Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dissolved Oxygen Primary Prod Activity
Uploaded by
api-269169613Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dissolved Oxygen Primary Prod Activity
Uploaded by
api-269169613Copyright:
Available Formats
Name: Galilea Patricio
AP Biology
AP Lab 12--DISSOLVED OXYGEN & AQUATIC PRIMARY PRODUCTIVITY
(LabBench)
Web address: http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench
Click on Lab 12: Dissolved Oxygen & Aquatic Primary Productivity
A. KEY CONCEPTS:
1. Dissolved Oxygen Availability in ponds and lakes. Using the following diagram
describe the effect that each of the factors has on availability of oxygen and explain why.
a. Temperature: As water increases in temperature, the ablilty to hold oxygen
decreases.
b. Light & Photosynthesis: Aquatic plants are able to produce more oxygen under bright
light.
c. Decomposition & Respiration: Microbal processes consume oxygen as organic
material decays.
d. Mixing & Turbulence: Wave action, waterfalls, and rapids aerate water and increase
the oxygen concentration.
e. Salinity: As the salinty in water increases, its ability to hold oxygen decreases.
2. Productivity: Define each of these terms in your own words.
a. Primary productivity: The rate at which photosynthetic organisms produce orgnic
compounds within an ecosystem.
b. Gross productivity: The photosynthetic production an organism produces in an
ecosystem.
c. Net productivity: The remaining organic materials after a photosynthetic organism
has consumed some of the organic compounds for cellulaar respiration.
3. Why do we use dissolved oxygen as a measure of productivity? Does productivity
include more than oxygen?
Oxygen is used to measure productivity because it is the easiest to measure the rate of
photosynthesis and respiration.
4. Using the diagrams below explain:
a. How does putting a sample of pond water and algae/freshwater plants in the light
enable us to measure gross productivity?
Algae/freshwater plants enable the production of O2 through photosynthesis.
b. How does putting a sample of pond water and algae/freshwater plants in the dark
enable us to measure respiration?
Placing algae/freshwater plants in the dark enables the consumption of O2 when there is
no photosynthesis occuring.
c. How does subtracting the two enable us to indirectly measure net productivity?
Subtracting the two enables the measurement of net productivity through
photosynthesis.
5. What are the three ways that primary productivity can be measured? Highlight the
way will be used in this lab?.
a. The amount of carbon dioxide used
b. The rate of sugar formation
c. The rate of oxygen production
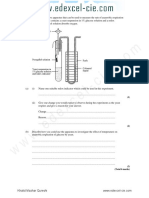
B. LAB PART 1: EFFECT OF TEMPERATURE ON DISSOLVED OXYGEN
We actually did this part of the lab already. Remind yourself of our experiment, our
procedures, and our conclusions. We were investigating the effect of the physical
factor of temperature on the percent dissolved oxygen in a body of water.
6. What is the relationship between water temperature and dissolved oxygen?
Warmer water holds less oxygen than cold water.
7. Explain why this relationship exists.
The relationship between water temperature and dissolved oxygen exists because of
waters ability to retain oxygen.
8. So, now explain why the fish in the aquarium (on the LabBench Web site) above the
radiator died?
The fish above the radiator died because the constant heat being released decreased
the amount of oxygen in the water.
C. A MODEL OF PRODUCTIVITY AS A FUNCTION OF DEPTH IN A LAKE
Now we are going to look at the biological factors that affect dissolved oxygen in a body
of water. Look at the experimental design on the LabBench Web site
(http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench/lab12/model.html). We are
taking a sample of pond water (with algae) and then modeling different depths in the
pond by using screening to block out successive amounts of light. One hundred percent
light for shallow depth, all the way to 0% light for deep ponds.
9. Why do we take an initial reading of dissolved oxygen? What purpose does this
serve in the experiment?
An initial reading of dissolved oxygen is taken to determine the amount of dissolved
oxygen. This is done to regulate the ocean in order to prevent dead zones.
10. Click on the closer look magnifying glass on the initial bottle. Why does the
animation show oxygen being diffusing out of the freshwater plants? What does this
signify?
The animation demonstrates oxygen diffusing out of the freshwater plants because of
photosynthesis which is evidence of O2 production.
11. Click on the closer look magnifying glass on the foil- covered bottle. Why does the
animation show oxygen diffusing into the freshwater plants? What does this signify?
