Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ACLS Practical Case Scenarios (1 June 2011)
Uploaded by
nersCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ACLS Practical Case Scenarios (1 June 2011)
Uploaded by
nersCopyright:
Available Formats
INSTITUTE FOR MEDICAL SIMULATION & EDUCATION
ACLS PRACTICAL SCENARIOS
Practical Teaching for Respiratory Arrest with a Pulse (Case 1)
You are a medical officer doing a pre-operative round when 60-year old patient started coughing violently and
becomes unconscious. Fortunately you have a nurse with you.
Trainee Action
Instructor Action
1. Perform initial steps of the universal
algorithm:
Assess Responsiveness
Call for Help
Call for Defibrillator
Unresponsive
2. Perform initial steps of the primary ABC
survey.
Airway - open airway
Breathing - Look, listen & feel
No Breathing
Circulation - Feel carotid artery
Pulse present
Resuscitation trolley is
available
Select Sinus
Patient cyanosed
3. Assess rhythm
Using quick look defibrillator paddles
Or
Attach to ECG lead as soon as possible
4. Initial rescue breathing by Bag-valve
mask
Reassess adequacy of ventilation
5. Intubate at once
Confirm tube placement
6. Establish iv access
Antecubital or external jugular vein
Normal saline solution
7. Monitor vital signs
Evaluate for causes of problem
Arrange for further ventilatory support
Observations:
1 June 2011
Page 1 of 15
Completed
(x or)
Comments
INSTITUTE FOR MEDICAL SIMULATION & EDUCATION
ACLS PRACTICAL SCENARIOS
Practical Teaching for Witnessed VF Adult Cardiac Arrest (Case 2)
A 55 year old man is visiting his mother, a patient in the general medicine ward. He suddenly grasps his chest,
and falls slowly to the floor.
Trainee Action
Instructor Action
1. Perform initial steps of the universal
algorithm:
Assess Responsiveness
Call for Help
Call for Defibrillator
Unresponsive
2. Perform initial steps of the primary
ABC survey.
Airway - open airway
Breathing - Look, listen & feel
No Breathing
Circulation - Feel carotid artery
No Pulse
3. Perform CPR immediately, until
defibrillator is available
Resuscitation trolley is
available
Select VF
Select Sinus
pulse present, no
breathing
4. Assess rhythm
Using quick look defibrillator paddles
Or
Attach to ECG lead as soon as
possible
5. Immediate defibrillation
Apply gel or pads to patient
Apply defibrillator paddles to patient
Check synchronizer switch OFF
Charge to 360 J (monphasic) or 150200 J (biphasic) (First shock must be
within 60 sec)
Confirm rhythm is VF
Shout Stand clear and shock patient
Reinitiate CPR immediately after shock
(at least for 1 2 mins)
Look at the rhythm again after a few
moments
6. Check pulse & check respiration
7. Intubate at once (1st rescuer)
Confirm tube placement
8. Establish iv access
Antecubital or external jugular vein
Normal saline solution
1 June 2011
Page 2 of 15
Completed
(x or)
Comments
INSTITUTE FOR MEDICAL SIMULATION & EDUCATION
ACLS PRACTICAL SCENARIOS
Trainee Action
9. Provide Medications appropriate for
blood pressure, heart rate and rhythm
Transfer to CCU with Lignocaine
infusion
Observations:
1 June 2011
Page 3 of 15
Instructor Action
Completed
(x or)
Comments
INSTITUTE FOR MEDICAL SIMULATION & EDUCATION
ACLS PRACTICAL SCENARIOS
Practical Teaching for Refractory VF/Pulseless VT (Case 3)
A 60 year old woman collapsed in the A & E department while a 12 lead ECG was done for her. You are the
only Medical Officer at around and you have a nurse to assist you.
Trainee Action
Instructor Action
1. Perform initial steps of the universal algorithm:
Assess Responsiveness
Call for Help
Call for Defibrillator
Unresponsive
2. Perform initial steps of the primary ABC
survey.
Airway - open airway
Breathing - Look, listen & feel
No Breathing
Circulation - Feel carotid artery
No Pulse
3. Perform CPR immediately, until defibrillator is
available
4.
Or
5.
