Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Air Prop
Uploaded by
Wrya SaeedOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Air Prop
Uploaded by
Wrya SaeedCopyright:
Available Formats
Calculation of ideal gas properties of dry air (h, u, and c) from the equation (T in K)
c p a bT cT 2 dT 3 ,
kJ
kmol K
Data and constants
Gas contant (Ru):
Mol wt (MW):
cp/cv at 300 K:
Coef. for cp and h:
273 K < T <1800 K
8.31447 kJ/(kmol K)
28.97 kg/kmol
1.4
a
b
c
d
28.11
1.967E-03 4.802E-06 -1.966E-09
e
131.31
Calculation of h, u, cp, cv, and k where T is INPUT. Reference temperature is 298.15 K.
h aT
INPUT T:
h=
h=
u=
u=
cp =
cp =
cv =
cv =
k=
b 2 c 3 d 4
kJ
T T T e,
2
3
4
kmol
1000
30334.0
1047.08
22019.5
760.08
32.913
1.1361
24.599
0.84910
1.3380
K
kJ/kmol
kJ/kg
kJ/kmol
kJ/kg
kJ/(kmol K)
kJ/(kg K)
kJ/(kmol K)
kJ/(kg K)
u h RuT ,
kJ
kmol
cv c p Ru ,
kJ
kmol K
cp Ru ,
kJ
kmol K
cp
cv
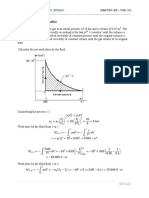
Calculation of T2, h2, and u2 given s1 = s2, P2, P1, and T1 using the equation
a ln
INPUT P2:
INPUT P1:
INPUT T1:
T2
P
c
d
b(T2 T1 ) T22 T12 T23 T13 Ru ln 2 0
T1
2
3
P1
(1)
500 kPa
100 kPa
300 K
Estimate T2 using constant, room temperature specific heats from the equation
T2 P2
T1 P1
Estimated T2:
k 1
k
475.1459 K
Calculate T2, h2, and u2 using Goal Seek and variable specific heats.
T2 =
Solve (1)
h2 =
h2 =
u2 =
u2 =
472.5867
0.000797
13779.8
475.6577
9850.496
340.024
K
(use Goal Seek to set this to zero by varying cell B21)
kJ/kmol
kJ/kg
kJ/kmol
kJ/kg
Calculation of T2, h2, and u2 given s1 = s2, v2, v1, and T1 using the equation
a Ru ln
INPUT V2:
INPUT V1:
INPUT T1:
T2
v
c
d
b(T2 T1 ) T22 T12 T23 T13 Ru ln 2 0
T1
2
3
v1
1 m^3/kg
10 m^3/kg
300 K
Estimate T2 using constant, room temperature specific heats from the equation
T2 v1
T1 v 2
Estimated T2:
k 1
753.5659 K
Calculate T2, h2, and u2 using Goal Seek and variable specific heats.
T2 =
Solve (1)
h2 =
h2 =
u2 =
u2 =
725.8582
-0.000334
21529.07
743.1505
15493.95
534.8272
K
(use Goal Seek to set this to zero by varying cell B21)
kJ/kmol
kJ/kg
kJ/kmol
kJ/kg
(1)
You might also like
- Air PropDocument4 pagesAir Propanup_nairNo ratings yet
- Solution Week 9Document6 pagesSolution Week 9Ariadne ChuaNo ratings yet
- HW 5 SolnDocument7 pagesHW 5 SolnNik Hafiy HafiziNo ratings yet
- BSGS Sample Problems 2 - BB CollabDocument21 pagesBSGS Sample Problems 2 - BB CollabNeo GarceraNo ratings yet
- Unit Nine Homework Solutions, November 9, 2010: V V R T T C S S Const C If V V R T DT C S SDocument5 pagesUnit Nine Homework Solutions, November 9, 2010: V V R T T C S S Const C If V V R T DT C S SAbubakar AdeniNo ratings yet
- Ciclo BraytonDocument17 pagesCiclo BraytonNubia Bergamini100% (2)
- Thermodynamics (Solved Prob)Document22 pagesThermodynamics (Solved Prob)Jubert Perez100% (1)
- Pipe Solved ProbsetDocument115 pagesPipe Solved ProbsetRemae Garci100% (1)
- ThermodynamicsDocument14 pagesThermodynamicssarathNo ratings yet
- Thermo 5th Chap09 P001Document39 pagesThermo 5th Chap09 P001Ahmad AlgarniNo ratings yet
- ME 24-221 Thermodynamics I Solutions To Extra Problems in Chapter 9: November 17, 2000 J. MurthyDocument6 pagesME 24-221 Thermodynamics I Solutions To Extra Problems in Chapter 9: November 17, 2000 J. MurthyKen Joshua ValenciaNo ratings yet
- CHE Thermodynamics Make-up Exam Q2 (40chDocument3 pagesCHE Thermodynamics Make-up Exam Q2 (40chkellykapperNo ratings yet
- HWSolutions PDFDocument42 pagesHWSolutions PDFJames AhnNo ratings yet
- Thermo 5th Chap17 P096Document19 pagesThermo 5th Chap17 P096UTA - Std - Elvin ChantreNo ratings yet
- A Stationary GasDocument10 pagesA Stationary GassugiantobarusNo ratings yet
- Unit Four Homework Solutions, September 23. 2010: Mechanical Engineering 370 ThermodynamicsDocument3 pagesUnit Four Homework Solutions, September 23. 2010: Mechanical Engineering 370 ThermodynamicsRengganis Putri ParmudyaNo ratings yet
