Professional Documents
Culture Documents
VTU 10CS32 Question Bank
Uploaded by
hanumantha12Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
VTU 10CS32 Question Bank
Uploaded by
hanumantha12Copyright:
Available Formats
Electronic Circuits
10CS32
VTU QUESTION BANK
UNIT-1: TRANSISTORS, UJTs, AND THYRISTORS
1. With neat figure, explain the construction and operational principle of an Unijunction
Transistor (UJT).
(10 marks) (July 2013)
2. Explain the effects of collector resistor, base current and supply voltage on the
operating point of a fixed bias circuit. Which is the ideal position for an operating
point on
the BJT fixed bias transistor circuit? Explain the above with neat diagrams.
(10 marks) (June 2012)
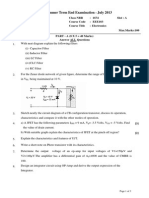
3. What is the operating point for the following voltage divider bias circuit?
(10 marks) (June 2012)
4. Sketch and explain with the circuit, the combination clippers which limit the
output between 5V.Assume diode voltage is 0.7V.
(10 marks) (June 2014)
5.What is Clamping? With neat diagram and waveform, explain the working of
negative clamper and also write the condition for stiff clamper.
(7 marks) (June 2014)
6. Explain Varactor diode with its characteristic curves. (3 marks) (June 2014)
7. Find the values of resistors Rb, Rc,Re and the transistor gain , for the circuit.
Ib=40A, Ic=4mA, Ve=2V, Vce=12V, Vcc=15V. Assume that the transistor used in the
circuit is a silicon transistor.
(10 marks) (July 2013)
8. Explain transistor in its fixed bias mode with relevant expression.
(10 marks) (Dec 2012)
9. With a neat sketch, explain transistor as a switch.
Dept. of CSE, SJBIT
(5 marks) (Dec 2012)
Electronic Circuits
10CS32
10. For the circuit shown calculate IB, IC, VCE, VC, VE, VB. Assume = 100.
(5 marks) (Dec 2012)
11. Explain the criteria for selecting a suitable operating point and factors affecting the
stability.
(10 marks) (Dec 2013)
12. Find the values of resistance RB, RC, RE and transistor gain , for the circuit shown in
Fig.Q1(b). Given that IB = 40 A, IC = 4mA, VE = 2V, VCE = 12V and supply voltage VCC
= 15V. Assume that the transistor used in the circuit is a silicon transistor.
(6 marks) (Dec 2013)
13. Explain transistor as a switch.
Dept. of CSE, SJBIT
(4 marks) (Dec 2013)
Electronic Circuits
10CS32
UNIT-2: FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS
1. Explain the working of a N-channel E-Mosfet with neat diagram. Explain with a
Diagram output characteristics of the same.
(10 Marks)(June 2012)
2. Find the values of voltages VD and VC for the circuit shown, Fig.Q2(b). Assume b =
100, VBE = 0.7 V, saturation drain current of JFET is 10 mA and pinch off voltage is5V.
(4 Marks)(June 2012)
3. With circuit diagram, explain base bias amplifier and give the importance of capacitor.
(6 Marks)(June 2012)
4. Explain the small signal operation of amplifiers.
(10 Marks)(June 2011)
5. For the circuit given below fig.Q2(c), (i) Calculate the input impedance of the base
with = 100; (ii) Draw the DC equivalent circuit; (ii) Draw the AC equivalent circuit
using T and model.
(10 Marks)(June 2014)
6. Explain the VI characteristics of n-channel JFET and define various conditions.
(10 Marks)(Dec 2012)
7. Mention merits and demerits of IGBT.
(10 Marks)(Dec 2012)
8. What are the differences between JFET & MOSFET.
(10 Marks)(June-July 2013)
9. With the help of neat figures, explain the construction and characteristics of N-channel
depletion MOSFET.
(10 Marks)(June-July 2013)
10. How Biasing configuration using De-MOSFET work. Justify. Given that saturation
drain current is 8mA, and the pinch off voltage is -2V. Determine the value of gate source
voltage, drain current and the drain source voltage.
