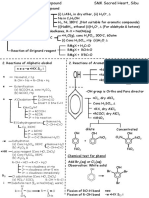
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry Form 6 STPM
Uploaded by
Chong Yin PingOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemistry Form 6 STPM
Uploaded by
Chong Yin PingCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemical Energetic
Guided by Mr. CB ANG Tel: 017-480 5531 STPM
Chemical Energetics
Exothermic reaction is a reaction that releases heat energy into its surroundings. The enthalpy of
the products is less than the enthalpy of the reactants, hence enthalpy change (H) is negative.
CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g) CO2 (g) + 2H2O (g)
H = - 892 kJ
Standard conditions refer to:
(i) Temperature = 25oC or 298K
(ii) Pressure = 1 atm
(iii) concentration of solution = 1.0 mol dm-3
(iv) reactants and products are at their normal physical states at 25oC and 1 atm
Q = MC
Endothermic reaction is a reaction that absorbs heat from the surroundings. The enthalpy of the
products is higher than the enthalpy of reactants. The enthalpy change (H) is positive.
C (s) + 2S (g) CS2 (l)
H = + 107 kJ
Examples of Exothermic Reactions :
Examples of Endothermic Reactions
a)Combustion of fuels
b)Oxidation of food in the respiration process
c)The rusting of Iron
d)Dissolving soluble bases in water
e)Neutralization Reactions
a) The dissolving of crystalline salts such as
CuSO4.5H2O, MgSO4.7H2O and
Na2CO3.10H2O
b) Melting process
c) Evaporation and boiling process
d) Thermal decomposition of salts
Definition of enthalpy of Formation - The standard enthalpy of combustion of an element is the enthalpy change when 1.0 mole of the substance is completely burnt in oxygen under standard condition of 298K and 1 atm.
Combustion - The standard enthalpy of combustion of an element is the enthalpy change when 1.0 mole of the substance is completely burnt in oxygen under standard condition of 298K and 1 atm.
Hydration - The standard enthalpy of hydration of an ion is the heat energy liberated when 1.0 mole of the gaseous ions is dissolved in water to form a solution at infinite dilution under standard
conditions of 298 K and 1 atmosphere
Solution
- The heat evolved or absorbed when 1.0 mole of solute dissolves in water to form an infinitely dilute solution
Neutralization-The heat evolved when one mole of H+ ions reacts with one mole of OH- ions to form one mole of water molecules under standard conditions of 298 K and 1 atm,
Atomization - The standard enthalpy of atomization (Hatom) of an element is the enthalpy change when one mole of gaseous atoms is formed from the elements in the standard state.
Bond energy -Bond energy (bond enthalpy) is the enthalpy change when 1 mole of covalent bonds between 2 atoms are broken in the gas phase
Ionization energy - First ionization energy for an element is the minimum energy required to lose one electron valence from 1 mole of gaseous atom to produce 1 mole of uni-positive gaseous ion
under standard conditions
Electron affinity- First affinity electron is the energy evolved when 1 mole of gaseous atom received electron to form 1 mole of uni-negative gaseous ion under the standard conditions
Chemical Energetic
Guided by Mr. CB ANG Tel: 017-480 5531 STPM
Enthalpy of Formation
Enthalpy of Hydration & Solution // Solubility of ionic solid in liquid
Note:
1. Enthalpy of formation for element to element is 0
2. The state of the elements most be from the most stable state at standard condition
Note:
1. Magnitude of the standard enthalpy of hydration is directly proportional to the charge on the
ion but inversely proportional to the ionic radius.
[STPM 2002] The N204 molecule is the dimer for the N02 molecule. The enthalpy of formation of
N204 and N02 are +9.67 kJ mol-1 and +33.86 kJ mol-1 respectively. Calculate the standard enthalpy
change for the formation (in kJ mol-1) of N204 from N02.
H hyd
2. Hsol = -Lattice energy + H hyd
A-58.05 kJ mol-1 B-24.19 kJ mol-1
[STPM 2002] When one mole of sodium bromide dissolves in water, the enthalpy change is -8 kJ
mol-1. If the lattice energy of sodium bromide and the hydration energy of the Na+ ion are -736
kJ mol-1 and -406 mol-1 respectively, what is the hydration energy of the Br- ion?
