Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IPhO2014 Theory Problem1
Uploaded by
mpecth0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views1 pageInternational Physics Olympiad
Theory Problem 1 of IPhO 2014
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentInternational Physics Olympiad
Theory Problem 1 of IPhO 2014
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views1 pageIPhO2014 Theory Problem1
Uploaded by
mpecthInternational Physics Olympiad
Theory Problem 1 of IPhO 2014
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Theoretical competition.
Tuesday, 15 July 2014 1/1
Problem 1 (9 points)
This problem consists of three independent parts.
Part A (3 points)
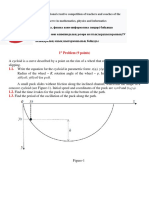
A small puck of mass ! is carefully placed onto the inner surface of the
thin hollow thin cylinder of mass ! and of radius !. Initially, the cylinder
rests on the horizontal plane and the puck is located at the height ! above
the plane as shown in the figure on the left. Find the interaction force !
between the puck and the cylinder at the moment when the puck passes
the lowest point of its trajectory. Assume that the friction between the
puck and the inner surface of the cylinder is absent, and the cylinder
moves on the plane without slipping. The free fall acceleration is !.
Part B (3 points)
A bubble of radius ! ! !!!! !", containing a diatomic ideal gas, has the soap film of thickness ! !
!"!! !! and is placed in vacuum. The soap film has the surface tension ! ! !!!! ! !"
!!
!
!
and the density
! ! !!!"
!
!"
!
. 1) Find formula for the molar heat capacity of the gas in the bubble for such a process when
the gas is heated so slowly that the bubble remains in a mechanical equilibrium and evaluate it; 2) Find
formula for the frequency ! of the small radial oscillations of the bubble and evaluate it under the
assumption that the heat capacity of the soap film is much greater than the heat capacity of the gas in the
bubble. Assume that the thermal equilibrium inside the bubble is reached much faster than the period of
oscillations.
Hint: Laplace showed that there is pressure difference between inside and outside of a curved
surface, caused by surface tension of the interface between liquid and gas, so that !! !
!!
!
.
Part C (3 points)
Initially, a switch ! is unshorted in the circuit shown in the figure on the right, a
capacitor of capacitance !! carries the electric charge !
!
, a capacitor of
capacitance ! is uncharged, and there are no electric currents in both coils of
inductance ! and !!, respectively. The capacitor starts to discharge and at the
moment when the current in the coils reaches its maximum value, the switch ! is
instantly shorted. Find the maximum current !
!"#
through the switch ! thereafter.
You might also like
- IPhO2012 Theoretical ProblemDocument5 pagesIPhO2012 Theoretical ProblemJohnJachersonNo ratings yet
- 2016 THDocument14 pages2016 THDavid SiriusNo ratings yet
- 2023PhysicsWOOT SyllabusDocument9 pages2023PhysicsWOOT SyllabusuprojhiashubhamNo ratings yet
- 2018 THDocument21 pages2018 THDavid SiriusNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 2021-2022: 1. Static Equilibria, Stress, and StrainDocument9 pagesSyllabus 2021-2022: 1. Static Equilibria, Stress, and StrainKrrish Pradhani9C11No ratings yet
- InPhO 2022 Mock ExamDocument5 pagesInPhO 2022 Mock ExamLuke HuangNo ratings yet
- Mech 301 HW2Document1 pageMech 301 HW2mertguneyli1No ratings yet
- Workbook FMDocument66 pagesWorkbook FMSubhash JhurawatNo ratings yet
- X23 T3 Tidal Capture PhenomenonDocument6 pagesX23 T3 Tidal Capture PhenomenonAarush MishraNo ratings yet
- Final Exam 2009 SPDocument15 pagesFinal Exam 2009 SPNick SnyderNo ratings yet
- IZhO 2009 Theory - EngDocument8 pagesIZhO 2009 Theory - EngMatei Ionita100% (1)
- IZhO 2015 Theory EngDocument5 pagesIZhO 2015 Theory EngShatoNo ratings yet
- Tushars NoteDocument25 pagesTushars Notevbg6v42dypNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument35 pagesFluid MechanicsarultkNo ratings yet