Oxygen is diffusing into the freshwater plants because the process of photosynthesis is
not occuring in the dark.
12. Click on the closer look magnifying glass on the 100% bottle under the light.
Why does the animation show oxygen diffusing both into and out of the freshwater
plants? What does this signify?
Oxygen is diffusing in and out of the freshwater plants because respiration and
photosynthesis are occuring.
D. ANALYSIS OF RESULTS
Lets look at the results that will allow you to calculate the different types of productivity.
13. Measuring Respiration: Remember that plants (producers) perform both
photosynthesis and respiration. To measure the amount of respiration that is happening
in the bottle, we measure the amount of dissolved oxygen in the initial sample and
then the amount of oxygen in the bottle kept in the dark. As shown in the illustration
below, you then subtract the amount of dissolved oxygen in the dark bottle from the
amount of dissolved oxygen in the initial bottle to calculate the amount of oxygen
consumed in respiration. I have added some possible measurements to help. Explain
why this calculation works.
The calulations work because it measures both pphotosynthetic and respiration activities
through the light and dark bottles.
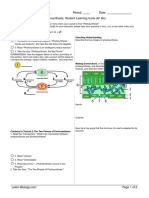
14. Measuring Gross Productivity: Remember gross productivity is the total amount of
sugars and oxygen produced by the plants in an ecosystem. I dont like how this Web
site shows you how to calculate gross productivity. The equation is correct, but it is a
short cut, so it makes it more difficult to understand. So follow me with the illustrations
and the possible measurements below.
So the illustration shows us there was 10mg increase in dissolved oxygen in the jar as a
result of photosynthesis in the last 24 hours and there was 5mg decrease in dissolved
oxygen in the jar as a result of respiration in the last 24 hours. So the gross productivity
(the full photosynthetic production in this ecosystem) of the algae in the bottle is the
5mg dissolved oxygen lost to respiration added back to the 10 mg dissolved oxygen
accumulated in the bottle kept in the light. So what the algae really produced in the
bottle was a total of 15mg dissolved oxygen, it just lost
5mg to respiration. And remember, the oxygen is an indirect measurement of the
sugars
produced in photosynthesis and lost in respiration.
10 mg oxygen gained 5 mg oxygen lost 15 mg oxygen as
+ =
from photosynthesis to respiration gross productivity
Now, in your own words, explain why this calculation works.
The calculations work because of the balanced amount oxygen that is lost and gained in
each bottle
15. Measuring Net Productivity: Remember net productivity is the amount of sugars
and dissolved oxygen produced by the plants in an ecosystem once you subtract out
what the producers have consumed in respiration. So we actually already calculated that
in the last example; I just called it net photosynthesis. Explain why this calculation
works.
The calculation for net productivity works because it demonstrates the initial amount of
dissolved oxygen and the amount that is consumed by the plant which gives the total net
productivity.
16. Print out the completed calculation table from Sample Problem page of the
LabBench Web site, fill in your predictions on the graph as well, and attach it to this lab
to show me that you have completed it.
17. Print out the Lab Quiz and attach it to this lab to show me that you completed it.
SUMMARY QUESTIONS
18. Would you expect the dissolved oxygen levels in water sampled from a stream
entering a lake to be
higher or lower than the dissolved oxygen levels in water sampled from the lake itself?
Explain.
I would expect there to be higher oxygen levels in a stream entering the lake than the
lake itslef because movement aerates the water. The lake could have plants that
produce oxygen thorugh photosynthesis, however there also is organic matter that
decays and cosumes oxygen.
19. Would you expect the dissolved oxygen levels in water sampled from a lake at
7AM to be higher or lower than the dissolved oxygen levels in water sampled at 5PM?
Explain.
I would expect there to be higher oxygen levels in a water sample from 7 AM than 5 PM
because of the difference of temperature and sunlight. In the morning the water is usuall
colder and much more sunlight than early evening.
20. One of the major sources of water pollution is the runoff from fertilizer used in
agriculture and on suburban lawns as well as golf courses. In particular, the nitrogen
and phosphorus nutrients in the fertilizer creates problems in the streams and ponds it
flows into. They cause algal blooms and eutrophication in lakes.
a. Why do nitrogen and phosphorus promote a lot of plant/algal growth?
