Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Volume and Surface Area
Uploaded by
api-290911775Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Volume and Surface Area
Uploaded by
api-290911775Copyright:
Available Formats
Volume and Surface Area
1.
Jun 80
a.
b.
2.
(Note: Volume of a pyramid =
2
An orange is 9 cm in diameter. If
9
of its juice is 72ml, how much juice
can you get from 7 such oranges?
[Volume of a sphere of radius
4
r r 3 . Assume that the orange is
3
a sphere]
Volume of cylinder = r 2 h , take =
5.
Two thirds of the juice is poured into
a cylindrical container 14 cm high
and diameter 7 cm. How many icecubes, each of sides 3 cm can be
added before the juice begins to
overflow?
Jun 84
A rectangular wooden beam of length 5
metres has a cross section of 20 cm by 15
cm. the wood has a density of 600 kg per
m3.
a. Calculate the volume of the beam
in cubic metres
b. Express the answer for a in
standard form.
c. Calculate the mass of the beam in
kg.
3.
Jun 85
A cylindrical object of height 21 cm has an
outer diameter of 28 cm and an inner
diameter of 24 cm. The material of which it
is made has a density of 6g per cm3.
Calculate, to the nearest kg, the mass of the
object
4.
Jun 88
A rectangular steel pyramid of height 6 cm
and base dimensions 11 cm by 16 cm, is
melted down and rolled into a cylinder of
height 7 cm.
Calculate
i. the radius of the cylinder in cm.
ii. the mass of the cylinder in kg, if the
density of the steel is 5g per cm3.
1
Ah,
3
22
)
7
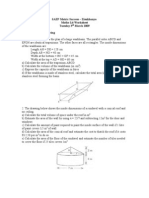
Jan 89
The figure above, not drawn to scale,
represents a fish tank in the shape of a
cuboid of height 30 cm.
i. Calculate the volume of the tank
ii. If there are 40 litres of water in the
tank, calculate the height of the water
in the tank.
6.
The total surface area of a triangular prism is
198 105 cm3 , what is its total surface area
in m3
7.
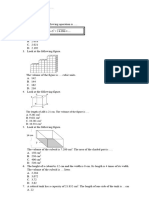
Jun 86
The diagram above, not drawn to scale,
shows a right triangular prism with AB = 15
cm, AD = AE = 10 cm and ED = 12 c.
Calculate the volume of the prism.
8.
Jun 91
The figure ABCDEF above, not drawn to
scale, represents a wedge with
measurements as shown. BC is
perpendicular to the plane FEDC.
Calculate
i. the length in cm of BD
ii. the surface area, in cm2, of the wedge
iii. the volume in cm3, of the wedge
iv. the size of angle BDC.
9.
11. Jun 96
Jan 91
22
and
7
V r 2 , where V = volume, r = radius and
h = height of the cylinder.
a. The internal dimensions of a sauce
pan shaped like a cylinder height
20 cm and diameter 35 cm.
Calculate to the nearest whole
number,
i. the area, in cm2, of the
bottom of the saucepan
ii. the largest volume of liquid,
in cm3, which the saucepan
can hold.
b. The saucepan is filled with water
which is then poured into a empty
cylindrical pot of radius 21 cm.
Calculate, to the nearest cm, the
height of the water level above the
bottom of the pot.
To answer this question use =
10. Resit 95
A closed cylinder has a base of diameter 14
cm and a vertical height of 20 cm. Take
22
. Calculate
7
i. the area, in cm2, of the base
ii. the volume, in cm3, of the cylinder
iii. Show that the total surface area is
1188cm2.
The diagram above, not drawn to scale,
represents a right open ended paper cone.
The slant height VX is 14cm, the base
diameter XY is 21 cm and VO is the height
of the cone.
22
[take
]
7
i. Calculate, in cm , the
circumference of the base of the
cone.
ii. Show that the height of the cone is
approximately 9.3 cm.
iii. Calculate the volume in cm3 of the
cone.
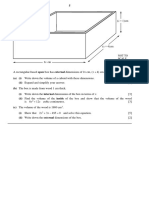
12. Jan 97
a.
b.
A rectangular tank is 8 m high and
its base is 4 m long and 3 m wide.
The tank is filled with water.
Calculate;
i. the area, in cm2, of the base of
the tank and write your answer
in standard form.
ii. the capacity, in litres, of the
tank. Use 100cm3 = 1 litre.
All the water from the rectangular
tank is pumped into a cylindrical
tank to a height of 8 m. Calculate
to, 3 significant figures, the radius
of the base of the cylindrical tank.
