Professional Documents
Culture Documents
5.2.3.3 Lab - Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 - ILM PDF
Uploaded by
Maksim KorsakovOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
5.2.3.3 Lab - Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 - ILM PDF
Uploaded by
Maksim KorsakovCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3
(Instructor Version)
Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only.
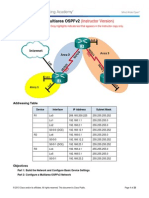
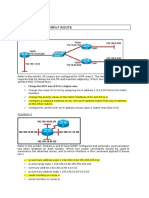
Topology
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 1 of 31
Lab Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3
Addressing Table
OSPF
Router ID
Interface
1.1.1.1
G0/0
192.168.1.1/24
2001:DB8:ACAD:A::1/64
FE80::1 link-local
N/A
S0/0/0
192.168.12.1/30
2001:DB8:ACAD:12::1/64
FE80::1 link-local
N/A
S0/0/1
192.18.13.1/30
2001:DB8:ACAD:13::1/64
FE80::1 link-local
N/A
G0/0
192.168.2.1/24
2001:DB8:ACAD:B::2/64
FE80::2 link-local
N/A
S0/0/0
192.168.12.2/30
2001:DB8:ACAD:12::2/64
FE80::2 link-local
N/A
S0/0/1
192.168.23.1/30
2001:DB8:ACAD:23::2/64
FE80::2 link-local
N/A
G0/0
192.168.3.1/24
2001:DB8:ACAD:C::3/64
FE80::3 link-local
N/A
S0/0/0
192.168.13.2/30
2001:DB8:ACAD:13::3/64
FE80::3 link-local
N/A
S0/0/1
192.168.23.2/30
2001:DB8:ACAD:23::3/64
FE80::3 link-local
N/A
PC-A
NIC
192.168.1.3/24
2001:DB8:ACAD:A::A/64
192.168.1.1
FE80::1
PC-B
NIC
192.168.2.3/24
2001:DB8:ACAD:B::B/64
192.168.2.1
FE80::2
PC-C
NIC
192.168.3.3/24
2001:DB8:ACAD:C::C/64
192.168.3.1
FE80::3
Device
R1
R2
R3
2.2.2.2
3.3.3.3
IP Address
Default Gateway
Objectives
Part 1: Build the Network and Load Device Configurations
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 2 of 31
Lab Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3
Part 2: Troubleshoot Layer 3 Connectivity
Part 3: Troubleshoot OSPFv2
Part 4: Troubleshoot OSPFv3
Background / Scenario
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) is a link-state routing protocol for IP networks. OSPFv2 is defined for IPv4
networks, and OSPFv3 is defined for IPv6 networks. OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 are completely isolated routing
protocols, changes in OSPFv2 do not affect OSPFv3 routing, and vice versa.
In this lab, a single-area OSPF network running OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 is experiencing problems. You have
been assigned to find the problems with the network and correct them.
Note: The routers used with CCNA hands-on labs are Cisco 1941 Integrated Services Routers (ISRs) with
Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)M3 (universalk9 image). Other routers and Cisco IOS versions can be used.
Depending on the model and Cisco IOS version, the commands available and output produced might vary
from what is shown in the labs. Refer to the Router Interface Summary Table at the end of this lab for the
correct interface identifiers.
Note: Make sure that the routers have been erased and have no startup configurations. If you are unsure,
contact your instructor.
Instructor Note: Refer to the Instructor Lab Manual for the procedures to initialize and reload devices.
Required Resources
3 Routers (Cisco 1941 with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)M3 universal image or comparable)
3 PCs (Windows 7, Vista, or XP with terminal emulation program, such as Tera Term)
Console cables to configure the Cisco IOS devices via the console ports
Ethernet and serial cables as shown in the topology
Part 1: Build the Network and Load Device Configurations
In Part 1, you will set up the network topology and configure basic settings on the PC hosts and routers.
Step 1: Cable the network as shown in the topology.
Step 2: Configure PC hosts.
Step 3: Load router configurations.
Load the following configurations into the appropriate router. All routers have the same passwords. The
privileged EXEC password is cisco. The password for console and vty access is class.
Router R1 Configuration:
conf t
service password-encryption
no ip domain lookup
hostname R1
enable secret class
line con 0
logging synchronous
password cisco
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 3 of 31
Lab Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3
login
line vty 0
password cisco
login
banner motd @Unauthorized Access is Prohibited!@
ipv6 unicast-routing
ipv6 router ospf 1
router-id 1.1.1.1
passive-interface g0/0
interface g0/0
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:a::1/64
ipv6 address fe80::1 link-local
!ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
!no shutdown
interface s0/0/0
clock rate 128000
ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0
!ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:12::1/64
ipv6 address fe80::1 link-local
ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
no shutdown
interface s0/0/1
ip address 192.168.13.1 255.255.255.0
!ip address 192.168.13.1 255.255.255.252
ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:13::1/64
ipv6 address fe80::1 link-local
ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
no shutdown
router ospf 1
network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 129.168.12.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
!network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
network 192.168.13.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
passive-interface g0/0
!router-id 1.1.1.1
end
Router R2 Configuration:
conf t
service password-encryption
no ip domain lookup
hostname R2
enable secret class
line con 0
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 4 of 31
Lab Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3
logging synchronous
password cisco
login
line vty 0
password cisco
login
banner motd @Unauthorized Access is Prohibited!@
ipv6 unicast-routing
ipv6 router ospf 1
router-id 2.2.2.2
!passive-interface g0/0
interface g0/0
ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0
ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:B::2/64
ipv6 address fe80::1 link-local
!no ipv6 address fe80::1 link-local
!ipv6 address fe80::2 link-local
!ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
no shutdown
interface s0/0/0
ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.252
ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:12::2/64
ipv6 address fe80::2 link-local
ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
no shutdown
interface s0/0/1
clock rate 128000
!ip address 192.168.23.1 255.255.255.252
ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:23::2/64
ipv6 address fe80::2 link-local
!ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
no shutdown
router ospf 1
network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
network 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
!passive-interface g0/0
end
Router R3 Configuration:
conf t
service password-encryption
no ip domain lookup
enable secret class
hostname R3
line con 0
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 5 of 31
Lab Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3
logging synchronous
password cisco
login
line vty 0
password cisco
login
banner motd @Unauthorized Access is Prohibited!@
interface g0/0
!ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0
ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:c::3/64
ipv6 address fe80::3 link-local
!ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
!no shutdown
interface s0/0/0
clock rate 128000
ip address 192.168.13.1 255.255.255.252
!ip address 192.168.13.2 255.255.255.252
ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:13::3/64
ipv6 address fe80::3 link-local
!ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
no shutdown
interface s0/0/1
ip address 192.168.23.2 255.255.255.252
ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:23::3/64
ipv6 address fe80::3 link-local
!ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
!no shutdown
!ipv6 unicast-routing
!ipv6 router ospf 1
!router-id 3.3.3.3
!passive-interface g0/0
router ospf 1
network 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
!network 192.168.13.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
!network 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
passive-interface g0/0
end
Part 2: Troubleshoot Layer 3 Connectivity
In Part 2, you will verify that Layer 3 connectivity is established on all interfaces. You will need to test both
IPv4 and IPv6 connectivity for all device interfaces.
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 6 of 31
Lab Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3
Step 1: Verify that the interfaces listed in the Addressing Table are active and configured with
the correct IP address information.
a. Issue the show ip interface brief command on all routers to verify that the interfaces are in an up/up
state. Record your findings.
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
R1 - G0/0 is administratively down
R2 - S0/0/1 is down
R3 - G0/0 & S0/0/1 are administratively down
R1# show ip interface brief
Interface
Embedded-Service-Engine0/0
GigabitEthernet0/0
GigabitEthernet0/1
Serial0/0/0
Serial0/0/1
IP-Address
unassigned
192.168.1.1
unassigned
192.168.12.1
192.168.13.1
OK?