Assess rhythm
Using quick look defibrillator paddles
Apply gel or pads to patient
Apply defibrillator paddles to patient
Check synchronizer switch OFF
Charge to 360 J (monophasic) or 150 - 200 J
(biphasic) (First shock must be within 60 sec)
Confirm rhythm is VF
Shout Stand clear then shock patient
Reinitiate CPR immediately after shock (at
least for 1 2 mins)
Look at the rhythm again after a few moments
Continue CPR
Attach to ECG lead as soon as possible
Immediate defibrillation
6. Intubate at once
Confirm tube placement
7. Establish iv access
Antecubital or external jugular vein
Normal saline solution
8. Adrenaline 1 mg IV push
Give 1 mg diluted in 10 ml of normal saline
(1:10,000 diluation) via IV / Intraosseous (IO)
/ Central Line Access
1 June 2011
Page 4 of 15
Resuscitation trolley is
available
Select VF
Select VF
Completed
(x or)
Comments
INSTITUTE FOR MEDICAL SIMULATION & EDUCATION
ACLS PRACTICAL SCENARIOS
Trainee Action
Instructor Action
9. Continue CPR for 30 60 secs after drug
10. Defibrillate within 30-60 sec after drug
administration
Check synchronizer switch OFF
Charge energy level
(a) Monophasic Use 360 J
(b) Biphasic 1st shock of 150 200J.
Subsequent shocks to escalate to the
maximum (as per the defib model)
Confirm rhythm is VF
Shout Stand clear then shock patient
Reinitiate CPR immediately after shock (at
least for 1 2 mins)
Look at the rhythm again
Continue CPR
11. Adrenaline 1 mg iv push
Give 1 mg diluted in 10 ml of normal saline via
IV / IO / Central Line
Inform trainee that rhythm
is still in VF
Inform trainee that rhythm
is still in VF, Select VF
If iv access delayed
12. Continue CPR for 30 60 secs
Defibrillate at 150 - 360J within 30-60 sec
after drug administration
Reinitiate CPR immediately after shock (at
least for 1 2 mins)
Look at the rhythm again
Continue CPR
rhythm is still in VF
13. IV Lignocaine 50 100 mg bolus or IV
Amiodarone 300 mg bolus
14. Continue CPR for 30 - 60 secs
Defibrillate at 150 - 360J within 30-60 sec
after drug administration
Reinitiate CPR immediately after shock (at
least for 1 2 mins)
Look at the rhythm again
Continue CPR
15. IV Lignocaine 50 100 mg bolus or IV
Amiodarone 150 mg bolus
16. Continue CPR for 30 - 60 secs
Defibrillate at 150 - 360J within 30-60 sec
after drug administration
1 June 2011
Page 5 of 15
rhythm is still in VF
Completed
(x or)
Comments
INSTITUTE FOR MEDICAL SIMULATION & EDUCATION
ACLS PRACTICAL SCENARIOS
Trainee Action
Reinitiate CPR immediately after shock (at
least for 1 2 mins)
Look at the rhythm again
Continue CPR
Instructor Action
17. Consider :
IV Magnesium sulfate 1-2 gm over 5 mins
18. Check pulse & check respiration
19. Support Airway & Breathing
20. Provide Medications Appropriate for Blood
Pressure
Transfer to CCU with Lignocaine infusion /
Amiodarone 150 mg
Observations:
1 June 2011
Page 6 of 15
Torsades de pointes
Pulse present, no breathing
Completed
(x or)
Comments
INSTITUTE FOR MEDICAL SIMULATION & EDUCATION
ACLS PRACTICAL SCENARIOS
Practical Teaching for Pulseless Electrical Activity (Case 4)
You are called to attend a patient found collapsed in the Ward. He was admitted 2 days ago for exacerbation of
Chronic Obstructive Airway Disease. You have a nurse to assist you.
Trainee Action
Instructor Action
1. Perform initial steps of the universal
algorithm:
Assess Responsiveness
Call for Help
Call for Defibrillator
Unresponsive
2. Perform initial steps of the primary
ABC survey.
