Professional Documents
Culture Documents
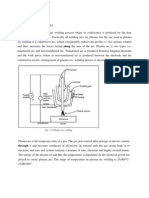
Solid Works Tutorial-Making Wind Turbine Blade
Uploaded by
محمد جوادCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Solid Works Tutorial-Making Wind Turbine Blade
Uploaded by
محمد جوادCopyright:
Available Formats
Ken Youssefi Introduction to Engineering E10
1
Various Blade designs
Ken Youssefi Introduction to Engineering E10
2
Ken Youssefi Introduction to Engineering E10
3
The Blade Shape
Ken Youssefi Introduction to Engineering E10
4
Design groups should conduct a thorough search of the Internet to obtain
information on wind turbine blade design and efficiency. Based on your
research, decide on the number and general shape of the blade.
Constraints:
Total dimension of the turbine blade assembly (diameter of the
swept area) should not exceed 6 inches.
The propeller must
fit within the 6 inch
diameter circle
6 in.
The Blade Shape
Ken Youssefi Introduction to Engineering E10
5
Blade length, measured from the edge of the hub, should not exceed
2.5 inch.
Blade height is limited by the thickness of the hub. It should not
exceed 0.25 inch.
There are no constraints on blade width
The tutorial in the following slides is based on the blade geometry and shape
shown above.
.7 in
.25
Height
Width
Modeling the Wind Turbine Blade
Ken Youssefi Introduction to Engineering E10
6
The hub for the wind turbine
blade has been modeled using
SolidWorks. Download the file
Hub seed SolidWorks located
in the E10 web site under
Wind Turbine Project section
Create the first Reference Plane
Ken Youssefi Introduction to Engineering E10
7
1. Select Sketch and choose the top surface of the
hub to draw.
4. Exit the sketch
2. Draw a line from
the center
3. Dimension the
line 0.25 inch
Create the first Reference Plane
Ken Youssefi Introduction to Engineering E10
8
1. Click on the icon to create the
reference plane
The reference plane passes
through the point and is
perpendicular to the line
2. Select the end of
the line as the first
reference.
3. Select the line
as the second
reference
Creating the Blade Profile at the Hub
Ken Youssefi Introduction to Engineering E10
9
Select Sketch and choose the first
reference plane to draw the blade
profile at the hub
From the View Orientation
menu choose the Normal To
option
Do not be concerned with
the size of the reference
plane; it is infinitely large.
Creating the Blade Profile at the Hub
Ken Youssefi Introduction to Engineering E10
10
Select Convert Entities to project the hub onto the sketch plane to use as a
reference for drawing the profile. Select the top and bottom edges as shown
Make sure you select edges and not surfaces. Zoom in for better view
Creating the Blade Profile at the Hub
Ken Youssefi Introduction to Engineering E10
11
Draw a vertical line from the
midpoints of the projected lines
Draw two more vertical lines on
either side of the previous line
Dimension both lines with
respect to the middle line, 0.35
inch. The 0.7 inch distance
represents the width of the
blade at the hub. (This is a
design variable; you may choose
a different value.)
Creating the Blade Profile at the Hub
Ken Youssefi Introduction to Engineering E10
12
The profile is constructed within
the 0.7 by 0.25 envelope
0.7
0.25
Construct a diagonal line
In this design, 5 points are selected. The end points of the diagonal line must be
included in your point selection. The location of other points are up to you and
will determine shape of the profile, which in turn will affect the power output.
Pt. 1
Pt. 2
Pt. 3
Pt. 4
Pt. 5
Use the spline command to draw
the curved portion of the profile
Creating the Blade Profile at the Hub
Ken Youssefi Introduction to Engineering E10
13
The shape of the spline curve could
be modified by selecting any point
and dragging it to a new position
Make sure the curve does not protrude
beyond the surface of the hub
Delete all construction lines
before exiting the sketch
Creating the Blade Profile at the Tip
Ken Youssefi Introduction to Engineering E10
14
Create the second reference
plane to draw the tip profile
This arrangement will create a blade
sweep area of 6 inch in diameter. It is the
maximum blade size allowed.
Select reference plane option, select the
first reference plane and enter the distance
between the tow planes, 2.75 inch.
2.75 in.
Reference plane to
draw the tip profile
Creating the Blade Profile at the Tip
Ken Youssefi Introduction to Engineering E10
15
Select Sketch and choose the
second reference plane to draw
the tip blade profile.
From the View Orientation
menu choose the Normal To
option.
Project the blade profile at the hub and the bottom
surface into the current sketch plane. This is used as
a reference to draw the tip profile
Creating the Blade Profile at the Tip
Ken Youssefi Introduction to Engineering E10
16
Draw a vertical line from the
midpoints of the projected
diagonal line.