13. Jan 99
[Take
22
]
7
i. A cylindrical metal drum of height
125 cm, has a capacity of 693
litres. Calculate the diameter of the
drum.
ii. Oil is poured into the drum for 1
hour 17 minutes at a rate of p litres
per minute until it just begin to
overflow. Calculate the value of p.
[100 cm3 = 1 litre]
14. Jun 99
A circular drain pipe, shown in the diagram
above, not drawn to scale, is 1 metre long,
with outer and inner radii of 20 cm and 15
cm respectively.
i. Draw a cross-sectional view of the
drainpipe, showing the
measurement of the inner and outer
radii.
Calculate;
ii. the area, in cm2, of the cross section
of the drain pipe.
iii. the amount, in cm3, of the material
required to construct the drain pipe.
iv. The capacity, in litres of the hallow
space of the drain pipe.
v. The volume, in litres , of water
passing through the pipe in 1
minute if the water flows through
the pipe at a speed of 1 metre per
second
[Take 3.14 ]
You might also like
- Master Plumber Exam Sample ProblemsDocument15 pagesMaster Plumber Exam Sample ProblemsJohn Aries Almelor SarzaNo ratings yet
- CheatsDB BSD VersionDocument40 pagesCheatsDB BSD VersionLucioNo ratings yet
- Reflection On Pay It ForwardDocument2 pagesReflection On Pay It ForwardJofel Delicana67% (3)
- Bali Tour Packages 7 Days and 6 Nights Tours Itinerary and ArrangementDocument5 pagesBali Tour Packages 7 Days and 6 Nights Tours Itinerary and ArrangementKumar ManvendraNo ratings yet
- You're The Best Part Love Song LyricsDocument1 pageYou're The Best Part Love Song LyricsJaxson DenoNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Mensuration 1.: ABCDE Is A PyramidDocument4 pagesAssignment - Mensuration 1.: ABCDE Is A Pyramid567gjNo ratings yet
- Math f1 Topic 4Document8 pagesMath f1 Topic 4Kennedy ChitayiNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-06-18 at 11.29.52 AMDocument4 pagesScreenshot 2023-06-18 at 11.29.52 AMJudaNo ratings yet
- Volume Word Problems - Level 3-4Document6 pagesVolume Word Problems - Level 3-4Nguyễn LongNo ratings yet
- Std 10_Math_Surface Area & Volumes_all Types Ques.Document11 pagesStd 10_Math_Surface Area & Volumes_all Types Ques.Guna DharshiniNo ratings yet
- Men Su Rations ClassifiedDocument58 pagesMen Su Rations ClassifiedMohammed BasitNo ratings yet
- Maths Lit Worksheet - Estimating and MeasuringDocument3 pagesMaths Lit Worksheet - Estimating and MeasuringCape Town After-School TutorialsNo ratings yet
- Cube Cuboid Volume Grade 5Document2 pagesCube Cuboid Volume Grade 5Meini ThamrinNo ratings yet
- Mock-3 (Practice Paper)Document11 pagesMock-3 (Practice Paper)Sharif HossainNo ratings yet
- MensurationDocument28 pagesMensurationrushabhNo ratings yet
- Calculate volumes and surface areas of common solidsDocument17 pagesCalculate volumes and surface areas of common solidssam_raunayNo ratings yet
- MENSURATION ASSIGNMENTDocument3 pagesMENSURATION ASSIGNMENTEarl Daniel ArcillaNo ratings yet
- 6893076-CL 9 - WS No. 3 - Surface Area and Volume - Sheena - Shiji - 22 - 23Document3 pages6893076-CL 9 - WS No. 3 - Surface Area and Volume - Sheena - Shiji - 22 - 23Sujayram PrasadNo ratings yet
- Surface, Area & Volumes 1Document5 pagesSurface, Area & Volumes 1Gaurav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cylinders Solid MensurationDocument2 pagesCylinders Solid MensurationKim LasayNo ratings yet
- Cylinders - Solid MensurationDocument2 pagesCylinders - Solid MensurationClifford GatonNo ratings yet
- Solid Geo Bim 3Document4 pagesSolid Geo Bim 3Rosmizar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Cylinder Volume and Surface Area Multiple ChoiceDocument3 pagesCylinder Volume and Surface Area Multiple ChoiceDhira Thalia AritonangNo ratings yet
- Task 4 - Maths F2 PDFDocument11 pagesTask 4 - Maths F2 PDFarisya amranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Solid GeometryDocument6 pagesChapter 12 - Solid Geometryg-46005995No ratings yet