C+24.19 kJ mol-
D +43.53 kJ mol-1
[STPM 2008] In industry, ethanoic acid can be prepared from the oxidation of ethanol with
oxygen. The standard enthalpies of formation of ethanoic acid, water and ethanol are 487 kJ
mol1, 286 kJ mol1 and 278 kJ mol1 respectively. The standard enthalpy change, in kJ mol1,
for the preparation is
A 1051
B 495
C 209
D +495
[STPM 2011] The standard enthalpy of formation of ethanol is -278 kJ per mole. Which equation
relates to the formation of ethanol under standard conditions?
A.
B.
C.
D.
2C(g) + 3H2(g)
2C(s) + 3H2(g)
2C(g) + 3H2(g)
4C(g) + 6H2(g)
+ 1/2O2 (g) C2H5OH(l)
+ 1/2O2 (g) C2H5OH(l)
+ 1/2O2 (g) C2H5OH(l)
+ O2 (g) 2C2H5OH(l)
[STPM 2013] The standard enthalpy of formation of CH3NHNH2, CO2 and H2O are +53 kJ mol-1,
-393 kJ mol-1 and -286 kJ mol-1 respectively. The standard enthalpy change for the following
reaction is -5116 kJ.
4 CH3NHNH2 (l) + 5 N2O4 (l) 4 CO2 (g) + 12 H2O (l) + 9 N2 (g)
A-1150 kJ mol-1
B -338 kJ mol-1
C-322 kJ mol-1
D+1 150 kJ mol-1
[STPM 2004] Which of the following cations has the highest hydration energy?
A Li+
B Na+
C K+ D Rb+
[STPM 2007] The radii of the four ions are as following:
Ion
Radius/nm
U+
0.345
V0.151
W2+
0.085
X2+
0.069
Which ion has the largest hydration energy ?
A. U+
B.V-
C. W2+
D. X2+
[STPM 2013] The energy cycle for sodium bromide is shown below.
What is the standard enthalpy of formation of N2O4?
A - 20 kJ mol-1 B - 100 kJ mol-1 C + 20 kJ mol-1 D + 100 kJ mol-1
Which enthalpy change represents the enthalpy of solution of sodium bromide?
A H1
B H2
C H3
D H4
Chemical Energetic
Guided by Mr. CB ANG Tel: 017-480 5531 STPM
Enthalpy of Combustion
Enthalpy of Atomization
Note :
1. Must be considered in excess oxygen
2. final product are usually carbon dioxide and water, and exothermic
3. Enthalpy of combustion are usually exothermic reaction
Note :
1. Changes from compound at the most stable state at standard condition to gaseous
2. No changes in the number of electron or proton
[STPM 2004] The standard enthalpy of combustion of methanol, carbon and
hydrogen is -715 kJ mol-1, -394 kJ mol-1 and -286 kJ mol-1 respectively. What is the standard
enthalpy of formation, in kJ mol of methanol?
A -251
B
-35
C +35
D
+251
[STPM 2005]Standard combustion enthalpies for 1,2-ethanediol (HOCH2CH2OH), carbon and
hydrogen are -1180.0 kJmol-1, -393.7 kJ mol-1 and -285.9 kJ mol-1 respectively. What is the
standard formation enthalpy, in kJ mol-1, for 1,2-ethanediol?
A 500.4
B 465.1
C +465.1
D +500.4
[STPM 2010] The standard enthalpy change, H for several reactions are shown below :
Reaction
H0/kJ
H2(g) + 02(g) H20(l)
-286
CH3CH3 + 7/2O2(g) 2CO2(g) + 3H2O(l)
-1560
C2H2(g) + 5/2 O2(g) 2CO2(g) + H2O
-1299
C2H4(g) + H2(g) C2H6(g)
-157
The value of enthalpy change C2H2 (g) + H2(g) C2H6(g) is
A.-132kJ
B. -154kJ
C. -486kJ
D. -3302KJ
[STPM 2000] Which of the following equations correctly represents the enthalpy of atomization
of sodium?
A Na(s) Na(l)
B Na(s) Na(g)
C Na(l) Na(g)
D Na(l) Na+(g)+ e
E Na(g) Na+(g)+ e
[STPM 2006]
Chemical Energetic
Guided by Mr. CB ANG Tel: 017-480 5531 STPM
Enthalpy of Neutralization
Ionization energy & Affinity electron
Note:
1. Neutralization between acid and alkaline to produce salt and water
2. Usually are exothermic reaction and depend on the strength of acid
3. Stronger the acid, higher the heat release for neutralization
4. Weak acid, less exothermic because some of the heat are absorb back to complete the
dissociation of acid
Note:
1. Involve changes in the number of electron only
2. Ionization energy removal of electron
3. Affinity of electron acceptance of electron
[STPM 2001]The diagram below shows the Born-Haber cycle for the formation of sodium
fluoride
[STPM 2008] The standard enthalpies of neutralization for the reactions between an aqueous
solution of sodium hydroxide and several
hydrohalic acids are given below.