Draw two more vertical lines on
either side of the previous line
Dimension both lines with respect
to the middle line, 0.175 inch. The
0.35 inch represents the width of
the blade at the tip, half of the
width at the hub. This is also a
design variable; you may choose a
different value
Creating the Blade Profile at the Tip
Ken Youssefi Introduction to Engineering E10
17
Use the Spline and line commands
to construct the tip profile. Follow
the same procedure as the profile
at the hub.
Delete all construction lines
before exiting the sketch
This shows the two blade
profiles, at the hub and at the
tip
Creating the Blade - Loft
Ken Youssefi Introduction to Engineering E10
18
Select the Loft command and
choose the two profile
Hub profile
Tip profile
Rounding the Blade Edges Fillet Command
Ken Youssefi Introduction to Engineering E10
19
The blade edges should be rounded
in order to obtain a model with
clean edges. The 3D printer is not
capable of modeling sharp edges.
Select the Fillet command,
choose the edges and provide
a radius for the fillet.
Fillet
Ken Youssefi Introduction to Engineering E10
20
Select the front edge
Assign a value
of 0.015 inch
to the front
edge
Select Fillet again and choose
the back edge and assign a
value of 0.01 inch
Completing the Rotor Pattern Command
Ken Youssefi Introduction to Engineering E10
21
Select the Circular Pattern
command
Select the axis of the circular
pattern, choose the circle
Choose the number of the blades
Check the Equal spacing box for full
360 deg.
Select the blade
Embossing the Hub
Ken Youssefi Introduction to Engineering E10
22
In order to identify your blade it has to be embossed with your group
number and lab. section.
Select Sketch and choose the top surface of
the hub. Use the Text command and write
your group number (G4) and lab. section
number (S8). Make sure the text is not too
close to the hole.
Embossing the Hub
Ken Youssefi Introduction to Engineering E10
23
Select the text and right click to
modify, move, scale,.
Embossing the Hub
Ken Youssefi Introduction to Engineering E10
24
Extrude the
text by 0.025
to 0.03 inch
Ken Youssefi Introduction to Engineering E10
25
The Rotor
Ken Youssefi Introduction to Engineering E10
26
You might also like
- Lesson 2 - Formular One Car DesignDocument25 pagesLesson 2 - Formular One Car DesignNdianabasi Udonkang100% (1)
- Project Report of Motorcycle ModelDocument15 pagesProject Report of Motorcycle ModelM Kashif RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Design and Optimization of Front Wheel AssemblyDocument69 pagesDesign and Optimization of Front Wheel Assemblynikhil pandkarNo ratings yet
- Wheelhub Integration of Electric Motor in FSEDocument35 pagesWheelhub Integration of Electric Motor in FSEShivam WankhedeNo ratings yet
- Auto Transmission - NotesDocument34 pagesAuto Transmission - Notesvandanaharikumar100% (2)
- Be Sem 8 Automobile Engineering NotesDocument75 pagesBe Sem 8 Automobile Engineering NotesVaibhav Vithoba Naik100% (7)
- Dynamometer Operation and PrinciplesDocument4 pagesDynamometer Operation and PrinciplesAngel OfrenNo ratings yet
- Design Project of ShaftDocument37 pagesDesign Project of Shaftniranjanbmazire100% (1)
- Design and Stress Analysis of Crankshaft For 4 Stroke Diesel EngineDocument17 pagesDesign and Stress Analysis of Crankshaft For 4 Stroke Diesel EngineSIDDH BHOSALE100% (3)
- Design and Analysis of Disc Brake and Caliper of Four WheelerDocument5 pagesDesign and Analysis of Disc Brake and Caliper of Four WheelerIJSTENo ratings yet
- Synchromesh Gearbox Definition Construction Working Principle Advantages Application Notes PDFDocument9 pagesSynchromesh Gearbox Definition Construction Working Principle Advantages Application Notes PDFMelanie MartinssonNo ratings yet
- Design - Report (PDR)Document8 pagesDesign - Report (PDR)Abhishek DixitNo ratings yet
