Professional Documents
Culture Documents
English k6 Asm2
Uploaded by
api-2604431960 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
163 views6 pagesOriginal Title
english k6 asm2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
163 views6 pagesEnglish k6 Asm2
Uploaded by
api-260443196Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
1
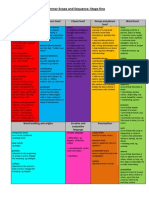
Scope and sequence of grammar and punctuation skills K6
The following scope and sequence of grammar and punctuation framework indicates those understandings and
terms which students might be expected to have control of by the end of each stage. It is arranged according to
levels of text organisation: from the broad text level to specifics of word level grammar. It indicates the stage at
which key concepts should be introduced. Concepts addressed in earlier stages should be reviewed and
consolidated according to student needs and syllabus requirements.
TEXT LEVEL COHESION
Early Stage 1 Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3
pronoun reference
determining the noun to
which a pronoun refers,
eg Koalas eat leaves.
Koalas are not bears.
They are
synonyms
words that have the same
or similar meaning,
eg leave/depart,
tired/weary
antonyms
words that have opposite
meanings, eg hot/cold,
arrive/leave
time connectives
words that sequence
information in texts,
eg first, next, finally
word families
words linked because they
deal with the same topic
nounpronoun
agreement
selection of the correct
pronoun (considering
number and gender) for
the noun or noun group to
which it refers, eg The girl
ate her lunch; The dogs
enjoyed their walk
Subjectverb agreement
selection of a verb form
which matches the
number of its subject
(noun or noun group),
eg They were at home;
The cat is sitting still; The
people are on the boat
homonyms and
homophones
homonyms: words
with the same sound
and the same spelling,
but a different meaning,
eg bark (tree), bark
(sound made by dog)
homophones: words
with the same sound
but different spelling
and meaning, eg fair,
fare
cohesive links
eg, pronouns,
conjunctions, connectives
connectives
words which link
paragraphs and
sentences, eg on the
other hand, however,
furthermore, therefore,
because, although
nominalisation
forming nouns from
verbs (eg reaction from
react or departure from
depart) or adjectives
(eg length from long,
eagerness from eager)
reference links
links that keep track of
the people, animals or
objects throughout a text;
usually nouns or
pronouns, eg Mabel
played netball on
Saturday. She fell over
and hurt her arm
SENTENCE LEVEL STRUCTURE OF THE SENTENCE
Early Stage 1 Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3
sentence
one or more clauses; a
key unit for expressing
ideas. A written sentence
begins with a capital letter
and ends with a full stop,
question mark or
exclamation mark, eg Kim
broke the vase. Kim
tripped on the step and
she broke the vase
compound sentence
two or more clauses
usually linked by a
coordinating conjunction,
eg The bell rang and Kim
went home
quoted (direct) speech
eg, Kim said, I want to go
home
complex sentence
an independent (main)
clause and a dependent
(subordinate) clause
linked by a subordinating
conjunction (indicating
time, place, manner,
reason, condition),
eg We all went outside
when the sun came out.
When the sun came out,
we all went outside
topic sentence
a sentence that introduces
the main idea or theme of
a paragraph
2
conjunction
joining word, eg and, so,
but
reported (indirect)
speech
eg, Kim said that she
wanted to go home
coordinating
conjunction
a word or words that link
phrases and clauses,
eg as, and, or, either/
neither, but, so, and, then
paragraph
two or more sentences
centred on the same
theme or idea; begins
with a topic sentence
(introducing the theme or
idea) in factual texts
quoted (direct) speech
eg, I am going to leave,
she said
reported (indirect)
speech
eg, She said that she
was going to leave
CLAUSE LEVEL STRUCTURE OF THE CLAUSE
Early Stage 1 Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3
statement
provides information,
eg I am leaving now
question
asks for an answer,
eg Are you busy?
command
tells us to do something,
eg Close the door
exclamation
for emphasis, eg I won!