(10 Marks)(June-July 2013)
11. What are the difference between BJTs and FETs?
(10 Marks)(Dec 2013)
12. Explain the working of a CMOS inverter.
(10 Marks)(Dec 2013)
13. Explain the construction .working and principle of operation of an n-channel JFET.
(10 Marks)(Dec 2013)
Dept. of CSE, SJBIT
Electronic Circuits
10CS32
UNIT-3: OPTOELECTRONIC DEVICES
1. Explain photodiode, photosensor, photo conductor and phototransistors with necessary
diagrams.
(10 Marks)(June 2012)
2. Find the value of RL for the circuit shown, Fig.Q3(b) such that the circuit gives a logic
high when the light incident on it is above 200 lux and the photo conductor has a resistance of
14kW at a light level of 100 lux, a = 0.5, power supply voltage is VCC = 10V and reference
voltage of zener diode is 3.5V.
(10 Marks)(June 2012)
3. What is multistage amplifier? With the neat circuit diagram explain two stage
CE amplifier and derive equation for voltage gain.
(10 Marks)(June 2014)
4. For the swamped amplifier shown fig.Q3(b) below, calculate; (i) Input impedance of the
base; (ii) The input impedance of the stage; (iii) AC input voltage to the base; (iv) Voltage
gain; (v) AC voltage across the load.
(10 Marks)(June 2014)
5. Explain the construction and working of phototransistor and mention its applications
(10 Marks)(Dec 2012)
6. What are optocouplers? Explain the working and characteristics of optocoupler.
(5 Marks)(Dec 2012)
7. Define the following terms: (i) Responsivity (ii) Detectivity (iii) Quantum efficiency (iv)
Noise equivalent power (v) Response time.
(5 Marks)(Dec 2012)
8. What is Phototransistor? Draw a schematic symbol of a phototransistor. Explain the V- I
characteristics also.
(10 Marks)(June-July 2013)
9. Explain different modes of operation of an LCD display. (10 Marks)(June-July 2013)
10. Discuss the classification of optoelectronic devices, in detail.
(7 Marks)(Dec 2013)
11. Explain with neat diagrams, the principle of operation, characteristics, advantages,
disadvantages and applications of a photodiode.
(8 Marks)(Dec 2013)
12. Briefly discuss with necessary diagrams, the basic operation and construction of LED.
(6 Marks)(Dec 2013)
Dept. of CSE, SJBIT
Electronic Circuits
10CS32
UNIT-4: SMALL SIGNAL ANALYSIS OF AMPLIFIERS
1. Graphically how h-parameters of a BJT are determined? Explain with neat diagram. Also
derive expression for input impedance and voltage gain for a BJT amplifier.
(10 Marks)(June 2012)
2. Give the hybrid equivalent model for the circuit shown, in Fig.Q4(b). Find input
impedance,voltage gain, current gain and output impedance. The h-parameters are hie = 1.5k,
hje = 100, hre = 1104, hoe = 25m A/V.
(10 Marks)(June 2012)
3. Explain the classification of amplifiers based on their operation.
(8 Marks)(June 2014)
4. Draw the DC load line and AC load line for a VDB amplifier.
(6 Marks)(June 2014)
5. With the circuit diagram explain push pull power amplifier and list the advantages and
disadvantages of push pull amplifier.
(6 Marks)(June 2014)
6. Derive expression for Ai, Zi, Av, Yo, Ap for a transistor amplifier using h-parameter
model.
(10 Marks) (Dec 2012)
7. Explain the need for cascading amplifier and with the block diagram, explain two stage
cascaded amplifier.
(10 Marks)(Dec 2012)
8. Draw the generalized h-parameter model of a transistor based amplifier and derive the
expression for Current gain, Input Impedance, Voltage Gain & Output admittance.
(8 Marks)(June-July 2013)
9. With a neat diagram, Explain the operation of Darlington Amplifier.
(6 Marks)(June-July 2013)
10. What are cascade amplifiers? What are the advantages offered by the amplifier.
(6 Marks)(June-July 2013).
Dept. of CSE, SJBIT
Electronic Circuits
10CS32
11. Explain the need for cascading amplifier and with the block diagram, explain two stage
cascaded amplifier.
(10 Marks)(Dec 2013)
12. Obtain the expression for current gain, input impedance voltage gain, output impedance
Power gain of a transistor amplifier using complete h parameter model.