An excessive amount of mitrogen and phosphorus promotes plant/algal growth because
they are the two nutrients needed for plant growth.
b. What is meant by algal bloom? (Look it up!)
Algal bloom is the rapid increase in algae population due to excessive amounts of
nutrients.
c. What problems do algal blooms cause in ponds & lakes? Why isnt a lot more
producers a good thing? (Look it up!)
Algal blooms cover the surface of the water and therfore not allowing other organisms
below them to recieve sunlight. A lot of producers is not necessarily a good thing
because they deposit organic matter at the bottom which is broken down by
decomposers. The decomposers consume the oxygen in the area so much that other
organisms can not recieve oxygen.
d. What is meant by eutrophication? (Look it up!)
Eutrophication is the introduction of an over abundance of nutrients in the water.
21. At what depthshallow or deepwill there be more primary productivity in a pond or
a lake? Explain.
There is more primary productivity at the surface of a pond or lake beacuse sunlight is
not able to reach the bottom of deep lake or pond.
22. In an experiment, why do we use the mean of class data to make conclusions
rather than individual student group data?
The mean of a class is used reather than individual student data becaue it is the average
of all the data that is collected.
23. AP exam FRQ (2008). Consumers in aquatic ecosystems depend on producers
for nutrition. a. Explain the difference between gross and net primary productivity.
Gross productivity is the total amount of organic compounds produced by a
photosynthetic organism. Net productivity, however, is the remaining amount of the
organic compounds after the photosynthetic organism has consumed what it needs for
cellular respiration.
b. Describe a method to determine net and gross primary productivity in a freshwater
pond over a 24- hour period.
To determine the net productivity of freshwater pond the initial amount of oxygen needs
to be recorded. After 24 hours the amount of oxygen is once again measured and
subtracted from the initial oxygen level. The amount of carbon dioxide that is consumed
and the amount of oxygen that is produced within the 24 hours is added to determine
gross productivity.
c. In an experiment, net primary productivity was measured, in the early spring, for
water samples taken from different depths of a freshwater pond in a temperate
deciduous forest.
Explain the data presented by the graph, including a description of the relative rates of
metabolic processes occurring at different depths of the pond.
The graph demonstrates net of primary producers based on the depth of water. The
deeper the pond is, the lower the net of primary producers are present in the pond. The
net of primary producers remained constant at a depth of approximately 25 meter.
d. Describe how the relationship between net primary productivity and depth would
be expected to differ if new data were collected in mid-summer from the same pond.
Explain your prediction.
If the data were to be collected in mid-summer the net of primary producers and depth
would differ because of the suns intensity during the summer. During the summer the
days are longer and can contribute to an increase of activity during this time.
6
You might also like
- AP Biology Primary Productivity Lab ReportDocument9 pagesAP Biology Primary Productivity Lab ReportVictor Martin100% (1)
- L Energy and Respiration I PDFDocument12 pagesL Energy and Respiration I PDFMichelle Yeap67% (3)
- Stella YOON - 4.4 Climate Change Qs - 1Document2 pagesStella YOON - 4.4 Climate Change Qs - 1Seo Young YOON100% (1)
- Evolution ReviewDocument3 pagesEvolution ReviewJenna Vong100% (1)