Hydrohalic acid
HF
HCl
HBr
HI
Standard enthalpy of neutralization/kJ mol1
68.6
57.6
57.3
57.2
The standard enthalpy of neutralization of HF is the most negative because .
What is the electron affinity, in kJ mol-1, of chlorine?
A -246 B
-275
C
-328
D
-820
A HF is the strongest acid.
B HF has the strongest covalent bond.
C the fluorine atom has the highest electronegativity.
D the fluorine ion has the most exothermic enthalpy of hydration.
[STPM 2008]Which equation illustrates the first ionization energy of the given element?
[STPM 2013] In an experiment, 0.500 g of magnesium metal was dissolved in an excess of dilute
hydrochloric acid in a calorimeter. The calorimeter recorded a temperature rise of 23.3 C. The
total heat capacity of the calorimeter and its contents is 410 J 0C-1. Calculate the heat released in
the experiment, and determine the standard enthalpy of reaction between magnesium metal and
dilute hydrochloric acid. [4]
[STPM 2009 ]
A C(g) C+(g) + e
C Cl(g) + e Cl(g)
B Na(s) Na+(g) + e
D O(g) + e O(g)
Chemical Energetic
Guided by Mr. CB ANG Tel: 017-480 5531 STPM
Hesss Law
Born Haber Cycle
The overall enthalpy change is equal to the sum of the enthalpy changes for the individual steps
in a reaction
Using the following data given, generate the Born Haber energy cycle and thus calculate the
lattice energy for sodium chloride.
Standard enthalpy of atomization for Na
Standard enthalpy of atomization for Cl
First ionization energy for Na
First electron affinity for Cl
[STPM 2005]
[STPM 2006]
= + 108 kJ mol-1
= + 121 kJ mol-1
= + 500 kJ mol-1
= - 364 kJ mol-1
You might also like
- Thermochemistry Module 1Document9 pagesThermochemistry Module 1PavithiranNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry Chapter 1Document69 pagesThermochemistry Chapter 1Febian HenryNo ratings yet
- STPM Chemistry Term 1 TOPIC 4 MATTERDocument31 pagesSTPM Chemistry Term 1 TOPIC 4 MATTERChris Lau75% (4)
- Group 2 Elements Sem 2 ChemistryDocument12 pagesGroup 2 Elements Sem 2 ChemistryChong Yin Ping100% (1)
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 3 Chapter 1Document47 pagesChemistry Form 6 Sem 3 Chapter 1Yuzamrah Awang Noh50% (2)
- Electrochemistry - Cont Module 4 STPMDocument10 pagesElectrochemistry - Cont Module 4 STPMPavithiranNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 3 Chapter 2Document52 pagesChemistry Form 6 Sem 3 Chapter 2Yuzamrah Awang NohNo ratings yet
- MOCK - TEST - (Chemistry) - Term 1 - 2015Document19 pagesMOCK - TEST - (Chemistry) - Term 1 - 2015Ung Hie HuongNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 2 04 Notes STPM 2014/2013Document27 pagesChemistry Form 6 Sem 2 04 Notes STPM 2014/2013Raj Nittiya SugumaranNo ratings yet
- STPM Chemistry Topic 18 Carbonyl Compound (Short Notes)Document1 pageSTPM Chemistry Topic 18 Carbonyl Compound (Short Notes)Chris Lau100% (2)
- Carbonyl Compounds: Properties, Reactions and TestsDocument32 pagesCarbonyl Compounds: Properties, Reactions and TestsYuzamrah Awang NohNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 3 Chapter 5Document51 pagesChemistry Form 6 Sem 3 Chapter 5Yuzamrah Awang Noh100% (1)
- Chemistry STPM Semester 2 Group 2Document7 pagesChemistry STPM Semester 2 Group 2kumutha83% (6)
- STPM Chemistry Topic 17 Hydroxyl Compound (Short Notes)Document1 pageSTPM Chemistry Topic 17 Hydroxyl Compound (Short Notes)Chris Lau100% (1)
- Chapter 18: (Group 14: C, Si, Ge, SN, PB)Document83 pagesChapter 18: (Group 14: C, Si, Ge, SN, PB)SIVANESVARAN100% (1)
- STPM Chemistry Topic 16 Haloalkanes (Short Notes)Document2 pagesSTPM Chemistry Topic 16 Haloalkanes (Short Notes)Chris LauNo ratings yet
