
Shays Rebellion- Armed uprising in Massachusetts by farmers, put down by
government troops.
Federalist- Advocated for stronger central government.
Anti-Federalist- Advocated for stronger state government, weaker central government.
Checks and Balances- Keeps one group or person from getting too much power.
Great Compromise- Established plan at a midpoint between new jersey and virginia
plans.
Separation of Powers- Divided government into distinct groups with separate roles.
Bill of Rights- Guaranteed rights, first amendment.
Limited Government- Government has controls put in place to keep it from exercising
too much power.
Precedent- Establishing a tradition or way of doing things.
Cabinet- Group of advisors to a leader.
Valley Forge- Continental troops trained here during revolutionary war.
Fall Honors United States History
11
Saratoga/Yorktown- Decisive battles, Saratoga resulted in Continental victory,
Yorktown resulted in the effective end of the war.
Treaty of Paris 1783- Ended revolutionary war.
Land Ordinance 1785- Established system of surveying and buying/selling land.
Northwest Ordinance 1787- Chartered multiple new states, first expansion of US.
Constitutional Convention- Convention to rewrite the US constitution in a better
manner.
Three Fifths Compromise- Determined that slaves were worth three fifths of a free man.
Democratic Republican Party- Advocated for States Rights.
Federalists Party- Advocated for a stronger central government.
Sons of Liberty- Opposed tax increases, tarred and feathered tax collectors.
Committees of Correspondence- Interim governments installed in the colonies before
the revolution.
Common Sense- Detailed why the colonies should revolt, written by Thomas Paine.
Bicameral Congress- A congress divided into two houses.
Boston Massacre- Massacre of colonials by British troops.
First Continental Congress- First convening of the US government, established basic
laws and customs.
Militia- Untrained army, usually made up of farmers.
Second Continental Congress- Rewrote the constitution, laid down other important
systems.
Natural Rights- Rights that could not be taken away by the government.
Virginia Plan- Electoral college votes based on size.
Fall Honors United States History
12
New Jersey Plan- Electoral college votes based on population.
Popular Sovereignty- Rule because the people allow it to be so.
Electoral College- Elects governing bodies by consent of the people.
Whiskey Rebellion- Protest against taxes, put down by federal troops.
Loose Construction- Broad interpretation of a document by court.
Strict Construction- Strict interpretation of a document by court.
XYZ Affair- Led to undeclared war between US and France.
Alien and Sedition Acts- Allowed president to deport or incarcerate immigrants.
Virginia and Kentucky Resolutions- Ruled Alien and Sedition Acts unconstitutional.
Impressment- Forcing American sailors to serve on a British ship.
War Hawks- Wanted war with Great Britain.
War of 1812- US attempted to gain land in Canada, failure.
Judicial Review- Legislative and Executive actions are subject to review by the Judiciary
branch of the government.
Narrative
This unit is where the United States as we know it today is born. The Continental
Congress takes over in the colonies, and the British are removed from power. The first
Continental Congress writes out the basic laws and customs for the United States, which were
later rewritten under the new Constitution drafted by the Second Continental Congress. While
this draft would later require multiple amendments such as the Bill of Rights, it provided a basic
design for how the United States would be governed. Eventually, the United States would declare
war on Great Britain in an effort to gain lands from Canada, however this war, known as the War
of 1812, ended in failure as the United States had its capital torched and boundaries were drawn
in much the same spots as they were before the war.
Fall Honors United States History
13
The citizens of the new United States had a collective feeling of national unity, and
although they had many problems to deal with in terms of how to run the country and what rights
are inherent to humanity, they were able to begin the United States as a nation.
Social
Standards
SSUSH4 The student will identify the ideological, military, and diplomatic aspects of the
American Revolution.
a. Explain the language, organization, and intellectual sources of the Declaration of
Independence; include the writing of John Locke and the role of Thomas Jefferson.
b. Explain the reason for and significance of the French alliance and foreign assistance
and the roles of Benjamin Franklin and the Marquis de Lafayette.
c. Analyze George Washington as a military leader; include the creation of a professional
military and the life of a common soldier, and describe the significance of the crossing of the
Delaware River and Valley Forge.
d. Explain the role of geography at the Battle of Yorktown, the role of Lord Cornwallis,
and the Treaty of Paris, 1783.
SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption
and implementation of the United States Constitution.
a. Explain how weaknesses in the Articles of Confederation and Daniel Shays Rebellion
led to a call for a stronger central government.
b. Evaluate the major arguments of the anti-Federalists and Federalists during the debate
on ratification of the Constitution as put forth in The Federalist concerning form of government,
factions, checks and balances, and the power of the executive, including the roles of Alexander
Hamilton and James Madison.
c. Explain the key features of the Constitution, specifically the Great Compromise,
separation of powers (influence of Montesquieu), limited government, and the issue of slavery.
d. Analyze how the Bill of Rights serves as a protector of individual and states rights.
e. Explain the importance of the Presidencies of George Washington and John Adams;
include the Whiskey Rebellion, non-intervention in Europe, and the development of political
parties (Alexander Hamilton).
SSUSH6 The student will analyze the impact of territorial expansion and population growth and
the impact of this growth in the early decades of the new nation.
a. Explain the Northwest Ordinances importance in the westward migration of
Americans, and on slavery, public education, and the addition of new states.
b. Describe Jeffersons diplomacy in obtaining the Louisiana Purchase from France and
the territorys exploration by Lewis and Clark.
Fall Honors United States History
14
c. Explain major reasons for the War of 1812 and the wars significance on the
development of a national identity.
d. Describe the construction of the Erie Canal, the rise of New York City, and the
development of the nations infrastructure.
e. Describe the reasons for and importance of the Monroe Doctrine.
Vocabulary
Federalist- Advocated for stronger central government.
Anti-Federalist- Advocated for stronger state government, weaker central government.
Great Compromise- Established plan at a midpoint between new jersey and virginia
plans.
Bill of Rights- Guaranteed rights, first amendment.
Limited Government- Government has controls put in place to keep it from exercising
too much power.
Precedent- Establishing a tradition or way of doing things.
Cabinet- Group of advisors to a leader.
Three Fifths Compromise- Determined that slaves were worth three fifths of a free man.
Democratic Republican Party- Advocated for States Rights.
Federalists Party- Advocated for a stronger central government.
Sons of Liberty- Opposed tax increases, tarred and feathered tax collectors.
Common Sense- Detailed why the colonies should revolt, written by Thomas Paine.
Boston Massacre- Massacre of colonials by British troops.
Militia- Untrained army, usually made up of farmers.
Natural Rights- Rights that could not be taken away by the government.
Popular Sovereignty- Rule because the people allow it to be so.
Fall Honors United States History
15
Whiskey Rebellion- Protest against taxes, put down by federal troops.
Tariff- Tax on imports or exports.
Alien and Sedition Acts- Allowed president to deport or incarcerate immigrants.
Virginia and Kentucky Resolutions- Ruled Alien and Sedition Acts unconstitutional.
Impressment- Forcing American sailors to serve on a British ship.
War Hawks- Wanted war with Great Britain.
Narrative
The early United States was a socially diverse place, consisting of immigrant groups
which had come from many different backgrounds and cultures. They had to work together to
build the nation essentially from the ground up. They established social policies, quarreled over
issues of national and state level government, and the culture of the United States as we know it
began to take shape. While the country was still far away from emancipation, there were already
talks of freeing the slaves among the founding fathers and the population at large, although this
did not happen until much later.
During and after the War of 1812, there was a sense of national unity as the citizens of the
new United States emerged from their first war wounded yet undefeated. The early Americans,
as they began to call themselves, believed themselves to be destined for greatness as the United
States grew in power and began expanding north and westward.
Economic
Fall Honors United States History
16
Standards
SSUSH4 The student will identify the ideological, military, and diplomatic aspects of the
American Revolution.
a. Explain the language, organization, and intellectual sources of the Declaration of
Independence; include the writing of John Locke and the role of Thomas Jefferson.
b. Explain the reason for and significance of the French alliance and foreign assistance
and the roles of Benjamin Franklin and the Marquis de Lafayette.
c. Analyze George Washington as a military leader; include the creation of a professional
military and the life of a common soldier, and describe the significance of the crossing of the
Delaware River and Valley Forge.
d. Explain the role of geography at the Battle of Yorktown, the role of Lord Cornwallis,
and the Treaty of Paris, 1783.
SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption
and implementation of the United States Constitution.
a. Explain how weaknesses in the Articles of Confederation and Daniel Shays Rebellion
led to a call for a stronger central government.
b. Evaluate the major arguments of the anti-Federalists and Federalists during the debate
on ratification of the Constitution as put forth in The Federalist concerning form of government,
factions, checks and balances, and the power of the executive, including the roles of Alexander
Hamilton and James Madison.
c. Explain the key features of the Constitution, specifically the Great Compromise,
separation of powers (influence of Montesquieu), limited government, and the issue of slavery.
d. Analyze how the Bill of Rights serves as a protector of individual and states rights.
e. Explain the importance of the Presidencies of George Washington and John Adams;
include the Whiskey Rebellion, non-intervention in Europe, and the development of political
parties (Alexander Hamilton).
SSUSH6 The student will analyze the impact of territorial expansion and population growth and
the impact of this growth in the early decades of the new nation.
a. Explain the Northwest Ordinances importance in the westward migration of
Americans, and on slavery, public education, and the addition of new states.
b. Describe Jeffersons diplomacy in obtaining the Louisiana Purchase from France and
the territorys exploration by Lewis and Clark.
c. Explain major reasons for the War of 1812 and the wars significance on the
development of a national identity.
d. Describe the construction of the Erie Canal, the rise of New York City, and the
development of the nations infrastructure.
e. Describe the reasons for and importance of the Monroe Doctrine.
Fall Honors United States History
17
Vocabulary
Shays Rebellion- Armed uprising in Massachusetts by farmers, put down by
government troops.
Limited Government- Government has controls put in place to keep it from exercising
too much power.
Land Ordinance 1785- Established system of surveying and buying/selling land.
Northwest Ordinance 1787- Chartered multiple new states, first expansion of US.
Three Fifths Compromise- Determined that slaves were worth three fifths of a free man.
Sons of Liberty- Opposed tax increases, tarred and feathered tax collectors.
Common Sense- Detailed why the colonies should revolt, written by Thomas Paine.
Whiskey Rebellion- Protest against taxes, put down by federal troops.
Tariff- Tax on imports or exports.
XYZ Affair- Led to undeclared war between US and France.
Alien and Sedition Acts- Allowed president to deport or incarcerate immigrants.
Virginia and Kentucky Resolutions- Ruled Alien and Sedition Acts unconstitutional.
Impressment- Forcing American sailors to serve on a British ship.
War Hawks- Wanted war with Great Britain.
Narrative
The early United States did not have much in the way of an economy, as it was almost
without exception an agrarian populace with relatively little trade compared to other countries at
the time such as France or Spain. After the revolution, the United States had issues getting other
countries to offer loans so they could repair the damage done during the war as well as build
infrastructure and create public services such as post offices and courthouses. Along with this,
the United States had trouble collecting taxes as the task was mostly left up to the states, all of
which had different ideas on what to tax and how much to tax it, as well as none of the states
having a single, unified currency which limited trade even within the United States.
Fall Honors United States History
18
The federal banking system began to function as a result of Alexander Hamiltons efforts,
and it began to collect taxes. The response to the taxes was mixed, and in some instances
rebellions even sprung up protesting the new tax system.
2A
Political
Standards
SSUSH6 The student will analyze the impact of territorial expansion and population growth and
the impact of this growth in the early decades of the new nation.
a. Explain the Northwest Ordinances importance in the westward migration of Americans, and
on slavery, public education, and the addition of new states.
b. Describe Jeffersons diplomacy in obtaining the Louisiana Purchase from France and the
territorys exploration by Lewis and Clark.
c. Explain major reasons for the War of 1812 and the wars significance on the development of a
national identity.
d. Describe the construction of the Erie Canal, the rise of New York City, and the development of
the nations infrastructure.
e. Describe the reasons for and importance of the Monroe Doctrine.
SSUSH7 Students will explain the process of economic growth, its regional and national impact
in the first half of the 19th century, and the different responses to it.
a. Explain the impact of the Industrial Revolution as seen in Eli Whitneys invention of the
cotton gin and his development of interchangeable parts for muskets.
b. Describe the westward growth of the United States; include the emerging concept of Manifest
Destiny.
c. Describe reform movements, specifically temperance, abolitionism, and public school.
d. Explain womens efforts to gain suffrage; include Elizabeth Cady Stanton and the Seneca Falls
Conference.
e. Explain Jacksonian Democracy, expanding suffrage, the rise of popular political culture, and
the development of American nationalism.
SSUSH8 The student will explain the relationship between growing north-south divisions and
westward expansion.
a. Explain how slavery became a significant issue in American politics; include the slave
rebellion of Nat Turner and the rise of abolitionism (William Lloyd Garrison, Frederick
Douglass, and the Grimke sisters).
b. Explain the Missouri Compromise and the issue of slavery in western states and territories.
c. Describe the Nullification Crisis and the emergence of states rights ideology; include the role
of John C. Calhoun and development of sectionalism.
Fall Honors United States History
d. Describe the war with Mexico and the Wilmot Proviso.
e. Explain how the Compromise of 1850 arose out of territorial expansion and population
growth.
Vocabulary
Industrial Revolution- The United States began to switch from an agrarian economy to an
industrialized economy.
Nationalism- Pride in ones country
Adams-Onis Treaty- Gained Florida and established boundary between US and Spain.
Monroe Doctrine- Stopped Colonialism in the western hemisphere
Spoils System- Politicians bought votes from immigrants.
Indian Removal Act- Forced Native Americans off of their land and onto reservations.
Trail of Tears- Trail the Cherokee followed to their reservation, more than 11,000 deaths
occurred.
Temperance Movement- Movement for equality and civil rights.
Abolitionist Movement- Wanted the emancipation of slaves.
Suffrage- The right to vote.
Seneca Falls Convention- Established the goals for the feminist movement.
Manifest Destiny- The belief that the US should stretch to the west coast.
Jacksonian Democracy (Age of Jackson)- Power to the common (white) man.
Compromise of 1850- Established the status of states acquired during the Mexican American
war as slave or free.
Missouri Compromise- Established one slave state for one free state to maintain status quo.
Nat Turners Rebellion- Failed slave uprising, led to harsher laws against slaves.
Nullification Crisis- States nullified a tariff ratified by northern politicians
19
Fall Honors United States History
20
Sectionalism- Ones own area is more important than the entire country
Mexican-American War- US takes over half of Mexico, establishes western boundary at the
pacific.
Wilmot Proviso- Sought to eliminate slavery in land acquired during the mexican-american war,
failed.
Tariff of 1816- Protected American manufacturing, raised prices of manufactured goods in the
South.
Nativist- Believed that immigrants are bad and that the US should be reserved for its own
citizens.
American System- Cotton from South, manufactured goods from North, banking establishments
paid for it all.
Whig- Opposed Jackson.
Utopian Community- Community where everything works flawlessly and harmoniously. New
York was an attempt at this.
Womens Movement- Early feminist movement, sought the right to vote.
Expansionist- Wanted the US to expand territorially.
Lone Star Republic- Texas before it was annexed.
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo- Ended Mexican American war with a US victory
California Gold Rush- Mass migration out west in hopes of finding gold.
Tariff of Abominations- Designed to protect Northern industry, ended up making manufactured
goods nearly unaffordable in the South.
Secede- When states left the Union.
Fugitive Slave Act- It is a crime not to return a slave to their owner.
Gadsden Purchase- Bought southern Arizona, allowed the transcontinental railroad to be built.
Fall Honors United States History
21
Marbury v. Madison- Formed the base for Judicial Review.
Narrative
During the mid 1800s, the United States was expanding constantly, spreading across the
continent in a race to get to the Pacific coast, even if it did mean declaring war on Mexico to do
so. As the country expanded, many debates arose as to the issue of slavery, and whether or not it
should be permitted in the new states as they joined the union. Some plans such as the Wilmot
Proviso demanded that new states should not permit slavery at all, while other plans such as the
Missouri Compromise permitted that for every slave state admitted to the union, one free state
must also be added. Even as more slave states were being added to the union, debates were being
held as to when to allow the slaves their freedom, if at all. Eventually, these debates reached the
tipping point when South Carolina became the first state to secede from the union.