Airway - open airway
Breathing - Look, listen & feel
No Breathing
Circulation - Feel carotid artery
No Pulse
3. Perform CPR immediately, until
defibrillator is available
Resuscitation trolley is
available
4. Assess rhythm
using quick look defibrillator paddles
or
attach to ECG lead as soon as
possible
Select junctional/Sinus
rhythm
history of vomiting,
bleeding GIT
history of COPD
Prolonged illness, metabolic
problems
history of renal failure,
calcium intake, ECG
peaked T, wide QRS, Sine
wave
5. Intubate at once
Confirm tube placement
6. Establish iv access
antecubital or external jugular vein
normal saline solution
7. Consider possible causes:
Hypovolemia
Hypoxia
Hydrogen ion-acidosis
Hyperkalemia
Hypothermia
history of cold water
drowning
Tablets
Drug overdose, history of
ingestion, pill bottle, young
patient
Thrombosis, coronary (ACS)
AMI, STEMI
Massive pulmonary embolism
history of recent operation,
use of oral contraceptive,
pleuritic chest pain
1 June 2011
Page 7 of 15
Completed
(xor)
Comments
INSTITUTE FOR MEDICAL SIMULATION & EDUCATION
ACLS PRACTICAL SCENARIOS
Trainee Action
Instructor Action
Tension pneumothorax
Tamponade, Cardiac
history of COPD, chest
injury. Neck veins
distended, trachea
deviation, unilateral breath
sound diminish
history of DXT, uraemia,
chestpain, Neck veins
distended, normal breath
sound
8. Continue CPR if iv access is delayed
Adrenaline 1 mg iv push
Give 1 mg diluted in 10 ml of normal
saline (1:10,000 diluation) via IV / IO
/ Central Line
9. Specific treatment
Fluid infusion
Hypovolemia
Ventilation
Hypoxia
Pericardiocentesis
Cardiac Tamponade
Needle decompression
Tension pneumothorax
Thrombolytic or surgery
Pulmonary embolism
Calcium chloride, bicarbonate, insulinglucose
Hyperkalemia
Specific antidote or treatment
Drug overdose
10. Prolonged resuscitation
Adrenaline 1mg IV push every 3-5
mins
Bicarbonate infusion is not
recommended as a routine agent. It
may be used judiciously in severe
metabolic acidosis, hyperkalemia or
TCA poisoning. When used, the
initial dose is 1-1.5 ml mEq/kg of
8.4% solution
Observations:
1 June 2011
Page 8 of 15
Completed
(xor)
Comments
INSTITUTE FOR MEDICAL SIMULATION & EDUCATION
ACLS PRACTICAL SCENARIOS
Practical Teaching for Asystole (Case 5)
A 55 year old patient is admitted to Medical Ward for chest pain. Patient becomes unresponsive. You are
Medical Officer of the ward. You have a nurse to assist you.
Trainee Action
Instructor Action
1. Perform initial steps of the universal
algorithm:
Assess Responsiveness
Call for Help
Call for Defibrillator
Unresponsive
2. Perform initial steps of the primary
ABC survey.
Airway - open airway
Breathing - Look, listen & feel
No Breathing
Circulation - Feel carotid artery
No Pulse
3. Perform CPR immediately, until
defibrillator is available
Resuscitation trolley is
available
Select Asystole
history of COPD
4. Assess rhythm
using quick look defibrillator paddles or
attach to ECG lead as soon as
possible
confirm Asystole in another lead
5. Intubate at once
Confirm tube placement
6. Establish iv access
antecubital or external jugular vein
normal saline solution
7. Consider possible causes:
Hypoxia
Hypokalemia
Hyperkalemia
CRF
Hypothermia
history of cold water
drowning
Acidosis
Drug overdose
Tricyclic Antidepressant,
history of ingestion, pill
bottle
8. Continue CPR
If iv access delayed
Adrenaline 1 mg IV push
Give 1 mg diluted in 10 ml of normal
saline (1:10,000 diluation) via IV / IO
/ Central Line
1 June 2011
Page 9 of 15
Completed
(x or)
Comments
INSTITUTE FOR MEDICAL SIMULATION & EDUCATION
ACLS PRACTICAL SCENARIOS
Trainee Action
Instructor Action
9. Specific treatment
Ventilation
Hypoxia
Calcium chloride, bicarbonate, insulinglucose
Hyperkalemia
Specific antidote or treatment
Drug overdose
10. Prolonged resuscitation
Adrenaline 1mg iv push every 3-5 mins
Bicarbonate infusion is not
recommended as a routine agent. It
may be used judiciously in severe
metabolic acidosis, hyperkalemia or
TCA poisoning. When used, the
initial dose is 1-1.5 ml mEq/kg of
8.4% solution
Observations:
1 June 2011
Page 10 of 15
Completed
(x or)
Comments
INSTITUTE FOR MEDICAL SIMULATION & EDUCATION
ACLS PRACTICAL SCENARIOS
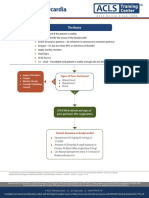
Practical Teaching for Bradycardia (Case 6)
You are at A & E, attending to a 67 year old woman complain of chest pain. You have a nurse to assist you.
Trainee Action
Instructor Action
1. Perform initial steps of the universal
algorithm:
Assess Responsiveness
Call for Help
Call for Defibrillator
Conscious
2. Perform initial steps of the primary ABC
survey.