- MPM Table of Reaction For Chemistry Sem 3Document4 pagesMPM Table of Reaction For Chemistry Sem 3STPMBAHARUNo ratings yet
- STPM Chemistry Form 6 Notes – The Periodic TableDocument5 pagesSTPM Chemistry Form 6 Notes – The Periodic TableAfz Min100% (3)
- Marking Scheme: Answer All Questions in This SectionDocument7 pagesMarking Scheme: Answer All Questions in This SectionlllNo ratings yet
- Analysis Past Year Chemistry SPM Question (2003-2017)Document7 pagesAnalysis Past Year Chemistry SPM Question (2003-2017)Ting TCNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules & Stoichiometry (STPM + Matriculation)Document14 pagesAtoms, Molecules & Stoichiometry (STPM + Matriculation)AlexTanYun-Kai100% (4)
- Appendix - Chemical Test, Routes of SynthesisDocument11 pagesAppendix - Chemical Test, Routes of Synthesisgoi_pin100% (4)
- SPM Chemistry Trial 2015-2017 ModuleDocument119 pagesSPM Chemistry Trial 2015-2017 Modulekhangsiean8950% (2)
- STPM Sem 3 Chemistry Note - Chapter AlkanesDocument21 pagesSTPM Sem 3 Chemistry Note - Chapter AlkanesSTPMBAHARU100% (3)
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 3 Chapter 3Document39 pagesChemistry Form 6 Sem 3 Chapter 3Yuzamrah Awang NohNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper 3 PDFDocument81 pagesChemistry Paper 3 PDFVentusNo ratings yet
- STPM Chemistry Chapter 2 sem 1Document4 pagesSTPM Chemistry Chapter 2 sem 1Aquila Wong40% (5)
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 3 Chapter 4Document44 pagesChemistry Form 6 Sem 3 Chapter 4Yuzamrah Awang Noh100% (1)
- Answer Chapter 1 MatterDocument23 pagesAnswer Chapter 1 MatterHanaOmarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 41Document4 pagesLesson 41MarcTnn100% (1)
- UTAR Chem Lab 1 Full Report Exp17Document4 pagesUTAR Chem Lab 1 Full Report Exp17Izykiel EdwardNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2: RedoxDocument1 pageExperiment 2: RedoxFu HongNo ratings yet
- Answer of Trial Paper of Maths T STPM 2014 Sem 1 SIGSDocument11 pagesAnswer of Trial Paper of Maths T STPM 2014 Sem 1 SIGSKenneth Chan100% (2)
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 21 Answer SchemeDocument9 pagest2 Chem Revision Ex 21 Answer SchemeNicholas OwNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Quiz Chapter 5 Form 4 @Document4 pagesChemistry Quiz Chapter 5 Form 4 @Mohd NorihwanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 7Document5 pagesChemistry Form 4 Chapter 7Azsyerrah Jahini67% (3)
- STPM Chemistry Form 6Document5 pagesSTPM Chemistry Form 6BabasChong100% (1)
- Biology STPM Lower 6 Chapter 1Document9 pagesBiology STPM Lower 6 Chapter 1kmbej91% (11)
- Uppp2 Sem 1 2017Document9 pagesUppp2 Sem 1 2017WWZNo ratings yet
- Taklimat Kerja KursusDocument33 pagesTaklimat Kerja KursusUng Hie HuongNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Semester 3 DefinitionDocument1 pageChemistry Semester 3 DefinitionYong ChoonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 6 Chap 03 NewDocument92 pagesChemistry Form 6 Chap 03 Newbrandam0% (1)
- STPM Biology Semester 2 Revision ExercisDocument39 pagesSTPM Biology Semester 2 Revision ExercisWendy LohNo ratings yet
- STPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 5 Reaction KineticsDocument22 pagesSTPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 5 Reaction KineticsChris Lau100% (12)
- STPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 6A Chemical EquilibriumDocument23 pagesSTPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 6A Chemical EquilibriumChris Lau100% (7)