Social
Standards
SSUSH6 The student will analyze the impact of territorial expansion and population growth and
the impact of this growth in the early decades of the new nation.
a. Explain the Northwest Ordinances importance in the westward migration of Americans, and
on slavery, public education, and the addition of new states.
b. Describe Jeffersons diplomacy in obtaining the Louisiana Purchase from France and the
territorys exploration by Lewis and Clark.
c. Explain major reasons for the War of 1812 and the wars significance on the development of a
national identity.
d. Describe the construction of the Erie Canal, the rise of New York City, and the development of
the nations infrastructure.
e. Describe the reasons for and importance of the Monroe Doctrine.
SSUSH7 Students will explain the process of economic growth, its regional and national impact
in the first half of the 19th century, and the different responses to it.
a. Explain the impact of the Industrial Revolution as seen in Eli Whitneys invention of the
cotton gin and his development of interchangeable parts for muskets.
b. Describe the westward growth of the United States; include the emerging concept of Manifest
Destiny.
c. Describe reform movements, specifically temperance, abolitionism, and public school.
d. Explain womens efforts to gain suffrage; include Elizabeth Cady Stanton and the Seneca Falls
Conference.
e. Explain Jacksonian Democracy, expanding suffrage, the rise of popular political culture, and
the development of American nationalism.
Fall Honors United States History
22
SSUSH8 The student will explain the relationship between growing north-south divisions and
westward expansion.
a. Explain how slavery became a significant issue in American politics; include the slave
rebellion of Nat Turner and the rise of abolitionism (William Lloyd Garrison, Frederick
Douglass, and the Grimke sisters).
b. Explain the Missouri Compromise and the issue of slavery in western states and territories.
c. Describe the Nullification Crisis and the emergence of states rights ideology; include the role
of John C. Calhoun and development of sectionalism.
d. Describe the war with Mexico and the Wilmot Proviso.
e. Explain how the Compromise of 1850 arose out of territorial expansion and population
growth.
Vocabulary
Nationalism- Pride in ones country
Spoils System- Politicians bought votes from immigrants.
Indian Removal Act- Forced Native Americans off of their land and onto reservations.
Trail of Tears- Trail the Cherokee followed to their reservation, more than 11,000 deaths
occurred.
Transcendentalist- Nature over reason.
Second Great Awakening- Christian revival occurring in the early 1800s.
Temperance Movement- Movement for equality and civil rights.
Abolitionist Movement- Wanted the emancipation of slaves.
Suffrage- The right to vote.
Seneca Falls Convention- Established the goals for the feminist movement.
Manifest Destiny- The belief that the US should stretch to the west coast.
Public School Reform- Started by Horace Mann, created national public schools.
Jacksonian Democracy (Age of Jackson)- Power to the common (white) man.
Fall Honors United States History
23
Nat Turners Rebellion- Failed slave uprising, led to harsher laws against slaves.
Sectionalism- Ones own area is more important than the entire country
Wilmot Proviso- Sought to eliminate slavery in land acquired during the mexican-american war,
failed.
Lowell Girl- Girl who worked in a textile factory.
Labor Union- Argued for better conditions and pay for factory workers.
Nativist- Believed that immigrants are bad and that the US should be reserved for its own
citizens.
Whig- Opposed Jackson.
Revivalist- Part of the Second Great Awakening
Mormon- New religion created in the US, offshoot of Christianity
Utopian Community- Community where everything works flawlessly and harmoniously. New
York was an attempt at this.
Freedman- A freed slave.
Womens Movement- Early feminist movement, sought the right to vote.
Expansionist- Wanted the US to expand territorially.
Santa Fe Trail- Connected Franklin, Missouri with Santa Fe, New Mexico.
Mountain Men- Lived in the Rocky Mountains, panning for gold.
Oregon Trail- Main trail leading west to California.
Lone Star Republic- Texas before it was annexed.
Alamo- 200 Texans died defending the church from Santa Anna
California Gold Rush- Mass migration out west in hopes of finding gold.
Forty-Niners- Miners who moved out west to California in the hopes of finding gold.
Fall Honors United States History
24
Hudson River School- Artistic and cultural movement focusing on the natural landscape of the
US.
Secede- When states left the Union.
Fugitive Slave Act- It is a crime not to return a slave to their owner.
Declaration of Sentiments- Feminists declaring what they want changed.
Narrative
During the mid 1800s, the United States was in a period of social upheaval as the
Abolitionist movement gained speed and demanded the immediate emancipation of slaves, the
feminist movement came into existence and pushed for womens suffrage as well as equal rights
and opportunities for women, and the second great awakening took place as the religious centers
of the country were filled with new ideas and a religious fervor not seen since. Along with this,
the debate over slavery continued to rage as the two sides of the argument grew ever more
divided until the breaking point where South Carolina seceded.
At the same time as this, many poor farmers and immigrants began to migrate out west to
California in the hopes of striking gold or claiming untouched farmland for themselves, as they
fanned out into the American interior and to the west coast, establishing many small towns as
they went, some of which are still around today.
Economic
Standards
SSUSH6 The student will analyze the impact of territorial expansion and population growth and
the impact of this growth in the early decades of the new nation.
a. Explain the Northwest Ordinances importance in the westward migration of Americans, and
on slavery, public education, and the addition of new states.
b. Describe Jeffersons diplomacy in obtaining the Louisiana Purchase from France and the
territorys exploration by Lewis and Clark.
c. Explain major reasons for the War of 1812 and the wars significance on the development of a
national identity.
d. Describe the construction of the Erie Canal, the rise of New York City, and the development of
the nations infrastructure.
e. Describe the reasons for and importance of the Monroe Doctrine.
Fall Honors United States History
25
SSUSH7 Students will explain the process of economic growth, its regional and national impact
in the first half of the 19th century, and the different responses to it.
a. Explain the impact of the Industrial Revolution as seen in Eli Whitneys invention of the
cotton gin and his development of interchangeable parts for muskets.
b. Describe the westward growth of the United States; include the emerging concept of Manifest
Destiny.
c. Describe reform movements, specifically temperance, abolitionism, and public school.
d. Explain womens efforts to gain suffrage; include Elizabeth Cady Stanton and the Seneca Falls
Conference.
e. Explain Jacksonian Democracy, expanding suffrage, the rise of popular political culture, and
the development of American nationalism.
SSUSH8 The student will explain the relationship between growing north-south divisions and
westward expansion.
a. Explain how slavery became a significant issue in American politics; include the slave
rebellion of Nat Turner and the rise of abolitionism (William Lloyd Garrison, Frederick
Douglass, and the Grimke sisters).
b. Explain the Missouri Compromise and the issue of slavery in western states and territories.
c. Describe the Nullification Crisis and the emergence of states rights ideology; include the role
of John C. Calhoun and development of sectionalism.
d. Describe the war with Mexico and the Wilmot Proviso.
e. Explain how the Compromise of 1850 arose out of territorial expansion and population
growth.
Vocabulary
Turnpike- A toll road, a large wooden pike barring the road was moved when travelers paid the
toll.
National Road- A road owned by the United States
Erie Canal- A canal connecting lake Erie and the Hudson River, built in 1825
Industrial Revolution- The United States began to switch from an agrarian economy to an
industrialized economy.
Interchangeable Parts- Parts in an object can be swapped out because they are all made to the
same specification.
Nationalism- Pride in ones country
Fall Honors United States History
26
Adams-Onis Treaty- Gained Florida and established boundary between US and Spain.
Monroe Doctrine- Stopped Colonialism in the western hemisphere
Jacksonian Democracy (Age of Jackson)- Power to the common (white) man.
Nullification Crisis- States nullified a tariff ratified by northern politicians
Lowell Girl- Girl who worked in a textile factory.
Tariff of 1816- Protected American manufacturing, raised prices of manufactured goods in the
South.
Labor Union- Argued for better conditions and pay for factory workers.
Cotton Gin- Invented by Eli Whitney, resulted in cotton being produced faster.
American System- Cotton from South, manufactured goods from North, banking establishments
paid for it all.
Whig- Opposed Jackson.
Santa Fe Trail- Connected Franklin, Missouri with Santa Fe, New Mexico.
Mountain Men- Lived in the Rocky Mountains, panning for gold.
Oregon Trail- Main trail leading west to California.
California Gold Rush- Mass migration out west in hopes of finding gold.
Forty-Niners- Miners who moved out west to California in the hopes of finding gold.
Tariff of Abominations- Designed to protect Northern industry, ended up making manufactured
goods nearly unaffordable in the South.
Gadsden Purchase- Bought southern Arizona, allowed the transcontinental railroad to be built.
Narrative
After the War of 1812, the US had incurred a massive national debt, which resulted in
large tax increases. As well as increasing taxes, the federal government sought to protect
Fall Honors United States History
27
Northern manufacturing from competition from European industries, at the cost of far more
expensive manufactured goods in the South. After the invention of the cotton gin, demand for
southern cotton grew massively and the plantation owners struggled to keep up with demand
from northern factories.
As well as the cotton gin, replaceable parts were invented by Eli Whitney. These new
parts were able to be mass-produced and later assembled into the finished product. This
invention revolutionized the manufacturing industry, and laid the foundations of the modern
methods of manufacturing such as the assembly line.
In the mid-1800s, gold was discovered in California. As the hopeful miners rushed
westward in hope of striking it rich, the US began the construction of the transcontinental
railroad. Upon its completion, it allowed for far safer and faster travel out west from cities and
stations in the East.
2B
Political
Standards
SSUSH9 The student will identify key events, issues, and individuals relating to the causes,
course, and consequences of the Civil War.
a. Explain the Kansas-Nebraska Act, the failure of popular sovereignty, Dred Scott case, and
John Browns Raid.
b. Describe President Lincolns efforts to preserve the Union as seen in his second inaugural
address and the Gettysburg speech and in his use of emergency powers, such as his decision to
suspend habeas corpus.
c. Describe the roles of Ulysses Grant, Robert E. Lee, Stonewall Jackson, William T. Sherman,
and Jefferson Davis.
d. Explain the importance of Fort Sumter, Antietam, Vicksburg, Gettysburg, and the Battle for
Atlanta and the impact of geography on these battles.
e. Describe the significance of the Emancipation Proclamation.
f. Explain the importance of the growing economic disparity between the North and the South
through an examination of population, functioning railroads, and industrial output.
SSUSH10 The student will identify legal, political, and social dimensions of Reconstruction.
a. Compare and contrast Presidential Reconstruction with Radical Republican Reconstruction.
b. Explain efforts to redistribute land in the South among the former slaves and provide advanced
education (Morehouse College) and describe the role of the Freedmens Bureau.
c. Describe the significance of the 13th, 14th, and 15th amendments.
d. Explain Black Codes, the Ku Klux Klan, and other forms of resistance to racial equality
during Reconstruction.
e. Explain the impeachment of Andrew Johnson in relationship to Reconstruction.
Fall Honors United States History
28
f. Analyze how the presidential election of 1876 and the subsequent compromise of 1877 marked
the end of Reconstruction.
Vocabulary
Kansas-Nebraska Act- Allowed people in Kansas and Nebraska to decide whether or not to
have slaves.
Popular Sovereignty- Rule by consent of the people.
Dred Scott v. Sanford- Ruled slaves as property and not people
States Rights- States should be able to overturn federal decisions.
Secession- States leaving the union.
Emancipation- The process by which slaves are freed.
Proclamation of 1863- Lincoln issued emancipation proclamation, freed slaves in south.
Thirteenth Amendment- Abolished slavery
Fourteenth Amendment- Gave blacks citizenship and equal protection under law.
Fifteenth Amendment- Granted right to vote to blacks
Black Codes- Designed to keep blacks in a system of virtual slavery.
Impeach- Public official is accused of breaking the law, usually results in being removed from
office.
Gettysburg Address- Dedicated Soldiers National Cemetery in Gettysburg, one of the most
well-known speeches in US history.
Sectionalism- Belief that ones own section of the country is more important than the country as
a whole.
Habeas Corpus- The right to a judge and trial.
Presidential Reconstruction- Lincolns plan for reconstruction, intended to leave as few harsh
feelings as possible.
Fall Honors United States History
29
Radical Republican- Believed the South had started the war and should pay for it.
Andrew Johnsons Impeachment- Johnson violated tenure of office, was impeached. One vote
short of conviction.
1876 Presidential Election- Very disputed election, resulted in Compromise of 1877.
Compromise of 1877- Ended reconstruction, put Hayes in office as president.
Lincolns Second Inaugural Address of 1865- Lincoln discusses plans for reconstruction, end
of the war.
Bleeding Kansas- Pro-slavery and abolitionists moved to Kansas to try and turn the state free
or slave, fought each other over it.
Know Nothings- Nativist party, strongly opposed immigrants and catholicism.
Anaconda Plan- Union plan to surround confederacy and cut off its supply chain.
Civil Rights Act of 1866- Granted citizenship and equal rights to all males.
Blockade- Naval restriction of an area, prevents ships from entering or leaving.
Republican Party- Union party, wanted emancipation and equal rights.
Copperhead- Northerner sympathetic to the South.
Narrative
Politically, the mid to late 1800s was a very hectic time as state and federal officials
battled over the status of new states as free or slave states as well as over the increasing burdens
of the tariffs on southern states used to prop up northern industry in a way the South did not
benefit from at all. This eventually reached the breaking point when South Carolina seceded
from the union. Eventually, the rest of the new Confederate states would follow suit. After a
Union garrison refused to give up their post at Fort Sumter until Lincoln gave them the order,
Confederate batteries fired on the fort. Lincoln used this opportunity to declare war on the South,
and for four years the United States was embroiled in the bloodiest single conflict ever endured.
Eventually, on April 9th, 1865, the civil war ended with a Union victory.
Lincoln began to lay out and execute plans to rebuild the country after the war, and the
time after the civil war became known as the reconstruction era. Reconstruction ended in 1877
with the election of president Hayes.
Fall Honors United States History
30
Social
Standards
SSUSH9 The student will identify key events, issues, and individuals relating to the causes,
course, and consequences of the Civil War.
a. Explain the Kansas-Nebraska Act, the failure of popular sovereignty, Dred Scott case, and
John Browns Raid.
b. Describe President Lincolns efforts to preserve the Union as seen in his second inaugural
address and the Gettysburg speech and in his use of emergency powers, such as his decision to
suspend habeas corpus.
c. Describe the roles of Ulysses Grant, Robert E. Lee, Stonewall Jackson, William T. Sherman,
and Jefferson Davis.
d. Explain the importance of Fort Sumter, Antietam, Vicksburg, Gettysburg, and the Battle for
Atlanta and the impact of geography on these battles.
e. Describe the significance of the Emancipation Proclamation.
f. Explain the importance of the growing economic disparity between the North and the South
through an examination of population, functioning railroads, and industrial output.
SSUSH10 The student will identify legal, political, and social dimensions of Reconstruction.
a. Compare and contrast Presidential Reconstruction with Radical Republican Reconstruction.
b. Explain efforts to redistribute land in the South among the former slaves and provide advanced
education (Morehouse College) and describe the role of the Freedmens Bureau.
c. Describe the significance of the 13th, 14th, and 15th amendments.
d. Explain Black Codes, the Ku Klux Klan, and other forms of resistance to racial equality
during Reconstruction.
e. Explain the impeachment of Andrew Johnson in relationship to Reconstruction.
f. Analyze how the presidential election of 1876 and the subsequent compromise of 1877 marked
the end of Reconstruction.
Vocabulary
Kansas-Nebraska Act- Allowed people in Kansas and Nebraska to decide whether or not to
have slaves.
Popular Sovereignty- Rule by consent of the people.
Dred Scott v. Sanford- Ruled slaves as property and not people
States Rights- States should be able to overturn federal decisions.
Fall Honors United States History
31
Secession- States leaving the union.
Emancipation- The process by which slaves are freed.
Proclamation of 1863- Lincoln issued emancipation proclamation, freed slaves in south.
Thirteenth Amendment- Abolished slavery
Fourteenth Amendment- Gave blacks citizenship and equal protection under law.
Fifteenth Amendment- Granted right to vote to blacks
Black Codes- Designed to keep blacks in a system of virtual slavery.
Carpetbagger- Northerner who went South during reconstruction to make money by scamming
Southerners.
Scalawag- Southerner who supported reconstruction and the republicans after the civil war.
Gettysburg Address- Dedicated Soldiers National Cemetery in Gettysburg, one of the most
well-known speeches in US history.