clause
a complete message or
thought expressed in
words:
a clause includes
at least one noun and
one verb
a clause may be a
sentence on its own
(main clause) or may
be combined with a
main clause to form
a sentence
a clause may tell us
about an action and
those involved in the
action, eg Mark (noun
doer) opened (verb
action verb) the door
(noun done to)
clause
a complete message or
thought expressed in
words:
a clause includes a verb
a clause includes a
subject (noun or noun
group that agrees with
the verb in person and
number), eg The
children ran to the bus
a clause may include
an object (additional
noun or noun group,
affected by the action),
eg The children ran to
the bus
a clause may be a
sentence on its own
(main clause) or may
be combined with a
main clause to form a
sentence
main clause
(independent clause)
a clause that can stand
alone as a complete
sentence, though it may
be joined with other
clauses, eg The child
came first
subordinate clause
(dependent clause)
a clause that cannot stand
alone as a sentence
voice
indicates who or what is
performing an action;
modified by changing the
beginning focus of a
clause:
active voice the
doer comes before the
verb, eg Mark (doer)
finished (verb) the work
(done to)
passive voice the
receiver of the action is
placed before the verb,
eg The work (receiver)
was finished (action) by
Mark (doer)
author voice
use of first-person and
third-person narration
3
GROUP AND PHRASE LEVEL
Structure of the noun group
Early Stage 1 Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3
noun group
a group of words built
around a noun that
describes or specifies
the noun:
may include articles or
adjectives, eg the sunny
day, a long and bumpy
road
may include two or
more nouns, eg boys
and girls, cats and dogs
noun group
a group of words built
around a noun that
describes or specifies
the noun:
may include different
types of articles,
adjectives and nouns
linked together, eg the
(article) three (number)
beautiful (opinion
adjective) native
(classifying adjective)
flowers (noun)
noun group
a group of words built
around a noun that
describes or specifies
the noun:
may include adjectival
phrases, eg the chair
next to my desk
may include adjectival/
relative clauses, eg the
chair that is next to my
desk
Structure of the verb group
Early Stage 1 Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3
verb group
a group of words built up
around a verb:
may include auxiliary
(helping) verbs,
eg She is sitting here
may include two or
more verbs, eg He
huffed and puffed
verb group
a group of words built up
around a verb:
may include a
preposition or adverb,
eg The plane took off
may include modal
verbs, eg It might be
finished tomorrow
may be complex verbs,
eg The plane started to
move
Structure of the adverbial phrase
Early Stage 1 Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3
where/when/how
adverbial phrase
contributes extra
information about the main
clause, eg where, when or
how, eg Kim broke the
vase in the morning
(when); My mother was
standing beside my bed
(where)
adverbial phrase
contributes extra
information about the
main clause, eg how,
when, where, why:
includes a preposition
plus a noun group
tells us more about the
action, eg Kim broke the
vase in the morning
(when); My mother was
standing beside my bed
(where); I went home
with a friend (with
whom)
4
WORD LEVEL
Nouns
Early Stage 1 Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3
noun
a naming word for a
person, place or thing
noun
a naming word for a
person, place or thing:
common noun,
eg girl, city
proper noun,
eg Mary, Sydney
concrete noun
(tangible, may be a
common noun or proper
noun)
abstract nouns, eg
happiness, surprise
noun
a naming word for a
person, place or thing:
singular, eg girl
plural, eg girls
collective, eg crowd
term of address,
eg Mr Jones
noun
a naming word for a
person, place or thing:
technical, eg nucleus
Articles
Early Stage 1 Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3
article
a, an, the
placed before a noun to
form part of a noun group;
may refer to a specific
person or thing (the), or a
non-specific person or
thing (a, an)
Adjectives
Early Stage 1 Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3
