Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2nd Benchmark Study Guide With Answers
Uploaded by
api-244714189Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2nd Benchmark Study Guide With Answers
Uploaded by
api-244714189Copyright:
Available Formats
Name ________________________
Class __________________________
th
nd
2 9 Weeks Benchmark Study GuideBenchmark is Wednesday, December 17 !!!
1. The process by which a gas changes to a liquid is called condensation
2. The main forms of precipitation are rain and snow
3. In dry weather, the level of the water table in an area drops
5. Old Faithful is a geyser
6. The main threat to rivers is human pollution
7. A pump is usually used to get water from a well
8. Artificial lakes are called reservoir
9. Most of the fresh water that is found on Earth is found in glaciers and polar ice caps
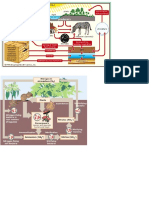
10. The repeated movement of water between Earth and the Atmosphere is called the water
cycle
11. Water that falls to Earth from the atmosphere is precipitation
14. When water absorbs enough heat, it evaporates
15. A tiny hole or space is a pore
16. Water that collects in pores and sinks into the ground is groundwater
17. A scientist who studies Earths water is called hydrologist
18. Upper layer of saturated rock and soil is the water table
19. Part of a river where the water is swift are the rapids
20. If a river has rapids and waterfalls then it is a youthful river.
21. A youthful river has fast moving water and a steep slope.
22. An old river has very slow movement.
23. An old river floods easily
24. A kettle/glacial lake forms after a retreating glacier.
25. Surface currents are formed by prevailing winds
26. When waves come near the shore, they break up and speed up.
27. Salt water will become denser if there is an increase in salinity
28. The gravitational pull that the moon exerts on Earth causes tides
29. The Coriolis effect is caused by the rotation of the earth
30. Deep currents are formed as water density changes
31. Streamlike movements of water that occur at or near the surface of the ocean are called
surface currents.
32. The curving of moving objects from a straight path due to the Earth's rotation is called the
Coriolis Effect.
33. If the ocean water freezes at the surface, ice will float on top of the water because ice is less
dense than liquid water. The dissolved solids are squeezed out of the ice and enter the liquid
water below the ice, causing its salinity to increase
34. When water contains more dissolved solids, its salinity increases.
35. Evaporation of surface water causes the salinity to increase.
Examine the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
36.
Number 2 indicates a wavelength.
37.
Number 1 indicates a crest.
38.
Number 4 indicates a wave height.
39.
Number 3 indicates a trough.
Examine the illustration below, and answer the questions that follow.
40. High tide occurs at 1 and 3.
41. Low tide occurs at 2 and 4.
42. Rust is produced by the oxidation of iron
43. The process in which water freezes and widens cracks in rock is called ice wedging
44. In nature, abrasion is the action of rocks and sediment grinding against each other and
wearing away exposed surfaces.
45. Plants can erode rock with their roots (mechanically) or leaves
(chemically)
Examine the diagram, and answer the question that follows.
46. Carbonic acid and limestone most likely caused the formations in the diagram above?
47. A kettle lake/glacial lake is a depression created by a glacier that usually gets filled with
water to form a lake or pond?
48. If enough rock falls from a mountain, a pile called a talus forms at the base of the slope.
49. All slopes undergo a very slow mass movement, called creep
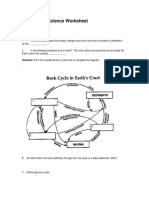
50. Explain the rock cycle and the ways in which each rock type is formed. _All rocks undergo
the rock cycle. Igneous rocks are formed by cooled lava or magma. Sedimentary rocks are
formed by compaction and cementation. Metamorphic rocks are formed by heat and pressure.
Any time a rock undergoes these things, other types of rocks are formed. For example, if a
sedimentary rock heats up and cools again, it will become an igneous rock. If a metamorphic
rock breaks up and compacts and cements, it will become a sedimentary rock, etc.
