Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Germany Government
Uploaded by
api-2474866910 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
337 views1 pageThe president of Germany is elected for a five-year term by a federal convention. The chancellor is elected by a majority vote in The Bundestag for a four-year term. There are three different types of courts in Germany. Ordinary Court deals with common cases such as criminal and civil cases.
Original Description:
Original Title
germany government
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe president of Germany is elected for a five-year term by a federal convention. The chancellor is elected by a majority vote in The Bundestag for a four-year term. There are three different types of courts in Germany. Ordinary Court deals with common cases such as criminal and civil cases.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
337 views1 pageGermany Government
Uploaded by
api-247486691The president of Germany is elected for a five-year term by a federal convention. The chancellor is elected by a majority vote in The Bundestag for a four-year term. There are three different types of courts in Germany. Ordinary Court deals with common cases such as criminal and civil cases.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
MARCH 24th, 2015
ISSUE 1
VOL 1
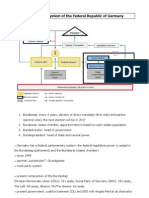
Government System of Germany
BACKGROUND:
The German government has a
bicameral parliament. There is an
upper house that consists of 69 seats
and a lower house of parliament that
consists of 598 deputies that are
elected for four years by the public.
The president of Germany is elected
for a five-year term by a federal
convention. Although the president is
the head of the state, they have little
influence on the government.
Germany also has a chancellor, elected
by the lower house of parliament, who
is the head of the government.
Germany consists of sixteen states
that have their own constitution and
legislature.
PRESIDENT:
The president is the head of the state
but has little to no actual power over
the government. During a federal
convention, the president is elected to
a five-year term. The convention
meets specifically for the election and
consists of the Bundestag and an
equal amount of elected members by
the state parliaments. Below is a
picture of the president of Germany,
Joachim Gauck.
BICAMERAL PARLIAMENT:
The Bundesrat, otherwise known as
the Federal Council and the upper
house, consists of 69 seats. Each state
has three to six representatives
determined by the states population.
The Bundestag, otherwise known as
the Federal Assembly or the lower
house of parliament, consists of 598
deputies. They are elected for four
years using direct voting and
proportional representations. If a party
wins more seats through direct voting
than they would have through
proportional representation more seats
are added.
THE COURTS OF GERMANY:
CHANCELLOR:
The chancellor is elected by a majority
vote in the Bundestag for a four-year
term. The first woman chancellor was
elected in 2005 and the chancellor
cannot be removed from office without
someone to succeed him or her. The
current chancellor is Angela Merkel.
She is also Forbes Magazines most
powerful woman in the world.
There are three different types of
courts in Germany.
Ordinary Court deals with common
cases such as criminal and civil cases.
Specialized Court hears challenges to
laws regarding fiscal, patent laws,
social, or labor.
Constitutional Court specializes is the
highest court and specializes in judicial
review.
You might also like
- Federal Republic of GermanyDocument4 pagesFederal Republic of GermanykalumyariNo ratings yet
- What Type of Government Does Germany HaveDocument2 pagesWhat Type of Government Does Germany HaveBryan PalmaNo ratings yet
- 2.5. Political System of GermanyDocument45 pages2.5. Political System of GermanyHemanth Kumar.SNo ratings yet
- Germany Gov System GcuDocument1 pageGermany Gov System Gcuapi-340854239No ratings yet
- Forms of GovernmentDocument2 pagesForms of GovernmentAni RukhadzeNo ratings yet
- Government System of GermanyDocument1 pageGovernment System of Germanyapi-279881853No ratings yet
- Paliament of GermanyDocument6 pagesPaliament of GermanyMujahid HassanNo ratings yet
- German GovDocument1 pageGerman Govapi-309379638No ratings yet
- Constitution of GermanyDocument11 pagesConstitution of GermanyAmmara KhalidNo ratings yet
- Comparative Legal System Assignment: Submitted By-Ishaan Khandelwal SM0119024Document9 pagesComparative Legal System Assignment: Submitted By-Ishaan Khandelwal SM0119024Ishaan KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Germany (Short Guide)Document4 pagesGermany (Short Guide)OLi ViaNo ratings yet
- Government System of Germany IIDocument1 pageGovernment System of Germany IIapi-279875155No ratings yet