Sectionalism- Belief that ones own section of the country is more important than the country as
a whole.
Habeas Corpus- The right to a judge and trial.
Presidential Reconstruction- Lincolns plan for reconstruction, intended to leave as few harsh
feelings as possible.
Radical Republican- Believed the South had started the war and should pay for it.
Morehouse College- First black college in US.
Andrew Johnsons Impeachment- Johnson violated tenure of office, was impeached. One vote
short of conviction.
Ku Klux Klan- White supremacist cult that originated to terrorize blacks and keep them from
exercising their freedoms after the civil war.
1876 Presidential Election- Very disputed election, resulted in Compromise of 1877.
Fall Honors United States History
32
Compromise of 1877- Ended reconstruction, put Hayes in office as president.
Lincolns Second Inaugural Address of 1865- Lincoln discusses plans for reconstruction, end
of the war.
Bleeding Kansas- Pro-slavery and abolitionists moved to Kansas to try and turn the state free
or slave, fought each other over it.
Underground Railroad- Network of safehouses to get slaves to Canada
Harpers Ferry- Location of John Browns attempted raid to start a slave uprising.
Know Nothings- Nativist party, strongly opposed immigrants and catholicism.
Civil Rights Act of 1866- Granted citizenship and equal rights to all males.
Republican Party- Union party, wanted emancipation and equal rights.
Copperhead- Northerner sympathetic to the South.
Narrative
During the civil war, the South still had a social structure much resembling a caste
system, with the highest rung being the owners of large plantations and the bottom rung being
the slaves who worked them. There was constant fighting over the status of slaves as well as the
fact that there were still slaves at all in a country that considered itself the land of the free. People
usually fell into two distinct stances on the issue of slavery; they were either pro-slavery-or for
slavery, or abolitionist- against slavery. The slaves themselves were still stuck in a position
where they had no hope of a better life, aside from finding their way north to Canada through the
underground railroad.
As the war progressed, Lincoln issued the Emancipation Proclamation, shifting the wars
tone from one over economics to one over morals. When the North won, concerns shifted to how
to rebuild the country, and the following years were filled with social turmoil as northerners tried
to abuse the destroyed southern economy and southerners continued to oppress the blacks even
after they were freed in the form of the KKK, which continued to be a major influence on social
issues up until the 1960s.
Economic
Standards
Fall Honors United States History
33
SSUSH9 The student will identify key events, issues, and individuals relating to the causes,
course, and consequences of the Civil War.
a. Explain the Kansas-Nebraska Act, the failure of popular sovereignty, Dred Scott case, and
John Browns Raid.
b. Describe President Lincolns efforts to preserve the Union as seen in his second inaugural
address and the Gettysburg speech and in his use of emergency powers, such as his decision to
suspend habeas corpus.
c. Describe the roles of Ulysses Grant, Robert E. Lee, Stonewall Jackson, William T. Sherman,
and Jefferson Davis.
d. Explain the importance of Fort Sumter, Antietam, Vicksburg, Gettysburg, and the Battle for
Atlanta and the impact of geography on these battles.
e. Describe the significance of the Emancipation Proclamation.
f. Explain the importance of the growing economic disparity between the North and the South
through an examination of population, functioning railroads, and industrial output.
SSUSH10 The student will identify legal, political, and social dimensions of Reconstruction.
a. Compare and contrast Presidential Reconstruction with Radical Republican Reconstruction.
b. Explain efforts to redistribute land in the South among the former slaves and provide advanced
education (Morehouse College) and describe the role of the Freedmens Bureau.
c. Describe the significance of the 13th, 14th, and 15th amendments.
d. Explain Black Codes, the Ku Klux Klan, and other forms of resistance to racial equality
during Reconstruction.
e. Explain the impeachment of Andrew Johnson in relationship to Reconstruction.
f. Analyze how the presidential election of 1876 and the subsequent compromise of 1877 marked
the end of Reconstruction.
Vocabulary
Kansas-Nebraska Act- Allowed people in Kansas and Nebraska to decide whether or not to
have slaves.
States Rights- States should be able to overturn federal decisions.
Carpetbagger- Northerner who went South during reconstruction to make money by scamming
Southerners.
Freedmens Bureau- Designed to aid former slaves in adjusting to society.
Sharecropper- Tenant farmer, works land that they dont own.
Fall Honors United States History
34
Tenant Farming- Landowner allows sharecroppers to farm their land for a fee.
Sectionalism- Belief that ones own section of the country is more important than the country as
a whole.
Presidential Reconstruction- Lincolns plan for reconstruction, intended to leave as few harsh
feelings as possible.
Radical Republican- Believed the South had started the war and should pay for it.
Morehouse College- First black college in US.
1876 Presidential Election- Very disputed election, resulted in Compromise of 1877.
Compromise of 1877- Ended reconstruction, put Hayes in office as president.
Lincolns Second Inaugural Address of 1865- Lincoln discusses plans for reconstruction, end
of the war.
Bleeding Kansas- Pro-slavery and abolitionists moved to Kansas to try and turn the state free
or slave, fought each other over it.
Anaconda Plan- Union plan to surround confederacy and cut off its supply chain.
Blockade- Naval restriction of an area, prevents ships from entering or leaving.
Narrative
Economically, the civil war was disastrous for the South. It resulted in the burning of an
entire state as well as almost the complete destruction of the Souths economy. The Northern
economy fared better due to its base in manufacturing, but still suffered massively due to the debt
the war raised as well as the social turmoil caused by it. Lincolns reconstruction plan resulted in
the country slowly rebuilding its economy, however full recovery was not made until the US
began to mobilize its army for WWI. After the slaves were emancipated, they often found a lack
of jobs and the black codes kept them from working in any higher paid jobs or getting an
education. Most of them reverted back to farming as sharecroppers, usually under their former
masters as landlords. This led to widespread economic abuse of sharecroppers as they struggled
to make a living or even any money at all.
3A
Political
Fall Honors United States History
35
Standards
SSUSH11 The student will describe the economic, social, and geographic impact of the growth
of big business and technological innovations after Reconstruction.
a. Explain the impact of the railroads on other industries, such as steel, and on the organization of
big business.
b. Describe the impact of the railroads in the development of the West; include the
transcontinental railroad, and the use of Chinese labor.
c. Identify John D. Rockefeller and the Standard Oil Company and the rise of trusts and
monopolies
d. Describe the inventions of Thomas Edison; include the electric light bulb, motion pictures, and
the phonograph, and their impact on American life
SSUSH12 The student will analyze important consequences of American industrial growth.
a. Describe Ellis Island, the change in immigrants origins to southern and eastern Europe and the
impact of this change on urban America.
b. Identify the American Federation of Labor and Samuel Gompers.
c. Describe the growth of the western population and its impact on Native Americans with
reference to Sitting Bull and Wounded Knee.
d. Describe the 1894 Pullman strike as an example of industrial unrest.
SSUSH13 The student will identify major efforts to reform American society and politics in the
Progressive Era.
a. Explain Upton Sinclairs The Jungle and federal oversight of the meatpacking industry.
b. Identify Jane Addams and Hull House and describe the role of women in reform movements.
c. Describe the rise of Jim Crow, Plessy v. Ferguson, and the emergence of the NAACP.
d. Explain Ida Tarbells role as a muckraker.
e. Describe the significance of progressive reforms such as the initiative, recall, and referendum;
direct election of senators; reform of labor laws; and efforts to improve living conditions for the
poor in cities.
f. Describe the conservation movement and the development of national parks and forests;
include the role of Theodore Roosevelt.
SSUSH14 The student will explain Americas evolving relationship with the world at the turn of
the twentieth century.
a. Explain the Chinese Exclusion Act of 1882 and anti-Asian immigration sentiment on the west
coast.
b. Describe the Spanish-American War, the war in the Philippines, and the debate over American
expansionism.
Fall Honors United States History
c. Explain U.S. involvement in Latin America, as reflected by the Roosevelt Corollary to the
Monroe Doctrine and the creation of the Panama Canal.
Vocabulary
Monopoly- A single company controlling its market
Trust- A group of investors managing the funds of multiple companies
Robber Baron- Entrepreneurs that used questionable business practices
Social Darwinism- The rich are rich because they are better
Sweatshop- Long hours in dangerous conditions for low wages.
Nativism- The belief that ones own people are superior to others.
Urbanization- The increased growth of cities.
Tenement- A cramped apartment-style dwelling with a landlord
Assimilate- To become American while contributing ethnic background and qualities
Jim Crow Laws- Designed to keep blacks oppressed
Progressivism- Social and economic progress were main goals
Muckraker- Journalist exposing bad business practices
Initiative- Began a large endeavor
Referendum- General vote
Recall- To remove an official from office
Settlement House- Inner city house providing social and recreational activities
Direct Primary- Voters directly elect candidates
NAACP- Main civil rights organization, fought for equal rights for blacks
36
Fall Honors United States History
18th Amendment- Began prohibition
19th Amendment- Gave women voting rights
Ellis Island- New York immigration center
Motion Picture Camera- Invented by Edison, no sound at first
American Federation of Labor- Labor union, fought for fair pay and better conditions
Hull House- First community center, founded by Jane Addams
Entrepreneur- Managed business, wanted to make money.
Laissez-Faire- Relaxed government control on the economy
Patent- Design cannot be recreated by others without a license for the patent
Bessemer Process- Quick, cheap way to make steel
Mass Production- Assembly line, higher output for lower cost.
Corporation- Business owned by shareholders
Cartel- Agreement between competing companies to manage prices and cut out competitors
Horizontal Integration- Buying out competitors
Vertical Integration- Buying entire chain from raw resources up
Company Town- Towns built for factory workers entirely owned by company
Collective Bargaining- Unions bargain with corporations to provide leverage for workers
Socialism- Government should distribute money equally
Knights of Labor- Major union in 1880s, fought for fair conditions for all workers
Angel Island- West coast version of Ellis Island
Americanization- Assimilating into American culture
37
Fall Honors United States History
Dawes Act- Survey and distribute land in native american tribes/reservations
Poll Tax- Designed to keep poor people and african americans from voting
Literacy Test- Designed to keep african americans from voting
Populist Party- Main goal was to benefit the people
Melting Pot- Belief that American society is made up of the best elements of immigrant
societies
Mass Transit- Busses, subways, trains, etc
Skyscrapers- Tall buildings made possible by large amounts of steel
Gilded Age- Wealth and prosperity before the depression
Mass Culture- Unified American culture made possible by radio
New South- Modernization of society and attitudes in South during gilded age
Land Grants- Government giving away land out west to further expansion
Homestead Act- Encouraged western migration, passed in 1862 by Lincoln
Grandfather Clause- Designed to keep african americans from voting
Protective Tariff- Designed to protect US industry from foreign competition
Suspension Bridge- Made possible by steel cables
Time Zones- Established to make post and telegrams easier to manage
Gospel of Wealth- Responsibility of philanthropy written by Carnegie
Captains of Industry- Positive term for industrial entrepreneurs
Square Deal- Conservation of natural resources, control of corporations, consumer protection,
proposed by Teddy Roosevelt.
Meat Inspection Act- Passed after The Jungle was written
38
Fall Honors United States History
39
Pure Food and Drug Act- Designed to guarantee food and drug safety and cleanliness
Progressive Party- Main goals were workers rights and industrialization
Narrative
As it would come to be known, the Gilded Age was filled with political upheaval as unions and
corporations lobbied for new laws to be passed limiting the other, civil rights movements sprang
up demanding equality and fair treatment, and two amendments were passed. The 18th
amendment started the era of prohibition in the hopes that alcohol would not be a factor in
American society, however it only caused a number of problems later on. The nineteenth
amendment was passed not long after, giving women the same right to vote as men. Along with
this, the Progressive party and the Populist party were founded and the Nativist movement
sprang up in response to the massive influx of immigrants.
Many political parties, most notably the Progressives, demanded that the government
switch over to direct primary elections, bypassing the electoral college and allowing citizens to
vote for their leaders themselves as well. As a result, all states formed some sort of system for
citizens to directly elect politicians.
Social
Standards
SSUSH11 The student will describe the economic, social, and geographic impact of the growth
of big business and technological innovations after Reconstruction.
a. Explain the impact of the railroads on other industries, such as steel, and on the organization of
big business.
b. Describe the impact of the railroads in the development of the West; include the
transcontinental railroad, and the use of Chinese labor.
c. Identify John D. Rockefeller and the Standard Oil Company and the rise of trusts and
monopolies
d. Describe the inventions of Thomas Edison; include the electric light bulb, motion pictures, and
the phonograph, and their impact on American life
SSUSH12 The student will analyze important consequences of American industrial growth.
a. Describe Ellis Island, the change in immigrants origins to southern and eastern Europe and the
impact of this change on urban America.
Fall Honors United States History
40
b. Identify the American Federation of Labor and Samuel Gompers.
c. Describe the growth of the western population and its impact on Native Americans with
reference to Sitting Bull and Wounded Knee.
d. Describe the 1894 Pullman strike as an example of industrial unrest.
SSUSH13 The student will identify major efforts to reform American society and politics in the
Progressive Era.
a. Explain Upton Sinclairs The Jungle and federal oversight of the meatpacking industry.
b. Identify Jane Addams and Hull House and describe the role of women in reform movements.
c. Describe the rise of Jim Crow, Plessy v. Ferguson, and the emergence of the NAACP.
d. Explain Ida Tarbells role as a muckraker.
e. Describe the significance of progressive reforms such as the initiative, recall, and referendum;
direct election of senators; reform of labor laws; and efforts to improve living conditions for the
poor in cities.
f. Describe the conservation movement and the development of national parks and forests;
include the role of Theodore Roosevelt.
SSUSH14 The student will explain Americas evolving relationship with the world at the turn of
the twentieth century.
a. Explain the Chinese Exclusion Act of 1882 and anti-Asian immigration sentiment on the west
coast.
b. Describe the Spanish-American War, the war in the Philippines, and the debate over American
expansionism.
c. Explain U.S. involvement in Latin America, as reflected by the Roosevelt Corollary to the
Monroe Doctrine and the creation of the Panama Canal.
Vocabulary
Monopoly- A single company controlling its market
Trust- A group of investors managing the funds of multiple companies
Robber Baron- Entrepreneurs that used questionable business practices
Social Darwinism- The rich are rich because they are better
Sweatshop- Long hours in dangerous conditions for low wages.
Nativism- The belief that ones own people are superior to others.
Fall Honors United States History
Urbanization- The increased growth of cities.
Tenement- A cramped apartment-style dwelling with a landlord
Assimilate- To become American while contributing ethnic background and qualities
Jim Crow Laws- Designed to keep blacks oppressed
Progressivism- Social and economic progress were main goals
Muckraker- Journalist exposing bad business practices
Initiative- Began a large endeavor
Referendum- General vote
Recall- To remove an official from office
Settlement House- Inner city house providing social and recreational activities
Direct Primary- Voters directly elect candidates
NAACP- Main civil rights organization, fought for equal rights for blacks
18th Amendment- Began prohibition
19th Amendment- Gave women voting rights
Ellis Island- New York immigration center
Motion Picture Camera- Invented by Edison, no sound at first
American Federation of Labor- Labor union, fought for fair pay and better conditions
Hull House- First community center, founded by Jane Addams
Entrepreneur- Managed business, wanted to make money.
Laissez-Faire- Relaxed government control on the economy
Patent- Design cannot be recreated by others without a license for the patent
41
Fall Honors United States History
Bessemer Process- Quick, cheap way to make steel
Mass Production- Assembly line, higher output for lower cost.
Corporation- Business owned by shareholders
Cartel- Agreement between competing companies to manage prices and cut out competitors
Horizontal Integration- Buying out competitors
Vertical Integration- Buying entire chain from raw resources up
Company Town- Towns built for factory workers entirely owned by company
Collective Bargaining- Unions bargain with corporations to provide leverage for workers
Socialism- Government should distribute money equally
Knights of Labor- Major union in 1880s, fought for fair conditions for all workers
Angel Island- West coast version of Ellis Island
Americanization- Assimilating into American culture
Dawes Act- Survey and distribute land in native american tribes/reservations
Poll Tax- Designed to keep poor people and african americans from voting
Literacy Test- Designed to keep african americans from voting
Populist Party- Main goal was to benefit the people
Melting Pot- Belief that American society is made up of the best elements of immigrant
societies
Mass Transit- Busses, subways, trains, etc
Skyscrapers- Tall buildings made possible by large amounts of steel
Gilded Age- Wealth and prosperity before the depression
Mass Culture- Unified American culture made possible by radio
42
Fall Honors United States History
43
New South- Modernization of society and attitudes in South during gilded age
Land Grants- Government giving away land out west to further expansion
Homestead Act- Encouraged western migration, passed in 1862 by Lincoln
Grandfather Clause- Designed to keep african americans from voting
Protective Tariff- Designed to protect US industry from foreign competition
Suspension Bridge- Made possible by steel cables
Time Zones- Established to make post and telegrams easier to manage
Gospel of Wealth- Responsibility of philanthropy written by Carnegie
Captains of Industry- Positive term for industrial entrepreneurs
Square Deal- Conservation of natural resources, control of corporations, consumer protection,
proposed by Teddy Roosevelt.