- Lab 2, Microscope Calculations - Lab Manual, 22 Final VersionDocument6 pagesLab 2, Microscope Calculations - Lab Manual, 22 Final VersionIsella ShoNo ratings yet
- Aerobic respiration diagram outlineDocument80 pagesAerobic respiration diagram outlineTori Hop Along Clinch100% (1)
- Enzyme ProtocolDocument6 pagesEnzyme Protocoltapas kunduNo ratings yet
- CIE A-Level Biology Topic 13 Photosynthesis Exam Questions: Alevelbiology - Co.ukDocument15 pagesCIE A-Level Biology Topic 13 Photosynthesis Exam Questions: Alevelbiology - Co.ukMaisarah HalimNo ratings yet
- 6.6.Q BANK SLdocxDocument20 pages6.6.Q BANK SLdocxNaz Gümüşlüoğlu100% (1)
- Cambridge AS Level Biology Enzymes Section C Initial Rate GraphDocument18 pagesCambridge AS Level Biology Enzymes Section C Initial Rate Graphlucifer100% (1)
- MIT Exam 2Document12 pagesMIT Exam 2Daniela Sanclemente100% (1)
- Carbohydrates NotesDocument5 pagesCarbohydrates NotesWutWut100% (1)
- Topic K Respiration H1 H2 2017 Tutorial QNDocument11 pagesTopic K Respiration H1 H2 2017 Tutorial QNliang yi choo100% (1)
- Transport QuestionsDocument12 pagesTransport QuestionsForm 4B100% (1)
- 2 Mem TransDocument6 pages2 Mem TransPhuong DoanNo ratings yet
- Exam Questions Aqa Trilogy Bioenergetics: Q1-6 Foundaton Q3-9 HigherDocument28 pagesExam Questions Aqa Trilogy Bioenergetics: Q1-6 Foundaton Q3-9 Higherapi-422428700No ratings yet
- 9700 w15 QP 13Document16 pages9700 w15 QP 13Hew Li Yang100% (1)
- Edexcel A-Level Biology Anaerobic Respiration PDFDocument15 pagesEdexcel A-Level Biology Anaerobic Respiration PDFBonnyNo ratings yet
- BIO 361 Exam 4 ReviewDocument45 pagesBIO 361 Exam 4 ReviewNigel Zhang100% (1)
- MCQ Chapter 1 Page 2Document27 pagesMCQ Chapter 1 Page 2Leen Alodat100% (1)
- Cell membrane structure and functionDocument146 pagesCell membrane structure and functiontess_15100% (1)
- Chapter 16 BB QA (Corrected)Document6 pagesChapter 16 BB QA (Corrected)Rafael G. Garcia SanchezNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Questions of Photosynthesis Only-2Document30 pagesEdexcel Questions of Photosynthesis Only-2Rokunuz Jahan Rudro100% (1)
- Calculating Water Potential Worksheet-2012 2Document4 pagesCalculating Water Potential Worksheet-2012 2aemilianne100% (1)
- Effect of Temperature On Membrane Permeability in Beetroot CellsDocument7 pagesEffect of Temperature On Membrane Permeability in Beetroot CellsFarihaEshratNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Revision Exercise (Chap 5-8) Paper 2 1Document19 pagesIGCSE Biology Revision Exercise (Chap 5-8) Paper 2 1Sze Jack100% (1)
- Biocomp Exam 2013Document11 pagesBiocomp Exam 2013e100% (1)
- TOPIC 3.5 - Photosynthesis (AP Bio) Student Learning Guide, (2021)Document6 pagesTOPIC 3.5 - Photosynthesis (AP Bio) Student Learning Guide, (2021)L Chan100% (1)
- Unit1 l1Document48 pagesUnit1 l1hassaan aly100% (1)
- Unit f211 1.1 Questions Microscopes Part 2Document41 pagesUnit f211 1.1 Questions Microscopes Part 2Hazel100% (1)
- 16 Microscopy ReviewDocument12 pages16 Microscopy Reviewapi-300931855100% (1)
- Ap Bio Formula SheetDocument2 pagesAp Bio Formula Sheetapi-262780431No ratings yet
- Ap Bio Enzyme Catalase Lab Ap 1Document16 pagesAp Bio Enzyme Catalase Lab Ap 1api-233187566100% (1)
- BIOL 103 - Final Exam Guide - Comprehensive Notes For The Exam (258 Pages Long!) - 2Document258 pagesBIOL 103 - Final Exam Guide - Comprehensive Notes For The Exam (258 Pages Long!) - 2Edwin Lee0% (1)
- Bio Exam ZsmuDocument84 pagesBio Exam ZsmuManthan Patil100% (1)
- Q1. The Diagram Shows A Summary of The Light-Independent Reaction of PhotosynthesisDocument34 pagesQ1. The Diagram Shows A Summary of The Light-Independent Reaction of PhotosynthesisChee Beng Yeap100% (1)