Airway - open airway
Breathing - Look, listen & feel
Breathing normal
Circulation - Feel carotid artery
Pulse present
Resuscitation trolley is
available
select 3rd degree heart
block
6. Monitor vital sign
B.P. 126/50, H.R. 42, RR
12 bpm
7. Check for serious signs and symptoms
Symptoms - chest pain, shortness of
breath, giddiness
Haemodynamically stable
Select decrease rate to 30
bpm
Inform trainee that patient
is confused (Pale, sweaty,
BP 80/40 mm Hg)
Patient Stabilised
3. Give oxygen via face mask
4. Establish iv access
antecubital or external jugular vein
normal saline solution
5. Assess rhythm
attach to ECG lead as soon as possible
Signs - confused, pulmonary
congestion
8. Do 12 lead ECG
9. Atropine 0.6 mg IV. May be repeated
at 3 5 min intervals up to a max
dose of 2.4 mg
Transcutaneous pacing
Dopamine 2 to20 mcg/kg/min
Adrenaline 2 to 10 mcg/min Infusion
Observations:
1 June 2011
Page 11 of 15
Completed
(x or)
Comments
INSTITUTE FOR MEDICAL SIMULATION & EDUCATION
ACLS PRACTICAL SCENARIOS
Practical Teaching for Wide Complex Tachycardia (Case 7)
A 55 year old woman presents to the emergency department complaining of palpitations and mild chest
discomfort. You are the Medical Officer on duty and you have a nurse to assist you.
Trainee Action
Instructor Action
1. Perform initial steps of the universal
algorithm:
Assess Responsiveness
Call for Help
Call for Defibrillator
Responsive
2. Perform initial steps of the primary ABC
survey.
Airway - open airway
Breathing - Look, listen & feel
Breathing present
Circulation - Feel carotid artery
Pulse present
Resuscitation trolley is
available
Select VT
Heart Rate : 180/min,
Blood Pressure (BP):
150/70
BP: 120/60
BP: 100/55
BP: 70/50
3. Give oxygen via face mask
4. Establish iv access
antecubital or external jugular vein
normal saline solution
5. Assess rhythm
attach to ECG lead as soon as possible
6. Assess the vital signs
Do a 12 lead ECG
7. IV Lignocaine 50 - 100 mg over 2 min or
IV Amiodarone 150 mg over 10 15
mins
Check vital sign
8. Repeat IV Lignocaine 50 100 mg over
2 min or IV Amiodarone 150 mg over 10
15 mins
Check vital signs
9.
If not definite or equivocal VT: IV
Adenosine 6 mg rapid iv push, repeat IV
Adenosine 12 mg rapid iv push if not
converted
check vital signs
10. Prepare for immediate cardioversion
IV sedation, hyperventilate patient
Immediate synchronised cardioversion
1 June 2011
Page 12 of 15
Completed
(x or)
Comments
INSTITUTE FOR MEDICAL SIMULATION & EDUCATION
ACLS PRACTICAL SCENARIOS
Trainee Action
Apply gel or pads to patient
Apply defibrillator paddles to patient
Check synchronizer switch ON
Charge to 100 J
Confirm rhythm is VT
Shout Stand clear then shock patient
Evaluate outcome
Instructor Action
Select Sinus
10. Check pulse
Present
11. Ask Team member to check blood
pressure
BP 100/60
12. Check breathing
No Respiration
Patient cyanosed
13. Open airway
Ventilate patient with Bag-valve mask
unit
14. Intubate patient at once
confirm tube placement
15. Monitor vital signs
Arrange for mechanical ventilation and
transfer to ICU with antiarrhythmic drug
therapy. (IV lignocaine infusion)
Observations:
1 June 2011
Page 13 of 15
Completed
(x or)
Comments
INSTITUTE FOR MEDICAL SIMULATION & EDUCATION
ACLS PRACTICAL SCENARIOS
Practical Teaching for Narrow Complex Tachycardia (Case 8)
A 54 year old woman presents to the emergency department complaining of palpitations for 2 days, with a
pulse of 180 bpm. You are the Medical Officer on duty and you have a nurse to assist you.
Trainee Action
Instructor Action
1. Perform initial steps of the universal
algorithm:
Assess Responsiveness
Call for Help
Call for Defibrillator
Responsive
2. Perform initial steps of the primary ABC
survey.
Airway - open airway
Breathing - Look, listen & feel
Breathing normal
Circulation - Feel carotid artery
Carotid pulse felt
Resuscitation trolley is
available
Select SVT
BP: 130/80
ECG: SVT rate 180 p/min
Not converted
9.