(10 Marks)(Dec 2013)
Dept. of CSE, SJBIT
Electronic Circuits
10CS32
UNIT 5: LARGE SIGNAL AMPLIFIERS, FEEDBACK AMPLIFIER
1. Large signal amplifier characteristics. Discuss harmonic distortion. Derive A2, A3, A4,
the amplitude of D,C, first, second, third, forth amplitude of harmonic components.
(10 Marks)(June 2012)
2. Derive expressions for gain, input resistance and output resistance of voltage shunt
Feedback amplifier with the help of neat diagram. For the opamp based inverting amplifier
circuit shown in Fig.Q5(b) find input impedance given that transimpedance, input
impedance and output impedance of opamp are 100 MW, 10 MW, and 100 W respectively.
(10 Marks)(June 2012)
3. Explain Voltage series feedback.
(8 Marks)(June 2014)
4. What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of negative feedbacks.
(6 Marks)(June 2014)
5. Describe Shunt Feedback.
(6 Marks)(June 2014)
6. Explain different FB amplifiers.
(8 Marks)(Dec 2012)
7. With the block diagram, explain the negative feedback in small signal amplifier.
(6 Marks)(Dec 2012)
8. An amplifier having a voltage gain of 60dB uses 1/20th of its output in negative feedback.
Calculate the gain with feedback, the percentage change in gain without and with feedback
consequent on 50% change in gm.
(6 Marks)(Dec 2012)
9. What are the advantages of negative feedback.?
(5 Marks)(July 2013)
10. Derive the relevant expression to prove that input resistance increases and output
resistance decreases in case of voltage series feedback.
(8 Marks)(July 2013)
11. Consider Opamp based inverting amplifier circuit. Identify the negative feedback.
Determine the trans impedance gain, the input impedance and output impedance of the
amplifier. The parameters are 100M, 10M and 100 respectively.
(7 Marks)(July 2013)
Dept. of CSE, SJBIT
Electronic Circuits
10CS32
12. What is ohmic region of EMOSFET? With the circuit diagram determine whether the
MOSFET is based in the ohmic region.
(7 Marks)(Dec 2013)
13. The EMOSFET in the circuit fig.Q5(b) has following parameters V= 4.5V = 75mA and
RDS(ON)=10W. Calculate the output voltage. Show the equivalent circuit.
(8 Marks)(Dec 2013)
14. Discus in detail CMOS Operation and power consumption.
Dept. of CSE, SJBIT
(5 Marks)(Dec 2013)
Electronic Circuits
10CS32
UNIT-6: SINUSOIDAL OSCILLATORS, WAVE-SHAPING CIRCUITS
1. Mention the conditions necessary for oscillations in a feedback amplifier circuit.
Determine the frequency at which the following circuit, shown in Figure would oscillate if
the loop gain criterion was met. Also determine the maximum value of R1 for sustained
oscillation.
(10 Marks)(June 2012)
2. With neat diagram and waveforms explain the working of a bistable multivibrator (BJT
based).
(10 Marks)(June 2012)
3. Explain Monostable Multivibrator.
(7 Marks)(June 2014)
4. Describe Low Pass Filter.
(7 Marks)(June 2014)
5. Explain Barkhausen Criteria.
(6 Marks)(June 2014)
6. Explain the construction and working of RC phase shift oscillator.
(8 Marks)(Dec 2012)
7. Find the frequency of the oscillations of a Colpitts oscillator having C1 = 150pF, C2 = 1.5
nF and L = 50H.
(7 Marks)(Dec 2012)
8. With a circuit diagram, explain the working of RC low pass and RC high pass circuits.
(5 Marks)(Dec 2012)
9. Explain the Barkhausen Criterion as referred to oscillators.
(6 Marks)(June-July 2013)
10. With a neat figure explain the operation of voltage controlled oscillator.
(7 Marks)(June-July 2013)
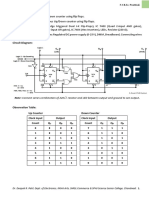
11. With neat figure and relevant waveforms explain the operation of Astable multivibrator
using 555 IC timer.
(7 Marks)(June-July 2013)
12. Draw the frequency response diagram of an AC amplifier and identify cut off frequency,
mid band gain.