- GermanyDocument2 pagesGermanyAlberto BielsaNo ratings yet
- Comparing GovernmentsDocument11 pagesComparing Governmentsapi-285956493No ratings yet
- Democracy Case Studies: Great Britain France GermanyDocument28 pagesDemocracy Case Studies: Great Britain France Germanyapi-3699641No ratings yet
- Federal Republic of GermanyDocument21 pagesFederal Republic of GermanyLawrence Gerald Lozada BerayNo ratings yet
- German GovernmentDocument1 pageGerman Governmentapi-282427998No ratings yet
- French and German LegislatureDocument7 pagesFrench and German LegislatureTariq KhanNo ratings yet
- Political System of GermanyDocument11 pagesPolitical System of GermanyMartina RadevskaNo ratings yet
- GermanyDocument15 pagesGermanyIraNo ratings yet
- German Constitution - An OverviewDocument22 pagesGerman Constitution - An OverviewThakur Manu PratapNo ratings yet
- Senior Ss ProjectDocument15 pagesSenior Ss Projectapi-317453657No ratings yet
- German GovernmentDocument1 pageGerman Governmentapi-339852413No ratings yet
- Lecture Espagne Et AllemagneDocument20 pagesLecture Espagne Et AllemagneabellefevreNo ratings yet
- Germany Government ComparisonDocument13 pagesGermany Government Comparisonapi-286033529No ratings yet
- 111 Germany CompilationDocument9 pages111 Germany CompilationMark Anthony Sañosa ArancinaNo ratings yet
- Politics of GermanyDocument69 pagesPolitics of GermanyJericko Perez AvilaNo ratings yet
- French ConstitutionDocument18 pagesFrench ConstitutionAmmara KhalidNo ratings yet
- Document (32) 1Document5 pagesDocument (32) 1Jawad ShahNo ratings yet
- France Pol. SystemDocument4 pagesFrance Pol. Systemsym_symNo ratings yet
- Newsletter of GermanyDocument3 pagesNewsletter of Germanyapi-239402332No ratings yet
- Germen Legal SystemDocument3 pagesGermen Legal Systemsvadha89No ratings yet
- Constitution of GermanyDocument9 pagesConstitution of GermanyAamir Hussain100% (1)
- Bundestag: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument7 pagesBundestag: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchirfanmNo ratings yet
- German GovernmentDocument1 pageGerman Governmentapi-325023148No ratings yet
- The Constitution of GermanyDocument12 pagesThe Constitution of GermanymbrijbhushanNo ratings yet
- French Government Guide 2012Document16 pagesFrench Government Guide 2012Mohamad FirdausNo ratings yet
- SCRIPTDocument10 pagesSCRIPTPhạm Gia NgọcNo ratings yet
- Referat The System of Government in Romania Compared To That of The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandDocument4 pagesReferat The System of Government in Romania Compared To That of The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Irelandandreil49875No ratings yet
- The PresidentDocument2 pagesThe Presidentapi-308905583No ratings yet
- FederalGovernment Group1Document43 pagesFederalGovernment Group1marklester liquiganNo ratings yet
- Franch Constituiton by Yasir FarhadDocument4 pagesFranch Constituiton by Yasir FarhadSaeeda AwanNo ratings yet
- Government in GermanyDocument2 pagesGovernment in Germanyapi-340183621No ratings yet
- System in AustriaDocument5 pagesSystem in AustriaLiliana ClimNo ratings yet
- French GovernmentDocument2 pagesFrench GovernmentPriya DasNo ratings yet
- One Nation One ElectionDocument7 pagesOne Nation One ElectionNikhil SinghNo ratings yet
- 05 Barcelona PoliticalsystemgermanyDocument1 page05 Barcelona Politicalsystemgermanyapi-282714140No ratings yet
- The British and German Political Systems 2Document1 pageThe British and German Political Systems 2xinerd2007No ratings yet
- The French RepublicDocument11 pagesThe French RepublicPhạm Gia NgọcNo ratings yet
- The UK Political SystemDocument1 pageThe UK Political SystemAnna MokeevaNo ratings yet
- GermanyDocument9 pagesGermanyAlberto BielsaNo ratings yet
- France Government SystemDocument1 pageFrance Government Systemapi-206879538No ratings yet
- French Constitution - Features, Comparison With Indian + Other Constitutions - CivilsdailyDocument7 pagesFrench Constitution - Features, Comparison With Indian + Other Constitutions - CivilsdailyAbhishek KhalkhoNo ratings yet
- Cosnita Andreea Florentina - Comparison Between The System of Government Romania - The United KingdomDocument4 pagesCosnita Andreea Florentina - Comparison Between The System of Government Romania - The United KingdomAndy AndreeaNo ratings yet
- A SHORT GUIDE TO THE French Political SystemDocument7 pagesA SHORT GUIDE TO THE French Political SystemKhalil AhmedNo ratings yet
- MONARCHY Vs REPUBLICDocument2 pagesMONARCHY Vs REPUBLICCordovilla10No ratings yet
- GovernmentnewsletterDocument2 pagesGovernmentnewsletterapi-280910440No ratings yet
- Dalton, Politics in Germany - Chapter 2Document12 pagesDalton, Politics in Germany - Chapter 2MicaNo ratings yet
- Politics of SwitzerlandDocument5 pagesPolitics of SwitzerlandNemanja NegrićNo ratings yet