- New Automotive Suspension SystemsDocument30 pagesNew Automotive Suspension SystemsAbubaker MuzayinNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Renewable Energy System: Student Presentation Kshitij Raj Dhara CH18B052Document14 pagesHybrid Renewable Energy System: Student Presentation Kshitij Raj Dhara CH18B052Kshitij Mysterio DharaNo ratings yet
- History of Suspension SystesmDocument6 pagesHistory of Suspension Systesmmangutkar_amit67% (3)
- Gear Trains - Lecture 10Document22 pagesGear Trains - Lecture 10priyankar007No ratings yet
- Emission Control On IC EngineDocument18 pagesEmission Control On IC Enginetarunskumar89% (19)
- Parametric Spur GearDocument11 pagesParametric Spur GearGoutam AcharjeeNo ratings yet
- Crankshaft Full Report 2Document208 pagesCrankshaft Full Report 2Anirudhreddy SafalNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Load Analysis and Optimization of A Fracture-Split Connecting RodDocument11 pagesDynamic Load Analysis and Optimization of A Fracture-Split Connecting RodRahul BadgujarNo ratings yet
- 08 CH-6, Fluid Motion Within Combustion ChamberDocument24 pages08 CH-6, Fluid Motion Within Combustion ChamberAhsan AliNo ratings yet
- Introduction To IC EnginesDocument76 pagesIntroduction To IC Engineskedirabduri88No ratings yet
- Oldham CouplingDocument5 pagesOldham CouplingArsh 837No ratings yet
- Vehicul HybridDocument89 pagesVehicul Hybridmihai_1957No ratings yet
- Drum Brake Design for BAJA VehicleDocument3 pagesDrum Brake Design for BAJA VehiclepravinkumarkrNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 02: Aim: To Study and Design of Knuckle Joint. TheoryDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 02: Aim: To Study and Design of Knuckle Joint. TheoryAnubhav Singh0% (1)
- Design and Analysis of Crankshaft For Internal Combustion EngineDocument5 pagesDesign and Analysis of Crankshaft For Internal Combustion EngineEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- MOdern Welding ProcessesDocument25 pagesMOdern Welding ProcessesAnwar Sadath M A50% (2)
- Engine DesignDocument60 pagesEngine DesignGuri DhindsaNo ratings yet
- EM BRAKING SYSTEMDocument15 pagesEM BRAKING SYSTEMKushal TamboliNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Method Axial ElementsDocument57 pagesFinite Element Method Axial ElementsAhmad FaidhiNo ratings yet
- Ic Engine Project ReportDocument6 pagesIc Engine Project ReportAtulkumarSutharNo ratings yet
- Inventor Gear Fastener TutorialDocument13 pagesInventor Gear Fastener TutorialIRONSAVIORNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Breaking SystemDocument27 pagesElectromagnetic Breaking SystemRaj KamalNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Analysis of A Car Chassis PDFDocument5 pagesDynamic Analysis of A Car Chassis PDFsultanu89No ratings yet
- Brake CalculationsDocument36 pagesBrake CalculationsAnuragKarnaNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion EnginesDocument70 pagesInternal Combustion EnginesPeter ParkerNo ratings yet
- Lecture 32 Thermal Engineering II (24.09.2020)Document63 pagesLecture 32 Thermal Engineering II (24.09.2020)Dr. BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Ic EngineDocument23 pagesIc EngineGanesh kumar100% (1)
- Presentation On Design of Transmission System For A GokartDocument21 pagesPresentation On Design of Transmission System For A GokartNikhil WarungaseNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis Using ANSYS Mechanical APDL ANSYS WorkbenchDocument5 pagesFinite Element Analysis Using ANSYS Mechanical APDL ANSYS WorkbenchPrashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Supercharger: BY Manhar 15AE60R18Document19 pagesSeminar On Supercharger: BY Manhar 15AE60R18Hatinderpal SinghNo ratings yet
- ANITS PPT On GREEN ENGINEDocument13 pagesANITS PPT On GREEN ENGINESampath KumarNo ratings yet
- Thermo Coupled Stress Analysis of Exhaust Manifold Assemblage Using ABAQUSDocument6 pagesThermo Coupled Stress Analysis of Exhaust Manifold Assemblage Using ABAQUSInfogain publicationNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided Design and Analysis of Disc Brake Rotors 2167 7670 1000144Document13 pagesComputer Aided Design and Analysis of Disc Brake Rotors 2167 7670 1000144A L Andriana SyaripNo ratings yet