- 1 Thermochemistry (Semester 2)Document32 pages1 Thermochemistry (Semester 2)Esther NgiengNo ratings yet
- ThermochemistryDocument31 pagesThermochemistryDavidson ChanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 1Document19 pagesChemistry Form 5 Chapter 1rhythm_no1No ratings yet
- Chemical Energetics (As) 2023 With AnswersDocument12 pagesChemical Energetics (As) 2023 With AnswersNurli SallehNo ratings yet
- Energy Changes PDFDocument13 pagesEnergy Changes PDFMuhammad AliNo ratings yet
- JPJC 2020 JC1 H2 Chemistry Tutorial on Chemical EnergeticsDocument13 pagesJPJC 2020 JC1 H2 Chemistry Tutorial on Chemical EnergeticsSalman ShethNo ratings yet
- Chap 6 WSDocument13 pagesChap 6 WSSaif AhmedNo ratings yet
- EnergrticsDocument31 pagesEnergrticsnaeem mushtaqNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 Chemical Energetics - n9 QuestionsDocument11 pagesTopic 7 Chemical Energetics - n9 QuestionsDaksha yashaNo ratings yet
- 2 Quizizz 2019 ptVIIIe DocDocument10 pages2 Quizizz 2019 ptVIIIe DocKM Tsang Ka ManNo ratings yet
- Energy ChangesDocument13 pagesEnergy ChangesLok Jun HaoNo ratings yet
- A Energetics Notes Chem Unit 1 - (New)Document8 pagesA Energetics Notes Chem Unit 1 - (New)Khaila SimmondNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- STPM Physics Sem 1 Circular MotionDocument5 pagesSTPM Physics Sem 1 Circular MotionChong Yin Ping0% (1)
- STPM Physics Sem 1 ThermodynamicsDocument8 pagesSTPM Physics Sem 1 ThermodynamicsChong Yin Ping0% (1)
- Physics 960 Constants and Fundamental QuantitiesDocument10 pagesPhysics 960 Constants and Fundamental QuantitiesZuraini Arshad0% (1)
- Math M Coursework Doc1Document1 pageMath M Coursework Doc1Wee Kwong YawNo ratings yet
- Anionic Ligands Names Neutral Ligands Names: Transition MetalDocument2 pagesAnionic Ligands Names Neutral Ligands Names: Transition MetalChong Yin PingNo ratings yet
- Anionic Ligands Names Neutral Ligands Names: Transition MetalDocument2 pagesAnionic Ligands Names Neutral Ligands Names: Transition MetalChong Yin PingNo ratings yet
- Name, NRIC, Chemistry Trial PaperDocument7 pagesName, NRIC, Chemistry Trial PaperZuraini ArshadNo ratings yet
- Complex Ions Naming Chemistry STPM Sem 2Document4 pagesComplex Ions Naming Chemistry STPM Sem 2Chong Yin PingNo ratings yet
- Group 2Document14 pagesGroup 2Chong Yin PingNo ratings yet
- Math M Coursework - Doc4Document1 pageMath M Coursework - Doc4Chong Yin PingNo ratings yet
- 964 SP Biology 2012Document123 pages964 SP Biology 2012Mohd SharulniZamNo ratings yet
- Anionic Ligands Names Neutral Ligands Names: Transition MetalDocument2 pagesAnionic Ligands Names Neutral Ligands Names: Transition MetalChong Yin PingNo ratings yet
- Math M Coursework - Doc3Document1 pageMath M Coursework - Doc3Chong Yin Ping100% (1)
- Maths CourseworkDocument2 pagesMaths CourseworkWee Kwong YawNo ratings yet
- Complex Ions Naming Chemistry STPM Sem 2Document4 pagesComplex Ions Naming Chemistry STPM Sem 2Chong Yin PingNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 2Document6 pagesChemistry Form 4 Chapter 2Mur_nie91% (22)
- Husband PrayerDocument3 pagesHusband PrayerChong Yin PingNo ratings yet
- SPM Percubaan 2008 MRSM Chemistry Paper 2Document33 pagesSPM Percubaan 2008 MRSM Chemistry Paper 2ChinWynn.com100% (10)
- STPM Physics 2008Document26 pagesSTPM Physics 2008Tang Siew Eng100% (2)
- Chapter 8 P2 AnswerDocument12 pagesChapter 8 P2 AnswerD_23_desNo ratings yet
- 1 Intro To PhysicsDocument33 pages1 Intro To Physicsharshasoni100% (6)
- 2.3 InertiaDocument6 pages2.3 Inertiatilak0203No ratings yet
- Process For Obtaining Pure TetrafluoroethyleneDocument6 pagesProcess For Obtaining Pure TetrafluoroethyleneAnil DhamankarNo ratings yet