IV Adenosine 6 mg flush iv line with 20
ml of normal saline
Not converted
IV Adenosine 12 mg flush iv line with 20
ml of normal saline
Converted but recur
IV Verapamil 1 mg / min (up to max 20
mg)
15 min later, not
converted
BP: 70/60
3. Assess rhythm
attach to ECG lead as soon as possible
4. Ask team member to check blood
pressure.
Ask patient whether she has shortness
of breath and chest pain
5. Give oxygen via face mask
6. Establish iv access
antecubital or external jugular vein
normal saline solution
7. Do a 12 lead ECG
8. Vagal maneuver
Carotid sinus massage
Valsalva manveuver
10. Check BP
1 June 2011
Page 14 of 15
Completed
(x or)
Comments
INSTITUTE FOR MEDICAL SIMULATION & EDUCATION
ACLS PRACTICAL SCENARIOS
Trainee Action
Instructor Action
Patient restless/weakness
11. Prepare for immediate synchronised
cardioversion
IV sedation
Apply gel or pads to patient
Apply defibrillator paddles to patient
Check synchronizer switch ON
Charge to 50 J
Confirm rhythm is SVT
Shout Stand clear then shock patient
Evaluate outcome [if not converted,
perform sychronised cardioversion
100J, 200J]
Select Sinus
12. Check pulse
Present
13. Ask Team member to check blood
pressure
BP 100/60
14. Check breathing
Respiration present
15. Assess responsiveness
Regain conscious
16. Oxygen via face mask
17. Transfer to CCU
Observations:
1 June 2011
Page 15 of 15
Completed
(x or)
Comments
You might also like
- Advanced Cardiac Life Support Quick Study Guide 2015 Updated GuidelinesFrom EverandAdvanced Cardiac Life Support Quick Study Guide 2015 Updated GuidelinesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Pediatric Advanced Life Support Quick Study Guide 2015 Updated GuidelinesFrom EverandPediatric Advanced Life Support Quick Study Guide 2015 Updated GuidelinesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- The Crash CartDocument39 pagesThe Crash Cartpramod kumawat100% (1)
- ACLS Algorithms (2011)Document6 pagesACLS Algorithms (2011)senbonsakuraNo ratings yet
- Pepp Als PretestDocument4 pagesPepp Als PretestDave BoppNo ratings yet
- ACLS Training - Most Important Points To RememberDocument5 pagesACLS Training - Most Important Points To RememberEman ElzeftawyNo ratings yet
- Non Surgical Management of Periapical Lesions Using Calcium HydroxideDocument6 pagesNon Surgical Management of Periapical Lesions Using Calcium HydroxideVinisha Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- ACLS Simulation ScenariosDocument14 pagesACLS Simulation ScenariosVanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- ACLS Study GuideDocument28 pagesACLS Study GuideNicole Berry100% (1)
- Pediatric Advanced Life Support: I. PALS System Approach AlgorithmDocument19 pagesPediatric Advanced Life Support: I. PALS System Approach AlgorithmIsabel Castillo100% (1)
- 15 item ACLS Drill ReviewDocument4 pages15 item ACLS Drill ReviewVal SolidumNo ratings yet
- Basic Life Support and Advanced Cardiovascular Life SupportDocument90 pagesBasic Life Support and Advanced Cardiovascular Life SupportRakhshanda khan100% (1)
- American Heart Association Guidelines For CPR 2015: Wanida Chongarunngamsang, MD. Faculty of Srinakarinwirot UniversityDocument49 pagesAmerican Heart Association Guidelines For CPR 2015: Wanida Chongarunngamsang, MD. Faculty of Srinakarinwirot UniversityZulkarnainBustamamNo ratings yet
- ACLS ECG Strip Interpretation and Study GuideDocument12 pagesACLS ECG Strip Interpretation and Study GuideMariana Berger100% (1)