- Mensuration FormulasDocument25 pagesMensuration FormulasIsrar Ahmad100% (1)
- Volume word problems solved step-by-stepDocument17 pagesVolume word problems solved step-by-stepJohnNo ratings yet
- Assignment- Surface Areas and VolumesDocument4 pagesAssignment- Surface Areas and VolumeslwhmrvavrodrljeuwoNo ratings yet
- SOLIMENDocument3 pagesSOLIMENKhay NochefrancaNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Section 4 - Surface Area and Volume of 3-D ShapesDocument10 pagesUnit 9 Section 4 - Surface Area and Volume of 3-D ShapesSuresh DevarajanNo ratings yet
- Mensuration revision problemsDocument6 pagesMensuration revision problemsHaseeb BadrNo ratings yet
- CH-12 Super 30Document4 pagesCH-12 Super 30Jay kumar MishraNo ratings yet
- Calculating surface areas and volumes of cylindrical objectsDocument6 pagesCalculating surface areas and volumes of cylindrical objectsMendoza Christian MarkNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 To 3 (Remedial)Document4 pagesAssignment 1 To 3 (Remedial)Dhira Thalia AritonangNo ratings yet
- Volume and Surface Area QuestionsDocument7 pagesVolume and Surface Area QuestionsThe Equinox DudeNo ratings yet
- CBSE Test Paper 02 Chapter 13 Surface Area and VolumeDocument11 pagesCBSE Test Paper 02 Chapter 13 Surface Area and Volumeankitkumarforyou8No ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument5 pagesAssignmentGeorgeAruNo ratings yet
- Doc-20231204-Wa0006 231206 001654Document6 pagesDoc-20231204-Wa0006 231206 001654schoolclass677No ratings yet
- Measurement Practice QuestionsDocument11 pagesMeasurement Practice QuestionsTamilore AdeboyejoNo ratings yet
- Remedial Practice Sheet of Grade VIII - Math - Surface Area and VolumeDocument2 pagesRemedial Practice Sheet of Grade VIII - Math - Surface Area and Volumevaishali14051980No ratings yet
- CH 12 Areas Related To Circles WorksheetDocument3 pagesCH 12 Areas Related To Circles WorksheetRuzal AnandNo ratings yet
- Area and VolumeDocument7 pagesArea and VolumekevomoriavinNo ratings yet
- Vpqrs PqrsDocument4 pagesVpqrs PqrsMarksuel Kweku AnanseNo ratings yet
- VolumesDocument7 pagesVolumesSushobhan SanyalNo ratings yet
- Surface Areas and VolumesDocument25 pagesSurface Areas and Volumessmi_santhosh0% (1)
- 2exp Vol Spheres Cones Pyramids 2Document3 pages2exp Vol Spheres Cones Pyramids 2John GohNo ratings yet
- Assignment Class X Srface Area and Volume CRPFDocument3 pagesAssignment Class X Srface Area and Volume CRPFCRPF School100% (1)
- CLASS-VIII SUB-MATHEMATICS MENSURATION(SURFACE AREA AND VOLUME) Worksheet-3(AdvanceDocument4 pagesCLASS-VIII SUB-MATHEMATICS MENSURATION(SURFACE AREA AND VOLUME) Worksheet-3(Advancetarun arora100% (1)
- Class VIII Math Mensuration Worksheet on Surface Area and VolumeDocument5 pagesClass VIII Math Mensuration Worksheet on Surface Area and VolumeTEJAS KALENo ratings yet
- Westminster International Schools: Math Revision: MensurationDocument22 pagesWestminster International Schools: Math Revision: MensurationTaSi Al BakriNo ratings yet
- STD 8 - Maths - Chapter 16 - NotesDocument7 pagesSTD 8 - Maths - Chapter 16 - NotesMamata MannaNo ratings yet
- Solid Homework 2Document4 pagesSolid Homework 2nadaynNo ratings yet
- Use & Convert Between Units P4Document4 pagesUse & Convert Between Units P4Ucok PandapotanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 II Volume (ENHANCE)Document17 pagesChapter 2 II Volume (ENHANCE)cakra75No ratings yet
- Volume and SurfaceArea Cylinder CBSE ICSEDocument5 pagesVolume and SurfaceArea Cylinder CBSE ICSEtripti aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Mensuration concepts for surface area and volume of combinations of solidsDocument10 pagesMensuration concepts for surface area and volume of combinations of solidssam00723100% (1)