Meat Inspection Act- Passed after The Jungle was written
Pure Food and Drug Act- Designed to guarantee food and drug safety and cleanliness
Progressive Party- Main goals were workers rights and industrialization
Narrative
The gilded age was a time of social upheaval as unions were formed and battled against
corporations for fair pay and better working conditions and muckrakers exposed extremely
dangerous practices on behalf of corporation owners. Some books published by muckrakers,
such as Upton Sinclairs The Jungle were so influential that they prompted new laws to be put
into place. Women found new rights and new opportunities during the gilded age as social norms
were relaxed and they were allowed to express themselves more in the cities as electric lighting
allowed people to continue their lives well after the sun had set for the first time in human
history.
Prohibition resulted in the formation of gangs around Bootlegging, or the illegal
shipping and sale of alcohol. The laws against this were often overlooked, and gang violence was
Fall Honors United States History
44
rampant throughout the cities as rival gangs vied for control of territory. This lead to the rise of
such notorious gangsters as Al Capone and Bugsy Siegel.
Economic
Standards
SSUSH11 The student will describe the economic, social, and geographic impact of the growth
of big business and technological innovations after Reconstruction.
a. Explain the impact of the railroads on other industries, such as steel, and on the organization of
big business.
b. Describe the impact of the railroads in the development of the West; include the
transcontinental railroad, and the use of Chinese labor.
c. Identify John D. Rockefeller and the Standard Oil Company and the rise of trusts and
monopolies
d. Describe the inventions of Thomas Edison; include the electric light bulb, motion pictures, and
the phonograph, and their impact on American life
SSUSH12 The student will analyze important consequences of American industrial growth.
a. Describe Ellis Island, the change in immigrants origins to southern and eastern Europe and the
impact of this change on urban America.
b. Identify the American Federation of Labor and Samuel Gompers.
c. Describe the growth of the western population and its impact on Native Americans with
reference to Sitting Bull and Wounded Knee.
d. Describe the 1894 Pullman strike as an example of industrial unrest.
SSUSH13 The student will identify major efforts to reform American society and politics in the
Progressive Era.
a. Explain Upton Sinclairs The Jungle and federal oversight of the meatpacking industry.
b. Identify Jane Addams and Hull House and describe the role of women in reform movements.
c. Describe the rise of Jim Crow, Plessy v. Ferguson, and the emergence of the NAACP.
d. Explain Ida Tarbells role as a muckraker.
e. Describe the significance of progressive reforms such as the initiative, recall, and referendum;
direct election of senators; reform of labor laws; and efforts to improve living conditions for the
poor in cities.
f. Describe the conservation movement and the development of national parks and forests;
include the role of Theodore Roosevelt.
SSUSH14 The student will explain Americas evolving relationship with the world at the turn of
the twentieth century.
Fall Honors United States History
45
a. Explain the Chinese Exclusion Act of 1882 and anti-Asian immigration sentiment on the west
coast.
b. Describe the Spanish-American War, the war in the Philippines, and the debate over American
expansionism.
c. Explain U.S. involvement in Latin America, as reflected by the Roosevelt Corollary to the
Monroe Doctrine and the creation of the Panama Canal.
Vocabulary
Monopoly- A single company controlling its market
Trust- A group of investors managing the funds of multiple companies
Robber Baron- Entrepreneurs that used questionable business practices
Social Darwinism- The rich are rich because they are better
Sweatshop- Long hours in dangerous conditions for low wages.
Nativism- The belief that ones own people are superior to others.
Urbanization- The increased growth of cities.
Tenement- A cramped apartment-style dwelling with a landlord
Assimilate- To become American while contributing ethnic background and qualities
Jim Crow Laws- Designed to keep blacks oppressed
Progressivism- Social and economic progress were main goals
Muckraker- Journalist exposing bad business practices
Initiative- Began a large endeavor
Referendum- General vote
Recall- To remove an official from office
Settlement House- Inner city house providing social and recreational activities
Fall Honors United States History
Direct Primary- Voters directly elect candidates
NAACP- Main civil rights organization, fought for equal rights for blacks
18th Amendment- Began prohibition
19th Amendment- Gave women voting rights
Ellis Island- New York immigration center
Motion Picture Camera- Invented by Edison, no sound at first
American Federation of Labor- Labor union, fought for fair pay and better conditions
Hull House- First community center, founded by Jane Addams
Entrepreneur- Managed business, wanted to make money.
Laissez-Faire- Relaxed government control on the economy
Patent- Design cannot be recreated by others without a license for the patent
Bessemer Process- Quick, cheap way to make steel
Mass Production- Assembly line, higher output for lower cost.
Corporation- Business owned by shareholders
Cartel- Agreement between competing companies to manage prices and cut out competitors
Horizontal Integration- Buying out competitors
Vertical Integration- Buying entire chain from raw resources up
Company Town- Towns built for factory workers entirely owned by company
Collective Bargaining- Unions bargain with corporations to provide leverage for workers
Socialism- Government should distribute money equally
Knights of Labor- Major union in 1880s, fought for fair conditions for all workers
46
Fall Honors United States History
Angel Island- West coast version of Ellis Island
Americanization- Assimilating into American culture
Dawes Act- Survey and distribute land in native american tribes/reservations
Poll Tax- Designed to keep poor people and african americans from voting
Literacy Test- Designed to keep african americans from voting
Populist Party- Main goal was to benefit the people
Melting Pot- Belief that American society is made up of the best elements of immigrant
societies
Mass Transit- Busses, subways, trains, etc
Skyscrapers- Tall buildings made possible by large amounts of steel
Gilded Age- Wealth and prosperity before the depression
Mass Culture- Unified American culture made possible by radio
New South- Modernization of society and attitudes in South during gilded age
Land Grants- Government giving away land out west to further expansion
Homestead Act- Encouraged western migration, passed in 1862 by Lincoln
Grandfather Clause- Designed to keep african americans from voting
Protective Tariff- Designed to protect US industry from foreign competition
Suspension Bridge- Made possible by steel cables
Time Zones- Established to make post and telegrams easier to manage
Gospel of Wealth- Responsibility of philanthropy written by Carnegie
Captains of Industry- Positive term for industrial entrepreneurs
47
Fall Honors United States History
48
Square Deal- Conservation of natural resources, control of corporations, consumer protection,
proposed by Teddy Roosevelt.
Meat Inspection Act- Passed after The Jungle was written
Pure Food and Drug Act- Designed to guarantee food and drug safety and cleanliness
Progressive Party- Main goals were workers rights and industrialization
Narrative
The Gilded Age brought industrialization to the United States, and allowed its economy
to soar to new heights out of the civil war and into the modern world of skyscrapers,
automobiles, and radios. Inventors such as Thomas Edison and entrepreneurs such as John D.
Rockefeller spread new technology and new products across the country and inventions such as
the radio created a singular sense of culture among the United States as all ears turned towards
the radio to listen to news broadcasts and families moved to the cities in search of better jobs in
the ever-expanding corporations that were bringing common brands and common quality to the
doorsteps of American families all over the country.
The government took a very laissez-faire approach towards this new economic growth
and only stepped in to do something in a few cases, almost always on the side of the corporations
during union strikes. The gilded age was an age of massive economic and industrial progress,
which paved the way for the United States to become a superpower during the upcoming world
wars.
3B
Political
Standards
SSUSH14 The student will explain Americas evolving relationship with the world at the turn of
the twentieth century.
a. Explain the Chinese Exclusion Act of 1882 and anti-Asian immigration sentiment on the west
coast.
Fall Honors United States History
49
b. Describe the Spanish-American War, the war in the Philippines, and the debate over American
expansionism.
c. Explain U.S. involvement in Latin America, as reflected by the Roosevelt Corollary to the
Monroe Doctrine and the creation of the Panama Canal.
SSUSH15 The student will analyze the origins and impact of U.S. involvement in World War I.
a. Describe the movement from U.S. neutrality to engagement in World War I, with reference to
unrestricted submarine warfare.
b. Explain the domestic impact of World War I, as reflected by the origins of the Great
Migration, the Espionage Act, and socialist Eugene Debs.
c. Explain Wilsons Fourteen Points and the proposed League of Nations.
d. Describe passage of the Eighteenth Amendment, establishing Prohibition, and the Nineteenth
Amendment, establishing woman suffrage.
SSUSH16 The student will identify key developments in the aftermath of WW I.
a. Explain how rising communism and socialism in the United States led to the Red Scare and
immigrant restriction.
b. Identify Henry Ford, mass production, and the automobile.
c. Describe the impact of radio and the movies.
d. Describe modern forms of cultural expression; include Louis Armstrong and the origins of
jazz, Langston Hughes and the Harlem Renaissance, Irving Berlin, and Tin Pan Alley.
Vocabulary
Imperialism- Extending power through military expansion
Boxer Rebellion- Chinese nationalist rebellion, put down by US and other national forces.
Open Door Policy- US had same deals as any other country with China.
Dollar Diplomacy- Further economic power through loans.
Roosevelt Corollary- Addendum to Monroe Doctrine, established US as policeman of western
hemisphere.
Great Migration- African Americans moving north in a search for new job openings
Reparations- Repaying damages caused in a war
Progressivism/Progressive Party- Goals were increased freedoms and economic prosperity.
Fall Honors United States History
50
Square Deal- Conserve resources, limit corporations, and protect consumers- Proposed by
Teddy Roosevelt.
Spheres of Influence- Area where a country has influence over
Panama Canal- Constructed to allow US ships to pass from pacific to atlantic and vice versa.
Hepburn Act- Gave ICC permission to regulate maximum railroad rates.
Extractive Economy- Resource based economy dependant on getting resources to
manufacturing-based economies.
Narrative
Economically, the US was growing at a startling rate. New factories were being built left
and right and the US was in search of new markets for its products. As the country expanded
westward and to new territories as well as opening itself up to the global market, the economy
grew with it and the United States experienced a period of relatively large economic growth with
the opening of China as a trading partner and the growth of the steel and railroad industries. As
these industries expanded, it became necessary to bring in more immigrants to work as unskilled
workers in the factories or on completing the transcontinental railroad as well as numerous other
endeavors such as the new rail networks and the growing oil industry.
Immigrants came by the millions into the United States as the industries requiring large
amounts of unskilled labor continued to expand and demanded even more immigrants as
unskilled labor. This continued well into WWI and beyond.
Social
Standards
SSUSH14 The student will explain Americas evolving relationship with the world at the turn of
the twentieth century.
a. Explain the Chinese Exclusion Act of 1882 and anti-Asian immigration sentiment on the west
coast.
b. Describe the Spanish-American War, the war in the Philippines, and the debate over American
expansionism.
c. Explain U.S. involvement in Latin America, as reflected by the Roosevelt Corollary to the
Monroe Doctrine and the creation of the Panama Canal.
SSUSH15 The student will analyze the origins and impact of U.S. involvement in World War I.
Fall Honors United States History
51
a. Describe the movement from U.S. neutrality to engagement in World War I, with reference to
unrestricted submarine warfare.
b. Explain the domestic impact of World War I, as reflected by the origins of the Great
Migration, the Espionage Act, and socialist Eugene Debs.
c. Explain Wilsons Fourteen Points and the proposed League of Nations.
d. Describe passage of the Eighteenth Amendment, establishing Prohibition, and the Nineteenth
Amendment, establishing woman suffrage.
SSUSH16 The student will identify key developments in the aftermath of WW I.
a. Explain how rising communism and socialism in the United States led to the Red Scare and
immigrant restriction.
b. Identify Henry Ford, mass production, and the automobile.
c. Describe the impact of radio and the movies.
d. Describe modern forms of cultural expression; include Louis Armstrong and the origins of
jazz, Langston Hughes and the Harlem Renaissance, Irving Berlin, and Tin Pan Alley.
Vocabulary
Imperialism- Extending power through military expansion
Yellow Press- Press that is not entirely truthful, more interested in selling than facts.
Jingoism- Support for a countrys military actions.
Militarism- Support for and use of a countrys military
Espionage Act- Allowed government to arrest and deport dissenters
Great Migration- African Americans moving north in a search for new job openings
Red Scare- Fear that communists were taking over the US.
Palmer Raids- Arrested and deported thousands of communists and anarchists in the US
Selective Service Act- Instituted military draft.
Progressivism/Progressive Party- Goals were increased freedoms and economic prosperity.
Social Darwinism- Rich were rich because they were better.
Urban League- Goal was to clean up and improve inner cities
Fall Honors United States History
52
Anti-Defamation League- Goal was to protect jews and other minorities from discrimination.
Conscientious Objector- Did not apply for the draft on moral grounds.
Sacco and Vanzetti- Anarchists accused of murder, put to death on faulty evidence.
Narrative
The late 1800s and early 1900s were a time where people pushed the limits of society as
the nation was industrializing, electricity brought power and light to the streets, and people
migrated into the cities in search of manufacturing jobs. The cities that were growing at an
immense rate became the centers of a cultural explosion as the immigrants that moved in brought
the culture and experience of ethnicities from across the globe. During WWI, the African
American population experienced a mass migration North to the cities and steel mills looking for
manufacturing jobs as WWI came into full swing and a labor shortage arose.
After WWI and the Russian Revolution, the population of the United States became
increasingly wary of a communist takeover of the country, and as a result many politicians were
elected that promised to deal with this threat. The culmination of the Red Scare, as it came to
be known, was the Palmer Raids, where thousands of communists and anarchists were arrested
and deported.
Economic
Standards
SSUSH14 The student will explain Americas evolving relationship with the world at the turn of
the twentieth century.
a. Explain the Chinese Exclusion Act of 1882 and anti-Asian immigration sentiment on the west
coast.
b. Describe the Spanish-American War, the war in the Philippines, and the debate over American
expansionism.
c. Explain U.S. involvement in Latin America, as reflected by the Roosevelt Corollary to the
Monroe Doctrine and the creation of the Panama Canal.
SSUSH15 The student will analyze the origins and impact of U.S. involvement in World War I.
a. Describe the movement from U.S. neutrality to engagement in World War I, with reference to
unrestricted submarine warfare.
b. Explain the domestic impact of World War I, as reflected by the origins of the Great
Migration, the Espionage Act, and socialist Eugene Debs.
c. Explain Wilsons Fourteen Points and the proposed League of Nations.
Fall Honors United States History
53
d. Describe passage of the Eighteenth Amendment, establishing Prohibition, and the Nineteenth
Amendment, establishing woman suffrage.
SSUSH16 The student will identify key developments in the aftermath of WW I.
a. Explain how rising communism and socialism in the United States led to the Red Scare and
immigrant restriction.
b. Identify Henry Ford, mass production, and the automobile.
c. Describe the impact of radio and the movies.
d. Describe modern forms of cultural expression; include Louis Armstrong and the origins of
jazz, Langston Hughes and the Harlem Renaissance, Irving Berlin, and Tin Pan Alley.
Vocabulary
Imperialism- Extending power through military expansion
Boxer Rebellion- Chinese nationalist rebellion, put down by US and other national forces.
Open Door Policy- US had same deals as any other country with China.
Dollar Diplomacy- Further economic power through loans.
Roosevelt Corollary- Addendum to Monroe Doctrine, established US as policeman of western
hemisphere.
Great Migration- African Americans moving north in a search for new job openings
Reparations- Repaying damages caused in a war
Progressivism/Progressive Party- Goals were increased freedoms and economic prosperity.
Square Deal- Conserve resources, limit corporations, and protect consumers- Proposed by
Teddy Roosevelt.
Spheres of Influence- Area where a country has influence over
Panama Canal- Constructed to allow US ships to pass from pacific to atlantic and vice versa.
Hepburn Act- Gave ICC permission to regulate maximum railroad rates.