Dept. of CSE, SJBIT
(8 Marks)(Dec 2013)
9
Electronic Circuits
10CS32
13. Define DECIBEL power gain, DECIBEL voltage gain. For the cascaded amplifier
shown below, calculate the decibel voltage gain of each stage and the overall decibel
gain.
(6 Marks)(Dec 2013)
14. Explain the various types of negative feedback amplifiers.
(6 Marks)(June 2011)
Dept. of CSE, SJBIT
10
Electronic Circuits
10CS32
UNIT-7: LINEAR POWER SUPPLIES, SWITCHED MODE POWER SUPPLIES
1. Explain regulated power supply parameters: Load regulation, line regulation, output
impedance. Ripple rejection factor. Determine the output ripple of a regulated power supply
which provides a ripple rejection of-80dB and a ripple voltage in the unregulated input were.
(10 Marks)(June 2012)
2. Explain buck regulator boost regulator and inverting regulator with neat diagram.
(10 Marks)(June 2012)
3. Describe the operation of Buck Regulator.
(10 Marks)(June 2014)
4.
(10 Marks)(June 2014)
5. Define the following. i) Load Regulation ii) Output Impedance iii) Ripple Rejection
Factor
(5 Marks)(June 2014)
6. Explain the construction and working of SMPS and mention different types of switching
Regulators.
(10 Marks)(Dec 2012)
7. Define the terms load regulation, line regulation and output resistance for a voltage
regulator.
(10 Marks)(Dec 2012)
8. Name the constituent parts of a linear regulated power supply. Describe the following
terms.
Dept. of CSE, SJBIT
(5 Marks)(June-July 2013)
11
Electronic Circuits
10CS32
9. Define Load regulation, Line Regulation, Ripple rejection factor, with respect to regulated
power supplies.
(5 Marks)(June-July 2013)
10. Explain the working of a Buck regulator.
(5 Marks)(June-July 2013)
11. Consider three terminal regulator circuit. Determine Load current, Current through
LM7812 Current through external transistor and Power dissipated in LM7812 with
Vbe=0.7V.
(5 Marks)(June-July 2013)
12. Explain the steps involved in custom design of mains transformer.
(6 marks )(Dec 2013)
13. What are SMPS? Compare linear power supplies with SMPS.
(7 Marks )(Dec 2013)
14. Explain the working of three terminal voltage regulator.
(7 marks )(Dec 2013)
Dept. of CSE, SJBIT
12
Electronic Circuits
10CS32
UNIT-8: OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
1. Explain with neat diagram: i) Peak detector circuit ii) Absolute value circuit and their
working.
(10 Marks)(June 2012)
2. Explain with neat diagram: i) Current to voltage converter ii) Voltage to current
converter and their working.
(10 Marks)(June 2012)
3. Explain Input Impedance.
(8 Marks)(June 2014)
4. With circuit diagram explain zero crossing detector.
(6 Marks)(June 2014)
5.
(6 Marks)(June 2014)
6. With relevant formulas, neat diagram and wave form explain op-amp Schmitt trigger.
(10 Marks)(Dec 2012)
7. Define the following terms of Op-amp: CMRR, PSRR, Slew Rate, Bandwidth and Open
Loop Gain.
(5 Marks)(June-July 2013)
8. With a neat diagram explain the operation of a peak detector circuit using op-amp.
(7 Marks)(June-July 2013)
9. Explain the Relaxation Oscillator circuit working with a neat circuit and its waveforms
using Op- amp.
(8 Marks)(June-July 2013)
10. Discuss the requirements of a good instrumentation amplifier.
(4 Marks)(Dec 2013)
11. Explain the of an OPAMP window comparator with circuit diagram.
(8 marks)(Dec 2013)