adjective
a word that describes a
noun
adjective
a word that describes a
noun:
describing, eg size,
colour, shape (big, red,
round, beautiful, sunny)
numbering, eg two
adjective
a word that describes a
noun:
possessive, eg our
comparative, eg bigger
adjective
a word that describes a
noun:
classifying, eg native
flower
modal, eg possible
answer
Pronouns
Early Stage 1 Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3
pronoun
a word that stands
instead of a noun, eg I,
me, he, she
pronoun
a word that stands instead
of a noun:
personal pronoun,
eg I, me, him, it
possessive pronoun,
eg This book is mine;
it is not yours
pronoun
a word that stands instead
of a noun:
relative pronoun,
eg who, that (for
people) and which,
that (for things)
5
Verbs
Early Stage 1 Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3
verb
a word that tells what is
happening or what is:
action verb (describes
doing or saying), eg run,
shout
thinking verb,
eg wonder
verb
a word that tells what is
happening or what is:
relating verb,
eg She is my teacher
feeling verb,
eg I liked the movie
possessing verb,
eg He has a new car
tense
eg, She went home (past);
Koalas eat leaves
(present); She will arrive
tomorrow (future)
elaborated tenses
multiple word tenses,
eg We have been working
for three hours
Adverbs
Early Stage 1 Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3
who/what/when/where
words
adverb
a word that describes a
verb or adjective to tell
when, where or how, eg
She sings occasionally;
He is really interesting
adverb
a word that tells something
about a verb, adjective or
another verb, eg manner,
place or time. Adverbs
may show:
modality, eg possibly
degree, eg very
comments or opinions,
eg luckily
Prepositions
Early Stage 1 Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3
preposition
placed in front of a noun
group to show where or
when, eg on the box
(where), before my
birthday (when)
preposition
placed in front of a noun
group to show time
(when), place (where),
manner (how) or causality
(why), eg in front of,
throughout, underneath
prepositional phrases
units of meaning within a
clause that begin with a
preposition; indicate how,
when, where or why, eg
She ran into the garden,
He is available from nine
oclock
6
WORD BUILDING AND ORIGINS
Early Stage 1 Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3
compound word
two words combined,
eg playground
base words
eg happy
prefixes
attached to the beginning
of a base word to change
the meaning, eg unhappy
suffixes
attached to the end of a
base word to change the
meaning, eg happily
word origins
the source and history
of words (etymology),
eg telephone (Greek),
pedestrian (Latin),
bungalow (Indian)
CREATIVE AND EVALUATIVE LANGUAGE
Early Stage 1 Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3
creative language
features
alliteration, eg slippery,
slithering snakes
onomatopoeia, eg the
wind whooshed
repetition
evaluative language
includes words used to
express feelings and
opinions, judgements and
assessments, eg it was an
excellent piece of writing
creative language
features
simile, eg She sings like
an angel
metaphor, eg She is an
angel
idiom, eg Pull yourself
together
personification, eg The
water licked at my feet
nonsense words,
spoonerisms,
neologisms, puns
evaluative language
words used to give a text
a particular perspective
(eg judgemental, critical,
emotional), to evoke a
particular audience
response, and to express
shades of feeling, meaning
or opinion, eg:
emotive language
modality (possibility,
probability, obligation,
conditionality)
creative language
features
emphasis
irony
humour
PUNCTUATION
Early Stage 1 Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3
capital letter
used for names and to
signal the beginning of a
sentence
full stop
used to signal the end of a
sentence
question mark
used to signal a question
exclamation mark
used to provide emphasis
quotation marks
used to signal quoted
(direct) speech
capital letter
used for proper nouns
question mark
used to signal the end of a
question
exclamation mark
used to signal the end of
an exclamation
comma
separates items in a list
quotation marks
used to signal dialogue,