- Lab - 1.09 - DNA Replication - Lab - BR2016 PDFDocument4 pagesLab - 1.09 - DNA Replication - Lab - BR2016 PDFBeth RobeliaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration GuideDocument8 pagesCellular Respiration GuideL Chan100% (1)
- Past Questions Cells N Biomolecules A Level BiologyDocument32 pagesPast Questions Cells N Biomolecules A Level BiologyZak berry100% (1)
- Edexcel Alevel Bio2b June 2006 QPDocument12 pagesEdexcel Alevel Bio2b June 2006 QPredrose_17100% (1)
- 2009 Year 11 Biology ExamDocument11 pages2009 Year 11 Biology ExamJay Li100% (1)
- Exam Questions 1. A Level Biology, AQA, Unit 2, June 2015Document19 pagesExam Questions 1. A Level Biology, AQA, Unit 2, June 2015Ryan JamesNo ratings yet
- Protein and Enzyme WorksheetDocument8 pagesProtein and Enzyme Worksheetanahita kazemifar100% (1)
- AQA Biology A-Level - Nucleic Acids QP DNA replicationDocument17 pagesAQA Biology A-Level - Nucleic Acids QP DNA replicationHuseyn AgazadeNo ratings yet
- 2015 Photosynthesis and Respiration Revision Tutorial AnsDocument18 pages2015 Photosynthesis and Respiration Revision Tutorial Ansliveaq100% (1)
- Variation and Evolution 5 HDocument10 pagesVariation and Evolution 5 HAlessandra EustaquioNo ratings yet
- Solan Bab 3 StrukturDocument5 pagesSolan Bab 3 StrukturMuhammad Amir100% (1)
- Bio Molecules Qs and MSDocument112 pagesBio Molecules Qs and MSAmaan Ahmed100% (1)
- Practical 2Document8 pagesPractical 2Ibrahim Muhamad0% (1)
- Plant Ecology: Understanding Interactions Between Organisms and EnvironmentDocument432 pagesPlant Ecology: Understanding Interactions Between Organisms and EnvironmentSanjana Srivastava100% (1)
- Bio October 2107 QP Unit 3Document16 pagesBio October 2107 QP Unit 3clyde100% (1)
- Q1.The Diagram Shows A Mitochondrion.: Feversham CollegeDocument56 pagesQ1.The Diagram Shows A Mitochondrion.: Feversham CollegeZaksd100% (1)
- Cell DivisionDocument60 pagesCell DivisionCharmaineNo ratings yet
- Microscopy & Cell Structure AS Biology 9700Document9 pagesMicroscopy & Cell Structure AS Biology 9700Asif Ayaz100% (1)
- Dissolved OxygenDocument9 pagesDissolved Oxygenapi-236697820No ratings yet
- Dissolved Oxygen Primary Prod Activity1Document7 pagesDissolved Oxygen Primary Prod Activity1api-235617848No ratings yet
- Dissolved Oxygen and Aquatic Productivity LabDocument6 pagesDissolved Oxygen and Aquatic Productivity Labapi-235548856No ratings yet
- Changes in Dissolved Oxygen Due To Salinity, Temperature, and LightDocument8 pagesChanges in Dissolved Oxygen Due To Salinity, Temperature, and Lightapi-300732604No ratings yet
- BTB PS CR LabDocument7 pagesBTB PS CR LabKathy XiangNo ratings yet
- 12 Do LabDocument3 pages12 Do LabRick MoraNo ratings yet
- The Prolific Afterlife of WhalesDocument2 pagesThe Prolific Afterlife of Whalesapi-264479456No ratings yet
- Apes - Unit 3 Study GuideDocument4 pagesApes - Unit 3 Study Guideapi-264479456No ratings yet
- Bozeman - Ecosystems Guided ViewingDocument2 pagesBozeman - Ecosystems Guided Viewingapi-264479456No ratings yet
- Bodlab 1Document3 pagesBodlab 1api-269169613No ratings yet
- How Big Is My PopulationDocument2 pagesHow Big Is My Populationapi-264479456No ratings yet
- BusinessletterDocument1 pageBusinessletterapi-264479456No ratings yet
- Apes-Introduction To The Worlds Biomes 1Document9 pagesApes-Introduction To The Worlds Biomes 1api-264479456No ratings yet
- Oceanacidificationlab 3Document5 pagesOceanacidificationlab 3api-264479456No ratings yet
- Apes TheeffectsofcoyoteremovalintexasDocument4 pagesApes Theeffectsofcoyoteremovalintexasapi-269169613No ratings yet
- Civil Service Exam Clerical Operations QuestionsDocument5 pagesCivil Service Exam Clerical Operations QuestionsJeniGatelaGatillo100% (3)