12. Explain the lead and lag type of phase shifter.
Dept. of CSE, SJBIT
(8 marks)(Dec 2013)
13
You might also like
- Ec6304 Ec IqbDocument10 pagesEc6304 Ec IqbmanikandanNo ratings yet
- Eee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits (15ee34) - Question PaperDocument4 pagesEee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits (15ee34) - Question PaperchaitanyaNo ratings yet
- EDC Question BankDocument12 pagesEDC Question BankSam SureshNo ratings yet
- EMP Question BankDocument7 pagesEMP Question BankDhamo DharanNo ratings yet
- Basic Question BankDocument4 pagesBasic Question Bankmanju.dsatmNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Unit - IDocument2 pagesQuestion Bank Unit - IprabuparthibanNo ratings yet
- Lic QPDocument11 pagesLic QPindumathythaniNo ratings yet
- Ae Paper GtuDocument9 pagesAe Paper GtuMehta HarshNo ratings yet
- Electronics CircuitDocument4 pagesElectronics CircuitSuresh PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Micro Electronics CicuitsDocument4 pagesMicro Electronics Cicuitsbalajibs203285No ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)Document2 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)HOD ECE KNCETNo ratings yet
- Electronic CircuitsDocument18 pagesElectronic CircuitsMythily VedhagiriNo ratings yet
- Ec6702 QBDocument10 pagesEc6702 QBPetrishia ArockiasamyNo ratings yet
- Beee QB Be3251Document8 pagesBeee QB Be3251SRINIVASAN.K.G MECW-AP/EEENo ratings yet
- Signal Conditioning Circuits Question Bank: Unit-1Document6 pagesSignal Conditioning Circuits Question Bank: Unit-1Nirmal Kumar PandeyNo ratings yet
- AE - Question BankDocument3 pagesAE - Question BankHiren J VasavaNo ratings yet
- BE3252 QB Unit4Document2 pagesBE3252 QB Unit4rkanthimathi86No ratings yet
- Ec6702 Ocn QPDocument6 pagesEc6702 Ocn QPJagadeesan DhanapalNo ratings yet
- Electronic 2 Continuous AssessmentDocument3 pagesElectronic 2 Continuous AssessmentJeewanthi BandaraNo ratings yet
- 2.electronics Circuits IIDocument9 pages2.electronics Circuits IImanimangaiNo ratings yet
- Sunday, February 5, 2012: Electronics Circuit-1 (Ec2205) Question Bank Electronics Circuit-1 (Ec2205)Document6 pagesSunday, February 5, 2012: Electronics Circuit-1 (Ec2205) Question Bank Electronics Circuit-1 (Ec2205)Murugeswari EswariNo ratings yet
- Svce EC6404 QBDocument11 pagesSvce EC6404 QBformyphdNo ratings yet
- Linear Integrated CircuitsDocument6 pagesLinear Integrated CircuitsRanganathan ThambirajanNo ratings yet
- VDD VrefDocument2 pagesVDD VrefSureshKumar SaravananNo ratings yet
- EC1X11 Electronic Devices and Circuits Nov Dec 2007Document3 pagesEC1X11 Electronic Devices and Circuits Nov Dec 2007aniruthgsabapathyNo ratings yet
- Electronics Circuits Feedback & Oscillators NotesDocument18 pagesElectronics Circuits Feedback & Oscillators NotesVenkat ChadalavadaNo ratings yet
- C.Abdul Hakeem College of Engineering & Technology Ec 2403 - RF & Microwave EngineeringDocument1 pageC.Abdul Hakeem College of Engineering & Technology Ec 2403 - RF & Microwave EngineeringJanani MunisamyNo ratings yet
- EC2403 - RF and Microwave Engineering Que PDFDocument7 pagesEC2403 - RF and Microwave Engineering Que PDFkhyatichavdaNo ratings yet
- Ec8351 Electronic Circuits I 1901883722 Ec8351 Ec IDocument19 pagesEc8351 Electronic Circuits I 1901883722 Ec8351 Ec IyogiNo ratings yet
- Question PaperDocument2 pagesQuestion PapertrsureshNo ratings yet
- What Is Intrinsic Stand of RatioDocument2 pagesWhat Is Intrinsic Stand of Ratiomurlak37No ratings yet
- EC8252 Question BankDocument11 pagesEC8252 Question BankPalaniappan Muthu TNo ratings yet
- Ec6016 Optoelectronics QB 2013 RegDocument7 pagesEc6016 Optoelectronics QB 2013 Regsridharparthipan0% (1)