- Stress: Dr. Jayesh PatidarDocument56 pagesStress: Dr. Jayesh PatidarDr. Jayesh Patidar100% (2)
- ACLS Full Lesson Plans PDFDocument60 pagesACLS Full Lesson Plans PDFVictoriano Mendez100% (1)
- ACLS DrugsDocument4 pagesACLS DrugsEduard Espeso Chiong-Gandul Jr.No ratings yet
- ACLS Algorithms SlideDocument26 pagesACLS Algorithms SlidehrsoNo ratings yet
- Closed Tibia and Fibula Fractures in 44-Year-Old Male PatientDocument25 pagesClosed Tibia and Fibula Fractures in 44-Year-Old Male Patientleonard0% (1)
- ACLS Drugs: Primary Medications Used in Cardiac Arrest AlgorithmsDocument10 pagesACLS Drugs: Primary Medications Used in Cardiac Arrest AlgorithmsChintami Octavia100% (1)
- Introd To ECG Code Blue Champs March 2019Document52 pagesIntrod To ECG Code Blue Champs March 2019james rukenya100% (1)
- ACLS Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support Provider Manual 2023From EverandACLS Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support Provider Manual 2023No ratings yet
- NailSurgery With Name ChangesDocument55 pagesNailSurgery With Name ChangesIde Bagoes InsaniNo ratings yet
- ACLS Written 2006 Precourse Self AssessmentDocument14 pagesACLS Written 2006 Precourse Self AssessmentmonickamsNo ratings yet
- Welcome TO Intensive Care UnitDocument42 pagesWelcome TO Intensive Care UnitKharene Lirazan100% (1)
- ACLS: Advanced Cardiac Life SupportDocument62 pagesACLS: Advanced Cardiac Life SupportAlemayehu beharuNo ratings yet
- Pals HandoutDocument49 pagesPals HandoutYasir AshfaqNo ratings yet
- Acls Provider: Advanced Cardiovascular Life SupportDocument1 pageAcls Provider: Advanced Cardiovascular Life SupportmaraínaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Airway Management: Leaugeay Webre, BS, CCEMT-P, Nremt-PDocument35 pagesAdvanced Airway Management: Leaugeay Webre, BS, CCEMT-P, Nremt-Pbasic100% (4)
- Acls Book PDFDocument63 pagesAcls Book PDFSabir Khan67% (3)
- CPR ACLS Study GuideDocument18 pagesCPR ACLS Study GuideJohn Phamacy100% (1)
- American Heart Association Guidelines For CPR 2015: Christopher RyalinoDocument50 pagesAmerican Heart Association Guidelines For CPR 2015: Christopher RyalinoLightNo ratings yet
- Antrim ED Handbook 2019Document238 pagesAntrim ED Handbook 2019Chris Jardine LiNo ratings yet
- Basic Life SupportDocument22 pagesBasic Life SupportTotoLesterNo ratings yet
- Dysrhythmia Advance Content Outline A1 - 2020.1.2Document3 pagesDysrhythmia Advance Content Outline A1 - 2020.1.2Kimberly Whiteside50% (2)
- AclsDocument85 pagesAclsJulia CostaNo ratings yet
- Brain Gate ReportDocument31 pagesBrain Gate ReportRahul Bansal50% (4)
- HSS Sotw 2017-18 ArDocument98 pagesHSS Sotw 2017-18 Arlf515No ratings yet
- 2010 Integrated Updated Circulation ACLS Acute Coronary Syndromes AlgorithmDocument1 page2010 Integrated Updated Circulation ACLS Acute Coronary Syndromes Algorithmms_lezahNo ratings yet
- ACLS PresentationDocument79 pagesACLS PresentationHumaira YasserNo ratings yet
- Basics of Mechanical Ventilation For Residents: DR Ghaleb Almekhlafi MD, SFCCM PSMMCDocument43 pagesBasics of Mechanical Ventilation For Residents: DR Ghaleb Almekhlafi MD, SFCCM PSMMCGHALEB A. Almekhlafi100% (1)
- On Emergency DrugsDocument25 pagesOn Emergency DrugsBikram Chhetry100% (1)
- AHA ACLS Written Test: Ready To Study? Start With FlashcardsDocument8 pagesAHA ACLS Written Test: Ready To Study? Start With FlashcardssallyNo ratings yet
- ACLSDocument46 pagesACLSYeoh Hong Shin100% (3)
- Paediatric Advanced Life Support: Resuscitation Council (UK)Document12 pagesPaediatric Advanced Life Support: Resuscitation Council (UK)zacklim_2000100% (1)