- A Stationary GasDocument9 pagesA Stationary GassugiantobarusNo ratings yet
- CH 09Document22 pagesCH 09hirenpatel_universalNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document34 pagesCH 10hirenpatel_universalNo ratings yet
- Solution #9Document7 pagesSolution #9KinnonPangNo ratings yet
- K 1.4 (Table A-2)Document1 pageK 1.4 (Table A-2)Mohamad FaruqNo ratings yet
- An Air-Standard Cycle Is Executed in A Closed SysDocument1 pageAn Air-Standard Cycle Is Executed in A Closed SysVincent BaguioNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Worked ExamplesDocument13 pagesThermodynamics Worked ExamplesSalah Salman100% (1)
- Tutorial 3 - Question 3Document1 pageTutorial 3 - Question 3DiablofireZANo ratings yet
- CHEM E6100 Exercise 2 2021Document1 pageCHEM E6100 Exercise 2 2021Shivarya Naskar 4-Yr B.Tech.: Ceramic Engg., IIT(BHU)No ratings yet
- Refrigeration Moran Shapiro Solution ManualDocument10 pagesRefrigeration Moran Shapiro Solution ManualNovaCastilloNo ratings yet
- Alcorcon PIPE Merged SolvedDocument80 pagesAlcorcon PIPE Merged SolvedBernalynMalinaoNo ratings yet
- Alcorcon Engineering Review Center: Power & Industrial Plant EngineeringDocument13 pagesAlcorcon Engineering Review Center: Power & Industrial Plant EngineeringNeil SequioNo ratings yet
- Brayton cycle analysis with compressor and turbine efficienciesThe title "TITLE Brayton cycle analysis with compressor and turbine efficienciesDocument52 pagesBrayton cycle analysis with compressor and turbine efficienciesThe title "TITLE Brayton cycle analysis with compressor and turbine efficienciesGiuseppe TestarossaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Exams PapersDocument23 pagesThermodynamics Exams PapersAbdul HafizNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermodynamics Exam 2018 Wirh SolutionsDocument9 pagesApplied Thermodynamics Exam 2018 Wirh SolutionsFarouk BassaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document9 pagesChapter 3ustadali12371% (7)
- Assignment3 TER1YDocument2 pagesAssignment3 TER1YBogdan ŞipoşNo ratings yet
- ME 24-221 Thermodynamics I Solutions Entropy ChangeDocument4 pagesME 24-221 Thermodynamics I Solutions Entropy ChangeMarcelo AlegriaNo ratings yet
- Department of Chemical Engineering, NITKDocument4 pagesDepartment of Chemical Engineering, NITKDechenPemaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Examples&SolutionDocument42 pagesChapter 9 Examples&SolutionSami ullahNo ratings yet
- Gas CycleDocument9 pagesGas CycleYahya Tawakal100% (1)
- Solution To Exam No. 2Document5 pagesSolution To Exam No. 2mozam haqNo ratings yet
- Me 354 Tutorial, Week #9 Jet-Propulsion Cycle: T (K) P (Kpa) 1 241 32 2 3 4 1400 P 5 6 32Document6 pagesMe 354 Tutorial, Week #9 Jet-Propulsion Cycle: T (K) P (Kpa) 1 241 32 2 3 4 1400 P 5 6 32Ken RequitilloNo ratings yet
- 2nd Law Analysis For A Control VolumeDocument13 pages2nd Law Analysis For A Control VolumeSergey ShkapovNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas EntropyDocument6 pagesIdeal Gas EntropyAlan A. AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Thermo ProblemsDocument8 pagesThermo ProblemsChrister John UyNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document63 pagesCH 3Hoi An Sze100% (7)
- HW 10Document2 pagesHW 10hangman001No ratings yet
- Gibbs Free Energy and Thermodynamic Functions ExplainedDocument40 pagesGibbs Free Energy and Thermodynamic Functions ExplainedDaniel Alvarez Vega67% (6)
- Engineering Science LGD 10703: Ideal GasDocument7 pagesEngineering Science LGD 10703: Ideal GasazzraNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.1ADocument53 pagesProblem 5.1ALuis PiscalNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Power Point - 3 - Thermodynamics & Heat CapacitiesDocument19 pagesMicrosoft Power Point - 3 - Thermodynamics & Heat CapacitiesHemanth KumarNo ratings yet