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
Method
unset
manual
unset
manual
manual
Status
Protocol
administratively down down
administratively down down
administratively down down
up
up
up
up
OK?
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
Method
unset
manual
unset
manual
unset
Status
Protocol
administratively down down
up
up
administratively down down
up
up
down
down
OK?
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
Method
unset
unset
unset
manual
manual
Status
administratively
administratively
administratively
up
administratively
R2# show ip interface bri
Interface
Embedded-Service-Engine0/0
GigabitEthernet0/0
GigabitEthernet0/1
Serial0/0/0
Serial0/0/1
IP-Address
unassigned
192.168.2.1
unassigned
192.168.12.2
unassigned
R3# show ip interface bri
Interface
Embedded-Service-Engine0/0
GigabitEthernet0/0
GigabitEthernet0/1
Serial0/0/0
Serial0/0/1
IP-Address
unassigned
unassigned
unassigned
192.168.3.1
192.168.23.2
down
down
down
down
Protocol
down
down
down
up
down
b. Issue the show run interface command to verify IP address assignments on all router interfaces.
Compare the interface IP addresses against the Addressing Table and verify the subnet mask
assignments. For IPv6, verify that the link-local address has been assigned. Record your findings.
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
R1 S0/0/0 & S0/0/1 incorrect subnet mask, should be 255.255.255.252
R2 G0/0 incorrect IPv6 link local address, S0/0/1 no IPv4 address
R3 G0/0 no IPv4 address, S0/0/0 incorrect IPv4 address
--R1 Intefaces --
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 7 of 31
Lab Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3
R1# show run interface g0/0
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 178 bytes
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
shutdown
duplex auto
speed auto
ipv6 address FE80::1 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::1/64
end
R1# show run interface s0/0/0
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 158 bytes
!
interface Serial0/0/0
ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0
ipv6 address FE80::1 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:12::1/64
ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
clock rate 2000000
end
R1# show run interface s0/0/1
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 138 bytes
!
interface Serial0/0/1
ip address 192.168.13.1 255.255.255.0
ipv6 address FE80::1 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:13::1/64
ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
end
--R2 Interfaces -R2# show run interface g0/0
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 168 bytes
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 8 of 31
Lab Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3
speed auto
ipv6 address FE80::1 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:B::2/64
end
R2# show run interface s0/0/0
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 160 bytes
!
interface Serial0/0/0
ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.252
ipv6 address FE80::2 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:12::2/64
ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
end
R2# show run interface s0/0/1
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 133 bytes
!
interface Serial0/0/1
no ip address
ipv6 address FE80::2 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:23::2/64
clock rate 128000
end
--R3 Interfaces --
R3# show run interface g0/0
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 155 bytes
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
no ip address
shutdown
duplex auto
speed auto
ipv6 address FE80::3 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:C::3/64
end
R3# show run interface s0/0/0
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 159 bytes
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 9 of 31
Lab Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3
!
interface Serial0/0/0
ip address 192.168.13.1 255.255.255.252
ipv6 address FE80::3 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:13::3/64
clock rate 128000
end
R3# show run interface s0/0/1
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 150 bytes
!
interface Serial0/0/1
ip address 192.168.23.2 255.255.255.252
shutdown
ipv6 address FE80::3 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:23::3/64
end
c.
Resolve all problems that are found. Record the commands used to correct the issues.
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
R1(config)# interface g0/0
R1(config-if)# no shutdown
R1(config-if)# interface s0/0/0
R1(config-if)# ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
R1(config-if)# interface s0/0/1
R1(config-if)# ip address 192.168.13.1 255.255.255.252
R1(config-if)# end
R2(config)# interface g0/0
R2(config-if)# no ipv6 address fe80::1 link-local
R2(config-if)# ipv6 address fe80::2 link-local
R2(config-if)# interface s0/0/1
R2(config-if)# ip address 192.168.23.1 255.255.255.252
R2(config-if)# end
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 10 of 31
Lab Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3
R3(config)# interface g0/0
R3(config-if)# ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)# no shutdown
R3(config-if)# interface s0/0/0
R3(config-if)# ip address 192.168.13.2 255.255.255.252
R3(config-if)# interface s0/0/1
R3(config-if)# no shutdown
R3(config-if)# end
d. Using the ping command, verify that each router has network connectivity with the serial interfaces on the
neighbor routers. Verify that the PCs can ping their default gateways. If problems still exist, continue
troubleshooting Layer 3 issues.
Part 3: Troubleshoot OSPFv2
In Part 3, you will troubleshoot OSPFv2 problems and make the necessary changes needed to establish
OSPFv2 routes and end-to-end IPv4 connectivity.
Note: LAN (G0/0) interfaces should not advertise OSPF routing information, but routes to these networks
should be in the routing tables.
Step 1: Test IPv4 end-to-end connectivity.
From each PC host, ping the other PC hosts in the topology to verify end-to-end connectivity.
Note: It may be necessary to disable the PC firewall before testing, to ping between PCs.
a. Ping from PC-A to PC-B. Were the pings successful? _____________ No
b. Ping from PC-A to PC-C. Were the pings successful? _____________ No
c.
Ping from PC-B to PC-C. Were the pings successful? _____________ No
Step 2: Verify that all interfaces are assigned to OSPFv2 area 0 on R1.
a. Issue the show ip protocols command to verify that OSPF is running and that all networks are
advertised in area 0. Verify that the router ID is set correctly. Record your findings.
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
Router ID is incorrectly configured. The router ID should be 1.1.1.1, not 192.168.13.1. The network
129.168.12.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 statement is incorrect. The network statement should be for 192.168.12.0/30.
R1# show ip protocols
*** IP Routing is NSF aware ***
Routing Protocol is "ospf 1"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Router ID 192.168.13.1
Number of areas in this router is 1. 1 normal 0 stub 0 nssa
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
129.168.12.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 11 of 31
Lab Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3
192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
192.168.13.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway
Distance
Distance: (default is 110)
Last Update
b. Make the necessary changes to the configuration on R1 based on the output from the show ip protocols
command. Record the commands used to correct the issues.
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
R1(config)# router
R1(config-router)#
R1(config-router)#
R1(config-router)#
R1(config-router)#
c.
ospf 1
no network 129.168.12.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
router-id 1.1.1.1
end
Issue the clear ip ospf process command if necessary.
d. Re-issue the show ip protocols command to verify that your changes had the desired effect.
e. Issue the show ip ospf interface brief command to verify that all interfaces are listed as OSPF networks
assigned to area 0.
R1# show ip ospf interface brief
Interface
Se0/0/0
Se0/0/1
Gi0/0
f.
PID
1
1
1
Area
0
0
0
IP Address/Mask
192.168.12.1/30
192.168.13.1/30
192.168.1.1/24
Cost
64
64
1
State
P2P
P2P
DR
Nbrs F/C
1/1
0/0
0/0
Issue the show ip ospf interface g0/0 command to verify that G0/0 is a passive interface.
Note: This information is also in the show ip protocols command.
R1# show ip ospf interface g0/0
GigabitEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up
Internet Address 192.168.1.1/24, Area 0, Attached via Network Statement
Process ID 1, Router ID 1.1.1.1, Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 1
Topology-MTID
Cost
Disabled
Shutdown
Topology Name
0
1
no
no
Base
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State DR, Priority 1
Designated Router (ID) 1.1.1.1, Interface address 192.168.1.1
No backup designated router on this network
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
oob-resync timeout 40
No Hellos (Passive interface)
Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS)
Cisco NSF helper support enabled
IETF NSF helper support enabled
Index 1/1, flood queue length 0
Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last flood scan length is 0, maximum is 0
Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 12 of 31
Lab Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3
Neighbor Count is 0, Adjacent neighbor count is 0
Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s)
g. Resolve any problems discovered on R1. List any additional changes made to R1. If no problems were
found on the device, then respond with no problems were found.