- Basic Life SupportDocument34 pagesBasic Life SupportEveline FebrinaNo ratings yet
- CPR AED Choking Guidelines for Healthcare ProvidersDocument2 pagesCPR AED Choking Guidelines for Healthcare Providersreyes markNo ratings yet
- ACLS and PALS Certification Practice QuestionsDocument11 pagesACLS and PALS Certification Practice Questionsdyah rahayu hutamiNo ratings yet
- Basic Life Support (BLS) Training Course: FeaturesDocument1 pageBasic Life Support (BLS) Training Course: FeaturesSheryl Fuentes De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Adult Basic Life Support Algorithm For Healthcare ProvidersDocument1 pageAdult Basic Life Support Algorithm For Healthcare ProvidersKavya ShreeNo ratings yet
- Normal Ranges Vital Signs 2017Document2 pagesNormal Ranges Vital Signs 2017Elvis Nguyen100% (1)
- Basic Mechanical Ventilation 2014Document62 pagesBasic Mechanical Ventilation 2014dragon66No ratings yet
- End Tidal Co2Document38 pagesEnd Tidal Co2brentupdegraffNo ratings yet
- Rapid Sequence InductionDocument8 pagesRapid Sequence InductionAngela Mitchelle NyanganNo ratings yet
- ACLS and MegacodeDocument33 pagesACLS and MegacodeMark Joseph100% (1)
- ACLS-Study-Guide-2011 MADE EASYDocument2 pagesACLS-Study-Guide-2011 MADE EASYFrances Albaña TevesNo ratings yet
- ACLS NotesDocument3 pagesACLS Notessaxmanwrv0% (1)
- ACLS QuizletDocument7 pagesACLS Quizletek.9006001No ratings yet
- Pals Pediatric BradycardiaDocument1 pagePals Pediatric BradycardiadarlingcarvajalduqueNo ratings yet
- Journal ClubDocument26 pagesJournal Clubysindhura23gmailcom100% (1)
- Pals Life SaverDocument13 pagesPals Life SaverStephany ZamorasNo ratings yet
- ACLS Review Guide for Cardiac Arrest Scenarios and TreatmentDocument29 pagesACLS Review Guide for Cardiac Arrest Scenarios and TreatmentJB Reyes100% (2)
- PALS 2015 Update - Nursing Grand RoundsDocument22 pagesPALS 2015 Update - Nursing Grand RoundshatsuneNo ratings yet
- Critical Care SedationFrom EverandCritical Care SedationAngelo Raffaele De GaudioNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- DSGNDGJMHDHHGVJVV, HGVCDXVCVXX X Xvbbhydvdsvsdc CvvvveeDocument1 pageDSGNDGJMHDHHGVJVV, HGVCDXVCVXX X Xvbbhydvdsvsdc CvvvveenersNo ratings yet
- DSGNDGJMHDHHGVJVV, HGVCDXVCVXX X Xvbbhydvdsvsdc CvvvveexssrrDocument1 pageDSGNDGJMHDHHGVJVV, HGVCDXVCVXX X Xvbbhydvdsvsdc CvvvveexssrrnersNo ratings yet
- DSGNDGJMHDHHGVJVV, HGVCDXVCVXX X Xvbbhydvdsvsdc CVVVVDocument1 pageDSGNDGJMHDHHGVJVV, HGVCDXVCVXX X Xvbbhydvdsvsdc CVVVVnersNo ratings yet
- DSGNDGJMHDHHGVJVV, HGVCDXVCVXX X Xvbbhydvdsvsdc CvvvveexssDocument1 pageDSGNDGJMHDHHGVJVV, HGVCDXVCVXX X Xvbbhydvdsvsdc CvvvveexssnersNo ratings yet
- DSGNDGJMHDHHGVJVV, HGVCDXVCVXX X XvbbhydvdsvsdDocument1 pageDSGNDGJMHDHHGVJVV, HGVCDXVCVXX X XvbbhydvdsvsdnersNo ratings yet
- DSGNDGJMHDHDocument1 pageDSGNDGJMHDHnersNo ratings yet
- DSGNDGJMHDHDocument1 pageDSGNDGJMHDHnersNo ratings yet
- DSGNDGJMHDHHGVJVV, HGVCDXVCVXX X Xvbbhydvdsvsdc CDocument1 pageDSGNDGJMHDHHGVJVV, HGVCDXVCVXX X Xvbbhydvdsvsdc CnersNo ratings yet
- SdfdafdsgsdgdsgdsgdsDocument1 pageSdfdafdsgsdgdsgdsgdsnersNo ratings yet
- DSGNDGJMHDHHGVJVV, HGVCDXVCVXX X XvbbhyDocument1 pageDSGNDGJMHDHHGVJVV, HGVCDXVCVXX X XvbbhynersNo ratings yet
- DSGNDGJMHDHDocument1 pageDSGNDGJMHDHnersNo ratings yet
- DSGNDGJMHDHDocument1 pageDSGNDGJMHDHnersNo ratings yet
- Type The Document TitleDocument2 pagesType The Document TitleHaymanAHMEDNo ratings yet