- IGCSE Maths Mensuration Ext Exam Qus Nov2010 AVGDocument7 pagesIGCSE Maths Mensuration Ext Exam Qus Nov2010 AVGKeshya Maleeza WeerakkodyNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 13 - Surface Areas and VolumesDocument112 pagesImportant Questions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 13 - Surface Areas and Volumesvedhik raajnNo ratings yet
- Surface Areas & VolumesDocument4 pagesSurface Areas & VolumesSubha VijayNo ratings yet
- Short Answer Questions 2 MarksDocument5 pagesShort Answer Questions 2 MarksArshit100% (1)
- 16 Volume 40 Questions 2019Document5 pages16 Volume 40 Questions 2019krishthefishNo ratings yet
- Pe 4 Solid MensurationDocument5 pagesPe 4 Solid MensurationJosuelle MadulaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16Document9 pagesChapter 16sanjeevNo ratings yet
- Barry The Fish With FingersDocument26 pagesBarry The Fish With FingersShahd Suliman ElshareefNo ratings yet
- Ilmuguru - Org - Soal PAS Bahasa Inggris Kelas 8 Semester 1 Tahun 2020Document5 pagesIlmuguru - Org - Soal PAS Bahasa Inggris Kelas 8 Semester 1 Tahun 2020Rien BiNo ratings yet
- Excerpt From in Light of Kriya YogaDocument3 pagesExcerpt From in Light of Kriya YogaavkrishnavblcNo ratings yet
- Math 5Document22 pagesMath 5JANICE G. FELIPENo ratings yet
- Cake Craft & Decorating 2013'02Document84 pagesCake Craft & Decorating 2013'02Alexa Rods100% (2)
- SaliagosDocument321 pagesSaliagosivansuv100% (1)
- The History and Development of the Armenian LanguageDocument2 pagesThe History and Development of the Armenian Languageetna26No ratings yet
- GE2 Listen Unit 1Document26 pagesGE2 Listen Unit 1hoad06bnNo ratings yet
- Performing Arts in The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesPerforming Arts in The PhilippinesAyu GalvezNo ratings yet
- Macbeth Is An Ancient Text That Has No Relevance or Parallels With Our Society Today.Document2 pagesMacbeth Is An Ancient Text That Has No Relevance or Parallels With Our Society Today.Anubhav PunethaNo ratings yet
- Graficos ScilabDocument47 pagesGraficos ScilabramosromanNo ratings yet
- How To Chant On BeadsDocument2 pagesHow To Chant On BeadsvdaNo ratings yet
- Alno July-2011Document46 pagesAlno July-2011Swapnil WellingNo ratings yet
- Marching Band Year Book Page 1Document2 pagesMarching Band Year Book Page 1api-549719383No ratings yet
- TeclisDocument4 pagesTeclisCharlie BowenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Stories SilhouettesDocument5 pagesLesson 1 - Stories Silhouettesapi-340974011No ratings yet
- British Poems & Short Stories: The Happy PrinceDocument25 pagesBritish Poems & Short Stories: The Happy PrinceNguyễn HàNo ratings yet
- Ecclesial Dimension of The LiturgyDocument30 pagesEcclesial Dimension of The LiturgyJohn Carl Aparicio100% (1)
- The Understudy (Fernando Alonso Fanfiction)Document4 pagesThe Understudy (Fernando Alonso Fanfiction)SmallTimeScribeNo ratings yet
- DictionaryDocument50 pagesDictionaryHeckmanJasonNo ratings yet
- Dota 2 Item List PricesDocument3 pagesDota 2 Item List PricesLabador LeoNo ratings yet
- Introduction-to-Hinduism NewDocument35 pagesIntroduction-to-Hinduism NewDennis RaymundoNo ratings yet
- John StudyDocument19 pagesJohn StudyEya Guerrero CalvaridoNo ratings yet
- The Lord of The Rings - The One Wiki To Rule Them All - FandojjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjmDocument1 pageThe Lord of The Rings - The One Wiki To Rule Them All - FandojjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjmArîfNo ratings yet
- Buddhist Heritage City of AmaravatiDocument26 pagesBuddhist Heritage City of AmaravatiVenkat Aha ANo ratings yet
- Notes: Arjuna Uvaca Sthita-Prajnasya Ka Bhasa Samadhi-Sthasya Keshava Sthita-Dhih Kim Prabhaseta Kim Asita Vrajeta KimDocument14 pagesNotes: Arjuna Uvaca Sthita-Prajnasya Ka Bhasa Samadhi-Sthasya Keshava Sthita-Dhih Kim Prabhaseta Kim Asita Vrajeta Kimamitshukla.iitkNo ratings yet