____________________________________________________________________________________
No problems were found
Instructor Note: The passive interface command was configured correctly in the original configs.
Step 3: Verify that all interfaces are assigned to OSPFv2 area 0 on R2.
a. Issue the show ip protocols command to verify that OSPF is running and that all networks are being
advertised in area 0. Verify that the router ID is set correctly. Record your findings.
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
Router ID is incorrect 192.168.12.2. The correct router ID is 2.2.2.2.
R2# show ip protocols
*** IP Routing is NSF aware ***
Routing Protocol is "ospf 1"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Router ID 192.168.12.2
Number of areas in this router is 1. 1 normal 0 stub 0 nssa
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
192.168.12.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
192.168.23.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway
Distance
Last Update
1.1.1.1
110
00:16:38
192.168.13.1
110
00:17:01
Distance: (default is 110)
b. Make the necessary changes to the configuration on R2 based on the output from the show ip protocols
command. Record the commands used to correct the issues.
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
R2(config)# router ospf 1
R2(config-router)# router-id 2.2.2.2
c.
Issue the clear ip ospf process command if necessary.
d. Re-issue the show ip protocols command to verify that your changes had the desired effect.
e. Issue the show ip ospf interface brief command to verify that all interfaces are listed as OSPF networks
assigned to area 0.
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 13 of 31
Lab Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3
R2# sh ip ospf interface brief
Interface
Se0/0/1
Se0/0/0
Gi0/0
f.
PID
1
1
1
Area
0
0
0
IP Address/Mask
192.168.23.1/30
192.168.12.2/30
192.168.2.1/24
Cost
64
64
1
State
P2P
P2P
DR
Nbrs F/C
0/0
1/1
0/0
Issue the show ip ospf interface g0/0 command to verify that G0/0 is a passive interface.
Note: This information is also available from the show ip protocols command.
R2# show ip ospf interface g0/0
GigabitEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up
Internet Address 192.168.2.1/24, Area 0, Attached via Network Statement
Process ID 1, Router ID 2.2.2.2, Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 1
Topology-MTID
Cost
Disabled
Shutdown
Topology Name
0
1
no
no
Base
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State DR, Priority 1
Designated Router (ID) 2.2.2.2, Interface address 192.168.2.1
No backup designated router on this network
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
oob-resync timeout 40
Hello due in 00:00:00
Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS)
Cisco NSF helper support enabled
IETF NSF helper support enabled
Index 1/1, flood queue length 0
Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last flood scan length is 0, maximum is 0
Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
Neighbor Count is 0, Adjacent neighbor count is 0
Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s)
g. Resolve any problems discovered on R2. List any additional changes made to R2. If no problems were
found on the device, then respond with no problems were found.
____________________________________________________________________________________
R2(config)# router ospf 1
R2(config-router)# passive-interface g0/0
Step 4: Verify that all interfaces are assigned to OSPFv2 area 0 on R3.
a. Issue the show ip protocols command to verify that OSPF is running and that all networks are being
advertised in area 0. Verify that the router ID is set correctly as well. Record your findings.
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
The router ID, 192.168.13.1 is incorrectly configured. The correct router ID for R3 is 3.3.3.3. The network
statements for 192.168.13.0/30 and 192.168.23.0/30 are missing.
R3# show ip protocols
*** IP Routing is NSF aware ***
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 14 of 31
Lab Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3
Routing Protocol is "ospf 1"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Router ID 192.168.13.1
Number of areas in this router is 1. 1 normal 0 stub 0 nssa
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Passive Interface(s):
GigabitEthernet0/0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway
Distance
Last Update
Distance: (default is 110)
b. Make the necessary changes to the configuration on R3 based on the output from the show ip protocols
command. Record the commands used to correct the issues.
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
R3(config)# router
R3(config-router)#
R3(config-router)#
R3(config-router)#
c.
ospf 1
network 192.168.13.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
network 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
router-id 3.3.3.3
Issue the clear ip ospf process command if necessary.
d. Re-issue the show ip protocols command to verify that your changes had the desired effect.
e. Issue the show ip ospf interface brief command to verify that all interfaces are listed as OSPF networks
assigned to area 0.
R3# show ip ospf interface brief
Interface
Se0/0/1
Se0/0/0
Gi0/0
f.
PID
1
1
1
Area
0
0
0
IP Address/Mask
192.168.23.2/30
192.168.13.2/30
192.168.3.1/24
Cost
64
64
1
State
P2P
P2P
DR
Nbrs F/C
1/1
1/1
0/0
Issue the show ip ospf interface g0/0 command to verify that G0/0 is a passive interface.
Note: This information is also in the show ip protocols command.
R3# show ip ospf interface g0/0
GigabitEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up
Internet Address 192.168.3.1/24, Area 0, Attached via Network Statement
Process ID 1, Router ID 3.3.3.3, Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 1
Topology-MTID
Cost
Disabled
Shutdown
Topology Name
0
1
no
no
Base
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State DR, Priority 1
Designated Router (ID) 3.3.3.3, Interface address 192.168.3.1
No backup designated router on this network
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
oob-resync timeout 40
No Hellos (Passive interface)
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 15 of 31
Lab Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3
Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS)
Cisco NSF helper support enabled
IETF NSF helper support enabled
Index 1/1, flood queue length 0
Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last flood scan length is 0, maximum is 0
Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
Neighbor Count is 0, Adjacent neighbor count is 0
Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s)
g. Resolve any problems discovered on R3. List any additional changes made to R3. If no problems were
found on the device, then respond with no problems were found.
____________________________________________________________________________________
No problems were found
Instructor Note: The passive interface command was configured correctly in the original configuration.
Step 5: Verify OSPF neighbor information.
a. Issue the show ip ospf neighbor command on all routers to view the OSPF neighbor information.
R1# show ip ospf neighbor
Neighbor ID
2.2.2.2
3.3.3.3
Pri
0
0
State
FULL/
FULL/
Dead Time
00:00:38
00:00:36
Address
192.168.12.2
192.168.13.2
Interface
Serial0/0/0
Serial0/0/1
Dead Time
00:00:33
00:00:35
Address
192.168.23.2
192.168.12.1
Interface
Serial0/0/1
Serial0/0/0
Dead Time
00:00:31
00:00:32
Address
192.168.23.1
192.168.13.1
Interface
Serial0/0/1
Serial0/0/0
R2# show ip ospf neighbor
Neighbor ID
3.3.3.3
1.1.1.1
Pri
0
0
State
FULL/
FULL/
R3# show ip ospf neighbor
Neighbor ID
2.2.2.2
1.1.1.1
Pri
0
0
State
FULL/
FULL/
Step 6: Verify OSPFv2 Routing Information.
a. Issue the show ip route ospf command to verify that each router has OSPFv2 routes to all non-adjoining
networks.
R1# show ip route ospf
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 16 of 31
Lab Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override
Gateway of last resort is not set
O
O
O
192.168.2.0/24 [110/65] via 192.168.12.2, 00:26:56, Serial0/0/0
192.168.3.0/24 [110/65] via 192.168.13.2, 00:12:20, Serial0/0/1
192.168.23.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
192.168.23.0 [110/128] via 192.168.13.2, 00:12:20, Serial0/0/1
[110/128] via 192.168.12.2, 00:26:56, Serial0/0/0
R2# show ip route ospf
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override
Gateway of last resort is not set
O
O
O
192.168.1.0/24 [110/65] via 192.168.12.1, 00:32:23, Serial0/0/0
192.168.3.0/24 [110/65] via 192.168.23.2, 00:17:47, Serial0/0/1
192.168.13.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
192.168.13.0 [110/128] via 192.168.23.2, 00:17:47, Serial0/0/1
[110/128] via 192.168.12.1, 00:32:23, Serial0/0/0
R3# show ip route ospf
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override
Gateway of last resort is not set
O
O
O
192.168.1.0/24 [110/65] via 192.168.13.1, 00:14:12, Serial0/0/0
192.168.2.0/24 [110/65] via 192.168.23.1, 00:14:12, Serial0/0/1
192.168.12.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
192.168.12.0 [110/128] via 192.168.23.1, 00:14:12, Serial0/0/1
[110/128] via 192.168.13.1, 00:14:12, Serial0/0/0
Are all OSPFv2 routes available? ________ yes
If any OSPFv2 routes are missing, what is missing?