Parent signature _________________________________
You might also like
- Mike Bickle Interview PDFDocument18 pagesMike Bickle Interview PDFAnthony D'Angelo100% (1)
- Moon Surface Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesMoon Surface Lesson Planapi-382263458No ratings yet
- Lithostratigraphy - WikipediaDocument10 pagesLithostratigraphy - Wikipediamae mahiyaNo ratings yet
- 10 HauserDocument4 pages10 HauserBeatriz ChilenoNo ratings yet
- 2.4 The Water CycleDocument4 pages2.4 The Water CycleKabir MdNo ratings yet
- Water CycleDocument61 pagesWater CycleMahenor EmadNo ratings yet
- The Water CycleDocument7 pagesThe Water Cyclekonkurs.wiedzy.o.irlandii.zschNo ratings yet
- Final Activity Sheet Week 1Document10 pagesFinal Activity Sheet Week 1Arlyn Pong Pling Pio100% (1)
- DumpDocument5 pagesDumpErick John FrontetasNo ratings yet
- The Water Cycle in 40 CharactersDocument6 pagesThe Water Cycle in 40 CharactersTridarsh ParakhNo ratings yet
- 1.3 The HydrosphereDocument5 pages1.3 The HydrosphereAnaNo ratings yet
- Our Changing Earth-Worksheet-Grade 7Document2 pagesOur Changing Earth-Worksheet-Grade 7mohamedfarhaan156No ratings yet
- KARAKTERISTIK HIDROSFERDocument1 pageKARAKTERISTIK HIDROSFEROktavia DitaNo ratings yet
- Origin of Water in EarthDocument2 pagesOrigin of Water in EarthDr. Nitish Priyadarshi100% (1)
- Water CycleDocument49 pagesWater CycleLyka Jane PesiganNo ratings yet
- Materials of The EarthDocument23 pagesMaterials of The Earthapi-422428700No ratings yet
- Geo definitions for weathering, tides, ocean currents and moreDocument3 pagesGeo definitions for weathering, tides, ocean currents and moreananya kNo ratings yet
- Water Cycle 1.1.1 (C-D)Document5 pagesWater Cycle 1.1.1 (C-D)Royal ComedianNo ratings yet
- Self Learning Module (SLM) : Earth ScienceDocument28 pagesSelf Learning Module (SLM) : Earth ScienceSofia Marie ChenNo ratings yet
- The Water CycleDocument5 pagesThe Water CycleMekala WithanaNo ratings yet
- Our Changing Earth NotesDocument3 pagesOur Changing Earth Notesaryan10No ratings yet
- Description of The Hydrologic CycleDocument9 pagesDescription of The Hydrologic CycleGaneswaraNo ratings yet
- Short Questions 5212Document10 pagesShort Questions 5212ganesh kallaNo ratings yet
- The Water Cycle Powerpoint - Ver - 3Document10 pagesThe Water Cycle Powerpoint - Ver - 3PreeNo ratings yet
- 142 Sol Amazing Facts Round RobinDocument5 pages142 Sol Amazing Facts Round RobinIchal PuzoNo ratings yet
- Short Questions 5213Document10 pagesShort Questions 5213ganesh kallaNo ratings yet
- Short Questions 520Document10 pagesShort Questions 520ganesh kallaNo ratings yet
- Short Questions 52134Document10 pagesShort Questions 52134ganesh kallaNo ratings yet
- 6 Water Cycle Transfer of EnergyDocument3 pages6 Water Cycle Transfer of EnergyTheodoreNo ratings yet
- Group 1 ReportDocument19 pagesGroup 1 ReportKimmy Jane FloresNo ratings yet
- Water CycleDocument11 pagesWater CycleVon Jerom Ocampo VirtucioNo ratings yet
- Landforms and Forces QuizDocument10 pagesLandforms and Forces Quizganesh kallaNo ratings yet
- 403 - Activities About The Hydrosphere.Document5 pages403 - Activities About The Hydrosphere.ULISESNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument1 pageQuestionsGabriel CarsaladeNo ratings yet
- Properties of Liquids and Role of WaterDocument4 pagesProperties of Liquids and Role of WaterKC MasedmanNo ratings yet