- Be3251 Basic Electrial, Electronics and Engineering: Important Questions and Question BankDocument8 pagesBe3251 Basic Electrial, Electronics and Engineering: Important Questions and Question BankSatheeswaran VNo ratings yet
- SRI VENKATESWARA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK FOR ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS & DESIGNDocument5 pagesSRI VENKATESWARA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK FOR ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS & DESIGN20BF1A04M6 sumanthNo ratings yet
- JSPM Narhe Technical Campus Basic Electronics Question BankDocument2 pagesJSPM Narhe Technical Campus Basic Electronics Question Banktejas chavanNo ratings yet
- Edc Question Bank R20 2021Document5 pagesEdc Question Bank R20 2021khadarskb19No ratings yet
- ECE Question Bank for IV Semester covering PDEs, Z-Transforms, Communication SystemsDocument8 pagesECE Question Bank for IV Semester covering PDEs, Z-Transforms, Communication SystemssgdhruvNo ratings yet
- EC6202 Electronic Devices and Circuits NotesDocument6 pagesEC6202 Electronic Devices and Circuits NotesrejinpaulpaulNo ratings yet
- EDC Key Concepts: Feedback Amplifiers, OscillatorsDocument5 pagesEDC Key Concepts: Feedback Amplifiers, OscillatorsK.Swetha PriyadharshiniNo ratings yet
- EC1201 Electronic Devices and Circuits NotesDocument6 pagesEC1201 Electronic Devices and Circuits NotesRameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK ON ELECTRONICS AND MICROPROCESSORSDocument6 pagesMECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK ON ELECTRONICS AND MICROPROCESSORSJagdish AdikesavanNo ratings yet
- MicrowaveDocument5 pagesMicrowaveragh1291No ratings yet
- R7100407 Electronic Devices & CircuitsDocument1 pageR7100407 Electronic Devices & CircuitssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Module-Wise Eln QBDocument5 pagesModule-Wise Eln QBRashmi SamantNo ratings yet
- Ec1351 Measurements and InstrumentationDocument0 pagesEc1351 Measurements and InstrumentationvlsijpNo ratings yet
- EC6202-Electronics Devices and CircuitsDocument6 pagesEC6202-Electronics Devices and Circuitssaravananvaratharajan4No ratings yet
- AE 1 EQ by Faiz SirDocument16 pagesAE 1 EQ by Faiz SirFaiz RangariNo ratings yet
- QP Model EcedDocument3 pagesQP Model EcedShree Ram Senthil SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits Question Bank PDFDocument8 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits Question Bank PDFVenkata SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Mic QbankDocument8 pagesMic QbankSuganya RajamanickamNo ratings yet
- Electronics Filters Circuits Exam QuestionsDocument3 pagesElectronics Filters Circuits Exam QuestionsMadhu Sudan SaraogiNo ratings yet
- EC6202-Electronics Devices and Circuits QBDocument6 pagesEC6202-Electronics Devices and Circuits QBneelam sanjeev kumarNo ratings yet
- Anna University Ec2251: Electronic Circuits Ii Sem / Year: Iv/ Ii QUESTION BANK - 2012 EditionDocument9 pagesAnna University Ec2251: Electronic Circuits Ii Sem / Year: Iv/ Ii QUESTION BANK - 2012 EditionJoseph AntoNo ratings yet
- Ec2403 Microwave Question BankDocument6 pagesEc2403 Microwave Question BankNasrin Rafee50% (2)
- Subject Name: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering / Ge 2151Document3 pagesSubject Name: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering / Ge 2151Gokul ChandrasekaranNo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions PART A - (5 2 10)Document2 pagesAnswer All Questions PART A - (5 2 10)Anonymous 4u5XkWGONo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsNo ratings yet