titles and quoted (direct)
speech
apostrophe
used to signify a
contraction
apostrophe
used to signify possession
comma
used to separate clauses
You might also like
- Dps Grammar Stage 1Document3 pagesDps Grammar Stage 1api-198669584No ratings yet
- ELT122-Week 1-3 (pg.14-19)Document38 pagesELT122-Week 1-3 (pg.14-19)Becira LiNo ratings yet
- Word Classes ExplainedDocument120 pagesWord Classes ExplainedkavilankuttyNo ratings yet
- The Simple Sentence: Parts of Speech Sentence AnalysisDocument7 pagesThe Simple Sentence: Parts of Speech Sentence AnalysismiriamacunaNo ratings yet
- Grammar Help Grade 4Document10 pagesGrammar Help Grade 4api-235903058No ratings yet
- Textbook 2Document91 pagesTextbook 2Anh PhanNo ratings yet
- The Grammar of EnglishDocument95 pagesThe Grammar of EnglishgratielageorgianastoicaNo ratings yet
- SSC Hacks - EnglishDocument202 pagesSSC Hacks - EnglishArun Dominic100% (1)
- Module 1 Eh TKT Handbook PDFDocument59 pagesModule 1 Eh TKT Handbook PDFCristian BritoNo ratings yet
- Preposition, Conjunction and ParticiplesDocument22 pagesPreposition, Conjunction and ParticiplesAudrey MonicaNo ratings yet
- Grammar Parts of Speech GuideDocument5 pagesGrammar Parts of Speech GuideTaufik IsmailNo ratings yet
- Tommy BoyDocument8 pagesTommy BoyawaiskhattakNo ratings yet
- NHA2 - Form ClassesDocument36 pagesNHA2 - Form Classes08AV2DNo ratings yet
- GNS 314 - (Comprehensive Note Till Direct and Indirect Speech)Document13 pagesGNS 314 - (Comprehensive Note Till Direct and Indirect Speech)Bn SulaimanNo ratings yet
- A. Part of Speech: Name: Nurul Aulia Ramadhani HRP NPM: 19052043Document7 pagesA. Part of Speech: Name: Nurul Aulia Ramadhani HRP NPM: 19052043Syarifah Tasya AlhabsyiNo ratings yet
- NHA2 - Form ClassesDocument36 pagesNHA2 - Form Classes08AV2DNo ratings yet
- Part of SpeechDocument4 pagesPart of SpeechJibran AyazNo ratings yet
- Compilation of GrammarDocument9 pagesCompilation of Grammarwinsyt35No ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument27 pagesParts of Speechelvire100% (1)
- Sentence CorrectionDocument10 pagesSentence CorrectionsanjivsingNo ratings yet
- Grammar On One Page Updated Sept302012Document1 pageGrammar On One Page Updated Sept302012api-261205798No ratings yet
- Pertemuan: 3 Lembaran Kerja Iii Mata Kuliah English Grammar SKS: 4 Kode: Hari/ Tanggal: WaktuDocument7 pagesPertemuan: 3 Lembaran Kerja Iii Mata Kuliah English Grammar SKS: 4 Kode: Hari/ Tanggal: WaktuAkwilla SylvaniaNo ratings yet
- Basic Grammar RulesDocument24 pagesBasic Grammar RulesAudit Department100% (1)
- Sentence AnalysisDocument32 pagesSentence AnalysisPantho BaruaNo ratings yet
- Addresser Context/message/contact/code Addressee Emotive Referential/poetic/phatic/metalingual ConativeDocument8 pagesAddresser Context/message/contact/code Addressee Emotive Referential/poetic/phatic/metalingual ConativeMiriam MessinaNo ratings yet
- Glossary - Module 1 (1) TEFLDocument26 pagesGlossary - Module 1 (1) TEFLAnum hanifNo ratings yet
- English Grammar Made EasyDocument17 pagesEnglish Grammar Made EasyAyaz Latif Siyal84% (19)
- Principles Concepts in Teaching Grammar 2Document53 pagesPrinciples Concepts in Teaching Grammar 2jheck alcazarNo ratings yet
- A Word and Its Form InflectionDocument17 pagesA Word and Its Form InflectionErvin EXorcistNo ratings yet
- English 111 ReviewerDocument7 pagesEnglish 111 ReviewerCharles IldefonsoNo ratings yet
- Syntax: The English LanguageDocument21 pagesSyntax: The English LanguageAndreea DeeaNo ratings yet
- Sentence ProblemsDocument53 pagesSentence Problemsdennise100% (1)
- Assmt Grammar HBET 2103Document16 pagesAssmt Grammar HBET 2103Wan Salmizan AzhaNo ratings yet
- Translation Indonesia - English: Class 6/LDocument29 pagesTranslation Indonesia - English: Class 6/LYuniharti KhoirunisaNo ratings yet
- Grammar Help Grade 5Document14 pagesGrammar Help Grade 5api-235903058100% (1)
- Parts of Speech 1Document9 pagesParts of Speech 1Sam YanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To English Language - 231009 - 173858Document57 pagesIntroduction To English Language - 231009 - 173858nicholas.ssekyanziNo ratings yet
- Alfa RO RuleDocument3 pagesAlfa RO RuleRaju NiraulaNo ratings yet