- Problems and SolutionsDocument37 pagesProblems and Solutionsalfrinjarj100% (2)
- Chemical Engineering Principles SATsDocument7 pagesChemical Engineering Principles SATsAli Hamza ManzoorNo ratings yet
- ALCORCON ENGINEERING REVIEW CENTER MECHANICAL ENGINEERING REFRESHER SET 1Document14 pagesALCORCON ENGINEERING REVIEW CENTER MECHANICAL ENGINEERING REFRESHER SET 1Neil SequioNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument84 pagesReviewerEdmil Jhon Ariquez100% (6)
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Handbook of Energy Data and Calculations: Including Directory of Products and ServicesFrom EverandHandbook of Energy Data and Calculations: Including Directory of Products and ServicesNo ratings yet
- Busbar RatingDocument64 pagesBusbar RatingAbdulla Nashith100% (1)
- وجية جرجس جزء 1Document207 pagesوجية جرجس جزء 1Anonymous mghI7I7pNo ratings yet
- VFD-S ΔϠδϠγ ϡΪΨΘγ ϞΒϗ ΐΘΘϜϟ άϫ ΎϤΩ ήϗDocument84 pagesVFD-S ΔϠδϠγ ϡΪΨΘγ ϞΒϗ ΐΘΘϜϟ άϫ ΎϤΩ ήϗWrya SaeedNo ratings yet
- Classic Control Course - Tamer AhmedDocument55 pagesClassic Control Course - Tamer Ahmedwadhahesmaeel100% (6)
- Bearing Capacity of Different Types of Soil - Engineering DiscoveriesDocument13 pagesBearing Capacity of Different Types of Soil - Engineering DiscoveriesWrya SaeedNo ratings yet
- تلخيص كود NEC في 200 صفحة فقطDocument204 pagesتلخيص كود NEC في 200 صفحة فقطWrya Saeed100% (1)
- 4 Essential Ground-Fault Protective Schemes You Should Know About - EEPDocument16 pages4 Essential Ground-Fault Protective Schemes You Should Know About - EEPWrya SaeedNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Design InformationDocument47 pagesPower Plant Design InformationSISWANTO100% (1)
- Ger 3183Document14 pagesGer 3183santoshkumar777No ratings yet
- Classic Control Course - Tamer AhmedDocument55 pagesClassic Control Course - Tamer Ahmedwadhahesmaeel100% (6)
- 15 Busbar ProtectionDocument21 pages15 Busbar ProtectionSristick100% (8)
- Lossofexcitation 130805045350 Phpapp01Document52 pagesLossofexcitation 130805045350 Phpapp01ahvaz1392bNo ratings yet
- Busbar RatingDocument64 pagesBusbar RatingAbdulla Nashith100% (1)
- 100% Stator Ground Fault Protection of Alternators by Low Frequency Injection and Using Real Power SignalDocument6 pages100% Stator Ground Fault Protection of Alternators by Low Frequency Injection and Using Real Power SignalWrya SaeedNo ratings yet
- Basics of SwitchboardsDocument60 pagesBasics of SwitchboardsRui Pedro SousaNo ratings yet
- Feeding System PDFDocument52 pagesFeeding System PDFWrya SaeedNo ratings yet
- مراحل التصميم المختلفة -كهرباءDocument5 pagesمراحل التصميم المختلفة -كهرباءWrya SaeedNo ratings yet
- Cathodic ProtectionDocument22 pagesCathodic ProtectionFakhr-e-Alam100% (1)
- Basics of Surge Protection SIEMENSDocument44 pagesBasics of Surge Protection SIEMENScleyvasNo ratings yet
- Lighting Design Part.1Document29 pagesLighting Design Part.1Wrya SaeedNo ratings yet
- Process Control Fundamentals 2Document73 pagesProcess Control Fundamentals 2Otuekong Ukpong100% (2)
- Book How They Work Hydraulics PDFDocument41 pagesBook How They Work Hydraulics PDFWrya SaeedNo ratings yet
- Guide For LV Compensation CubiclesDocument44 pagesGuide For LV Compensation CubiclesARVINDNo ratings yet
- Basics of SwitchboardsDocument60 pagesBasics of SwitchboardsRui Pedro SousaNo ratings yet
- Shneider PDFDocument87 pagesShneider PDFWrya SaeedNo ratings yet
- تقدير الاحمال الكهربية لأي مبنيDocument5 pagesتقدير الاحمال الكهربية لأي مبنيWrya SaeedNo ratings yet
- IESLuxLevel 1Document12 pagesIESLuxLevel 1tr_nisitNo ratings yet
- NEW Chapter 13 Generator Protection PDFDocument70 pagesNEW Chapter 13 Generator Protection PDFWrya SaeedNo ratings yet
- مراحل التصميم المختلفة -كهرباءDocument5 pagesمراحل التصميم المختلفة -كهرباءWrya SaeedNo ratings yet