- Provas - Olimpiada AmericanaDocument48 pagesProvas - Olimpiada AmericanaGabriel Oliveira MartinsNo ratings yet
- How Does Rocket Propulsion Work?: ClassroomDocument4 pagesHow Does Rocket Propulsion Work?: ClassroomNishant TharkarNo ratings yet
- HW w2012 PDFDocument98 pagesHW w2012 PDFJuvyneil Echon CartelNo ratings yet
- 33 National Semifinal Chinese Physics Olympiad Questions, 2016Document7 pages33 National Semifinal Chinese Physics Olympiad Questions, 2016RandomNo ratings yet
- Phys B 1st Semester LBQsDocument11 pagesPhys B 1st Semester LBQsCanjiNo ratings yet
- Practice FinalDocument4 pagesPractice FinalChennaiSuperkingsNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Competition: January 11, 2019 Please Read This FirstDocument8 pagesTheoretical Competition: January 11, 2019 Please Read This FirstAydın MammadovNo ratings yet
- RuPhO 2019Document3 pagesRuPhO 2019Champion ReaderNo ratings yet
- (T3) Balloon QuestionDocument3 pages(T3) Balloon QuestionCretu NicolaeNo ratings yet
- Surface TensionDocument4 pagesSurface TensionPranjal SinghalNo ratings yet
- Midterm3 KeyDocument6 pagesMidterm3 KeyJeremy LevyNo ratings yet
- CMDocument139 pagesCMLawrence Lim Ah KowNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument3 pagesPhysicsmickey_disney93No ratings yet
- Review/Diagnostic Homework, Physics 4304, Dr. Charles W. MylesDocument5 pagesReview/Diagnostic Homework, Physics 4304, Dr. Charles W. MylesNur SyahirahNo ratings yet
- Memt313-001/002 Eric Borquist, PHD Supplemental Material: Pressure Inside A Soap Bubble and A Liquid DropDocument2 pagesMemt313-001/002 Eric Borquist, PHD Supplemental Material: Pressure Inside A Soap Bubble and A Liquid DropHanna JbrNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument12 pagesFinalAlejandroNo ratings yet
- A LeakDocument12 pagesA LeakMohamad OmarNo ratings yet
- PHYDocument10 pagesPHYChristineNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument14 pagesPhysicsAden.No ratings yet
- Fluid DynamicsDocument17 pagesFluid DynamicsAngelique ReyesNo ratings yet
- PH202 Chapter 13 SolutionsDocument28 pagesPH202 Chapter 13 SolutionsShubh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 9 Physics Practical SyllabusDocument2 pagesICSE Class 9 Physics Practical SyllabusKaushal DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Gas PressureDocument10 pages3.3 Gas PressureNURUL FAEZAH BINTI MUSTAPA MoeNo ratings yet
- Time: 2hour: Bangladesh Physics Olympiad National Camp-2021Document3 pagesTime: 2hour: Bangladesh Physics Olympiad National Camp-2021Abid KhanNo ratings yet
- 00 Sampe For Question S & AnsDocument5 pages00 Sampe For Question S & Ansmail2sgarg_841221144No ratings yet
- PHYS Train IMPACT 2022Document18 pagesPHYS Train IMPACT 2022Ganbold AriunboldNo ratings yet
- PC1431 Assignment 2 AnswersDocument19 pagesPC1431 Assignment 2 AnswersMikael Lee0% (3)
- Simple Harmonic Oscillator: Challenge Problems Problem 1: Dimensional Analysis, Estimation and ConceptsDocument7 pagesSimple Harmonic Oscillator: Challenge Problems Problem 1: Dimensional Analysis, Estimation and ConceptsSushant SharmaNo ratings yet
- Math Mock IA - Brachistochrone CurveDocument3 pagesMath Mock IA - Brachistochrone Curvephurhiufukhfurh urhfuhNo ratings yet
- Value of G by Compound PendulumDocument8 pagesValue of G by Compound PendulumMohammad Ameer hamzaNo ratings yet
- 12 Damped Harmonic OscillatorDocument3 pages12 Damped Harmonic OscillatorBora CanbulaNo ratings yet
- Sample Emc2Document6 pagesSample Emc2Prajwal DasNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Problem 1. Tea Ceremony and Physics of BubblesDocument4 pagesTheoretical Problem 1. Tea Ceremony and Physics of BubblesKhoa NguyễnNo ratings yet
- G11 Final Revision Worksheet AjnkhlygDocument10 pagesG11 Final Revision Worksheet Ajnkhlygrishi.amaravathi123No ratings yet
- Qualifying Exam Part I 2015-2Document6 pagesQualifying Exam Part I 2015-2puput123No ratings yet
- Test 1 FRQDocument6 pagesTest 1 FRQ390108263No ratings yet
- As Forces, Density & PressureDocument16 pagesAs Forces, Density & PressureconnielsayedNo ratings yet