- All About EarthDocument5 pagesAll About EarthAnnalisa TealdiNo ratings yet
- 1st Q Worksheet 2 Energy CyclesDocument13 pages1st Q Worksheet 2 Energy CyclesCornelio T. BavieraNo ratings yet
- Hydrosphere Notes GeoDocument8 pagesHydrosphere Notes GeoMary Ingrid BumatayNo ratings yet
- Earth Science: WeatheringDocument4 pagesEarth Science: WeatheringLucky GeminaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Rain, Thunder and LightningDocument3 pagesChapter 13 Rain, Thunder and Lightningbittuchintu100% (1)
- Water CycleDocument10 pagesWater CycleBagongNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Quarter 2 Week 1 - Ruby May AquinoDocument11 pagesEarth Science Quarter 2 Week 1 - Ruby May AquinoRuby AquinoNo ratings yet
- List of Terms Earth and Space ScienceDocument5 pagesList of Terms Earth and Space Scienceapi-345837027No ratings yet
- Water Cycle - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument10 pagesWater Cycle - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediasofianina05No ratings yet
- 5 Impending Signs of Landslides and Sinkholes Continuation... Feb. 8 2021Document23 pages5 Impending Signs of Landslides and Sinkholes Continuation... Feb. 8 2021Shiela Jean H. RescoNo ratings yet
- Water ResourcesDocument27 pagesWater Resourcessharon ranjitha paulNo ratings yet
- The Sun Powers the Water CycleDocument6 pagesThe Sun Powers the Water CycleCinta KimiaNo ratings yet
- Explanation WatercycleDocument1 pageExplanation WatercycleGita NoviantiNo ratings yet
- UD 3 The Hydrosphere 1º ESO PDFDocument7 pagesUD 3 The Hydrosphere 1º ESO PDFPaulaNo ratings yet
- The Water Cycle Explained in 40 CharactersDocument3 pagesThe Water Cycle Explained in 40 CharactersNaveen PrabhuNo ratings yet
- ELS Worksheet (Grade 11)Document4 pagesELS Worksheet (Grade 11)Kristhia Cyra RiveraNo ratings yet
- Hydrologic Cycle and Water Cycle: (Summary)Document1 pageHydrologic Cycle and Water Cycle: (Summary)Francess Mae AlonzoNo ratings yet
- The Water Cycle: Answer The Following QuestionsDocument1 pageThe Water Cycle: Answer The Following Questionsapi-297681510No ratings yet
- Exogenic Processes or Denudation: 2 Semester: Earth ScienceDocument5 pagesExogenic Processes or Denudation: 2 Semester: Earth ScienceLeshauna CaleighNo ratings yet
- September Science Notes - )Document7 pagesSeptember Science Notes - )CyrusquinonesNo ratings yet
- Lo 1Document7 pagesLo 1Ali Ehab Talaat Abd Elazeem علي ايهاب طلعت عبد العظيمNo ratings yet
- 3 The Water CycleDocument2 pages3 The Water CycleiggyNo ratings yet
- PDC Topic - Understanding and Designing For A Bioregions Climate and Landscape - Terra PermaDocument18 pagesPDC Topic - Understanding and Designing For A Bioregions Climate and Landscape - Terra Permagns_vcNo ratings yet
- ES8005 Mid Term2Document5 pagesES8005 Mid Term2heartisrechargedNo ratings yet
- Geography ch-5 NotesDocument20 pagesGeography ch-5 NotesMASTER RK7No ratings yet
- ESE150-2 M1 HW3 VillaramaDocument6 pagesESE150-2 M1 HW3 VillaramaThortheGreayNo ratings yet
- Evaporation, Transpiration and Precipitation | Water Cycle for Kids | Children's Water BooksFrom EverandEvaporation, Transpiration and Precipitation | Water Cycle for Kids | Children's Water BooksNo ratings yet
