Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Compiler Phases
Uploaded by
SandeepKumarCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Compiler Phases
Uploaded by
SandeepKumarCopyright:
Available Formats
a compiler is divided into 7 phases, basically from the original character stream, to the
target machine code, assuming you want to run it on a machine, or virtual machine for
that matter.
Which is shown in the following diagram:
Lexical Analyzer lexical analysis breaks
down the entire text of the program into the
smallest atomic units, called tokens, at the
same time throwing out unnecessary
information such as white space and
comments.
Syntax Analyzer syntax analysis,
otherwise known as parsing, takes the tokens
produced from lexical analysis and groups
them into grammatical structures.
Semantic Analyzer semantic analysis
utilizes the syntax tree and information in the
symbol table to check the semantic
consistency of the source program with the
language definition. This is also where typechecking is done.
Intermediate Code Generator generates
an explicit low-level or machine-like
intermediate representation, having two
properties: it should be easy to produce and it
should be easy to translate into the target machine.
Code Optimization code optimization attempts to improve the intermediate code so
a better target code will result. Usually better means faster, but other objectives may be
desired, such as shorter code, or target code that consumes less power.
Code Generator code generation takes as input the intermediate representation as a
result of code optimization, and produces the target code (e.g. machine code) to be
executed by the machine (or virtual machine).
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Coa TestDocument2 pagesCoa TestSandeepKumarNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Test 1Document4 pagesTest 1SandeepKumarNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- HTML 1 & 2 AnswersDocument1 pageHTML 1 & 2 AnswersSandeepKumarNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Database TestDocument7 pagesDatabase TestSandeepKumarNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- 2.what Is JVMDocument1 page2.what Is JVMjaikumar_22No ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- 1 FundamentalDocument5 pages1 FundamentalSandeepKumarNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- MatricsDocument58 pagesMatricsSandeepKumarNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- What Is VBScriptDocument15 pagesWhat Is VBScriptSandeepKumarNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
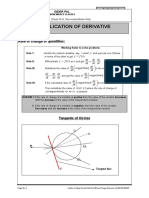
- Application of DerivativesDocument15 pagesApplication of DerivativesSandeepKumarNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
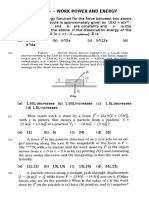
- PHYSICS - WORK, POWER AND ENERGY FORMULASDocument3 pagesPHYSICS - WORK, POWER AND ENERGY FORMULASSandeepKumarNo ratings yet
- HTML 1Document8 pagesHTML 1SandeepKumarNo ratings yet
- HTML 2Document6 pagesHTML 2SandeepKumarNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Computer Graphics 1: City Classes: Sandeep Sir's AcademyDocument4 pagesComputer Graphics 1: City Classes: Sandeep Sir's AcademySandeepKumarNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Computer Science Multiple Choice QuizDocument9 pagesComputer Science Multiple Choice QuizSandeepKumarNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
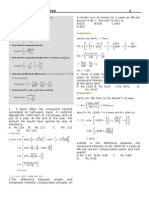
- Aptitute: Compound Interest With AnswersDocument4 pagesAptitute: Compound Interest With AnswersSandeepKumarNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Combined June GK + GK BytesDocument19 pagesCombined June GK + GK BytesSandeepKumarNo ratings yet
- Blood Relation Quiz SolutionsDocument3 pagesBlood Relation Quiz SolutionsSandeepKumarNo ratings yet
- Compiler PhasesDocument1 pageCompiler PhasesSandeepKumarNo ratings yet
- Blood Relation Quiz SolutionsDocument3 pagesBlood Relation Quiz SolutionsSandeepKumarNo ratings yet
- InheritanceDocument9 pagesInheritanceSandeepKumarNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- TriggersDocument14 pagesTriggersSandeepKumarNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Blood Relationswith AnswersDocument4 pagesBlood Relationswith AnswersSandeepKumarNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions (40%)Document4 pagesMultiple Choice Questions (40%)SandeepKumarNo ratings yet
- Blood Relation Quiz SolutionsDocument3 pagesBlood Relation Quiz SolutionsSandeepKumarNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- General KnowledgeDocument141 pagesGeneral KnowledgeRAVI KUMAR83% (12)
- Aptitute - AverageDocument1 pageAptitute - AverageSandeepKumarNo ratings yet
- INFORMATION SECURITY DOCUMENT ANALYSISDocument13 pagesINFORMATION SECURITY DOCUMENT ANALYSISSandeepKumarNo ratings yet
- Computer ApplicationsV Isual Basic ProgrammingDocument3 pagesComputer ApplicationsV Isual Basic ProgrammingSandeepKumar0% (1)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Ra RCDocument47 pagesRa RCSandeepKumarNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)