- 2011 ExamPaperS5Document10 pages2011 ExamPaperS5Michael LeungNo ratings yet
- Problem Mix (10 Points) : TheoryDocument2 pagesProblem Mix (10 Points) : Theorykaran kumarNo ratings yet
- Daily Life Uses of Differentiation and IntegrationDocument15 pagesDaily Life Uses of Differentiation and IntegrationMohd Nasha Hafizulhilmi87% (15)
- Assignment N1Document9 pagesAssignment N1Rania ChNo ratings yet
- Proving Dark Energy is an inflationary force by showing its function in the formation of Super Clusters.From EverandProving Dark Energy is an inflationary force by showing its function in the formation of Super Clusters.No ratings yet
- Broiler ProductionDocument13 pagesBroiler ProductionAlexa Khrystal Eve Gorgod100% (1)
- DISCHARGE PLAN CuyosDocument6 pagesDISCHARGE PLAN CuyosShaweeyah Mariano BabaoNo ratings yet
- Ymrtc LogDocument26 pagesYmrtc LogVinicius Silveira0% (1)
- Tetra IntroductionDocument65 pagesTetra Introductionuniversidaddistrital100% (2)
- How To Present A Paper at An Academic Conference: Steve WallaceDocument122 pagesHow To Present A Paper at An Academic Conference: Steve WallaceJessicaAF2009gmtNo ratings yet
- AcousticsDocument122 pagesAcousticsEclipse YuNo ratings yet
- IPM GuidelinesDocument6 pagesIPM GuidelinesHittesh SolankiNo ratings yet
- LicencesDocument5 pagesLicencesstopnaggingmeNo ratings yet
- Hindi ShivpuranDocument40 pagesHindi ShivpuranAbrar MojeebNo ratings yet
- Will Smith BiographyDocument11 pagesWill Smith Biographyjhonatan100% (1)
- Pricing of A Revolutionary ProductDocument22 pagesPricing of A Revolutionary ProductiluvparixitNo ratings yet
- The BetterPhoto Guide To Creative Digital Photography by Jim Miotke and Kerry Drager - ExcerptDocument19 pagesThe BetterPhoto Guide To Creative Digital Photography by Jim Miotke and Kerry Drager - ExcerptCrown Publishing GroupNo ratings yet
- Introduction To M365 PresentationDocument50 pagesIntroduction To M365 Presentationlasidoh0% (1)
- Life in The Ancient WorldDocument48 pagesLife in The Ancient Worldjmagil6092100% (1)
- REAL BABY FOOD: Easy All-Natural Recipes For Your Baby and Toddler by Jenna HelwigDocument8 pagesREAL BABY FOOD: Easy All-Natural Recipes For Your Baby and Toddler by Jenna HelwigHoughton Mifflin Harcourt Cookbooks50% (2)
- Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications: Basic Structures: Sets, Functions, Sequences, and SumsDocument61 pagesDiscrete Mathematics and Its Applications: Basic Structures: Sets, Functions, Sequences, and SumsBijori khanNo ratings yet
- Flying ColorsDocument100 pagesFlying ColorsAgnieszkaAgayo20% (5)
- Taylor Et Al v. Acxiom Corporation Et Al - Document No. 91Document40 pagesTaylor Et Al v. Acxiom Corporation Et Al - Document No. 91Justia.comNo ratings yet
- PreviewpdfDocument83 pagesPreviewpdfJohana GavilanesNo ratings yet
- Benko Gambit-Jacobs and Kinsman, 1999Document163 pagesBenko Gambit-Jacobs and Kinsman, 1999johnson Greker100% (3)
- Usm 1Document47 pagesUsm 1Abhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Mode of Action of Vancomycin: L D D D D DDocument8 pagesMode of Action of Vancomycin: L D D D D DNolanNo ratings yet
- Rare Malignant Glomus Tumor of The Esophagus With PulmonaryDocument6 pagesRare Malignant Glomus Tumor of The Esophagus With PulmonaryRobrigo RexNo ratings yet
- A SURVEY OF ENVIRONMENTAL REQUIREMENTS FOR THE MIDGE (Diptera: Tendipedidae)Document15 pagesA SURVEY OF ENVIRONMENTAL REQUIREMENTS FOR THE MIDGE (Diptera: Tendipedidae)Batuhan ElçinNo ratings yet
- What Says Doctors About Kangen WaterDocument13 pagesWhat Says Doctors About Kangen Waterapi-342751921100% (2)
- Ch06 Allocating Resources To The ProjectDocument55 pagesCh06 Allocating Resources To The ProjectJosh ChamaNo ratings yet
- Use of Travelling Waves Principle in Protection Systems and Related AutomationsDocument52 pagesUse of Travelling Waves Principle in Protection Systems and Related AutomationsUtopia BogdanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 and 2Document4 pagesUnit 1 and 2Aim Rubia100% (1)
- MV Lec PDFDocument102 pagesMV Lec PDFJonas Datu100% (1)