- Organic Light-Emitting Transistors: Towards the Next Generation Display TechnologyFrom EverandOrganic Light-Emitting Transistors: Towards the Next Generation Display TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Physics and Technology of Crystalline Oxide Semiconductor CAAC-IGZO: Application to LSIFrom EverandPhysics and Technology of Crystalline Oxide Semiconductor CAAC-IGZO: Application to LSINo ratings yet
- Video EnhancementDocument29 pagesVideo Enhancementhanumantha12No ratings yet
- Misty Charm Cost SheetDocument1 pageMisty Charm Cost Sheethanumantha12No ratings yet
- Whitepaper PDFDocument20 pagesWhitepaper PDFMarceloCanalesNo ratings yet
- Hanun and His FriendsDocument1 pageHanun and His Friendshanumantha12No ratings yet
- Hello WorldDocument1 pageHello Worldhanumantha12No ratings yet
- Ecsyll6 PDFDocument22 pagesEcsyll6 PDFantharmukiNo ratings yet
- PHD Result 2015Document474 pagesPHD Result 2015skdwarakaNo ratings yet
- Raju GentlemanDocument1 pageRaju Gentlemanhanumantha12No ratings yet
- Student Attendance ImprovementDocument7 pagesStudent Attendance Improvementhanumantha12No ratings yet
- General TheoryDocument1 pageGeneral Theoryhanumantha12No ratings yet
- Raju GentlemanDocument1 pageRaju Gentlemanhanumantha12No ratings yet
- World WarDocument1 pageWorld Warhanumantha12No ratings yet
- Course File ContentsDocument6 pagesCourse File Contentshanumantha12No ratings yet
- How To Book of Writing Skills - Words at Work - Letters, Email, Reports, Resumes, Job Applications, Plain EnglishDocument105 pagesHow To Book of Writing Skills - Words at Work - Letters, Email, Reports, Resumes, Job Applications, Plain EnglishYogi ShahNo ratings yet
- Hello WorldDocument1 pageHello Worldhanumantha12No ratings yet
- Ug C Workload and Code Ethics RegulationDocument4 pagesUg C Workload and Code Ethics RegulationAmirtham Valan ArasuNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Mosfets1Document43 pagesUnit 1 Mosfets1hanumantha12No ratings yet
- 09-12-2016 Jnanavardhan Presentation 1Document53 pages09-12-2016 Jnanavardhan Presentation 1hanumantha12No ratings yet
- Using The PowersupplyDocument4 pagesUsing The Powersupplyhanumantha12No ratings yet
- MEC Unit 2 Notes by HanumantharajuDocument62 pagesMEC Unit 2 Notes by Hanumantharajuhanumantha12100% (1)
- Analog Communication Notes ECE DEPT BMSITDocument319 pagesAnalog Communication Notes ECE DEPT BMSIThanumantha12100% (2)
- Third Semester Module 1 and 2 AE NotesDocument128 pagesThird Semester Module 1 and 2 AE Noteshanumantha12No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of CMOS VLSI Notes ECE Dept BmsitDocument244 pagesFundamentals of CMOS VLSI Notes ECE Dept Bmsithanumantha12100% (2)
- LSB Image StegoDocument40 pagesLSB Image StegoAnshul BansalNo ratings yet
- Career Handbook 2015Document36 pagesCareer Handbook 2015hanumantha12No ratings yet
- VTU Exam TipsDocument5 pagesVTU Exam Tipshanumantha12No ratings yet
- EET SafetyManual Ug2012Document25 pagesEET SafetyManual Ug2012rizalNo ratings yet
- Latex Tutorial by Dr. M. C. HanumantharajuDocument18 pagesLatex Tutorial by Dr. M. C. Hanumantharajuhanumantha12No ratings yet
- Gradient Fusion Method for Night Video Enhancement: log ( (1) 1) (,) log Ψ − + Ψ = Ψ Max ΨDocument4 pagesGradient Fusion Method for Night Video Enhancement: log ( (1) 1) (,) log Ψ − + Ψ = Ψ Max Ψhanumantha12No ratings yet
- It0201 Electron Devices and CircuitsDocument5 pagesIt0201 Electron Devices and Circuitshanumantha12No ratings yet
- R1170x e DatasheetDocument30 pagesR1170x e DatasheetgeslabNo ratings yet
- Analog ElectronicsDocument23 pagesAnalog ElectronicsRushiraj DesaiNo ratings yet
- Verilog ProgramsDocument40 pagesVerilog ProgramssundaraiahNo ratings yet
