Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SRA M: Sram and Dram
Uploaded by
Shalabh Srivastava0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views9 pagesThis document discusses two types of computer memory technologies: SRAM and DRAM, and then focuses on Magnetoresistive random-access memory (MRAM) as a promising alternative. MRAM uses magnetic tunnel junctions (MTJs) as its basic memory unit. An MTJ consists of two ferromagnetic layers separated by a thin insulating layer, and it can store data as the relative orientation of the magnetic fields in each layer. The document explains how the magnetic fields are oriented to represent a 1 or 0, and how this affects the tunneling of polarized electrons across the junction, enabling data reading and writing.
Original Description:
group presentation
Original Title
MTJ
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses two types of computer memory technologies: SRAM and DRAM, and then focuses on Magnetoresistive random-access memory (MRAM) as a promising alternative. MRAM uses magnetic tunnel junctions (MTJs) as its basic memory unit. An MTJ consists of two ferromagnetic layers separated by a thin insulating layer, and it can store data as the relative orientation of the magnetic fields in each layer. The document explains how the magnetic fields are oriented to represent a 1 or 0, and how this affects the tunneling of polarized electrons across the junction, enabling data reading and writing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views9 pagesSRA M: Sram and Dram
Uploaded by
Shalabh SrivastavaThis document discusses two types of computer memory technologies: SRAM and DRAM, and then focuses on Magnetoresistive random-access memory (MRAM) as a promising alternative. MRAM uses magnetic tunnel junctions (MTJs) as its basic memory unit. An MTJ consists of two ferromagnetic layers separated by a thin insulating layer, and it can store data as the relative orientation of the magnetic fields in each layer. The document explains how the magnetic fields are oriented to represent a 1 or 0, and how this affects the tunneling of polarized electrons across the junction, enabling data reading and writing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
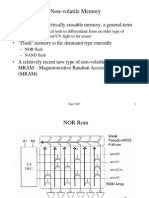
SRAM and DRAM
SEMICONDUCTOR
INDUSTRY
SRA
M
MRA
M
DRA
Magnetoresistive random access
memory
MRAM:
small size
low power consumption
non-volatility
Unit cells called MTJ
MAGNETIC TUNNEL JUNTIONS
(MTJ):
Thin insulating non-magnetic
material (IM) between the layers
of two ferromagnetic materials
NM
FM
Spin polarization -Ferromagnet
Ferromagnate shown is
pinned in specific direction
Unpolarised current passed
through ferromagnetic layer
Polarised current tunnels
through insulating layer (NM)
2nd FM
NM
1st FM
Magnetic tunnel junction-parallel
Free layer (2nd FM) has same
orientation as pinned Layer
(1st FM)
Polarised current tunnels
through NM
Current easily passes
through 2nd Layer
LOW MAGNETO
RESISTANCE MR
HIGH CONDUCTANCE G
7
FM
NM
FM
Magnetic tunnel junction-atiparallel
Free layer (2nd FM) has
opposite orientation as
pinned Layer (1st FM)
Polarised current tunnels
through NM
Polarised current is reflected
back by 2nd Layer
HIGH MAGNETO
RESISTANCE MR
LOW CONDUCTANCE G
7
Magnetic tunnel junction-DOS
DOS of each electron spin in the
ferromagnetic electrode shifted against
the other because of the exchange
splitting caused by the internal
magnetic field.