- Lap 4 PresentationDocument43 pagesLap 4 PresentationCencen EbajayNo ratings yet
- Randi Ramadhan - 2001032054 - 2C D3 TLDocument8 pagesRandi Ramadhan - 2001032054 - 2C D3 TLRandii RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Gramma IDocument49 pagesGramma ITesfu HettoNo ratings yet
- TKT GlossaryDocument30 pagesTKT Glossaryerischolar2003No ratings yet
- ADVERBIALS - Quick GuideDocument9 pagesADVERBIALS - Quick GuideRona CamposNo ratings yet
- Definitions and ExamplesDocument9 pagesDefinitions and Examplesnninda divaNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech OverviewDocument4 pagesParts of Speech OverviewValentina SeoaneNo ratings yet
- CEBGADocument28 pagesCEBGACZYSTYNo ratings yet
- CEBallDocument70 pagesCEBallCZYSTYNo ratings yet
- Word ClassesDocument12 pagesWord ClassesNalin HettiarachchiNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument3 pagesParts of SpeechTaha AhmadNo ratings yet
- Active Voice: Ah!, Ouch!, Well!)Document4 pagesActive Voice: Ah!, Ouch!, Well!)Made GadingNo ratings yet
- Syntax: A Guide to Parts of Speech, Phrase Structure, and Sentence TypesDocument36 pagesSyntax: A Guide to Parts of Speech, Phrase Structure, and Sentence TypesAneu DamayantiNo ratings yet
- Syntax OralDocument21 pagesSyntax OralDavid PrýglNo ratings yet
- GrammarDocument32 pagesGrammarAndres MinguezaNo ratings yet
- PEG SkriptaDocument85 pagesPEG SkriptaArnesa DžulanNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument9 pagesParts of SpeechJose BrabanteNo ratings yet
- Morpholoical ProcessesDocument30 pagesMorpholoical ProcessesLuqman HakimNo ratings yet
- Easy Learning How to Use English: Your essential guide to accurate EnglishFrom EverandEasy Learning How to Use English: Your essential guide to accurate EnglishRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Back to School: 1,001 Facts You Learned and Forgot in High SchoolFrom EverandBack to School: 1,001 Facts You Learned and Forgot in High SchoolRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- s3 Geo ChecklistDocument8 pagess3 Geo Checklistapi-260443196No ratings yet
- s2 Geo ChecklistDocument9 pagess2 Geo Checklistapi-260443196No ratings yet
- s1 Geo ChecklistDocument6 pagess1 Geo Checklistapi-260443196No ratings yet
- History s1 Past and Present Fam LifeDocument4 pagesHistory s1 Past and Present Fam Lifeapi-260443196No ratings yet
- st2 Geography Aust Features FinalDocument7 pagesst2 Geography Aust Features Finalapi-260443196No ratings yet
- Checklist Geo Es1Document3 pagesChecklist Geo Es1api-260443196No ratings yet
- The Way We Were - s1Document8 pagesThe Way We Were - s1api-260443196No ratings yet
- History s2 Sampleu1Document5 pagesHistory s2 Sampleu1api-245531652No ratings yet
- Es1 History Unit Personal and Family HistoriesaDocument4 pagesEs1 History Unit Personal and Family Historiesaapi-2604431960% (1)
- History s3 Australian ColoniesDocument5 pagesHistory s3 Australian Coloniesapi-260443196No ratings yet
- History s3 Australia As A NationDocument5 pagesHistory s3 Australia As A Nationapi-260443196No ratings yet
- History Es1 Personal Family HistoryDocument3 pagesHistory Es1 Personal Family Historyapi-260443196No ratings yet
- st1 Geography Australian Places FinalDocument8 pagesst1 Geography Australian Places Finalapi-260443196No ratings yet
- st2 Geography Aust Neighbours FinalDocument8 pagesst2 Geography Aust Neighbours Finalapi-260443196No ratings yet
- st3 Connections and Perceptions FinalDocument8 pagesst3 Connections and Perceptions Finalapi-260443196No ratings yet
- st2 Geography Natural Environment FinalDocument10 pagesst2 Geography Natural Environment Finalapi-260443196No ratings yet
- st2 Geography National Park FinalDocument9 pagesst2 Geography National Park Finalapi-260443196No ratings yet
- st3 Geography Contemporary Landuse FinalDocument6 pagesst3 Geography Contemporary Landuse Finalapi-260443196No ratings yet
- st1 Geography Local Places FinalDocument9 pagesst1 Geography Local Places Finalapi-260443196No ratings yet
- st1 Geography Around World FinalDocument4 pagesst1 Geography Around World Finalapi-260443196No ratings yet
- st1 Geography Weather FinalDocument6 pagesst1 Geography Weather Finalapi-260443196No ratings yet