- Development of CNG Injection EngineDocument8 pagesDevelopment of CNG Injection EngineShasahank JoshiNo ratings yet
- Problems On Engineering Drawing 1st YearDocument30 pagesProblems On Engineering Drawing 1st YearKrishna AsharNo ratings yet
- Solid Works Tutorial Wind Turbine Blade1Document27 pagesSolid Works Tutorial Wind Turbine Blade1Ignacio Ramírez RomeroNo ratings yet
- The Blade Design: TutorialDocument27 pagesThe Blade Design: TutorialOsama AlwakkafNo ratings yet
- Making Helical Gear in Creo 1.0Document6 pagesMaking Helical Gear in Creo 1.0UmairZahidNo ratings yet
- En-Catia v5r13 Designer Guide Chapter9-Working With Wireframe and Surface Design WorkbenchDocument40 pagesEn-Catia v5r13 Designer Guide Chapter9-Working With Wireframe and Surface Design Workbenchmictlan56100% (1)
- Catia Exercises With Image Aid ExplanationDocument38 pagesCatia Exercises With Image Aid ExplanationKaran KatochNo ratings yet
- Solid Edge - Tund8Document30 pagesSolid Edge - Tund8Edmund Laugasson100% (4)
- EN-Catia v5r13 Designer Guide Chapter9-Working With Wireframe and Surface Design Workbench PDFDocument40 pagesEN-Catia v5r13 Designer Guide Chapter9-Working With Wireframe and Surface Design Workbench PDFNhan LeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Formula One Car DesignDocument15 pagesLesson 3 - Formula One Car DesignNdianabasi UdonkangNo ratings yet
- EGR 110 Inventor Lecture FeaturesDocument28 pagesEGR 110 Inventor Lecture FeaturesdineshThangavelNo ratings yet
- Making 3D Threads in Solidworks 2009Document16 pagesMaking 3D Threads in Solidworks 2009Quiqua Acosta Fonseca0% (1)
- Lesson 1 - Formula One Car DesignDocument16 pagesLesson 1 - Formula One Car DesignNdianabasi Udonkang100% (1)
- Introduction To Engineering, E10. 1Document35 pagesIntroduction To Engineering, E10. 1Mani KandanNo ratings yet
- NX 9 for Beginners - Part 2 (Extrude and Revolve Features, Placed Features, and Patterned Geometry)From EverandNX 9 for Beginners - Part 2 (Extrude and Revolve Features, Placed Features, and Patterned Geometry)No ratings yet
- Mass Transfer HMTDocument6 pagesMass Transfer HMTمحمد جوادNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer HMTDocument6 pagesMass Transfer HMTمحمد جوادNo ratings yet
- Application For Apprentice / Artisan Trainee BATCH 2014Document1 pageApplication For Apprentice / Artisan Trainee BATCH 2014محمد جوادNo ratings yet
- RP11LDocument18 pagesRP11Lمحمد جوادNo ratings yet
- 60 Days To Fit ProgramDocument7 pages60 Days To Fit ProgramJorge Radrusian PiocudaNo ratings yet
- 1 Presentation Echometer QRod Quick Rod DesignDocument23 pages1 Presentation Echometer QRod Quick Rod DesignNIno Lenin Yupanqui SanchezNo ratings yet
- 60 Days To Fit ProgramDocument7 pages60 Days To Fit ProgramJorge Radrusian PiocudaNo ratings yet
- HIT Jobs 8 5 17Document2 pagesHIT Jobs 8 5 17محمد جوادNo ratings yet
- Winter 2016 Fee Schedule Grad INTLDocument1 pageWinter 2016 Fee Schedule Grad INTLمحمد جوادNo ratings yet
- Correcting SentencesDocument3 pagesCorrecting Sentencesمحمد جوادNo ratings yet
- PrintDocument2 pagesPrintمحمد جوادNo ratings yet
- PrintDocument2 pagesPrintمحمد جوادNo ratings yet
- 3RefrigerationCycle PDFDocument14 pages3RefrigerationCycle PDFYhn DfNo ratings yet
- Ielts Writing ModuleDocument40 pagesIelts Writing Moduleمحمد جوادNo ratings yet
- Gatsp 1Document9 pagesGatsp 1zbalouch15No ratings yet
- Solar RadiationDocument7 pagesSolar Radiation5886552No ratings yet
- RP11LDocument18 pagesRP11Lمحمد جوادNo ratings yet
- Energy Resources and UtilizationDocument34 pagesEnergy Resources and UtilizationHassan Safdar MalikNo ratings yet
- Ref 2 Q#7Document4 pagesRef 2 Q#7محمد جوادNo ratings yet
- 2010 EE SummerSemester 2012 E10Document1 page2010 EE SummerSemester 2012 E10محمد جوادNo ratings yet
- 170 Rotational InertiaDocument3 pages170 Rotational Inertiaمحمد جوادNo ratings yet