- To A Rocky MoonDocument524 pagesTo A Rocky Moonnevadamike_001No ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science LESSON 7Document60 pagesEarth and Life Science LESSON 7Kayla Kaye MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- Geological Characteristics of Epithermal Precious and Base Metal DepositsDocument38 pagesGeological Characteristics of Epithermal Precious and Base Metal DepositsRenzo YaringañoNo ratings yet
- Rossi, Marcianus Filomeno - A Trip To MarsDocument110 pagesRossi, Marcianus Filomeno - A Trip To Marspoutourrou0% (1)
- Technology and Livelihood Education NAILCARE 9 & 10Document4 pagesTechnology and Livelihood Education NAILCARE 9 & 10corazon cellonaNo ratings yet
- Authentic Listening: Arts, Science, Travel Advice and VolcanoesDocument4 pagesAuthentic Listening: Arts, Science, Travel Advice and VolcanoesTrần Minh Trang Đặng0% (1)
- Engineering Geology Site VisitDocument31 pagesEngineering Geology Site VisitIkhwan Z.79% (14)
- Solution Manual For The Earth System 3 e 3rd Edition Lee R Kump James F Kasting Robert G CraneDocument14 pagesSolution Manual For The Earth System 3 e 3rd Edition Lee R Kump James F Kasting Robert G CraneShawnPerryopke100% (36)
- Global Warming and Climate Change: Causes and EffectsDocument22 pagesGlobal Warming and Climate Change: Causes and EffectsRonix Ong100% (1)
- Rocks and Minerals Practice TestDocument13 pagesRocks and Minerals Practice TestlastofspadesNo ratings yet
- National Parks: A Kid's Guide To America's Parks, Monuments, and LandmarksDocument22 pagesNational Parks: A Kid's Guide To America's Parks, Monuments, and LandmarksBlack Dog & Leventhal100% (4)
- DRRR-Week 3Document5 pagesDRRR-Week 3Ren Andaleon CortezNo ratings yet
- Summative Test Earth and Space 10 Name: - Grade/Section: - ScoreDocument4 pagesSummative Test Earth and Space 10 Name: - Grade/Section: - ScoreZy RianNo ratings yet
- J 1751-3928 2006 tb00284 XDocument26 pagesJ 1751-3928 2006 tb00284 XdamasM1No ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science - Grade 11,12 - Test QuestionsDocument8 pagesEarth and Life Science - Grade 11,12 - Test QuestionsNice D. ElseNo ratings yet
- Mid-term English Test AnswersDocument21 pagesMid-term English Test AnswersĐức Anh TrịnhNo ratings yet
- Greece BrochureDocument12 pagesGreece Brochureapi-217451912No ratings yet
- Clinical Impressions Volume12no2Document33 pagesClinical Impressions Volume12no2audrey100% (1)
- Alterasi DiengDocument4 pagesAlterasi DiengKing Abdul AzizNo ratings yet
- Why Study History in 40 CharactersDocument106 pagesWhy Study History in 40 CharactersAnkur Bhatnagar100% (1)
- SEACG2020 Parallel SessionDocument1 pageSEACG2020 Parallel SessionRamadhani Yasyfi CyselaNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Volcano HazardsDocument7 pagesDifferent Types of Volcano HazardsMa. Michaela Agape EstacioNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Module 10: Movements of Plates and Formation of Folds and FaultsDocument24 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Module 10: Movements of Plates and Formation of Folds and FaultsRhy cabanes123100% (5)
- Final Examination in Science 6: St. Joseph College of Canlaon, IncDocument20 pagesFinal Examination in Science 6: St. Joseph College of Canlaon, IncALVEN OYANGORINNo ratings yet
- Voicu GoldMetallogenyGuianaShieldDocument26 pagesVoicu GoldMetallogenyGuianaShieldMarco AponteNo ratings yet
- Geologic Evolution of The Himalayan Tibetan Orogen 205 PDFDocument73 pagesGeologic Evolution of The Himalayan Tibetan Orogen 205 PDFmohanongcNo ratings yet