Electron states closer to the Fermi
energy predominantly contributes to
the tunneling current
Number of electrons that can tunnel
through the barrier is limited by the
number of filled states on the left
electrode and the number of unfilled
states on the right electrode
TMR = =
PL =
PR =
Transmission Electron Microscope - TEM
(001)
Transmission Electron Microscope - TEM
You might also like
- PPTDocument12 pagesPPTajaydev2224No ratings yet
- Magnetoresistive Random Access Memory (MRAM)Document29 pagesMagnetoresistive Random Access Memory (MRAM)sanjeevshrestyNo ratings yet
- Tariq Hashmat Tauheed: - Under The Supervision of Prof. M. HasanDocument23 pagesTariq Hashmat Tauheed: - Under The Supervision of Prof. M. HasanDudekula UsenNo ratings yet
- MFL Nava NDT Level III TipsDocument5 pagesMFL Nava NDT Level III TipsShanmuga Navaneethan100% (1)
- M-RAM (Magnetoresistive - RandomDocument46 pagesM-RAM (Magnetoresistive - RandomMuhammed ZakeerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SpintronicsDocument17 pagesIntroduction To SpintronicsPanchi Sharma0% (1)
- SpintronicsDocument39 pagesSpintronicsChandana Bl100% (3)
- Introduction To SpintronicsDocument24 pagesIntroduction To SpintronicsSudhish Kumar FeninNo ratings yet
- Spin-Transfer Torque MRAM (STT-MRAM) : Challenges and ProspectsDocument8 pagesSpin-Transfer Torque MRAM (STT-MRAM) : Challenges and ProspectsQueary OnlyNo ratings yet
- MRAMDocument15 pagesMRAMJoyitaNo ratings yet
- 3.1.1 Advantages: ModificationDocument20 pages3.1.1 Advantages: ModificationjoehodohNo ratings yet
- Magneto ResistanceDocument33 pagesMagneto ResistanceAkshdeep kaurNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SpintronicsDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Spintronicsram17yadav100% (1)
- Ling Zhou Mag SensorsDocument22 pagesLing Zhou Mag SensorsAboDilanNo ratings yet
- Physics and Applications of SpintronicsDocument16 pagesPhysics and Applications of SpintronicsPhaniendra KundetiNo ratings yet
- Spin Electronic DevicesDocument8 pagesSpin Electronic DevicesAmal RejiNo ratings yet
- Nanomagnetism: R. A. BuhrmanDocument26 pagesNanomagnetism: R. A. BuhrmanMohammad RameezNo ratings yet
- Fpga Implementation Technologies: Flash-Based FpgasDocument8 pagesFpga Implementation Technologies: Flash-Based FpgasdeekshaNo ratings yet
- Physics Assignment Presentation Sem-2Document16 pagesPhysics Assignment Presentation Sem-219L129 - SAMRITHA DNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Particle TestingDocument73 pagesMagnetic Particle TestingMAXX ENGINEERS0% (1)
- Form 3 or 4 Magnetism and Electromagnetism Notes For WebsiteDocument24 pagesForm 3 or 4 Magnetism and Electromagnetism Notes For Websiteapi-255989257No ratings yet
- Spin Tronic SDocument21 pagesSpin Tronic SSaleem MohamedNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Spintronic Transistors: P. Uma Sathyakam VIT UniversityDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Spintronic Transistors: P. Uma Sathyakam VIT UniversityANKUR KUMAR 20BEE0236No ratings yet
- Spintronic Memristors: Franklin Geo Francis E7B Roll No. 14 Guide: Mr. Binesh TDocument42 pagesSpintronic Memristors: Franklin Geo Francis E7B Roll No. 14 Guide: Mr. Binesh TAarathy UdayabhanuNo ratings yet
- Seminar Draft Report: Giant Magnetoresistance (GMR)Document24 pagesSeminar Draft Report: Giant Magnetoresistance (GMR)Jain MundasseryNo ratings yet
- SpintronicsDocument41 pagesSpintronicssamir_kumar_4No ratings yet
- MramDocument15 pagesMramVeerendra VermaNo ratings yet
- Magnetoresistive Random Access Memory: D1 D2 D3 B1 B2Document3 pagesMagnetoresistive Random Access Memory: D1 D2 D3 B1 B2SanjeebNo ratings yet
- Dilute Magnetic SemiconductorDocument35 pagesDilute Magnetic SemiconductorAli Khan100% (1)
- EE360 - Magnetic CircuitsDocument48 pagesEE360 - Magnetic Circuitsبدون اسمNo ratings yet
- 8-Magnetic CeramicsDocument23 pages8-Magnetic CeramicsbawokeNo ratings yet
- Spin Valve TransistorDocument29 pagesSpin Valve Transistorsuhail iqbalNo ratings yet