____________________________________________________________________________________
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 17 of 31
Lab Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3
All OSPFv2 routes are present.
b. If any routing information is missing, resolve these issues.
Instructor Note: All problems should have been resolved.
Step 7: Verify IPv4 end-to-end connectivity.
From each PC, verify that IPv4 end-to-end connectivity exists. PCs should be able to ping the other PC hosts
in the topology. If IPv4 end-to-end connectivity does not exist, then continue troubleshooting to resolve any
remaining issues.
Note: It may be necessary to disable the PC firewall to ping between PCs.
Part 4: Troubleshoot OSPFv3
In Part 4, you will troubleshoot OSPFv3 problems and make the necessary changes needed to establish
OSPFv3 routes and end-to-end IPv6 connectivity.
Note: LAN (G0/0) interfaces should not advertise OSPFv3 routing information, but routes to these networks
should be contained in the routing tables.
Step 1: Test IPv6 end-to-end connectivity.
From each PC host, ping the IPv6 addresses of the other PC hosts in the topology to verify IPv6 end-to-end
connectivity.
Note: It may be necessary to disable the PC firewall to ping between PCs.
Step 2: Verify that IPv6 unicast routing has been enabled on all routers.
a. An easy way to verify that IPv6 routing has been enabled on a router is to use the show run | section
ipv6 unicast command. By adding this pipe (|) section to the show run command, the ipv6 unicastrouting command displays if IPv6 routing has been enabled.
Note: The show run command can also be issued without any pipe, and then a manual search for the
ipv6 unicast-routing command can be done.
Issue the command on each router. Record your findings.
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
R3 does not have ipv6 unicast routing enabled.
R1# show run | section ipv6 unicast
ipv6 unicast-routing
R2# show run | section ipv6 unicast
ipv6 unicast-routing
R3# show run | section ipv6 unicast
R3#
b. If IPv6 unicast routing is not enabled on one or more routers, enable it now. Record the commands used
to correct the issues.
____________________________________________________________________________________
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 18 of 31
Lab Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3
____________________________________________________________________________________
R3(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing
Step 3: Verify that all interfaces are assigned to OSPFv3 area 0 on R1.
a. Issue the show ipv6 protocols command and verify that the router ID is correct. Also verify that the
expected interfaces are displayed under area 0.
Note: If no output is generated from this command, then the OSPFv3 process has not been configured.
Record your findings.
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
Router ID is correct. The network for G0/0 interface is advertised in the OSPFv3 process.
R1# show ipv6 protocols
IPv6 Routing Protocol is "connected"
IPv6 Routing Protocol is "ospf 1"
Router ID 1.1.1.1
Number of areas: 1 normal, 0 stub, 0 nssa
Interfaces (Area 0):
Serial0/0/1
Serial0/0/0
Redistribution:
None
IPv6 Routing Protocol is "ND"
b. Make the necessary configuration changes to R1. Record the commands used to correct the issues.
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
R1(config)# interface g0/0
R1(config-if)# ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
c.
Issue the clear ipv6 ospf process command if necessary.
d. Re-issue the show ipv6 protocols command to verify that your changes had the desired effect.
e. Issue the show ipv6 ospf interface brief command to verify that all interfaces are listed as OSPF
networks assigned to area 0.
f.
Issue the show ipv6 ospf interface g0/0 command to verify that this interface is set not to advertise
OSPFv3 routes.
R1# show ipv6 ospf interface g0/0
GigabitEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up
Link Local Address FE80::1, Interface ID 3
Area 0, Process ID 1, Instance ID 0, Router ID 1.1.1.1
Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 1
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State WAITING, Priority 1
No designated router on this network
No backup designated router on this network
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 19 of 31
Lab Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
No Hellos (Passive interface)
Wait time before Designated router selection 00:00:23
Graceful restart helper support enabled
Index 1/3/3, flood queue length 0
Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last flood scan length is 0, maximum is 0
Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
Neighbor Count is 0, Adjacent neighbor count is 0
Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s)
g. Resolve any problems discovered on R1. List any additional changes made to R1. If no problems were
found on the device, then respond with no problems were found.
____________________________________________________________________________________
No problems were found, G0/0 is already a passive OSPFv3 interface.
Step 4: Verify that all interfaces are assigned to OSPFv3 area 0 on R2.
a. Issue the show ipv6 protocols command and verify the router ID is correct. Also verify that the expected
interfaces display under area 0.
Note: If no output is generated from this command, then the OSPFv3 process has not been configured.
Record your findings.
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
Router ID is correct, interfaces G0/0 & S0/0/1 are missing
R2# show ipv6 protocols
IPv6 Routing Protocol is "connected"
IPv6 Routing Protocol is "ospf 1"
Router ID 2.2.2.2
Number of areas: 1 normal, 0 stub, 0 nssa
Interfaces (Area 0):
Serial0/0/0
Redistribution:
None
IPv6 Routing Protocol is "ND"
b. Make the necessary configuration changes to R2. Record the commands used to correct the issues.
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
R2(config)# interface g0/0
R2(config-if)# ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
R2(config-if)# interface s0/0/1
R2(config-if)# ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
c.
Issue the clear ipv6 ospf process command if necessary.
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 20 of 31
Lab Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3
d. Re-issue the show ipv6 protocols command to verify that your changes had the desired effect.
e. Issue the show ipv6 ospf interface brief command to verify that all interfaces are listed as OSPF
networks assigned to area 0.
f.
Issue the show ipv6 ospf interface g0/0 command to verify that this interface is not set to advertise
OSPFv3 routes.
R2# show ipv6 ospf interface g0/0
GigabitEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up
Link Local Address FE80::2, Interface ID 3
Area 0, Process ID 1, Instance ID 0, Router ID 2.2.2.2
Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 1
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State WAITING, Priority 1
No designated router on this network
No backup designated router on this network
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
Hello due in 00:00:04
Wait time before Designated router selection 00:00:05
Graceful restart helper support enabled
Index 1/2/2, flood queue length 0
Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last flood scan length is 0, maximum is 0
Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
Neighbor Count is 0, Adjacent neighbor count is 0
Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s)
g. List any additional changes made to R2. If no problems were found on the device, then respond with no
problems were found.
____________________________________________________________________________________
R2(config)# ipv6 router ospf 1
R2(config-rtr)# passive-interface g0/0
Step 5: Verify that all interfaces are assigned to OSPFv3 area 0 on R3.
a. Issue the show ipv6 protocols command and verify that the router ID is correct. Also verify that the
expected interfaces display under area 0.
Note: If no output is generated from this command, then the OSPFv3 process has not been configured.
Record your findings.
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
OSPFv3 has not been configured on this router.
R3# show ipv6 protocols
b. Make the necessary configuration changes to R3. Record the commands used to correct the issues.
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 21 of 31
Lab Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3
R3(config)# ipv6 router ospf 1
R3(config-rtr)# router-id 3.3.3.3
R3(config-rtr)# passive-interface g0/0
R3(config-rtr)# interface g0/0
R3(config-if)# ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
R3(config-if)# interface s0/0/0
R3(config-if)# ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
R3(config-if)# interface s0/0/1
R3(config-if)# ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
c.