Extractive Economy- Resource based economy dependant on getting resources to
manufacturing-based economies.
Fall Honors United States History
54
Narrative
Economically, the US was growing at a startling rate. New factories were being built left
and right and the US was in search of new markets for its products. As the country expanded
westward and to new territories as well as opening itself up to the global market, the economy
grew with it and the United States experienced a period of relatively large economic growth with
the opening of China as a trading partner and the growth of the steel and railroad industries. As
these industries expanded, it became necessary to bring in more immigrants to work as unskilled
workers in the factories or on completing the transcontinental railroad as well as numerous other
endeavors such as the new rail networks and the growing oil industry.
Immigrants came by the millions into the United States as the industries requiring large
amounts of unskilled labor continued to expand and demanded even more immigrants as
unskilled labor. This continued well into WWI and beyond.
4A
Political
Standards
SSUSH16 The student will identify key developments in the aftermath of WW I.
a. Explain how rising communism and socialism in the United States led to the Red Scare and
immigrant restriction.
b. Identify Henry Ford, mass production, and the automobile.
c. Describe the impact of radio and the movies.
d. Describe modern forms of cultural expression; include Louis Armstrong and the origins of
jazz, Langston Hughes and the Harlem Renaissance, Irving Berlin, and Tin Pan Alley.
SSUSH17 The student will analyze the causes and consequences of the Great Depression.
a. Describe the causes, including overproduction, underconsumption, and stock market
speculation that led to the stock market crash of 1929 and the Great Depression.
b. Explain factors (include over-farming and climate) that led to the Dust Bowl and the resulting
movement and migration west.
c. Explain the social and political impact of widespread unemployment that resulted in
developments such as Hoovervilles.
SSUSH18 The student will describe Franklin Roosevelts New Deal as a response to the
depression and compare the ways governmental programs aided those in need.
a. Describe the creation of the Tennessee Valley Authority as a works program and as an effort to
control the environment.
Fall Honors United States History
55
b. Explain the Wagner Act and the rise of industrial unionism.
c. Explain the passage of the Social Security Act as a part of the second New Deal.
d. Identify Eleanor Roosevelt as a symbol of social progress and womens activism.
e. Identify the political challenges to Roosevelts domestic and international leadership; include
the role of Huey Long, the court packing bill, and the Neutrality Act.
Vocabulary
Kellogg-Briand Pact- Promise by nations to solve disputes diplomatically
Dawes Plan- Plan to solve war reparations
Scopes Trial- Tennessee against professor for teaching evolution
Volstead Act- Carried out 18th amendment
Speculation- Investing in hopes of gain
Great Depression- Massive economic downturn
Dust Bowl- Severe dust storms in the 1930s
Okies- Residents of Oklahoma
Hoovervilles- Shanty towns built during the 1930s
New Deal- Series of plans and acts by FDR to fix the US economy
TVA- Tennessee Valley Authority, rebuilt South during depression and brought electricity
Second New Deal- Second stage of FDRs New Deal
Social Security Act- Limited risks in US economy/personal funds
Court Packing- Roosevelt packing supreme court to get New Deal acts passed
Collective Bargaining- Groups bargain with factory owners for better conditions
Black Cabinet- First negro public policy advisors
Wagner Act- Established employees rights
Fall Honors United States History
56
Welfare State- Government controls welfare of the people
Neutrality Act of 1939- Roosevelt lobbied for congress not to go to war, US declared intent not
to get involved in WWII.
Narrative
In the 1920s, the Republican party was almost guaranteed to win elections as the
economy was booming. Along with this, the Progressives were pushing for increased social and
political rights for workers and common people. When the great depression hit, Hoover was
president and his philosophy was to let the economy and businesses fix themselves. This plan did
not greatly help the depression, and as a result the first democrat in years was elected, Franklin
Delano Roosevelt. He brought sweeping changes to US economic policy, and instituted the New
Deal programs aimed at bringing the US economy back and putting in ways to prevent it from
crashing again such as Social Security and Medicare-Medicaid. He used a controversial method
known as Court Packing when he attempted to fill the Supreme Court with new justices that
would rule favorably on his New Deal programs.
The US intended to stay out of WWI, and continued to do so while providing arms and
ammunition to the Triple Entente countries until the interception of the Zimmerman note,
prompting the US involvement in WWI. This brought a swift end to the war.
Social
Standards
SSUSH16 The student will identify key developments in the aftermath of WW I.
a. Explain how rising communism and socialism in the United States led to the Red Scare and
immigrant restriction.
b. Identify Henry Ford, mass production, and the automobile.
c. Describe the impact of radio and the movies.
d. Describe modern forms of cultural expression; include Louis Armstrong and the origins of
jazz, Langston Hughes and the Harlem Renaissance, Irving Berlin, and Tin Pan Alley.
SSUSH17 The student will analyze the causes and consequences of the Great Depression.
a. Describe the causes, including overproduction, underconsumption, and stock market
speculation that led to the stock market crash of 1929 and the Great Depression.
b. Explain factors (include over-farming and climate) that led to the Dust Bowl and the resulting
movement and migration west.
c. Explain the social and political impact of widespread unemployment that resulted in
developments such as Hoovervilles.
Fall Honors United States History
57
SSUSH18 The student will describe Franklin Roosevelts New Deal as a response to the
depression and compare the ways governmental programs aided those in need.
a. Describe the creation of the Tennessee Valley Authority as a works program and as an effort to
control the environment.
b. Explain the Wagner Act and the rise of industrial unionism.
c. Explain the passage of the Social Security Act as a part of the second New Deal.
d. Identify Eleanor Roosevelt as a symbol of social progress and womens activism.
e. Identify the political challenges to Roosevelts domestic and international leadership; include
the role of Huey Long, the court packing bill, and the Neutrality Act.
Vocabulary
Model T- First commercially successful automobile.
Bull Market- Share prices are rising.
Buying on Margin- Buying with credit and a down payment
Kellogg-Briand Pact- Promise by nations to solve disputes diplomatically
Fundamentalism- Hardline belief in something
Scopes Trial- Tennessee against professor for teaching evolution
Volstead Act- Carried out 18th amendment
Bootlegger- Sold illegal alcohol
Flapper- Woman who contradicted social norms
Lost Generation- Generation that came of age during WWI
Jazz- New type of music
Harlem Renaissance- Flourishing of African-American culture in Harlem
Speculation- Investing in hopes of gain
Great Depression- Massive economic downturn
Bread Line- Line for free bread at soup kitchens
Fall Honors United States History
58
Dust Bowl- Severe dust storms in the 1930s
Okies- Residents of Oklahoma
Hoovervilles- Shanty towns built during the 1930s
Localism- Preference for ones own locality
Bonus Army- Vets during depression wanting their bonuses
New Deal- Series of plans and acts by FDR to fix the US economy
Fireside Chat- Evening radio addresses by FDR
Social Security Act- Limited risks in US economy/personal funds
Collective Bargaining- Groups bargain with factory owners for better conditions
Black Cabinet- First negro public policy advisors
The Wizard of Oz- First movie with sound and color
Wagner Act- Established employees rights
Narrative
In the 1920s, the US economy was booming and Republican politicians were more or less
guaranteed elections because of how well the economy was doing. As well as having a continual
stream of Republican leaders, the Progressive movement came about and began to bring about
social and political changes as the country became a center of change in more ways than one.
When the great depression hit and savings were lost in an afternoon, the society of the US came
to the sudden realization that their practices of margin buying and stock speculation were the
cause of the massive economic downturn. When WWI came about, the US banded together and
the people of the country revitalized their culture as a mass migration of african americans north
to take up jobs in the factories resulted in a flourishing of african american culture and literature
in what would become known as the Harlem Renaissance.
Economic
Standards
Fall Honors United States History
59
SSUSH16 The student will identify key developments in the aftermath of WW I.
a. Explain how rising communism and socialism in the United States led to the Red Scare and
immigrant restriction.
b. Identify Henry Ford, mass production, and the automobile.
c. Describe the impact of radio and the movies.
d. Describe modern forms of cultural expression; include Louis Armstrong and the origins of
jazz, Langston Hughes and the Harlem Renaissance, Irving Berlin, and Tin Pan Alley.
SSUSH17 The student will analyze the causes and consequences of the Great Depression.
a. Describe the causes, including overproduction, underconsumption, and stock market
speculation that led to the stock market crash of 1929 and the Great Depression.
b. Explain factors (include over-farming and climate) that led to the Dust Bowl and the resulting
movement and migration west.
c. Explain the social and political impact of widespread unemployment that resulted in
developments such as Hoovervilles.
SSUSH18 The student will describe Franklin Roosevelts New Deal as a response to the
depression and compare the ways governmental programs aided those in need.
a. Describe the creation of the Tennessee Valley Authority as a works program and as an effort to
control the environment.
b. Explain the Wagner Act and the rise of industrial unionism.
c. Explain the passage of the Social Security Act as a part of the second New Deal.
d. Identify Eleanor Roosevelt as a symbol of social progress and womens activism.
e. Identify the political challenges to Roosevelts domestic and international leadership; include
the role of Huey Long, the court packing bill, and the Neutrality Act.
Vocabulary
Mass Production- Production method using factories, more goods made cheaper.
Model T- First commercially successful automobile.
Bull Market- Share prices are rising.
Buying on Margin- Buying with credit and a down payment
Teapot Dome Scandal- Bribery incident over oil fields, 1921-22
Dawes Plan- Plan to solve war reparations
Fall Honors United States History
Modernization- Upgrading to modern standards
Speculation- Investing in hopes of gain
Great Depression- Massive economic downturn
Bread Line- Line for free bread at soup kitchens
Dust Bowl- Severe dust storms in the 1930s
Okies- Residents of Oklahoma
Hoovervilles- Shanty towns built during the 1930s
Black Tuesday- Day of wall street crash, Oct. 24th 1929
Localism- Preference for ones own locality
Trickle-down Economics- Money from rich will find its way to the poor
Bonus Army- Vets during depression wanting their bonuses
New Deal- Series of plans and acts by FDR to fix the US economy
TVA- Tennessee Valley Authority, rebuilt South during depression and brought electricity
Second New Deal- Second stage of FDRs New Deal
Social Security Act- Limited risks in US economy/personal funds
Collective Bargaining- Groups bargain with factory owners for better conditions
The Wizard of Oz- First movie with sound and color
Wagner Act- Established employees rights
Welfare State- Government controls welfare of the people
60
Fall Honors United States History
61
Narrative
Economically, the early 1920s was a time where it was possible to get rich by doing very
little and every American was finding economic success in their jobs as they migrated into the
cities and invested their life savings as every stock was going up at astronomically high rates.
Businesses found money for any possible venture, and investors were willing to invest on even
the most bizarre, obscure ideas, regardless of whether or not they might work. This all came to a
halt in 1929, when the stock market crashed and the years of impulse buying, stock speculation,
and credit buying came crashing to a screeching halt as the economy tanked and descended into
the great depression. The depression lasted until WWI, where the US government employed
millions in the fight against the Triple Alliance in Europe. During the war, factory workers were
in high demand and people moved into the cities and factories en masse to fill these roles.
4B
Political
Standards
SSUSH19 The student will identify the origins, major developments, and the domestic impact of
World War II, especially the growth of the federal government.
a. Explain A. Philip Randolphs proposed march on Washington, D.C., and President Franklin D.
Roosevelts response.
b. Explain the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor and the internment of Japanese- Americans,
German-Americans, and Italian-Americans.
c. Explain major events; include the lend-lease program, the Battle of Midway, D-Day, and the
fall of Berlin.
d. Describe war mobilization, as indicated by rationing, war-time conversion, and the role of
women in war industries.
e. Describe the Manhattan Project at Los Alamos and the scientific, economic, and military
implications of developing the atomic bomb.
f. Compare the geographic locations of the European Theater and the Pacific Theater and the
difficulties the U.S. faced in delivering weapons, food, and medical supplies to troops.
SSUSH20 The student will analyze the domestic and international impact of the Cold War on the
United States.
a. Describe the creation of the Marshall Plan, U.S. commitment to Europe, the Truman Doctrine,
and the origins and implications of the containment policy.
b. Explain the impact of the new communist regime in China and the outbreak of the Korean War
and how these events contributed to the rise of Senator Joseph McCarthy.
Fall Honors United States History
c. Describe the Cuban Revolution, the Bay of Pigs, and the Cuban missile crisis.
d. Describe the Vietnam War, the Tet Offensive, and growing opposition to the war.
e. Explain the role of geography on the U.S. containment policy, the Korean War, the Bay of
Pigs, the Cuban missile crisis, and the Vietnam War.
SSUSH21 The student will explain the impact of technological development and economic
growth on the United States, 1945-1975.
a. Describe the baby boom and its impact as shown by Levittown and the Interstate Highway
Act. b. Describe the impact television has had on American culture; include the presidential
debates (Kennedy/Nixon, 1960) and news coverage of the Civil Rights Movement.
c. Analyze the impact of technology on American life; include the development of the personal
computer and the expanded use of air conditioning.
Vocabulary
Neutrality Act of 1939- US would not get involved in WWII
Lend-Lease Act- Allowed allied nations to buy weapons
Executive Order 8802- Desegregated the military
Rationing- Certain amounts of food per person
Manhattan Project- Project to build atomic weapons
Kamikaze- Japanese suicide bomber
Island Hopping- Process of capturing islands
Appeasement- Giving in to demands to avoid war
Holocaust- Millions of undesirables slaughtered by Nazis
Los Alamos- Site of first nuclear detonation
Allied Powers- US, UK, France, Australia, USSR
Axis Powers- Germany, Italy, Japan
Internment of Japanese Americans- Japanese Americans held in prison camps until the war
ended
62
Fall Honors United States History
Atom Bomb- Nuclear weapons, dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki
Marshall Plan- US plan to rebuild Europe
Truman Doctrine- US policy of containing communism
Totalitarianism- Government where the people have no say
Anti-Semitic- Jew-hating
Blitzkrieg- German offensive into France and Russia. (Translation- Lightning War)
Unconditional Surrender- Surrender without options
Tuskegee Airmen- First african-american fighter pilots
Nuremberg Laws- Laws passed after WWII over the treatment of other humans
Genocide- The extermination of a race or ethnicity
Yalta Conference- Allies planning how to divide up Germany after the war
United Nations- Organization dedicated to keeping peace and settling disputes after WWII
Geneva Convention- Put limits on warfare
Satellite State- State that is a de-facto colony
Cold War- Tensions between US and Soviet Union
Iron Curtain- Soviet wall separating west and east europe
Containment- Keeping communism from spreading
NATO- North Atlantic Treaty Organization against the Warsaw Pact
Warsaw Pact- Soviet alliance against NATO
Mao Zedong- communist leader of China
38th Parallel- Separates North and South Korea
63
Fall Honors United States History
64
Arms Race- US and Soviet Union building up weapons
Brinkmanship- Skirting the edge of war
Eisenhower Doctrine- Country could request US aid if it was threatened
Red Scare- Fear of Communism
Hollywood Ten- Anti-Americans in Hollywood
McCarthyism- The government is filled with Communist infiltrators
Julius and Ethel Rosenberg- Spies for the Soviets, gave them the atomic bomb designs
Narrative
The time between the end of WWI and the mid Cold War was filled with sweeping
changes to US policy as the country took a more aggressive stance in world politics and began to
exercise its military might first in WWII where the US played a major part in the defeat of the
Germans, Italians, and Japanese and the following conflicts in Korea and Vietnam as the country
vastly expanded its military power and reach across the entire globe. After WWII, the US
enacted the Marshall plan to help rebuild European nations after the war as well as enacting the
Eisenhower Doctrine making provisions to aid countries threatened by others and the North
Atlantic Treaty Organization, or NATO, to stop the Warsaw Pact and communism from
spreading. The US also enacted the Truman Doctrine, which was a policy of containing
communism and not allowing it to spread. This resulted in the Korean War, the Vietnam War, and
numerous other small conflicts.
Social
Standards
SSUSH19 The student will identify the origins, major developments, and the domestic impact of
World War II, especially the growth of the federal government.
a. Explain A. Philip Randolphs proposed march on Washington, D.C., and President Franklin D.
Roosevelts response.
b. Explain the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor and the internment of Japanese- Americans,
German-Americans, and Italian-Americans.
c. Explain major events; include the lend-lease program, the Battle of Midway, D-Day, and the
fall of Berlin.