- Paper Presentation of SpintronicsDocument13 pagesPaper Presentation of SpintronicsSujith ReddyNo ratings yet
- Presentation Chapter 4 PDFDocument31 pagesPresentation Chapter 4 PDFsirawdinkgetachew15No ratings yet
- Letters: Electromotive Force and Huge Magnetoresistance in Magnetic Tunnel JunctionsDocument5 pagesLetters: Electromotive Force and Huge Magnetoresistance in Magnetic Tunnel Junctionsparra MedinaNo ratings yet
- Ch4 Ee5440 Part I TMR MramDocument45 pagesCh4 Ee5440 Part I TMR Mramcheng huangfuNo ratings yet
- SPINTRONICSDocument33 pagesSPINTRONICSSyam Pradeep ReddyNo ratings yet
- Non Volatile MemoryDocument16 pagesNon Volatile MemoryvinutkumarNo ratings yet
- M-Type Tubes - IntroductionDocument16 pagesM-Type Tubes - Introductionmrunal gajbhiye100% (3)
- Chapter 1. Introduction To Magnetic TestingDocument12 pagesChapter 1. Introduction To Magnetic TestingGaurav ChopraNo ratings yet
- Review Notes For RT10Document16 pagesReview Notes For RT10Daniel MontesNo ratings yet
- MPT-Test PresentationDocument38 pagesMPT-Test PresentationIrfan KhanNo ratings yet
- Ch.16 MagnetismDocument34 pagesCh.16 MagnetismPaul Levis RioNo ratings yet
- Spin Valve TransistorDocument29 pagesSpin Valve TransistorEeshan MishraNo ratings yet
- MagnetronDocument23 pagesMagnetronsahilNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Circuits: Satyam Kumar: 21SCSE1010304 Tushar Talan: 21SCSE1010405 Ankit Kumar: 21SCSE1011261Document13 pagesMagnetic Circuits: Satyam Kumar: 21SCSE1010304 Tushar Talan: 21SCSE1010405 Ankit Kumar: 21SCSE1011261SATYAM KUMAR 21SCSE1010304No ratings yet
- Transformers TheoryDocument67 pagesTransformers TheoryKansal Samarth100% (2)
- Magnetic Field and Field Lines-FDocument20 pagesMagnetic Field and Field Lines-FjamaluddinNo ratings yet
- 3.4. Magnetism Part 2 SDocument21 pages3.4. Magnetism Part 2 ShiransfNo ratings yet
- MagnetronDocument49 pagesMagnetronakceo4848No ratings yet
- Nanoelectronics 12: Department of ElectronicsDocument30 pagesNanoelectronics 12: Department of Electronicskandimalla_rajaneeshNo ratings yet
- T02 - Electromagnetism (Complete)Document24 pagesT02 - Electromagnetism (Complete)rvjf8bwrj2No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Magnets)Document53 pagesChapter 1 (Magnets)eyoule abdiNo ratings yet
- SpintronicsDocument13 pagesSpintronicsshailendraNo ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument5 pagesMagnetismAhmad ZebNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism Part 2Document24 pagesElectromagnetism Part 2MJ LopezNo ratings yet
- Synapse and Simulation SetupDocument3 pagesSynapse and Simulation SetupGovind NarasimmanNo ratings yet
- Spintronics: Presented by CH - PRAGATHI (11C31A0497)Document20 pagesSpintronics: Presented by CH - PRAGATHI (11C31A0497)SaNtosh KomakulaNo ratings yet
- Magneto-Resistive and Spin Valve Heads: Fundamentals and ApplicationsFrom EverandMagneto-Resistive and Spin Valve Heads: Fundamentals and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Small Dynamos and How to Make Them - Practical Instruction on Building a Variety of Machines Including Electric MotorsFrom EverandSmall Dynamos and How to Make Them - Practical Instruction on Building a Variety of Machines Including Electric MotorsNo ratings yet
- Scanning and Transmission Electron Microscopy: A Bit of Theory, A Lot of PracticeDocument37 pagesScanning and Transmission Electron Microscopy: A Bit of Theory, A Lot of PracticeShalabh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Phenomena in IN THIN FILMS AND MICROELECTRONIC MATERIALSDocument9 pagesDiffusion Phenomena in IN THIN FILMS AND MICROELECTRONIC MATERIALSShalabh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Laser Radiation Safety Course LDocument1 pageLaser Radiation Safety Course LShalabh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Game Theory: Mixed StrategiesDocument13 pagesGame Theory: Mixed StrategiesShalabh SrivastavaNo ratings yet