- AIAA Papers TemplateDocument8 pagesAIAA Papers Templateمحمد جواد100% (1)
- Foreign PolicyDocument11 pagesForeign Policyمحمد جواد0% (1)
- Development of A Hydro-Mechanical Hydraulic Hybrid Drive Train With Independent Wheel Torque Control For An Urban Passenger VehicleDocument11 pagesDevelopment of A Hydro-Mechanical Hydraulic Hybrid Drive Train With Independent Wheel Torque Control For An Urban Passenger Vehicleمحمد جوادNo ratings yet
- Speed Breaker Power Generation MechanismsDocument32 pagesSpeed Breaker Power Generation MechanismsChetan Tiwary0% (1)
- Tower Bridge: London, EnglandDocument21 pagesTower Bridge: London, Englandمحمد جوادNo ratings yet
- PAPA Admission FormDocument1 pagePAPA Admission Formمحمد جوادNo ratings yet
- 75-Centrifugal Pump Vibration Caused by Supersynchronous Shaft Instability - DRS&SMPDocument14 pages75-Centrifugal Pump Vibration Caused by Supersynchronous Shaft Instability - DRS&SMPمحمد جوادNo ratings yet
- A Text Book On Automobile Chassis and Body Engineering (ADocument58 pagesA Text Book On Automobile Chassis and Body Engineering (Ahunny29100% (2)
- Problem Set 1 CirclesDocument2 pagesProblem Set 1 Circlesapi-339611548100% (1)
- AdvancesDocument328 pagesAdvanceshanumsj123No ratings yet
- Unit Testing in Delphi by Nick Hodges 110214Document36 pagesUnit Testing in Delphi by Nick Hodges 110214air4gbNo ratings yet
- Digital Image Processing TechniquesDocument34 pagesDigital Image Processing Techniquesaishuvc1822No ratings yet
- Tut 5. Two-Column Hammerhead Pier PDFDocument35 pagesTut 5. Two-Column Hammerhead Pier PDFOscar Varon BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Anchor BayDocument56 pagesAnchor BayAnonymous dHyxmDNo ratings yet
- Digital and Analog SignalsDocument10 pagesDigital and Analog SignalsSrishti GargNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Term1 Properties of 2-D Shapes Lesson 7Document4 pagesGrade 6 Term1 Properties of 2-D Shapes Lesson 7Ayanda Siphesihle NdlovuNo ratings yet
- PID CONTROL SIMULATIONDocument6 pagesPID CONTROL SIMULATIONadrianordsNo ratings yet
- Types of VerbDocument4 pagesTypes of VerbFaisal MalikNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Class 10 CBSE (NCERT)Document369 pagesMathematics Class 10 CBSE (NCERT)LinoNo ratings yet
- Lighting SchemesDocument7 pagesLighting SchemesSharath CherryNo ratings yet
- Ee242 Lect06 TwoportsDocument32 pagesEe242 Lect06 TwoportsZyad IskandarNo ratings yet
- Measurement of SubstructureDocument24 pagesMeasurement of SubstructureAamaniVeeranam80% (10)
- PEA ClocksDocument50 pagesPEA ClocksSuresh Reddy PolinatiNo ratings yet
- Rac NotesDocument16 pagesRac NotesJohnRay LominoqueNo ratings yet
- Heat Combustion Laboratory ReportDocument8 pagesHeat Combustion Laboratory ReportSteven Lee100% (1)
- Ductile deformation finite strain analysisDocument27 pagesDuctile deformation finite strain analysisJorgeBarriosMurielNo ratings yet
- Kitchen Chemistry ExperimentDocument7 pagesKitchen Chemistry ExperimentMss FaixaNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Weber and MorrisDocument12 pagesDiffusion Weber and MorrisFarah El ShahawyNo ratings yet
- MMW Module 2.2 (Part 2)Document6 pagesMMW Module 2.2 (Part 2)ROJE DANNELL GALVANNo ratings yet
- Full Paper Template IRC 2020Document3 pagesFull Paper Template IRC 2020Mobina AbdulRaufNo ratings yet
- 3-Lecture 03 Translational Mechanical System3-SDocument23 pages3-Lecture 03 Translational Mechanical System3-SHamza KhanNo ratings yet
- Splunk Skills Assessment-UpdatedDocument14 pagesSplunk Skills Assessment-Updatedtsegay.csNo ratings yet
- Business Analyst TrainingDocument3 pagesBusiness Analyst TrainingMuniswamaiah Mohan100% (1)
- SQL SlidesDocument65 pagesSQL SlidescopsamostoNo ratings yet
- Post GreeDocument15 pagesPost GreeDwi PraptiNo ratings yet
- Mic 2282Document10 pagesMic 2282mariusz sNo ratings yet
- Clone Steps RmanDocument10 pagesClone Steps RmanKishore AdikarNo ratings yet
- Cross Taping - A Practical Guide 12Document2 pagesCross Taping - A Practical Guide 12jfjjfjfjjfjfNo ratings yet