Issue the clear ipv6 ospf process command if necessary.
d. Re-issue the show ipv6 protocols command to verify that your changes had the desired effect.
e. Issue the show ipv6 ospf interface brief command to verify that all interfaces are listed as OSPF
networks assigned to area 0.
f.
Issue the show ipv6 ospf interface g0/0 command to verify that this interface is set not to advertise
OSPFv3 routes.
R3# show ipv6 ospf interface g0/0
GigabitEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up
Link Local Address FE80::3, Interface ID 3
Area 0, Process ID 1, Instance ID 0, Router ID 3.3.3.3
Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 1
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State DR, Priority 1
Designated Router (ID) 3.3.3.3, local address FE80::3
No backup designated router on this network
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
No Hellos (Passive interface)
Graceful restart helper support enabled
Index 1/1/1, flood queue length 0
Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last flood scan length is 0, maximum is 0
Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
Neighbor Count is 0, Adjacent neighbor count is 0
Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s)
g. Resolve any problems discovered on R3. List any additional changes made to R3. If no problems were
found on the device, then respond with no problems were found.
____________________________________________________________________________________
No problems were found as long as G0/0 was configured as a passive OSPFv3 interface in Step 5b.
Step 6: Verify that all routers have correct neighbor adjacency information.
a. Issue the show ipv6 ospf neighbor command to verify that adjacencies have formed between
neighboring routers.
R1# show ipv6 ospf neighbor
OSPFv3 Router with ID (1.1.1.1) (Process ID 1)
Neighbor ID
Pri
State
Dead Time
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Interface ID
Interface
Page 22 of 31
Lab Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3
3.3.3.3
2.2.2.2
0
0
FULL/
FULL/
00:00:34
00:00:32
6
6
Serial0/0/1
Serial0/0/0
R2# sh ipv6 ospf neighbor
OSPFv3 Router with ID (2.2.2.2) (Process ID 1)
Neighbor ID
3.3.3.3
1.1.1.1
Pri
0
0
State
FULL/
FULL/
Dead Time
00:00:32
00:00:30
Interface ID
7
6
Interface
Serial0/0/1
Serial0/0/0
R3# sh ipv6 ospf neighbor
OSPFv3 Router with ID (3.3.3.3) (Process ID 1)
Neighbor ID
2.2.2.2
1.1.1.1
Pri
0
0
State
FULL/
FULL/
Dead Time
00:00:32
00:00:37
Interface ID
7
7
Interface
Serial0/0/1
Serial0/0/0
b. Resolve any OSPFv3 adjacency issues that still exist.
Instructor Note: All adjacency issues should have been resolved in earlier steps.
Step 7: Verify OSPFv3 routing information.
a. Issue the show ipv6 route ospf command, and verify that OSPFv3 routes exist to all non-adjoining
networks.
R1# show ipv6 route ospf
IPv6 Routing Table - default - 10 entries
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - Static, U - Per-user Static route
B - BGP, R - RIP, I1 - ISIS L1, I2 - ISIS L2
IA - ISIS interarea, IS - ISIS summary, D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external
ND - ND Default, NDp - ND Prefix, DCE - Destination, NDr - Redirect
O - OSPF Intra, OI - OSPF Inter, OE1 - OSPF ext 1, OE2 - OSPF ext 2
ON1 - OSPF NSSA ext 1, ON2 - OSPF NSSA ext 2
O
2001:DB8:ACAD:B::/64 [110/65]
via FE80::2, Serial0/0/0
O
2001:DB8:ACAD:C::/64 [110/65]
via FE80::3, Serial0/0/1
O
2001:DB8:ACAD:23::/64 [110/128]
via FE80::2, Serial0/0/0
via FE80::3, Serial0/0/1
R2# show ipv6 route ospf
IPv6 Routing Table - default - 10 entries
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - Static, U - Per-user Static route
B - BGP, R - RIP, I1 - ISIS L1, I2 - ISIS L2
IA - ISIS interarea, IS - ISIS summary, D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external
ND - ND Default, NDp - ND Prefix, DCE - Destination, NDr - Redirect
O - OSPF Intra, OI - OSPF Inter, OE1 - OSPF ext 1, OE2 - OSPF ext 2
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 23 of 31
Lab Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3
O
O
O
ON1 - OSPF NSSA ext 1, ON2 - OSPF NSSA ext 2
2001:DB8:ACAD:A::/64 [110/65]
via FE80::1, Serial0/0/0
2001:DB8:ACAD:C::/64 [110/65]
via FE80::3, Serial0/0/1
2001:DB8:ACAD:13::/64 [110/128]
via FE80::1, Serial0/0/0
via FE80::3, Serial0/0/1
R3# show ipv6 route ospf
IPv6 Routing Table - default - 10 entries
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - Static, U - Per-user Static route
B - BGP, R - RIP, I1 - ISIS L1, I2 - ISIS L2
IA - ISIS interarea, IS - ISIS summary, D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external
ND - ND Default, NDp - ND Prefix, DCE - Destination, NDr - Redirect
O - OSPF Intra, OI - OSPF Inter, OE1 - OSPF ext 1, OE2 - OSPF ext 2
ON1 - OSPF NSSA ext 1, ON2 - OSPF NSSA ext 2
O
2001:DB8:ACAD:A::/64 [110/65]
via FE80::1, Serial0/0/0
O
2001:DB8:ACAD:B::/64 [110/65]
via FE80::2, Serial0/0/1
O
2001:DB8:ACAD:12::/64 [110/128]
via FE80::1, Serial0/0/0
via FE80::2, Serial0/0/1
Are all OSPFv3 routes available? ________ yes
If any OSPFv3 routes are missing, what is missing?
____________________________________________________________________________________
All OSPFv3 routes are present.
b. Resolve any routing issues that still exist.
Instructor Note: All OSPFv3 routes issues should have been resolved.
Step 8: Verify IPv6 end-to-end connectivity.
From each PC, verify that IPv6 end-to-end connectivity exists. PCs should be able to ping each interface on
the network. If IPv6 end-to-end connectivity does not exist, then continue troubleshooting to resolve remaining
issues.
Note: It may be necessary to disable the PC firewall to ping between PCs.
Reflection
Why would you troubleshoot OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 separately?
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 do not share routing information and their configuration is completely independent.
Troubleshooting for these two protocols should be done independently.
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 24 of 31
Lab Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3
Router Interface Summary Table
Router Interface Summary
Router Model
Ethernet Interface #1
Ethernet Interface #2
Serial Interface #1
Serial Interface #2
1800
Fast Ethernet 0/0
(F0/0)
Fast Ethernet 0/1
(F0/1)
Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0)
Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1)
1900
Gigabit Ethernet 0/0
(G0/0)
Gigabit Ethernet 0/1
(G0/1)
Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0)
Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1)
2801
Fast Ethernet 0/0
(F0/0)
Fast Ethernet 0/1
(F0/1)
Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0)
Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1)
2811
Fast Ethernet 0/0
(F0/0)
Fast Ethernet 0/1
(F0/1)
Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0)
Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1)
2900
Gigabit Ethernet 0/0
(G0/0)
Gigabit Ethernet 0/1
(G0/1)
Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0)
Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1)
Note: To find out how the router is configured, look at the interfaces to identify the type of router and how many
interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all the combinations of configurations for each router
class. This table includes identifiers for the possible combinations of Ethernet and Serial interfaces in the device.
The table does not include any other type of interface, even though a specific router may contain one. An
example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be
used in Cisco IOS commands to represent the interface.
Device Configs - Final
Router R1
R1#sh run
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 2010 bytes
!
version 15.2
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
service password-encryption
!
hostname R1
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
enable secret 4 06YFDUHH61wAE/kLkDq9BGho1QM5EnRtoyr8cHAUg.2
!
no aaa new-model
memory-size iomem 15
!
ip cef
!