- st1 Geography Aboriginal Connections FinalDocument4 pagesst1 Geography Aboriginal Connections Finalapi-260443196No ratings yet
- st3 Geography Bushfire Mitigation FinalDocument8 pagesst3 Geography Bushfire Mitigation Finalapi-260443196No ratings yet
- Est1 Geography School Grounds FinalDocument6 pagesEst1 Geography School Grounds Finalapi-260443196No ratings yet
- Es1 Get Into GymDocument10 pagesEs1 Get Into Gymapi-260443196No ratings yet
- st3 Why Live Where FinalDocument5 pagesst3 Why Live Where Finalapi-260443196No ratings yet
- Es1 Be Active YbDocument10 pagesEs1 Be Active Ybapi-260443196No ratings yet
- Es1 Start UpDocument15 pagesEs1 Start Upapi-260443196No ratings yet
- Danunit 1Document14 pagesDanunit 1api-260443196No ratings yet
- Jean Keating's Prison TreatiseDocument41 pagesJean Keating's Prison Treatise:Lawiy-Zodok:Shamu:-ElNo ratings yet
- The Black AssassinDocument21 pagesThe Black AssassinThe Black AssassinNo ratings yet
- Pongattum Inba Uravu ... SynopsisDocument3 pagesPongattum Inba Uravu ... SynopsisanuciaaNo ratings yet
- Criminal CaseDocument50 pagesCriminal CasegiovanniNo ratings yet
- Revilla Vs SandiganbayanDocument32 pagesRevilla Vs Sandiganbayanavrille100% (1)
- Hon 230 Group Project Final Report 2Document44 pagesHon 230 Group Project Final Report 2api-487372609No ratings yet
- (Key) Relative ClausesDocument16 pages(Key) Relative ClausesThu UyenNo ratings yet
- Death Penalty - For and Against - SummaryDocument2 pagesDeath Penalty - For and Against - SummaryJuanjo Alonso Tresguerres92% (13)
- Jason Galanis Opening StatementDocument19 pagesJason Galanis Opening StatementBreitbart NewsNo ratings yet
- Debasics 101: By: MeDocument36 pagesDebasics 101: By: MeFerminNo ratings yet
- Declarative Sentence: Simply Makes A Statement or Expresses An Opinion. in Other Words, It Makes ADocument8 pagesDeclarative Sentence: Simply Makes A Statement or Expresses An Opinion. in Other Words, It Makes ACriza CatadmanNo ratings yet
- Wolverton - Book Mystery Stalks The PrairieDocument65 pagesWolverton - Book Mystery Stalks The PrairieLionel Elyansun100% (3)
- Source 2Document16 pagesSource 2Mubiru IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Elphos Erald: Relay '15 To Bring ChangeDocument12 pagesElphos Erald: Relay '15 To Bring ChangeThe Delphos HeraldNo ratings yet
- People v. Gonzales-FloresDocument9 pagesPeople v. Gonzales-FloresAnonymous 33LIOv6LNo ratings yet
- Valmonte CaseDocument27 pagesValmonte Casejane_rocketsNo ratings yet
- Factoring Formulas: Key to Solving Math ProblemsDocument6 pagesFactoring Formulas: Key to Solving Math ProblemsSharmaineNo ratings yet
- Prison StudiesDocument2 pagesPrison StudiesEl BarbudoNo ratings yet
- 06 Motion To Release On RecognizanceDocument3 pages06 Motion To Release On RecognizanceTeodoro Jose BrunoNo ratings yet
- Les Mis Study Guide pt2Document4 pagesLes Mis Study Guide pt2Adam Winkler100% (1)
- Public Act 336Document4 pagesPublic Act 336Arielle BreenNo ratings yet
- Obstruction and Illegal Search CaseDocument2 pagesObstruction and Illegal Search CaseMark Co100% (5)
- New Indictment Against Ken MillsDocument3 pagesNew Indictment Against Ken MillsWKYC.comNo ratings yet
- Comparison of The Actual Provisions Are As FollowsDocument3 pagesComparison of The Actual Provisions Are As FollowsClarizza De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Michael Leatherwood MotionDocument128 pagesMichael Leatherwood MotionThisIsFusionNo ratings yet
- Spotlight 5915 Yani Tseng: I Keep Learning: Audio PlayerDocument21 pagesSpotlight 5915 Yani Tseng: I Keep Learning: Audio PlayerIs-ma PontiNo ratings yet
- Emily Bronte's Wuthering Heights (Bloom's Guides)Document97 pagesEmily Bronte's Wuthering Heights (Bloom's Guides)mgm86100% (3)
- Section Particulars: Indian Penal Code (IPC) 1860Document12 pagesSection Particulars: Indian Penal Code (IPC) 1860Mayra Singh100% (1)
- Dismissal of Communist Government (Kerala Administrative Service)Document50 pagesDismissal of Communist Government (Kerala Administrative Service)Vineeth VNo ratings yet
- Future Tenses ExplainedDocument6 pagesFuture Tenses ExplainedЧарли ЖутиNo ratings yet