- Nama PotretDocument1 pageNama PotretnersNo ratings yet
- Nama LandcapeDocument1 pageNama LandcapenersNo ratings yet
- Perkalian Sampai 100Document2 pagesPerkalian Sampai 100nersNo ratings yet
- Pencegahan Dan Pengendalian Infeksi Pleno I Standar Ppi 1 Skor SKOR MaksimalDocument4 pagesPencegahan Dan Pengendalian Infeksi Pleno I Standar Ppi 1 Skor SKOR MaksimalnersNo ratings yet
- Nama LandcapeDocument1 pageNama LandcapenersNo ratings yet
- Bcls ExamDocument4 pagesBcls ExamnersNo ratings yet
- Bcls ExamDocument4 pagesBcls ExamnersNo ratings yet
- Book 2Document3 pagesBook 2nersNo ratings yet
- Toxi TestDocument4 pagesToxi TestFrank NobodNo ratings yet
- Mad Wife Struck OffDocument8 pagesMad Wife Struck OffDr John CrippenNo ratings yet
- Treatment Plan AssignmentDocument2 pagesTreatment Plan AssignmentyourzxtrulyNo ratings yet
- CS PresentationDocument38 pagesCS PresentationMarriam Malik100% (3)
- Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation: Unusual Techniques For Unusual Situations ConclusionDocument8 pagesCardiopulmonary Resuscitation: Unusual Techniques For Unusual Situations ConclusionIlham AkbarNo ratings yet
- English Meeting 2Document10 pagesEnglish Meeting 2Tya DwiNo ratings yet
- Diabetes - Oral KnowledgeDocument19 pagesDiabetes - Oral KnowledgeKSeegurNo ratings yet
- Weekly Reflective Journal on Gyne Ward and ICU Clinical AreasDocument2 pagesWeekly Reflective Journal on Gyne Ward and ICU Clinical AreasRowena Marie Endoso BetonioNo ratings yet
- Guide to Chemotherapy Drugs and Side EffectsDocument38 pagesGuide to Chemotherapy Drugs and Side EffectsTrixia CamporedondoNo ratings yet
- Arterial Line Waveform Interpretation UHL Childrens Intensive Care GuidelineDocument5 pagesArterial Line Waveform Interpretation UHL Childrens Intensive Care GuidelineDhony100% (1)
- Prof Qaisar Khan TrialsDocument56 pagesProf Qaisar Khan TrialsAsim NajamNo ratings yet
- Rationale: Most Patients Prescribed To Receive Platelet Transfusions Exhibit Moderate ToDocument2 pagesRationale: Most Patients Prescribed To Receive Platelet Transfusions Exhibit Moderate TojoanneNo ratings yet
- Time, Final Rinse Protocol and EndodonticsDocument1 pageTime, Final Rinse Protocol and EndodonticsvaamdevaaNo ratings yet
- USG Hernia ScrotalisDocument4 pagesUSG Hernia ScrotalisStevent RichardoNo ratings yet
- TENSProtocolby DR Deirdre WalshDocument15 pagesTENSProtocolby DR Deirdre WalshGuy Hill100% (1)
- Evaluation of Hypoglycemia: & Insulin Autoimmune Syndrome (Hirata Disease)Document15 pagesEvaluation of Hypoglycemia: & Insulin Autoimmune Syndrome (Hirata Disease)Anonymous B3J9sWNo ratings yet
- Laporan - Pendahuluan PJK FixDocument8 pagesLaporan - Pendahuluan PJK FixNndaydnaNo ratings yet
- SedativesDocument3 pagesSedativesOana AndreiaNo ratings yet
- 11.50 DR Stella George, Diabetic and Metabolic EmergenciesDocument49 pages11.50 DR Stella George, Diabetic and Metabolic Emergenciesamir ahmadNo ratings yet
- Rift Valley FeverDocument9 pagesRift Valley Feverapi-390015550No ratings yet
- Pancreas Functions and DiseasesDocument18 pagesPancreas Functions and DiseasesLisa PalabaoNo ratings yet
- Presentation Syntax Score TCT 2008 PDFDocument33 pagesPresentation Syntax Score TCT 2008 PDFElla MihNo ratings yet
- ENG - S.A.F.E.R.®/NeoGraft® Hair Transplant Technique & DeviceDocument3 pagesENG - S.A.F.E.R.®/NeoGraft® Hair Transplant Technique & DeviceMedicamatNo ratings yet
- SAMPLE Common Medical AbbreviationsDocument10 pagesSAMPLE Common Medical AbbreviationsReina AzaresNo ratings yet