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 25 of 31
Lab Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3
no ip domain lookup
ipv6 unicast-routing
ipv6 cef
multilink bundle-name authenticated
!
interface Embedded-Service-Engine0/0
no ip address
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
ipv6 address FE80::1 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::1/64
ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
no ip address
shutdown
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface Serial0/0/0
ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
ipv6 address FE80::1 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:12::1/64
ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
clock rate 128000
!
interface Serial0/0/1
ip address 192.168.13.1 255.255.255.252
ipv6 address FE80::1 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:13::1/64
ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
!
router ospf 1
router-id 1.1.1.1
passive-interface GigabitEthernet0/0
network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
network 192.168.13.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
!
ip forward-protocol nd
!
no ip http server
no ip http secure-server
!
ipv6 router ospf 1
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 26 of 31
Lab Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3
router-id 1.1.1.1
passive-interface GigabitEthernet0/0
!
control-plane
!
banner motd ^CUnauthorized Access is Prohibited!^C
!
line con 0
password 7 060506324F41
logging synchronous
login
line aux 0
line 2
no activation-character
no exec
transport preferred none
transport input all
transport output pad telnet rlogin lapb-ta mop udptn v120 ssh
stopbits 1
line vty 0
password 7 00071A150754
login
transport input all
line vty 1 4
login
transport input all
!
scheduler allocate 20000 1000
!
end
Router R2
R2#sh run
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 2010 bytes
!
version 15.2
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
service password-encryption
!
hostname R2
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
enable secret 4 06YFDUHH61wAE/kLkDq9BGho1QM5EnRtoyr8cHAUg.2
!
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 27 of 31
Lab Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3
no aaa new-model
memory-size iomem 15
!
ip cef
!
no ip domain lookup
ipv6 unicast-routing
ipv6 cef
multilink bundle-name authenticated
!
interface Embedded-Service-Engine0/0
no ip address
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
ipv6 address FE80::2 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:B::2/64
ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
no ip address
shutdown
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface Serial0/0/0
ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.252
ipv6 address FE80::2 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:12::2/64
ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
!
interface Serial0/0/1
ip address 192.168.23.1 255.255.255.252
ipv6 address FE80::2 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:23::2/64
ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
clock rate 128000
!
router ospf 1
router-id 2.2.2.2
passive-interface GigabitEthernet0/0
network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
network 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
!
ip forward-protocol nd
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 28 of 31
Lab Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3
!
no ip http server
no ip http secure-server
!
ipv6 router ospf 1
router-id 2.2.2.2
passive-interface GigabitEthernet0/0
!
control-plane
!
banner motd ^CUnauthorized Access is Prohibited!^C
!
line con 0
password 7 094F471A1A0A
logging synchronous
login
line aux 0
line 2
no activation-character
no exec
transport preferred none
transport input all
transport output pad telnet rlogin lapb-ta mop udptn v120 ssh
stopbits 1
line vty 0
password 7 14141B180F0B
login
transport input all
line vty 1 4
login
transport input all
!
scheduler allocate 20000 1000
!
end
Router R3
R3#sh run
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 2049 bytes
!
version 15.2
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
service password-encryption
!
hostname R3
!
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 29 of 31
Lab Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
enable secret 4 06YFDUHH61wAE/kLkDq9BGho1QM5EnRtoyr8cHAUg.2
!
no aaa new-model
memory-size iomem 15
!
ip cef
!
no ip domain lookup
ipv6 unicast-routing
ipv6 cef
multilink bundle-name authenticated
!
!
interface Embedded-Service-Engine0/0
no ip address
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
ipv6 address FE80::3 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:C::3/64
ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
no ip address
shutdown
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface Serial0/0/0
ip address 192.168.13.2 255.255.255.252
ipv6 address FE80::3 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:13::3/64
ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
clock rate 128000
!
interface Serial0/0/1
ip address 192.168.23.2 255.255.255.252
ipv6 address FE80::3 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:23::3/64
ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
!
router ospf 1
router-id 3.3.3.3
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 30 of 31
Lab Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3
passive-interface GigabitEthernet0/0
network 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 192.168.13.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
network 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
!
ip forward-protocol nd
!
no ip http server
no ip http secure-server
!
ipv6 router ospf 1
router-id 3.3.3.3
passive-interface GigabitEthernet0/0
!
control-plane
!
banner motd ^CUnauthorized Access is Prohibited!^C
!
line con 0
password 7 02050D480809
logging synchronous
login
line aux 0
line 2
no activation-character
no exec
transport preferred none
transport input all
transport output pad telnet rlogin lapb-ta mop udptn v120 ssh
stopbits 1
line vty 0
password 7 104D000A0618
login
transport input all
line vty 1 4
login
transport input all
!
scheduler allocate 20000 1000
!
end
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 31 of 31
You might also like
- 5.2.3.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Advanced Single-Area OSPFv2 - ILM PDFDocument14 pages5.2.3.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Advanced Single-Area OSPFv2 - ILM PDFMaksim Korsakov100% (12)
- 6.2.3.10 Lab - Troubleshooting Multiarea OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 - ILM PDFDocument29 pages6.2.3.10 Lab - Troubleshooting Multiarea OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 - ILM PDFMaksim Korsakov95% (19)
- 5.1.5.8 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced Features - ILMDocument12 pages5.1.5.8 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced Features - ILMرافد البركي75% (12)
- Lab 8.3.3.6Document10 pagesLab 8.3.3.6Justine DuranNo ratings yet
- IP Routing Protocols All-in-one: OSPF EIGRP IS-IS BGP Hands-on LabsFrom EverandIP Routing Protocols All-in-one: OSPF EIGRP IS-IS BGP Hands-on LabsNo ratings yet