Fall Honors United States History
65
d. Describe war mobilization, as indicated by rationing, war-time conversion, and the role of
women in war industries.
e. Describe the Manhattan Project at Los Alamos and the scientific, economic, and military
implications of developing the atomic bomb.
f. Compare the geographic locations of the European Theater and the Pacific Theater and the
difficulties the U.S. faced in delivering weapons, food, and medical supplies to troops.
SSUSH20 The student will analyze the domestic and international impact of the Cold War on the
United States.
a. Describe the creation of the Marshall Plan, U.S. commitment to Europe, the Truman Doctrine,
and the origins and implications of the containment policy.
b. Explain the impact of the new communist regime in China and the outbreak of the Korean War
and how these events contributed to the rise of Senator Joseph McCarthy.
c. Describe the Cuban Revolution, the Bay of Pigs, and the Cuban missile crisis.
d. Describe the Vietnam War, the Tet Offensive, and growing opposition to the war.
e. Explain the role of geography on the U.S. containment policy, the Korean War, the Bay of
Pigs, the Cuban missile crisis, and the Vietnam War.
SSUSH21 The student will explain the impact of technological development and economic
growth on the United States, 1945-1975.
a. Describe the baby boom and its impact as shown by Levittown and the Interstate Highway
Act. b. Describe the impact television has had on American culture; include the presidential
debates (Kennedy/Nixon, 1960) and news coverage of the Civil Rights Movement.
c. Analyze the impact of technology on American life; include the development of the personal
computer and the expanded use of air conditioning.
Vocabulary
Neutrality Act of 1939- US would not get involved in WWII
Lend-Lease Act- Allowed allied nations to buy weapons
Executive Order 8802- Desegregated the military
Rationing- Certain amounts of food per person
Manhattan Project- Project to build atomic weapons
Kamikaze- Japanese suicide bomber
Island Hopping- Process of capturing islands
Fall Honors United States History
Appeasement- Giving in to demands to avoid war
Holocaust- Millions of undesirables slaughtered by Nazis
Los Alamos- Site of first nuclear detonation
Allied Powers- US, UK, France, Australia, USSR
Axis Powers- Germany, Italy, Japan
Internment of Japanese Americans- Japanese Americans held in prison camps until the war
ended
Atom Bomb- Nuclear weapons, dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki
Marshall Plan- US plan to rebuild Europe
Truman Doctrine- US policy of containing communism
Totalitarianism- Government where the people have no say
Anti-Semitic- Jew-hating
Blitzkrieg- German offensive into France and Russia. (Translation- Lightning War)
Unconditional Surrender- Surrender without options
Tuskegee Airmen- First african-american fighter pilots
Nuremberg Laws- Laws passed after WWII over the treatment of other humans
Genocide- The extermination of a race or ethnicity
Yalta Conference- Allies planning how to divide up Germany after the war
United Nations- Organization dedicated to keeping peace and settling disputes after WWII
Geneva Convention- Put limits on warfare
Satellite State- State that is a de-facto colony
66
Fall Honors United States History
67
Cold War- Tensions between US and Soviet Union
Iron Curtain- Soviet wall separating west and east europe
Containment- Keeping communism from spreading
NATO- North Atlantic Treaty Organization against the Warsaw Pact
Warsaw Pact- Soviet alliance against NATO
Mao Zedong- communist leader of China
38th Parallel- Separates North and South Korea
Arms Race- US and Soviet Union building up weapons
Brinkmanship- Skirting the edge of war
Eisenhower Doctrine- Country could request US aid if it was threatened
Red Scare- Fear of Communism
Hollywood Ten- Anti-Americans in Hollywood
McCarthyism- The government is filled with Communist infiltrators
Julius and Ethel Rosenberg- Spies for the Soviets, gave them the atomic bomb designs
Narrative
During WWII, the civil rights of women and minorities became an intensely heated
debate as Executive Order 8802 was signed by President Roosevelt desegregating the military
and allowing african americans the right to serve in the armed forces as well as women taking up
jobs in factories as all the men were at war. Along with this, after the Japanese attack on Pearl
Harbor, the President authorized the forced relocation, or internment of, millions of JapaneseAmericans who had moved into the country anywhere from one to three generations earlier.
These Japanese Americans were kept in internment camps where they lived in tight quarters and
were not allowed to leave the camps, which were surrounded by barbed wire fences and armed
guards. When the war ended, the debate over civil rights came into full swing, resulting in the
Civil Rights Movement and the rise of Martin Luther King, Malcolm X, and Rosa Parks.
Fall Honors United States History
68
Economic
Standards
SSUSH19 The student will identify the origins, major developments, and the domestic impact of
World War II, especially the growth of the federal government.
a. Explain A. Philip Randolphs proposed march on Washington, D.C., and President Franklin D.
Roosevelts response.
b. Explain the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor and the internment of Japanese- Americans,
German-Americans, and Italian-Americans.
c. Explain major events; include the lend-lease program, the Battle of Midway, D-Day, and the
fall of Berlin.
d. Describe war mobilization, as indicated by rationing, war-time conversion, and the role of
women in war industries.
e. Describe the Manhattan Project at Los Alamos and the scientific, economic, and military
implications of developing the atomic bomb.
f. Compare the geographic locations of the European Theater and the Pacific Theater and the
difficulties the U.S. faced in delivering weapons, food, and medical supplies to troops.
SSUSH20 The student will analyze the domestic and international impact of the Cold War on the
United States.
a. Describe the creation of the Marshall Plan, U.S. commitment to Europe, the Truman Doctrine,
and the origins and implications of the containment policy.
b. Explain the impact of the new communist regime in China and the outbreak of the Korean War
and how these events contributed to the rise of Senator Joseph McCarthy.
c. Describe the Cuban Revolution, the Bay of Pigs, and the Cuban missile crisis.
d. Describe the Vietnam War, the Tet Offensive, and growing opposition to the war.
e. Explain the role of geography on the U.S. containment policy, the Korean War, the Bay of
Pigs, the Cuban missile crisis, and the Vietnam War.
SSUSH21 The student will explain the impact of technological development and economic
growth on the United States, 1945-1975.
a. Describe the baby boom and its impact as shown by Levittown and the Interstate Highway
Act. b. Describe the impact television has had on American culture; include the presidential
debates (Kennedy/Nixon, 1960) and news coverage of the Civil Rights Movement.
c. Analyze the impact of technology on American life; include the development of the personal
computer and the expanded use of air conditioning.
Vocabulary
Fall Honors United States History
Neutrality Act of 1939- US would not get involved in WWII
Lend-Lease Act- Allowed allied nations to buy weapons
Executive Order 8802- Desegregated the military
Rationing- Certain amounts of food per person
Manhattan Project- Project to build atomic weapons
Kamikaze- Japanese suicide bomber
Island Hopping- Process of capturing islands
Appeasement- Giving in to demands to avoid war
Holocaust- Millions of undesirables slaughtered by Nazis
Los Alamos- Site of first nuclear detonation
Allied Powers- US, UK, France, Australia, USSR
Axis Powers- Germany, Italy, Japan
Internment of Japanese Americans- Japanese Americans held in prison camps until the war
ended
Atom Bomb- Nuclear weapons, dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki
Marshall Plan- US plan to rebuild Europe
Truman Doctrine- US policy of containing communism
Totalitarianism- Government where the people have no say
Anti-Semitic- Jew-hating
Blitzkrieg- German offensive into France and Russia. (Translation- Lightning War)
Unconditional Surrender- Surrender without options
Tuskegee Airmen- First african-american fighter pilots
69
Fall Honors United States History
Nuremberg Laws- Laws passed after WWII over the treatment of other humans
Genocide- The extermination of a race or ethnicity
Yalta Conference- Allies planning how to divide up Germany after the war
United Nations- Organization dedicated to keeping peace and settling disputes after WWII
Geneva Convention- Put limits on warfare
Satellite State- State that is a de-facto colony
Cold War- Tensions between US and Soviet Union
Iron Curtain- Soviet wall separating west and east europe
Containment- Keeping communism from spreading
NATO- North Atlantic Treaty Organization against the Warsaw Pact
Warsaw Pact- Soviet alliance against NATO
Mao Zedong- communist leader of China
38th Parallel- Separates North and South Korea
Arms Race- US and Soviet Union building up weapons
Brinkmanship- Skirting the edge of war
Eisenhower Doctrine- Country could request US aid if it was threatened
Red Scare- Fear of Communism
Hollywood Ten- Anti-Americans in Hollywood
McCarthyism- The government is filled with Communist infiltrators
Julius and Ethel Rosenberg- Spies for the Soviets, gave them the atomic bomb designs
70
Fall Honors United States History
71
Narrative
The US went into WWII while still recovering from the effects of the Great Depression,
and the country was still reeling from the crushing economic disaster of the 1930s. When the war
started, the US governments need for war materials put people back to work and resulted in the
full recovery of the US economy.as every resource the country had was devoted to the sole
purpose of making war and defeating the Axis Powers. As the war ended, the factories that had
previously been making war materials switched to consumer products as the country shifted back
into a peacetime economy. The country had incurred massive debts during the war, so taxes were
raised to accommodate for this.
During the Cold War, the US defense industry grew massively as the US entered an arms
race with the Soviet Union. This trend continues to this day, as the US defense industry supplies
much of the worlds weapons.
5A
Political
Standards
SSUSH19 The student will identify the origins, major developments, and the domestic impact of
World War II, especially the growth of the federal government.
a. Explain A. Philip Randolphs proposed march on Washington, D.C., and President Franklin D.
Roosevelts response.
b. Explain the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor and the internment of Japanese- Americans,
German-Americans, and Italian-Americans.
c. Explain major events; include the lend-lease program, the Battle of Midway, D-Day, and the
fall of Berlin.
d. Describe war mobilization, as indicated by rationing, war-time conversion, and the role of
women in war industries.
e. Describe the Manhattan Project at Los Alamos and the scientific, economic, and military
implications of developing the atomic bomb.
f. Compare the geographic locations of the European Theater and the Pacific Theater and the
difficulties the U.S. faced in delivering weapons, food, and medical supplies to troops.
SSUSH20 The student will analyze the domestic and international impact of the Cold War on the
United States.
a. Describe the creation of the Marshall Plan, U.S. commitment to Europe, the Truman Doctrine,
and the origins and implications of the containment policy.
Fall Honors United States History
72
b. Explain the impact of the new communist regime in China and the outbreak of the Korean War
and how these events contributed to the rise of Senator Joseph McCarthy.
c. Describe the Cuban Revolution, the Bay of Pigs, and the Cuban missile crisis.
d. Describe the Vietnam War, the Tet Offensive, and growing opposition to the war.
e. Explain the role of geography on the U.S. containment policy, the Korean War, the Bay of
Pigs, the Cuban missile crisis, and the Vietnam War.
SSUSH21 The student will explain the impact of technological development and economic
growth on the United States, 1945-1975.
a. Describe the baby boom and its impact as shown by Levittown and the Interstate Highway
Act. b. Describe the impact television has had on American culture; include the presidential
debates (Kennedy/Nixon, 1960) and news coverage of the Civil Rights Movement.
c. Analyze the impact of technology on American life; include the development of the personal
computer and the expanded use of air conditioning.
d. Describe the impact of competition with the USSR as evidenced by the launch of Sputnik I
and President Eisenhowers actions.
SSUSH22 The student will identify dimensions of the Civil Rights Movement, 1945-1970.
a. Explain the importance of President Trumans order to integrate the U.S. military and the
federal government.
b. Identify Jackie Robinson and the integration of baseball.
c. Explain Brown v. Board of Education and efforts to resist the decision.
d. Describe the significance of Martin Luther King, Jr.s Letter from a Birmingham Jail and his I
Have a Dream Speech.
e. Describe the causes and consequences of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights
Act of 1965.
SSUSH23 The student will describe and assess the impact of political developments between
1945 and 1970.
a. Describe the Warren Court and the expansion of individual rights as seen in the Miranda
decision.
b. Describe the political impact of the assassination of President John F. Kennedy; include the
impact on civil rights legislation.
c. Explain Lyndon Johnsons Great Society; include the establishment of Medicare.
d. Describe the social and political turmoil of 1968; include the assassinations of Martin Luther
King, Jr. and Robert F. Kennedy, and the events surrounding the Democratic National
Convention.
SSUSH24 The student will analyze the impact of social change movements and organizations of
the 1960s.
Fall Honors United States History
73
a. Compare and contrast the Student Non-Violent Coordinating Committee (SNCC) and the
Southern Christian Leadership Conference (SCLC) tactics; include sit-ins, freedom rides, and
changing composition.
b. Describe the National Organization of Women and the origins and goals of the modern
womens movement.
c. Analyze the anti-Vietnam War movement.
d. Analyze Cesar Chavez and the United Farm Workers movement.
e. Explain the importance of Rachel Carsons Silent Spring and the resulting developments;
include Earth Day, the creation of the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), and the modern
environmental movement.
f. Describe the rise of the conservative movement as seen in the presidential candidacy of Barry
Goldwater (1964) and the election of Richard M. Nixon (1968).
Vocabulary
Domino Theory- If one country falls to communism, others around it will.
Deferment- Putting off something until a later date
Bay of Pigs- Failed invasion of Cuba
Tet Offensive- North Vietnamese offensive against South Vietnam/US
Interstate Highway Act- Created highway system in US for defense
Vietnam War- N. Vietnam/ Viet Cong vs South Vietnam/US
Cuban Missile Crisis- USSR placed nukes in Cuba, nearly caused war
1960 Kennedy Nixon Debate- Kennedy made first debate, ended up winning
Warren Court- Worked to expand personal freedoms
Johnsons Great Society- Eliminate poverty and racism via government programs
Medicare- Medical insurance for the elderly
Silent Spring- Written by Rachel Carson, began environmental movement.
EPA- Environmental Protection Agency, keeps water clean and regulates use of pesticides
Conservative Movement- Logic and faith over self-centered behavior
Fall Honors United States History
74
Miranda v. Arizona- Established rights of the accused
Civil Rights Act of 1957- Voting rights bill, first legislation towards equal rights
Montgomery Bus Boycott- Boycott of segregated busses
SNCC- Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee- Helped to organize protesters
Freedom Ride- Protesters using interstate busses to challenge segregation
Civil Rights Act of 1964- Outlawed discrimination based on sex or race
24th Amendment- Outlawed poll tax
Black Power- Slogan for self-determination by african americans
Black Panthers- Militant self-defense party, wanted socialism
Democratic National Convention- Democratic Debates
Taft-Hartley Act- Restricts the activities and power of labor unions
Fair Deal- Truman changing healthcare/education, etc
AFL-CIO- American Federation of Labor/Congress of Industrial Organization- Unions
Urban Renewal- Efforts to revitalize the inner cities
De Jure Segregation- Segregation by law
De Facto Segregation- Segregation by preference
Brown v. Board of Education- Court declared segregation of schools unconstitutional
March on Washington- More than 200,000 protesters rally at washington for equal rights
Gulf of Tonkin Resolution- Allowed the president to exercise war powers without constitutional
approval
Equal Rights Amendment- Guaranteed equal rights to women
Fall Honors United States History
75
Freedom Summer- Project to register as many voters as possible
Roe v. Wade- Right of privacy extended to abortions
Medicaid- Medical aid for low-income families
Hawks- Wanted war, particularly in Vietnam
Doves- Wanted peace, anti-war politicians
Students for a Democratic Society- Socialist organizing group during the 60s-70s
Kent State University- Protesters set fire to ROTC building, guards fired on crowd
Narrative
As WWII came to a close, the US began preparing to combat the next threat, the Soviet
Union and Communism. The US formed a series of alliances and a treaty known as the North
Atlantic Treaty Organization, or NATO, as well as a pacific counterpart to it to combat Chinese,
Vietnamese, and Korean communism as well as aiding in the reconstruction of Japan to the point
where the country became a valuable ally in the fight against communism as well as an excellent
trading partner. The US expanded its economic influence throughout the war-torn countries as
they emerged from WWII, and gave massive economic assistance to countries under the
Marshall Plan. Germany, Japan, and later South Korea all became allies and good trading
partners as the US found itself deeper and deeper in the Cold War.
At home, the US struggled with appeasing the general public over its continued
operations in Vietnam, until the government finally gave in and pulled out of the country,
allowing communist forces to invade the South.
Social
Standards
SSUSH19 The student will identify the origins, major developments, and the domestic impact of
World War II, especially the growth of the federal government.
a. Explain A. Philip Randolphs proposed march on Washington, D.C., and President Franklin D.