- Template WFP-Expenditure Form 2024Document22 pagesTemplate WFP-Expenditure Form 2024Joey Simba Jr.No ratings yet
- Sinclair User 1 Apr 1982Document68 pagesSinclair User 1 Apr 1982JasonWhite99No ratings yet
- ERIKS Dynamic SealsDocument28 pagesERIKS Dynamic Sealsdd82ddNo ratings yet
- Ailunce HD1 Software ManualDocument33 pagesAilunce HD1 Software ManualMarc LaBarberaNo ratings yet
- Analyze and Design Sewer and Stormwater Systems with SewerGEMSDocument18 pagesAnalyze and Design Sewer and Stormwater Systems with SewerGEMSBoni ClydeNo ratings yet
- Dep 32.32.00.11-Custody Transfer Measurement Systems For LiquidDocument69 pagesDep 32.32.00.11-Custody Transfer Measurement Systems For LiquidDAYONo ratings yet
- Indian Standard: Pla Ing and Design of Drainage IN Irrigation Projects - GuidelinesDocument7 pagesIndian Standard: Pla Ing and Design of Drainage IN Irrigation Projects - GuidelinesGolak PattanaikNo ratings yet
- Guidelines - MIDA (Haulage)Document3 pagesGuidelines - MIDA (Haulage)Yasushi Charles TeoNo ratings yet
- Dolni VestoniceDocument34 pagesDolni VestoniceOlha PodufalovaNo ratings yet
- Pemaknaan School Well-Being Pada Siswa SMP: Indigenous ResearchDocument16 pagesPemaknaan School Well-Being Pada Siswa SMP: Indigenous ResearchAri HendriawanNo ratings yet
- Jesd8 15aDocument22 pagesJesd8 15aSridhar PonnurangamNo ratings yet
- Arta Kelmendi's resume highlighting education and work experienceDocument2 pagesArta Kelmendi's resume highlighting education and work experienceArta KelmendiNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension Exercise, May 3rdDocument3 pagesReading Comprehension Exercise, May 3rdPalupi Salwa BerliantiNo ratings yet
- Google Earth Learning Activity Cuban Missile CrisisDocument2 pagesGoogle Earth Learning Activity Cuban Missile CrisisseankassNo ratings yet
- HP HP3-X11 Exam: A Composite Solution With Just One ClickDocument17 pagesHP HP3-X11 Exam: A Composite Solution With Just One ClicksunnyNo ratings yet
- Typical T Intersection On Rural Local Road With Left Turn LanesDocument1 pageTypical T Intersection On Rural Local Road With Left Turn Lanesahmed.almakawyNo ratings yet
- Individual Performance Commitment and Review Form (Ipcrf) : Mfos Kras Objectives Timeline Weight Per KRADocument4 pagesIndividual Performance Commitment and Review Form (Ipcrf) : Mfos Kras Objectives Timeline Weight Per KRAChris21JinkyNo ratings yet
- Alternate Tuning Guide: Bill SetharesDocument96 pagesAlternate Tuning Guide: Bill SetharesPedro de CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- (123doc) - Chapter-24Document6 pages(123doc) - Chapter-24Pháp NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Study Guide 2023-IvDocument7 pagesDermatology Study Guide 2023-IvUnknown ManNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Additional Mathematics Revision PatDocument7 pagesForm 4 Additional Mathematics Revision PatJiajia LauNo ratings yet
- Prac Res Q2 Module 1Document14 pagesPrac Res Q2 Module 1oea aoueoNo ratings yet
- Role of PAODocument29 pagesRole of PAOAjay DhokeNo ratings yet
- Process Financial Transactions and Extract Interim Reports - 025735Document37 pagesProcess Financial Transactions and Extract Interim Reports - 025735l2557206No ratings yet
- 02 Slide Pengenalan Dasar MapinfoDocument24 pages02 Slide Pengenalan Dasar MapinfoRizky 'manda' AmaliaNo ratings yet
- SBI Sample PaperDocument283 pagesSBI Sample Paperbeintouch1430% (1)
- Efaverenz p1Document4 pagesEfaverenz p1Pragat KumarNo ratings yet
- Condition Based Monitoring System Using IoTDocument5 pagesCondition Based Monitoring System Using IoTKaranMuvvalaRaoNo ratings yet