- 11.1.2 Lab - Implement eBGP For IPv4Document20 pages11.1.2 Lab - Implement eBGP For IPv4Lilifilm OfficialNo ratings yet
- 3.4.1.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Basic PPP With Authentication - ILMDocument23 pages3.4.1.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Basic PPP With Authentication - ILMvincent67% (3)
- 5.1.2.13 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 On A Multiaccess Network - ILM PDFDocument13 pages5.1.2.13 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 On A Multiaccess Network - ILM PDFMaksim Korsakov95% (20)
- 7.4.3.5 Lab - Configuring Basic EIGRP For IPv6 - ILM PDFDocument17 pages7.4.3.5 Lab - Configuring Basic EIGRP For IPv6 - ILM PDFMaksim Korsakov97% (31)
- 16.1.4 Lab - Configure Route Redistribution Using BGPDocument11 pages16.1.4 Lab - Configure Route Redistribution Using BGPnetcom htktNo ratings yet
- 9.3.1.4 Packet Tracer - Implementing A Subnetted IPv6 Addressing Scheme InstructionsDocument3 pages9.3.1.4 Packet Tracer - Implementing A Subnetted IPv6 Addressing Scheme InstructionsAhmadHijazi100% (2)
- 6.2.3.8 Lab - Configuring Multiarea OSPFv2 - ILM PDFDocument23 pages6.2.3.8 Lab - Configuring Multiarea OSPFv2 - ILM PDFMaksim Korsakov98% (51)
- Chapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using The AS - PATH Attribute: TopologyDocument8 pagesChapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using The AS - PATH Attribute: TopologyMeliko ianNo ratings yet
- 3 Router Igrp Configuration LabDocument5 pages3 Router Igrp Configuration LabSiddhant SingalNo ratings yet
- Cisco Access Control Lists (ACL)Document54 pagesCisco Access Control Lists (ACL)Paul100% (2)
- Case Study 2 - BGPDocument2 pagesCase Study 2 - BGPClaudio Cabello SotoNo ratings yet
- Nexus 7000 Lab Guide PDFDocument46 pagesNexus 7000 Lab Guide PDFAung Zaw LinNo ratings yet
- How To Configure A Cisco Layer 3 SwitchDocument5 pagesHow To Configure A Cisco Layer 3 SwitchTuan PhamNo ratings yet
- AB - CCNA Voice Quick Reference GuideDocument31 pagesAB - CCNA Voice Quick Reference GuideSrdjan MilenkovicNo ratings yet
- CCNA Security Lab 14 - Cisco IOS SYSLOG and SNMP Configuration - CLIDocument12 pagesCCNA Security Lab 14 - Cisco IOS SYSLOG and SNMP Configuration - CLIvelramsenNo ratings yet
- CCIE Cert Service Provider Lab 1Document2 pagesCCIE Cert Service Provider Lab 1Waqas YounasNo ratings yet
- BGP Route Reflector Lab PDFDocument4 pagesBGP Route Reflector Lab PDFjnahamedNo ratings yet
- Private VLAN (PVLAN) On Cisco Catalyst Switch: Protected Port Previous TutorialDocument6 pagesPrivate VLAN (PVLAN) On Cisco Catalyst Switch: Protected Port Previous TutorialMin Min ZawNo ratings yet
- Hardrock Hallelujah3 v4 0Document83 pagesHardrock Hallelujah3 v4 0jbgibarraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF TopologyDocument24 pagesChapter 4 Lab 4-1, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF TopologyErid RocaNo ratings yet
- LABDCT 2001 (Guide) Nexus.7000Document44 pagesLABDCT 2001 (Guide) Nexus.7000kds20850No ratings yet
- 6.2.3.9 Lab - Configuring Multiarea OSPFv3 - ILM PDFDocument19 pages6.2.3.9 Lab - Configuring Multiarea OSPFv3 - ILM PDFMaksim Korsakov96% (26)
- Tutorial BGP Multihoming Techniques SANOG24Document176 pagesTutorial BGP Multihoming Techniques SANOG24kmadNo ratings yet
- Intro To OTVDocument29 pagesIntro To OTVSon Tran Hong NamNo ratings yet
- Lab 6.4.1Document14 pagesLab 6.4.1Janeza JangNo ratings yet
- Configuring BGPDocument116 pagesConfiguring BGPShaikh SadikNo ratings yet
- CCNP Final Exam PDFDocument12 pagesCCNP Final Exam PDFMauro Di CesareNo ratings yet
- CCNPv6 ROUTE Lab6-1 BGP Config InstructorDocument15 pagesCCNPv6 ROUTE Lab6-1 BGP Config InstructorMiguel Andres Castañeda OrtegaNo ratings yet
- 6.2.3.9 Lab - Troubleshooting VLAN Configurations - SolutionDocument17 pages6.2.3.9 Lab - Troubleshooting VLAN Configurations - SolutionHeelohs Sinatra100% (1)
- 8.7.1.3 Lab - (Optional) Configuring A Remote Access VPN Server and Client - InstructorDocument30 pages8.7.1.3 Lab - (Optional) Configuring A Remote Access VPN Server and Client - InstructorSalem TrabelsiNo ratings yet
- Lab01 Basic VOIP ConfigurationDocument8 pagesLab01 Basic VOIP ConfigurationMohammed ElmadaniNo ratings yet
- CCIE-LAB-K1 IGP拓扑和L2配置Document32 pagesCCIE-LAB-K1 IGP拓扑和L2配置Partha DashNo ratings yet
- BGP Configuration Steps PDFDocument29 pagesBGP Configuration Steps PDFKaran Mishra0% (1)
- 9.3.1.2 CCNA Skills Integration ChallengeDocument7 pages9.3.1.2 CCNA Skills Integration ChallengeCristianFelipeSolarteOrozco100% (1)
- Ccnpv7 Route Lab7-5 MP-BGP StudentDocument17 pagesCcnpv7 Route Lab7-5 MP-BGP StudentMed TisNo ratings yet
- 300 101Document484 pages300 101Diego Suarez0% (1)
- Cisco IOS Modes TutorialDocument11 pagesCisco IOS Modes Tutorialheruye mulugetaNo ratings yet
- Lab 6.3 Config IBGP and EBGP Sessions, Local Prefernce and MEDDocument3 pagesLab 6.3 Config IBGP and EBGP Sessions, Local Prefernce and MEDAtilio AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Router Switch CommandscDocument128 pagesRouter Switch CommandscIonel GherasimNo ratings yet
- Configuring Site To Site IPSec VPN Tunnel Between Cisco RoutersDocument7 pagesConfiguring Site To Site IPSec VPN Tunnel Between Cisco RoutersIwatch YouNo ratings yet
- 9.4.1.8 Lab - Configuring ASA 5510 Clientless and AnyConnect Remote Access SSL VPNs Using ASDM - InstructorDocument53 pages9.4.1.8 Lab - Configuring ASA 5510 Clientless and AnyConnect Remote Access SSL VPNs Using ASDM - InstructorSalem TrabelsiNo ratings yet
- Lab MPLSDocument562 pagesLab MPLSThanhNN0312No ratings yet
- Configuring Multi-Area OSPFv3Document16 pagesConfiguring Multi-Area OSPFv3etitahNo ratings yet
- Cisco IOS IP SLAs Configuration GuideDocument332 pagesCisco IOS IP SLAs Configuration GuideenragonNo ratings yet
- Commande CiscoDocument5 pagesCommande CiscoMessaoud LacmessNo ratings yet
- Examen Final Ccnp-Route V7-YellowDocument20 pagesExamen Final Ccnp-Route V7-Yellowatramoy100% (2)
- LTRARC-2002 Introduction To IOS-XR Lab Guide: Speakers: Brad Edgeworth Ramiro Garza Rios Rajesh PatkiDocument106 pagesLTRARC-2002 Introduction To IOS-XR Lab Guide: Speakers: Brad Edgeworth Ramiro Garza Rios Rajesh PatkiAyoub AmineNo ratings yet
- Cisco Certified Security Professional A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandCisco Certified Security Professional A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Campus Networks: Practical Analysis of Cisco and LAN ProtocolsFrom EverandTroubleshooting Campus Networks: Practical Analysis of Cisco and LAN ProtocolsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Alcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsFrom EverandAlcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsNo ratings yet
- The Complete One-Week Preparation for the Cisco Ccent/Ccna Icnd1 Exam 640-822: Second Edition (March 2011)From EverandThe Complete One-Week Preparation for the Cisco Ccent/Ccna Icnd1 Exam 640-822: Second Edition (March 2011)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 7.5.1.1 Portfolio RIP and EIGRP Instructions IG PDFDocument4 pages7.5.1.1 Portfolio RIP and EIGRP Instructions IG PDFMaksim Korsakov100% (4)