- Applied Physical Metallurgy Sixth EditionDocument597 pagesApplied Physical Metallurgy Sixth EditionT.c. Ertuğrul Sağlık67% (6)
- MSDS SummaryDocument7 pagesMSDS SummaryHeru HarnadiNo ratings yet
- Organic Process Research & Development, 19 (3), 444-448 - 2015Document5 pagesOrganic Process Research & Development, 19 (3), 444-448 - 2015rrgodboleNo ratings yet
- Caustic Soda ChE 308Document24 pagesCaustic Soda ChE 308gcavagliNo ratings yet
- Mole Ratio More PracticeDocument2 pagesMole Ratio More PracticeHeidy VegaNo ratings yet
- Hi 93711Document2 pagesHi 93711Manuel OrtizNo ratings yet
- 2 Year Chemistry Weightage: V. Kumar Dean Sri Chaitanya Educational Institutions HyderabadDocument4 pages2 Year Chemistry Weightage: V. Kumar Dean Sri Chaitanya Educational Institutions Hyderabadnithish0% (1)
- Identification of Acid Radicals (Anions) : Prepared by R.K. Malik'S Newton Classes, RanchiDocument7 pagesIdentification of Acid Radicals (Anions) : Prepared by R.K. Malik'S Newton Classes, RanchiAadarsh YadavNo ratings yet
- Spu BookDocument121 pagesSpu BookAngga Aprian DinataNo ratings yet
- Art Integrated Learning: Kendriya Vidyalaya C.I.S.F. Bhilai Subject: Chemistry Class: XIIDocument32 pagesArt Integrated Learning: Kendriya Vidyalaya C.I.S.F. Bhilai Subject: Chemistry Class: XIIRANJEETA UIKEY 12ANo ratings yet
- Ionic BondingDocument51 pagesIonic BondingAaditya MKNo ratings yet
- Describe The Mechanism of Halogenation Reaction in BenzeneDocument3 pagesDescribe The Mechanism of Halogenation Reaction in BenzeneNur DiniNo ratings yet
- Hand Book of Water, Air and Soil AnalysisDocument123 pagesHand Book of Water, Air and Soil Analysissha2sala50% (2)
- Chlorine PDFDocument96 pagesChlorine PDFNatthapat YingyongpitimongkolNo ratings yet
- Master Spa Legend Owner's ManualDocument68 pagesMaster Spa Legend Owner's ManualMaster Spa PartsNo ratings yet
- Bad Ruz Zaman 2009Document8 pagesBad Ruz Zaman 2009Abraham Becerra AranedaNo ratings yet
- Full Download Introduction To Management Accounting 16th Edition Horngren Test BankDocument36 pagesFull Download Introduction To Management Accounting 16th Edition Horngren Test Bankjack9716pe100% (40)
- Lesson 2 Non-Metals and Moles G11Document61 pagesLesson 2 Non-Metals and Moles G11Jodell CampbellNo ratings yet
- SMK Lutong: Bahagian ADocument13 pagesSMK Lutong: Bahagian ABenjamin HiNo ratings yet
- As Level Chemistry (Inorganic Chemistry)Document83 pagesAs Level Chemistry (Inorganic Chemistry)Amani EnkaraNo ratings yet
- Word Problems in Organic ChemistryDocument70 pagesWord Problems in Organic ChemistryreghuuchihaNo ratings yet
- Ch4 Watertreatment DisinfectionDocument30 pagesCh4 Watertreatment DisinfectionSUBHAM KumarNo ratings yet
- KSBDocument21 pagesKSBOktiara Dwita PertiwiNo ratings yet
- Clorox Plus Tilex Mildew Root Penetrator RemoverDocument9 pagesClorox Plus Tilex Mildew Root Penetrator RemoverMuhammad Iqbal ChandioNo ratings yet
- Goon SecretsDocument15 pagesGoon SecretsburnerNo ratings yet
- Elements, Compounds, & MixturesDocument72 pagesElements, Compounds, & MixturesWendz ArominNo ratings yet
- BA-203970-gb-CPR-tronic 02 Family-Public PDFDocument112 pagesBA-203970-gb-CPR-tronic 02 Family-Public PDFahoirebaNo ratings yet
- Honors Chemistry EquationsDocument2 pagesHonors Chemistry EquationsShadae ClarkeNo ratings yet
- CBSE NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 3: Back of Chapter QuestionsDocument9 pagesCBSE NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 3: Back of Chapter QuestionsNarayanamurthy AmirapuNo ratings yet