Roosevelts response.
b. Explain the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor and the internment of Japanese- Americans,
German-Americans, and Italian-Americans.
Fall Honors United States History
76
c. Explain major events; include the lend-lease program, the Battle of Midway, D-Day, and the
fall of Berlin.
d. Describe war mobilization, as indicated by rationing, war-time conversion, and the role of
women in war industries.
e. Describe the Manhattan Project at Los Alamos and the scientific, economic, and military
implications of developing the atomic bomb.
f. Compare the geographic locations of the European Theater and the Pacific Theater and the
difficulties the U.S. faced in delivering weapons, food, and medical supplies to troops.
SSUSH20 The student will analyze the domestic and international impact of the Cold War on the
United States.
a. Describe the creation of the Marshall Plan, U.S. commitment to Europe, the Truman Doctrine,
and the origins and implications of the containment policy.
b. Explain the impact of the new communist regime in China and the outbreak of the Korean War
and how these events contributed to the rise of Senator Joseph McCarthy.
c. Describe the Cuban Revolution, the Bay of Pigs, and the Cuban missile crisis.
d. Describe the Vietnam War, the Tet Offensive, and growing opposition to the war.
e. Explain the role of geography on the U.S. containment policy, the Korean War, the Bay of
Pigs, the Cuban missile crisis, and the Vietnam War.
SSUSH21 The student will explain the impact of technological development and economic
growth on the United States, 1945-1975.
a. Describe the baby boom and its impact as shown by Levittown and the Interstate Highway
Act. b. Describe the impact television has had on American culture; include the presidential
debates (Kennedy/Nixon, 1960) and news coverage of the Civil Rights Movement.
c. Analyze the impact of technology on American life; include the development of the personal
computer and the expanded use of air conditioning.
d. Describe the impact of competition with the USSR as evidenced by the launch of Sputnik I
and President Eisenhowers actions.
SSUSH22 The student will identify dimensions of the Civil Rights Movement, 1945-1970.
a. Explain the importance of President Trumans order to integrate the U.S. military and the
federal government.
b. Identify Jackie Robinson and the integration of baseball.
c. Explain Brown v. Board of Education and efforts to resist the decision.
d. Describe the significance of Martin Luther King, Jr.s Letter from a Birmingham Jail and his I
Have a Dream Speech.
e. Describe the causes and consequences of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights
Act of 1965.
Fall Honors United States History
77
SSUSH23 The student will describe and assess the impact of political developments between
1945 and 1970.
a. Describe the Warren Court and the expansion of individual rights as seen in the Miranda
decision.
b. Describe the political impact of the assassination of President John F. Kennedy; include the
impact on civil rights legislation.
c. Explain Lyndon Johnsons Great Society; include the establishment of Medicare.
d. Describe the social and political turmoil of 1968; include the assassinations of Martin Luther
King, Jr. and Robert F. Kennedy, and the events surrounding the Democratic National
Convention.
SSUSH24 The student will analyze the impact of social change movements and organizations of
the 1960s.
a. Compare and contrast the Student Non-Violent Coordinating Committee (SNCC) and the
Southern Christian Leadership Conference (SCLC) tactics; include sit-ins, freedom rides, and
changing composition.
b. Describe the National Organization of Women and the origins and goals of the modern
womens movement.
c. Analyze the anti-Vietnam War movement.
d. Analyze Cesar Chavez and the United Farm Workers movement.
e. Explain the importance of Rachel Carsons Silent Spring and the resulting developments;
include Earth Day, the creation of the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), and the modern
environmental movement.
f. Describe the rise of the conservative movement as seen in the presidential candidacy of Barry
Goldwater (1964) and the election of Richard M. Nixon (1968).
Vocabulary
Tet Offensive- North Vietnamese offensive against South Vietnam/US
Baby Boom- Massive increase in birthrate following WWII
Levittown- Mass-constructed suburban housing
Vietnam War- N. Vietnam/ Viet Cong vs South Vietnam/US
1960 Kennedy Nixon Debate- Kennedy made first debate, ended up winning
Air Conditioning- Control of climate in a building
Personal Computer- First small computers
Fall Honors United States History
Consumerism- Emphasis on consuming rather than producing
Rock and Roll- New music, came to define US culture
Beatnik- Young person from 1950s-60s
Warren Court- Worked to expand personal freedoms
Johnsons Great Society- Eliminate poverty and racism via government programs
Medicare- Medical insurance for the elderly
National Organization of Women- Pushed for women's rights and equality in the workplace
United Farm Workers- Cesar Chavez, farmers union
Silent Spring- Written by Rachel Carson, began environmental movement.
Conservative Movement- Logic and faith over self-centered behavior
Miranda v. Arizona- Established rights of the accused
Civil Rights Act of 1957- Voting rights bill, first legislation towards equal rights
Montgomery Bus Boycott- Boycott of segregated busses
Sit-in- Using segregated seats and waiting until served
SNCC- Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee- Helped to organize protesters
Freedom Ride- Protesters using interstate busses to challenge segregation
Civil Rights Act of 1964- Outlawed discrimination based on sex or race
24th Amendment- Outlawed poll tax
Black Power- Slogan for self-determination by african americans
Black Panthers- Militant self-defense party, wanted socialism
Democratic National Convention- Democratic Debates
78
Fall Honors United States History
79
Fair Deal- Truman changing healthcare/education, etc
Sunbelt- Warm climates, lower taxes, high economic opportunities. Mostly southern states.
Nuclear Family- Father mother, two children.
Television- Revolutionized mass media
Inner City- Heavily urbanized area
Urban Renewal- Efforts to revitalize the inner cities
De Jure Segregation- Segregation by law
De Facto Segregation- Segregation by preference
Brown v. Board of Education- Court declared segregation of schools unconstitutional
Letters from a Birmingham Jail- Letters from MLK against a cautious approach to civil rights
March on Washington- More than 200,000 protesters rally at washington for equal rights
Counterculture- Going against ordinary culture of the time
Generation Gap- Difference of opinion between multiple generations
Equal Rights Amendment- Guaranteed equal rights to women
Freedom Summer- Project to register as many voters as possible
Roe v. Wade- Right of privacy extended to abortions
Hawks- Wanted war, particularly in Vietnam
Doves- Wanted peace, anti-war politicians
Students for a Democratic Society- Socialist organizing group during the 60s-70s
Kent State University- Protesters set fire to ROTC building, guards fired on crowd
Narrative
Fall Honors United States History
80
After WWII, the US experienced a massive growth in birth rates as soldiers returned
home and looked to start families. These children became known as the Baby Boomers, and grew
up in the very conservative era of the 1950s and 1960s. During the 1950s, McCarthyism spread
and the general public was suspicious of anything even remotely hinting at leftist or communist
behavior. While suspected communists werent rounded up by the thousands and deported like
the Palmer Raids of the 1910s, the reputations of many political leaders and private individuals
were ruined as a result of what was in effect a wild goose chase searching for communist
infiltrators in the United States.
At the onset of the Tet Offensive during the Vietnam War, public opinion turned strongly
against continued involvement in Vietnam and the country entered a period of intense anti war
sentiment, often to the point where veterans were beaten and their houses vandalized.
Economic
Standards
SSUSH19 The student will identify the origins, major developments, and the domestic impact of
World War II, especially the growth of the federal government.
a. Explain A. Philip Randolphs proposed march on Washington, D.C., and President Franklin D.
Roosevelts response.
b. Explain the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor and the internment of Japanese- Americans,
German-Americans, and Italian-Americans.
c. Explain major events; include the lend-lease program, the Battle of Midway, D-Day, and the
fall of Berlin.
d. Describe war mobilization, as indicated by rationing, war-time conversion, and the role of
women in war industries.
e. Describe the Manhattan Project at Los Alamos and the scientific, economic, and military
implications of developing the atomic bomb.
f. Compare the geographic locations of the European Theater and the Pacific Theater and the
difficulties the U.S. faced in delivering weapons, food, and medical supplies to troops.
SSUSH20 The student will analyze the domestic and international impact of the Cold War on the
United States.
a. Describe the creation of the Marshall Plan, U.S. commitment to Europe, the Truman Doctrine,
and the origins and implications of the containment policy.
b. Explain the impact of the new communist regime in China and the outbreak of the Korean War
and how these events contributed to the rise of Senator Joseph McCarthy.
c. Describe the Cuban Revolution, the Bay of Pigs, and the Cuban missile crisis.
Fall Honors United States History
81
d. Describe the Vietnam War, the Tet Offensive, and growing opposition to the war.
e. Explain the role of geography on the U.S. containment policy, the Korean War, the Bay of
Pigs, the Cuban missile crisis, and the Vietnam War.
SSUSH21 The student will explain the impact of technological development and economic
growth on the United States, 1945-1975.
a. Describe the baby boom and its impact as shown by Levittown and the Interstate Highway
Act. b. Describe the impact television has had on American culture; include the presidential
debates (Kennedy/Nixon, 1960) and news coverage of the Civil Rights Movement.
c. Analyze the impact of technology on American life; include the development of the personal
computer and the expanded use of air conditioning.
d. Describe the impact of competition with the USSR as evidenced by the launch of Sputnik I
and President Eisenhowers actions.
SSUSH22 The student will identify dimensions of the Civil Rights Movement, 1945-1970.
a. Explain the importance of President Trumans order to integrate the U.S. military and the
federal government.
b. Identify Jackie Robinson and the integration of baseball.
c. Explain Brown v. Board of Education and efforts to resist the decision.
d. Describe the significance of Martin Luther King, Jr.s Letter from a Birmingham Jail and his I
Have a Dream Speech.
e. Describe the causes and consequences of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights
Act of 1965.
SSUSH23 The student will describe and assess the impact of political developments between
1945 and 1970.
a. Describe the Warren Court and the expansion of individual rights as seen in the Miranda
decision.
b. Describe the political impact of the assassination of President John F. Kennedy; include the
impact on civil rights legislation.
c. Explain Lyndon Johnsons Great Society; include the establishment of Medicare.
d. Describe the social and political turmoil of 1968; include the assassinations of Martin Luther
King, Jr. and Robert F. Kennedy, and the events surrounding the Democratic National
Convention.
SSUSH24 The student will analyze the impact of social change movements and organizations of
the 1960s.
a. Compare and contrast the Student Non-Violent Coordinating Committee (SNCC) and the
Southern Christian Leadership Conference (SCLC) tactics; include sit-ins, freedom rides, and
changing composition.
Fall Honors United States History
82
b. Describe the National Organization of Women and the origins and goals of the modern
womens movement.
c. Analyze the anti-Vietnam War movement.
d. Analyze Cesar Chavez and the United Farm Workers movement.
e. Explain the importance of Rachel Carsons Silent Spring and the resulting developments;
include Earth Day, the creation of the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), and the modern
environmental movement.
f. Describe the rise of the conservative movement as seen in the presidential candidacy of Barry
Goldwater (1964) and the election of Richard M. Nixon (1968).
Vocabulary
Baby Boom- Massive increase in birthrate following WWII
Levittown- Mass-constructed suburban housing
Interstate Highway Act- Created highway system in US for defense
Air Conditioning- Control of climate in a building
Personal Computer- First small computers
Consumerism- Emphasis on consuming rather than producing
Johnsons Great Society- Eliminate poverty and racism via government programs
United Farm Workers- Cesar Chavez, farmers union
EPA- Environmental Protection Agency, keeps water clean and regulates use of pesticides
Taft-Hartley Act- Restricts the activities and power of labor unions
Sunbelt- Warm climates, lower taxes, high economic opportunities. Mostly southern states.
Information Industries- Information intensive industries like computing or networking
Franchise Business- Franchisee allows business to access their proprietary knowledge and
produce a product with it
AFL-CIO- American Federation of Labor/Congress of Industrial Organization- Unions
Multinational Corporations- Controls goods/services in more than their home country
Fall Honors United States History
83
Inner City- Heavily urbanized area
Urban Renewal- Efforts to revitalize the inner cities
Medicaid- Medical aid for low-income families
Narrative
As the US left WWII, the country had incurred massive debts from war expenditures.
Taxes were raised to cover for this massive debt, and companies switched their production from
wartime industries to peacetime consumer goods in an effort to fill the newly reopened gap in
consumer products, as all of the economy put itself towards the war effort in order to supply the
military as it fought back the Axis Powers and as such had produced almost no consumer goods
during the time of the war due to the scarcity of materials, lack of available labor, as well as the
government quotas to fill in order to keep the US war machine running.
As companies expanded, they looked to the emerging markets in the countries the US
was aiding under the Marshall plan and established began to establish factories there as well as
selling products to the people in those countries.
5B
Political
Standards
SSUSH25 The student will describe changes in national politics since 1968.
a. Describe President Richard M. Nixons opening of China, his resignation due to the Watergate
scandal, changing attitudes toward government, and the Presidency of Gerald Ford.
b. Explain the impact of Supreme Court decisions on ideas about civil liberties and civil rights;
include such decisions as Roe v. Wade (1973) and the Bakke decision on affirmative action.
c. Explain the Carter administrations efforts in the Middle East; include the Camp David
Accords, his response to the 1979 Iranian Revolution, and the Iranian hostage crisis.
d. Describe domestic and international events of Ronald Reagans presidency; include
Reaganomics, the Iran-contra scandal, and the collapse of the Soviet Union.
e. Explain the relationship between Congress and President Bill Clinton; include the North
American Free Trade Agreement and his impeachment and acquittal.
f. Analyze the 2000 presidential election and its outcome, emphasizing the role of the electoral
college.
Fall Honors United States History
84
g. Analyze the response of President George W. Bush to the attacks of September 11, 2001, on
the United States, the war against terrorism, and the subsequent American interventions in
Afghanistan and Iraq.
Vocabulary
Stagflation- Stagnant economy with inflation
OPEC- Middle eastern countries controlling oil prices
Conservative Movement- Logic and faith over self-centered behavior
New Right- Post-WWII Conservative movement
Supply-side Economics- Focus on producers and producing
NAFTA- Lowered trade barriers between US, Canada, and Mexico
Savings and Loan Crisis- Failure of savings and loans associations in the US
Contract with America- Republican plan to shrink government, reduce taxes
EU- European Union, Europe trying to compete with US economically
Narrative
Politically, the US was filled with scandals, crises, and issues of national security
as the country endured scandals and crises year after year, culminating in the 9/11 attacks
on the World Trade Center.
Nixon resigned following the Watergate Scandal, where he was nearly impeached
for being involved in the break-in of the Democrat headquarters. Carter failed to free the
hostages taken when the American Embassy in Iran was overrun, Clinton was found to
have been in an affair with his secretary, and Bush dragged the country into an
unwinnable war in the Middle East. Reagan, while he did have a few shortcomings, was
often looked upon as the best president the US has ever had by many at the time, and this
view holds true to this day with many. After the terrorist attacks on 9/11, the US
government began to pass a series of legislation that allowed the government to begin to
peer into the personal lives of US citizens, something which is still hotly debated.
Fall Honors United States History
85
Social
Standards
SSUSH25 The student will describe changes in national politics since 1968.
a. Describe President Richard M. Nixons opening of China, his resignation due to the Watergate
scandal, changing attitudes toward government, and the Presidency of Gerald Ford.
b. Explain the impact of Supreme Court decisions on ideas about civil liberties and civil rights;
include such decisions as Roe v. Wade (1973) and the Bakke decision on affirmative action.
c. Explain the Carter administrations efforts in the Middle East; include the Camp David
Accords, his response to the 1979 Iranian Revolution, and the Iranian hostage crisis.
d. Describe domestic and international events of Ronald Reagans presidency; include
Reaganomics, the Iran-contra scandal, and the collapse of the Soviet Union.
e. Explain the relationship between Congress and President Bill Clinton; include the North
American Free Trade Agreement and his impeachment and acquittal.
f. Analyze the 2000 presidential election and its outcome, emphasizing the role of the electoral
college.
g. Analyze the response of President George W. Bush to the attacks of September 11, 2001, on
the United States, the war against terrorism, and the subsequent American interventions in
Afghanistan and Iraq.
Vocabulary
Silent Majority- Group that does not express its opinions publicly
Southern Strategy- Gaining support via racism
Affirmative Action- Forcing a change
Watergate- Nixon was involved in a robbery
Executive Privilege- President has certain privileges others do not have.