- 7.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring Basic EIGRP For IPv4 - ILM PDFDocument16 pages7.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring Basic EIGRP For IPv4 - ILM PDFMaksim Korsakov97% (35)
- 7.4.3.5 Lab - Configuring Basic EIGRP For IPv6 - ILM PDFDocument17 pages7.4.3.5 Lab - Configuring Basic EIGRP For IPv6 - ILM PDFMaksim Korsakov97% (31)
- 6.2.3.9 Lab - Configuring Multiarea OSPFv3 - ILM PDFDocument19 pages6.2.3.9 Lab - Configuring Multiarea OSPFv3 - ILM PDFMaksim Korsakov96% (26)
- 6.3.1.1 Digital Trolleys Instructions IG PDFDocument6 pages6.3.1.1 Digital Trolleys Instructions IG PDFMaksim Korsakov100% (1)
- 6.2.3.8 Lab - Configuring Multiarea OSPFv2 - ILM PDFDocument23 pages6.2.3.8 Lab - Configuring Multiarea OSPFv2 - ILM PDFMaksim Korsakov98% (51)
- 4.4.2.3 Lab - Configuring A Wireless Router and Client - ILM PDFDocument17 pages4.4.2.3 Lab - Configuring A Wireless Router and Client - ILM PDFMaksim Korsakov50% (2)
- 6.0.1.2 Leaving On A Jet Plane Instructions IG PDFDocument3 pages6.0.1.2 Leaving On A Jet Plane Instructions IG PDFMaksim Korsakov100% (2)
- 4.1.2.10 Lab - Investigating Wireless Implementations - ILM PDFDocument3 pages4.1.2.10 Lab - Investigating Wireless Implementations - ILM PDFMaksim Korsakov50% (2)
- 5.1.2.13 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 On A Multiaccess Network - ILM PDFDocument13 pages5.1.2.13 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 On A Multiaccess Network - ILM PDFMaksim Korsakov95% (20)
- 5.3.1.1 OSPF Troubleshooting Mastery Instructions IG PDFDocument3 pages5.3.1.1 OSPF Troubleshooting Mastery Instructions IG PDFMaksim KorsakovNo ratings yet
- 4.5.1.1 Inside and Outside Control Instructions - IG PDFDocument4 pages4.5.1.1 Inside and Outside Control Instructions - IG PDFMaksim Korsakov100% (4)
- 5.0.1.2 DR and BDR Elections Instructions IG PDFDocument2 pages5.0.1.2 DR and BDR Elections Instructions IG PDFMaksim KorsakovNo ratings yet
- 3.3.1.1 Linking Up Instructions - IG PDFDocument2 pages3.3.1.1 Linking Up Instructions - IG PDFMaksim Korsakov100% (1)
- 1.2.1.8 Lab - Selecting Switching Hardware - ILM PDFDocument5 pages1.2.1.8 Lab - Selecting Switching Hardware - ILM PDFMaksim Korsakov83% (6)
- 3.2.2.4 Lab - Troubleshooting EtherChannel - ILM PDFDocument25 pages3.2.2.4 Lab - Troubleshooting EtherChannel - ILM PDFMaksim Korsakov94% (34)
- 3.2.1.4 Lab - Configuring EtherChannel - ILMDocument23 pages3.2.1.4 Lab - Configuring EtherChannel - ILMAndre M.100% (6)
- 1.3.1.1 Layered Network Design Simulation Instructions - IG PDFDocument5 pages1.3.1.1 Layered Network Design Simulation Instructions - IG PDFMaksim Korsakov100% (4)
- 2.1.2.10 Lab - Building A Switched Network With Redundant Links - ILM PDFDocument18 pages2.1.2.10 Lab - Building A Switched Network With Redundant Links - ILM PDFMaksim Korsakov84% (37)
- 3.0.1.2 Imagine This Instructions - IG PDFDocument2 pages3.0.1.2 Imagine This Instructions - IG PDFMaksim Korsakov100% (1)
- 2.4.3.4 Lab - Configuring HSRP and GLBP - ILM PDFDocument20 pages2.4.3.4 Lab - Configuring HSRP and GLBP - ILM PDFMaksim Korsakov91% (23)
- 2.3.2.3 Lab - Configuring Rapid PVST+, PortFast, and BPDU Guard - ILM PDFDocument28 pages2.3.2.3 Lab - Configuring Rapid PVST+, PortFast, and BPDU Guard - ILM PDFMaksim Korsakov91% (56)
- 2.0.1.2 Stormy Traffic Instructions IG PDFDocument2 pages2.0.1.2 Stormy Traffic Instructions IG PDFMaksim Korsakov60% (5)
- 1.0.1.2 Network by Design Instructions - IGDocument3 pages1.0.1.2 Network by Design Instructions - IGMaksim Korsakov80% (10)
- Combine 1Document80 pagesCombine 1Canatoy, Christian G.No ratings yet
- Ict 120 - Task 2 Individual AssessmentDocument10 pagesIct 120 - Task 2 Individual AssessmentAritra ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Private Message - WikipediaDocument21 pagesPrivate Message - WikipediaJeremy Ray MurrayNo ratings yet
- HillstonDocument70 pagesHillstonCARMEN FLOR AYLLON BASURTO100% (2)
- Understand BGP EVPN+VXLAN Control-Plane and Data-PlaneDocument18 pagesUnderstand BGP EVPN+VXLAN Control-Plane and Data-PlaneAbdelhaiNo ratings yet
- Manipulating The Network With PacketFuDocument5 pagesManipulating The Network With PacketFuKeith LeeNo ratings yet
- 8.3.1.4 Packet Tracer - Implementing A Subnetted IPv6 Addressing SchemeDocument3 pages8.3.1.4 Packet Tracer - Implementing A Subnetted IPv6 Addressing SchemeParthPatel0% (1)
- Chapter 6: BGP: BGP Terminology, Concepts and OperationDocument12 pagesChapter 6: BGP: BGP Terminology, Concepts and OperationJordi KlerigaNo ratings yet
- Managing information & knowledge individual assignmentsDocument3 pagesManaging information & knowledge individual assignmentsአረጋዊ ሐይለማርያምNo ratings yet
- DHCP Module Explains Dynamic IP AssignmentDocument7 pagesDHCP Module Explains Dynamic IP AssignmentkillartnNo ratings yet
- Dna Software Routing Subscription PDFDocument46 pagesDna Software Routing Subscription PDFkanggodolananNo ratings yet
- Penawaran WebsiteDocument4 pagesPenawaran WebsiteAtila AprilianaNo ratings yet
- How prefix-lists work and match prefixes and subnet masksDocument18 pagesHow prefix-lists work and match prefixes and subnet masksYusuf MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document7 pagesTutorial 3s18k03z25No ratings yet
- Easy Virtual Network Configuration GuideDocument80 pagesEasy Virtual Network Configuration GuideTuran MuslimzadeNo ratings yet
- Real-Exams 642-891 Exam.q.and.a v7.0Document369 pagesReal-Exams 642-891 Exam.q.and.a v7.0Anonymous GRmXX2v2No ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument5 pagesProject ReportPrakhar RastogiNo ratings yet
- CN Final QuesDocument9 pagesCN Final QuesPavvitNo ratings yet
- Cisco 7600 Config GuideDocument444 pagesCisco 7600 Config GuidePeter KidiavaiNo ratings yet
- Internet Technology: Tribhuwan University Institute of Science and TechnologyDocument5 pagesInternet Technology: Tribhuwan University Institute of Science and TechnologySaroj GaireNo ratings yet
- COIT20261 Routing and Switching - Assign2 - Term1 - 2023Document4 pagesCOIT20261 Routing and Switching - Assign2 - Term1 - 2023thshoyNo ratings yet
- MA5800C Product DescriptionDocument7 pagesMA5800C Product DescriptionAlexander PischulinNo ratings yet
- D Link DSL 2750u Users Manual 119561Document103 pagesD Link DSL 2750u Users Manual 119561Asr JamesNo ratings yet
- CCIE Voice Study Guide v3.0Document329 pagesCCIE Voice Study Guide v3.0Farooq Jaleel100% (1)
- Diagnostic Utilities TCP IPDocument1 pageDiagnostic Utilities TCP IPMir Farhan Ali AbediNo ratings yet
- S3900 Series: Innovative Virtual Cluster Switching TechniqueDocument6 pagesS3900 Series: Innovative Virtual Cluster Switching TechniqueAzizul HakimNo ratings yet
- Wireless and Mobile All-IP Networks: Authors: Yi-Bing Lin and Ai-Chun Pang Publisher: Wiley ISBN: 0-471-74922-2Document6 pagesWireless and Mobile All-IP Networks: Authors: Yi-Bing Lin and Ai-Chun Pang Publisher: Wiley ISBN: 0-471-74922-2vphuc1984No ratings yet
- MTATT2017c4 PDFDocument340 pagesMTATT2017c4 PDFjoelbravobritoNo ratings yet
- Regras FirewallDocument2 pagesRegras FirewallFernanda AmarokeNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv-1Document33 pagesUnit Iv-1InnocentNo ratings yet