- Analogue II Exams Eee 2210 Mechatronics-PrintreadyDocument4 pagesAnalogue II Exams Eee 2210 Mechatronics-PrintreadyMike ShakespeareNo ratings yet
- Multistage AmplifierDocument22 pagesMultistage AmplifierVijay AnandhNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Node and Mesh Analysis1Document59 pagesUnit 4 Node and Mesh Analysis1Alerda MaatrixxNo ratings yet
- 16BT70408 - Low Power Cmos Vlsi DesignDocument1 page16BT70408 - Low Power Cmos Vlsi DesignS KkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Op-AmpDocument25 pagesChapter 4 Op-Ampfirst lastNo ratings yet
- Linear Circuit Analysis: Time Domain, Phasor, and Laplace Transform ApproachesDocument7 pagesLinear Circuit Analysis: Time Domain, Phasor, and Laplace Transform ApproachesestebanlaragomezNo ratings yet
- Fan7602-U2 SMDDocument18 pagesFan7602-U2 SMDLefter TironNo ratings yet
- Transient Analysis of Electrical Circuits Using Runge-Kutta Method and Its ApplicationDocument5 pagesTransient Analysis of Electrical Circuits Using Runge-Kutta Method and Its ApplicationSwati kNo ratings yet
- TL610912 - Current SenseDocument28 pagesTL610912 - Current SenseLucas dos Santos LuizNo ratings yet
- Sect. 3.3 Construction of Equivalent Circuit ModelDocument8 pagesSect. 3.3 Construction of Equivalent Circuit ModelPiero TorpocoNo ratings yet
- TDA2003 stereo amplifier schematic to PCB designDocument7 pagesTDA2003 stereo amplifier schematic to PCB designSiegrique Ceasar A. JalwinNo ratings yet
- NCP81220 DDocument27 pagesNCP81220 DLoc Nguyen HuyNo ratings yet
- 3-bit asynchronous Up/Down counter flip-flopsDocument2 pages3-bit asynchronous Up/Down counter flip-flopsIshtiaque Ahmed TanimNo ratings yet
- CristalDocument1 pageCristalPablo BarbozaNo ratings yet
- Mosfet Small SignalDocument7 pagesMosfet Small SignalTabraizShahNo ratings yet
- Wideband frequency modulation of phase lock loopsDocument5 pagesWideband frequency modulation of phase lock loopsMostafa M. SamiNo ratings yet
- Find the Load Voltage vL for Circuit with Two Op-AmpsDocument21 pagesFind the Load Voltage vL for Circuit with Two Op-AmpsSoulz Zampa100% (1)
- Active Filters-: First Order Low Pass and High Pass FiltersDocument5 pagesActive Filters-: First Order Low Pass and High Pass FiltersLavanya RatalaNo ratings yet
- EE4605, "Integrated Circuits and Systems For Wireless Applications"Document15 pagesEE4605, "Integrated Circuits and Systems For Wireless Applications"debdutt13No ratings yet
- Introduction To FET-Field Effect TransistorDocument2 pagesIntroduction To FET-Field Effect TransistorRushikesh TrimbakeNo ratings yet
- UC384XA-BW Current Mode PWM Controller: (UC3842A-BW/ 43A-BW/ 44A-BW/ 45A-BW)Document10 pagesUC384XA-BW Current Mode PWM Controller: (UC3842A-BW/ 43A-BW/ 44A-BW/ 45A-BW)Damir SkarepNo ratings yet
- Filter-Free Design Helps Class-D Audio Amplifier ImplementationsDocument6 pagesFilter-Free Design Helps Class-D Audio Amplifier ImplementationsDirson Volmir WilligNo ratings yet
- LM566C Voltage Controlled Oscillator: General DescriptionDocument7 pagesLM566C Voltage Controlled Oscillator: General DescriptiondksxmasterNo ratings yet
- M54HC194 M74HC194: 4 Bit Pipo Shift RegisterDocument12 pagesM54HC194 M74HC194: 4 Bit Pipo Shift RegisternooorNo ratings yet
- Realize and Design A 4 Digit Hex Counter Using Asynchronous One Digit HexcountersDocument5 pagesRealize and Design A 4 Digit Hex Counter Using Asynchronous One Digit Hexcountersneha yarrapothuNo ratings yet
- NJM2059 eDocument5 pagesNJM2059 etecnojassNo ratings yet
- Circuit Network Analysis B-Tech Electrical EngineeringDocument2 pagesCircuit Network Analysis B-Tech Electrical EngineeringPatel DipenNo ratings yet