Pardon- President can waive a crime
Conservative Movement- Logic and faith over self-centered behavior
Christian Fundamentalist- Literal interpretation of the Bible
Amnesty- Pardon extended by government
Fall Honors United States History
86
New Right- Post-WWII Conservative movement
Moral Majority- Associated with fundamentalist christians and republicans
AIDS- STD, became a serious epidemic.
Iranian Hostage Crisis- US embassy in Iran taken over by students
Glasnost- Openness
Perestroika- Listening
Iran-Contra Affair- Provided funds to Contra rebels in Nicaragua by selling arms to Iran
Impeachment- President accused of a crime
Taliban- Islamic group that took power in the middle east
Weapons of Mass Destruction- weapons capable of causing widespread destruction (Nukes,
mustard gas, etc.)
9/11- Terrorist attacks that brought down the WTC and prompted US action in Afghanistan
Operation Enduring Freedom- US war on terrorism
Apartheid- South African segregation
Contract with America- Republican plan to shrink government, reduce taxes
Al Qaeda- Islamic terrorist group responsible for 9/11
Department of Homeland Security- Organization dedicated to defending the US from a
homeland attack
Patriot Act- Designed to stop terrorism, ended up limiting freedoms
No Child Left Behind- Aimed to make sure everyone got an equal education, ended up slowing
down entire education system
Narrative
Fall Honors United States History
87
As the US emerged from the Vietnam war and continued on in the Cold War, the US
culture was captivated with the successes of the Space Race, as Americans became the first to
orbit the Earth, to send a probe to Mars, and became the first to set foot on the Moon, eventually
going back five more times. The US constructed a number of space stations such as Skylab and
the vast majority of the still functioning International Space Station as a result of the general
public support of NASA. Back on Earth, the country was plagued with crises such as the IranContra Affair, the Iranian Hostage Crisis, and the Watergate Scandal as well as the Oil Crisis of
1979. When the US emerged from all these, it found itself entering the Persian Gulf War against
Saddam Husseins army, and the US public was united in its cause to end terrorism after the
World Trade Center attacks on September 11th, 2001, resulting in a war in the Middle East which
continues to this day.
Economic
Standards
SSUSH25 The student will describe changes in national politics since 1968.
a. Describe President Richard M. Nixons opening of China, his resignation due to the Watergate
scandal, changing attitudes toward government, and the Presidency of Gerald Ford.
b. Explain the impact of Supreme Court decisions on ideas about civil liberties and civil rights;
include such decisions as Roe v. Wade (1973) and the Bakke decision on affirmative action.
c. Explain the Carter administrations efforts in the Middle East; include the Camp David
Accords, his response to the 1979 Iranian Revolution, and the Iranian hostage crisis.
d. Describe domestic and international events of Ronald Reagans presidency; include
Reaganomics, the Iran-contra scandal, and the collapse of the Soviet Union.
e. Explain the relationship between Congress and President Bill Clinton; include the North
American Free Trade Agreement and his impeachment and acquittal.
f. Analyze the 2000 presidential election and its outcome, emphasizing the role of the electoral
college.
g. Analyze the response of President George W. Bush to the attacks of September 11, 2001, on
the United States, the war against terrorism, and the subsequent American interventions in
Afghanistan and Iraq.
Vocabulary
Stagflation- Stagnant economy with inflation
OPEC- Middle eastern countries controlling oil prices
Conservative Movement- Logic and faith over self-centered behavior
Fall Honors United States History
88
New Right- Post-WWII Conservative movement
Supply-side Economics- Focus on producers and producing
NAFTA- Lowered trade barriers between US, Canada, and Mexico
Savings and Loan Crisis- Failure of savings and loans associations in the US
Contract with America- Republican plan to shrink government, reduce taxes
EU- European Union, Europe trying to compete with US economically
Narrative
President Nixon, while he was president, opened China to US trade, resulting in the
manufacture of cheap goods in the country as companies closed down their US-based factories to
make their products in China at a lower cost. As president Ronald Reagan came into office, he
brought with him a series of sweeping tax cuts and spending reforms in an effort to take the
heavy tax load off of the businesses in order to stimulate the US economy. On the other side of
this, OPEC enacted a series of changes to the oil industry, resulting in a massive spike in oil
prices which resulted in the oil crisis of 1979. As Clinton took office, he raised taxes back to the
levels before Reagan had taken office. NAFTA also went into effect, stimulating the Mexican
economy as more cheap goods flowed into the US and American manufacturing flowed out of
the country, taking jobs previously held by Americans with it. When Bush came into office, he
raised taxes again as the US began its war on terror, costing the country trillions of dollars and
resulting in another series of debt crises.
You might also like
- The American Revolution - A Visual History - DK Publishing (DK Publishing, Smithsonian, 2016, 9781465446077, Eng) PDFDocument362 pagesThe American Revolution - A Visual History - DK Publishing (DK Publishing, Smithsonian, 2016, 9781465446077, Eng) PDFFrédéric Pili100% (3)
- 00-2012 APUSH Exam Web Study GuideDocument125 pages00-2012 APUSH Exam Web Study GuideJunaid Shaikh50% (2)
- CH2 The Thirteen Colonies and The British EmpireDocument15 pagesCH2 The Thirteen Colonies and The British EmpireNicole TorresNo ratings yet
- History of the United States I CLEP Quick Prep SheetFrom EverandHistory of the United States I CLEP Quick Prep SheetRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- NAQT You Gotta KnowDocument42 pagesNAQT You Gotta Knowluigiram1No ratings yet
- George Washington's Eye - Landscape, Architecture, and Design at Mount Vernon (Joseph Manca) PDFDocument342 pagesGeorge Washington's Eye - Landscape, Architecture, and Design at Mount Vernon (Joseph Manca) PDFDaniel MaftNo ratings yet
- Thirteen Colonies and English Empire Amsco ch2Document16 pagesThirteen Colonies and English Empire Amsco ch2ftacct5No ratings yet
- Revolutionary War Battles Chart Answers 2017Document4 pagesRevolutionary War Battles Chart Answers 2017api-314922612100% (2)
- Cabinet Battle #1 Close ReadDocument5 pagesCabinet Battle #1 Close ReadMichael Milton78% (18)
- AP US History Study Guide 2Document59 pagesAP US History Study Guide 2dssguy99No ratings yet
- Apush Short EssaysDocument10 pagesApush Short EssaysDean FosterNo ratings yet
- AP Us History ReviewDocument76 pagesAP Us History ReviewGregarious JCNo ratings yet
- APUSH Short Study GuideDocument8 pagesAPUSH Short Study Guidejoshua_98548No ratings yet
- 1898 Ohio Society Sons of The American Revolution YearbookDocument336 pages1898 Ohio Society Sons of The American Revolution YearbookEugene Bond100% (1)
- One Pager by Period Review PacketDocument11 pagesOne Pager by Period Review PacketJul TolNo ratings yet
- Military - American War For Independence - General George Washington ArtifactsDocument97 pagesMilitary - American War For Independence - General George Washington ArtifactsThe 18th Century Material Culture Resource Center100% (4)
- 2 Southern Ne Middle ColoniesDocument53 pages2 Southern Ne Middle Coloniesapi-294843376100% (1)
- American Revolution Unit TestDocument4 pagesAmerican Revolution Unit Testapi-317235205100% (2)
- Lesson 6 The Declaration - of - IndependenceDocument16 pagesLesson 6 The Declaration - of - Independencefishertr1No ratings yet
- AP US History ReviewDocument12 pagesAP US History Reviewwhattup100% (22)
- US History EOC Study GuideDocument16 pagesUS History EOC Study GuideJalen ChaneyNo ratings yet
- Ultimate APUSH Terms! :DDocument92 pagesUltimate APUSH Terms! :DPandaManderNo ratings yet
- Famous People of The USA: HomeworkDocument7 pagesFamous People of The USA: HomeworkGangan TudorNo ratings yet
- 'The Road Appeared To Be Full of Red Coats ': An Episode in The Forage War: The Battle of Millstone, 20 January 1777Document32 pages'The Road Appeared To Be Full of Red Coats ': An Episode in The Forage War: The Battle of Millstone, 20 January 1777John U. Rees100% (3)
- Assignment I UsDocument9 pagesAssignment I UsUrvashi ChandranNo ratings yet
- AP U.S. History Overall Brinkley Textbook OutlineDocument24 pagesAP U.S. History Overall Brinkley Textbook OutlineMatthew FerreeNo ratings yet
- Hush Portfolio Total 1Document32 pagesHush Portfolio Total 1api-305333696No ratings yet
- Josh Middlebrooks Full PortfolioDocument49 pagesJosh Middlebrooks Full Portfolioapi-305333365No ratings yet
- Portfolio Project MMDocument31 pagesPortfolio Project MMapi-305332109No ratings yet
- Portfolio 1aDocument51 pagesPortfolio 1aapi-306113316No ratings yet
- Portfolio Project 1Document39 pagesPortfolio Project 1api-306093447No ratings yet
- Honors U.S History Unit Portfolio Project Michelle Voykovic Allatoona High SchoolDocument43 pagesHonors U.S History Unit Portfolio Project Michelle Voykovic Allatoona High Schoolapi-305492195No ratings yet
- Portfolio Narrative DocumentDocument55 pagesPortfolio Narrative Documentapi-305132981No ratings yet
- TatiyannathorneportfolioDocument39 pagesTatiyannathorneportfolioapi-306092886No ratings yet
- Finished ProjectDocument52 pagesFinished Projectapi-308217009No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - The Colonial Period (1607-1776) - Expanded NotesDocument3 pagesChapter 1 - The Colonial Period (1607-1776) - Expanded Notes84883310No ratings yet
- Us History 1Document33 pagesUs History 1attiq100% (1)
- AMH2010 Final Exam Study NotesDocument11 pagesAMH2010 Final Exam Study NotesChristineNo ratings yet
- APUSH Colonial ProjectDocument8 pagesAPUSH Colonial ProjectcorwinmdNo ratings yet
- Material 658E63F0Document31 pagesMaterial 658E63F0MaryamNo ratings yet
- Colonization of America in DetailDocument14 pagesColonization of America in DetailPravinNo ratings yet
- American Civ Summary s2Document5 pagesAmerican Civ Summary s2sbrahma271985No ratings yet
- American History I Final Exam ReviewDocument9 pagesAmerican History I Final Exam ReviewJosh PardueNo ratings yet
- United States History Teacher NotesDocument114 pagesUnited States History Teacher Notesapi-197150255No ratings yet
- One Pager by Period Review PacketDocument11 pagesOne Pager by Period Review Packetone of manyNo ratings yet
- 04 History of United States StudentsDocument6 pages04 History of United States StudentsDenisa Alexandra AdamNo ratings yet
- FRQ Chapter 1-5Document5 pagesFRQ Chapter 1-5Sumera SubzwariNo ratings yet
- 1st Chunk of US History VocabDocument15 pages1st Chunk of US History VocabiameunwoobaeNo ratings yet
- Essay History 1 QuintanaDocument3 pagesEssay History 1 QuintanaFiorella QuintanaNo ratings yet
- I. First European Explorations of North America: A) SpainDocument20 pagesI. First European Explorations of North America: A) SpainaelythNo ratings yet
- US HISTORY Mid Term Exam Study Guide 1Document5 pagesUS HISTORY Mid Term Exam Study Guide 1Trung HậuNo ratings yet
- OboiDocument6 pagesOboiVera WuNo ratings yet
- Apush CH 5-8 Study GuideDocument13 pagesApush CH 5-8 Study Guideapi-235754768No ratings yet
- Historia Cultural de Estados Unidos: 2. A Brief History of The United States 2.1. Pre-Colonial AmericaDocument8 pagesHistoria Cultural de Estados Unidos: 2. A Brief History of The United States 2.1. Pre-Colonial AmericaGema SuarezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Trans Plantations & BorderlandsDocument6 pagesChapter 2 - Trans Plantations & BorderlandsDavid W.100% (2)
- APUSH 3.0 - Study GuideDocument9 pagesAPUSH 3.0 - Study GuideMLT doodlesNo ratings yet
- Colonial History (1600-1763) : Ap Ush-1 Semester Vocabulary ListDocument5 pagesColonial History (1600-1763) : Ap Ush-1 Semester Vocabulary ListRaiya VeerjeeNo ratings yet
- Apush Unit 1 VocabularyDocument3 pagesApush Unit 1 Vocabularyapi-450369672No ratings yet
- First Lesson Plan Euro ExplDocument7 pagesFirst Lesson Plan Euro ExplAdrian HerreraNo ratings yet
- IB HOA Independent MovementsDocument3 pagesIB HOA Independent MovementsVictorJonesJr.No ratings yet
- Colonization, Revolution, and the New Republic: Beginnings to 1860From EverandColonization, Revolution, and the New Republic: Beginnings to 1860No ratings yet
- Colonizing The AmericasDocument11 pagesColonizing The AmericasSeth AdlerNo ratings yet
- Lecture ch06Document37 pagesLecture ch06api-171412573No ratings yet
- BA Cult Final NotesDocument18 pagesBA Cult Final Notesesmabahadiir84No ratings yet
- APUSH Midterm Study GuideDocument22 pagesAPUSH Midterm Study GuideKaity Emerson100% (1)
- Whites vs. IndiansDocument2 pagesWhites vs. IndiansMandy TorresNo ratings yet
- Wa0052.Document6 pagesWa0052.Art WorldNo ratings yet
- The Struggle for Imperial Unity: Recollections & ExperiencesFrom EverandThe Struggle for Imperial Unity: Recollections & ExperiencesNo ratings yet
- Great Epochs in American History, Vol. II The Planting Of The First Colonies: 1562—1733From EverandGreat Epochs in American History, Vol. II The Planting Of The First Colonies: 1562—1733No ratings yet
- Gale Researcher Guide for: Finding Common Themes in American Colonial SocietyFrom EverandGale Researcher Guide for: Finding Common Themes in American Colonial SocietyNo ratings yet
- Why Was There An American Revolution? History Non Fiction Books for Grade 3 | Children's History BooksFrom EverandWhy Was There An American Revolution? History Non Fiction Books for Grade 3 | Children's History BooksNo ratings yet
- The War That Made AmericaDocument2 pagesThe War That Made Americaapi-339764898No ratings yet
- Libellus de Historia: Answer KeyDocument38 pagesLibellus de Historia: Answer KeyDezNo ratings yet
- A Short History of Orange County NY - Malcolm BoothDocument34 pagesA Short History of Orange County NY - Malcolm BoothSteve Skye100% (1)
- South Carolina Dept of Archives and History - Sources For The American RevolutionDocument28 pagesSouth Carolina Dept of Archives and History - Sources For The American RevolutionClay PetersonNo ratings yet
- Biography First 3 Presidents and First LadiesDocument26 pagesBiography First 3 Presidents and First Ladiesapi-267452057No ratings yet
- Readers TheaterDocument6 pagesReaders Theaterapi-401347632No ratings yet
- Hamilton Lesson HandoutsDocument6 pagesHamilton Lesson Handoutsapi-512625125No ratings yet
- The American Revolution 1776Document10 pagesThe American Revolution 1776albertmorales82No ratings yet
- American Pageant Chapter 10 Reading Questions and Terms PDFDocument5 pagesAmerican Pageant Chapter 10 Reading Questions and Terms PDFvaulted armorNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 GuideDocument2 pagesUnit 3 Guidemia racicNo ratings yet
- Manitou Telehandler MLT X 841 MLT X 1041 145 Ps St3a s1 Service Manual 647885en Usm2!12!2020Document22 pagesManitou Telehandler MLT X 841 MLT X 1041 145 Ps St3a s1 Service Manual 647885en Usm2!12!2020marygray070882maw100% (29)
- 100most InflDocument496 pages100most InflpisucamiNo ratings yet
- HIS "Many Who Wandered in Darkness"Document50 pagesHIS "Many Who Wandered in Darkness"Raimundo SousaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9-10 Apush Study GuideDocument15 pagesChapter 9-10 Apush Study Guideapi-237316331No ratings yet
- Making A Case For The Congaree Creek Archaeology ParkDocument131 pagesMaking A Case For The Congaree Creek Archaeology ParkThe State NewspaperNo ratings yet
- George Washington On The Victory of AmericaDocument7 pagesGeorge Washington On The Victory of AmericadennisNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document8 pagesUnit 5Alejandro MartínezNo ratings yet
- U.S History SparkCharts 1492-1877Document14 pagesU.S History SparkCharts 1492-1877Nicole Key100% (4)