Professional Documents
Culture Documents
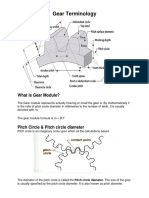
Pitch Diameter, D
Uploaded by
Ahmed Nahrawy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views2 pagesGears Specs.
Original Title
Gear
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGears Specs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views2 pagesPitch Diameter, D
Uploaded by
Ahmed NahrawyGears Specs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Pitch diameter, d
A predefined diametral positon on the gear where the
circular tooth thickness, pressure angle and helix angles
are defined. The standard pitch diameter is a basic
dimension and cannot be measured, but is a location where
other measurements are made. Its value is based on the
number of teeth, the normal module (or normal diametral
pitch), and the helix angle. It is calculated as:
in metric units or in imperial units.
Operating pitch diameters
!iameters determined from the number of teeth and the
center distance at which gears operate.
"#
$xample for
pinion:
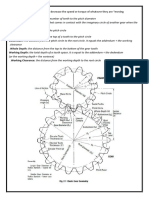
Outside diameter, D
o
!iameter of the gear, measured from the tops of the teeth.
Root diameter
!iameter of the gear, measured at the base of the tooth.
Addendum, a
%adial distance from the pitch surface to the outermost
point of the tooth. a & (D
o
' D) ( )
Dedendum, b
%adial distance from the depth of the tooth trough to the
pitch surface. b & (D ' rootdiameter) ( )
Whole depth, h
t
The distance from the top of the tooth to the root* it is
e+ual to addendum plus dedendum or to working depth
plus clearance.
Clearance
!istance between the root circle of a gear and the
addendum circle of its mate.
Working depth
!epth of engagement of two gears, that is, the sum of their
operating addendums.
Circular pitch, p
!istance from one face of a tooth to the corresponding
face of an ad,acent tooth on the same gear, measured along
the pitch circle.
Diametral pitch, p
d
%atio of the number of teeth to the pitch diameter. -ould
be measured in teeth per inch or teeth per centimeter.
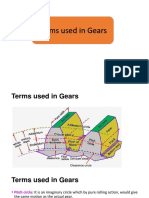
Base circle
In involute gears, where the tooth profile is the involute of
the base circle. The radius of the base circle is somewhat
smaller than that of the pitch circle.
You might also like
- Operative Dentistry in the Phantom LabFrom EverandOperative Dentistry in the Phantom LabRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Kom Gear TerminologyDocument3 pagesKom Gear Terminologydhilip_sacetNo ratings yet
- The Essential Handsaw Book: Projects & Techniques for Mastering a Timeless Hand ToolFrom EverandThe Essential Handsaw Book: Projects & Techniques for Mastering a Timeless Hand ToolNo ratings yet
- Gear TerminologyDocument19 pagesGear TerminologyZandro GagoteNo ratings yet
- DENTURES: The Ultimate Guide to Dentures & Denture Care for a Beautifully Restored SmileFrom EverandDENTURES: The Ultimate Guide to Dentures & Denture Care for a Beautifully Restored SmileNo ratings yet
- Gear terminology guide for key termsDocument5 pagesGear terminology guide for key termsRabia ZulqarnainNo ratings yet
- Digitization in Dentistry: Clinical ApplicationsFrom EverandDigitization in Dentistry: Clinical ApplicationsPriyanka JainNo ratings yet
- Gear NomenclatureDocument41 pagesGear NomenclatureViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- Plate 3 Mach ElDocument2 pagesPlate 3 Mach ElTheodore BaaNo ratings yet
- Terminology SpurDocument3 pagesTerminology SpurNimish Pande100% (1)
- Gearthread 120918023938 Phpapp01Document50 pagesGearthread 120918023938 Phpapp01Bakkiya RajNo ratings yet
- Gear TerminologyDocument11 pagesGear TerminologyGoutam AcharjeeNo ratings yet
- Gear Terms Explained: Pitch Circle, Diametral Pitch and MoreDocument10 pagesGear Terms Explained: Pitch Circle, Diametral Pitch and MoreJawad Ullah100% (2)
- GR Nom1Document6 pagesGR Nom1Mohan Raj JercyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Information: Spur GearsDocument6 pagesEngineering Information: Spur GearsLuis MarcosNo ratings yet
- Gear TerminologyDocument12 pagesGear TerminologyLuis Daniel De La GarzaNo ratings yet
- Me472 10Document0 pagesMe472 10dreadwarriorNo ratings yet
- Gear TerminologyDocument42 pagesGear Terminologyyair Enrique Romero OspinoNo ratings yet
- Tooth ThicknessDocument9 pagesTooth ThicknessPraveen VundrajavarapuNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument15 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentrdksjNo ratings yet
- Gear Terms and DefinitionsDocument5 pagesGear Terms and DefinitionsAaron_Liu_1555No ratings yet
- Notes On Spur Gears: DefinitionsDocument6 pagesNotes On Spur Gears: DefinitionsKrishna Murari MauryaNo ratings yet
- Gears, Splines, and Serrations: Unit 24Document8 pagesGears, Splines, and Serrations: Unit 24Satish Dhandole100% (1)
- History of GearsDocument52 pagesHistory of GearsAnthony FajardoNo ratings yet
- Group 3 (Gears)Document52 pagesGroup 3 (Gears)CherrydhelNo ratings yet
- GEARS & GEAR TRAINS: KEY TERMINOLOGYDocument32 pagesGEARS & GEAR TRAINS: KEY TERMINOLOGYMuhammed Ali ASNo ratings yet
- Gear definitions and formulasDocument7 pagesGear definitions and formulasNakkolopNo ratings yet
- Gear Anatomy and EquationsDocument5 pagesGear Anatomy and EquationspetsatNo ratings yet
- Gear Definitions and FormulasDocument8 pagesGear Definitions and FormulasSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- GearsDocument9 pagesGearsMark CruzNo ratings yet
- Gear Management PDFDocument3 pagesGear Management PDFNoimuddin NeogNo ratings yet
- Gear and FormulaDocument7 pagesGear and FormulahrsreenathNo ratings yet
- Spur Gears: - Two Are in MeshDocument3 pagesSpur Gears: - Two Are in Meshmostafa aliNo ratings yet
- Module 3 PDF File SPUR GEARSDocument6 pagesModule 3 PDF File SPUR GEARSAdolfo KayeNo ratings yet
- Gear Notes - SlideDocument19 pagesGear Notes - SlideNEF RIDERSNo ratings yet
- Gears FundamentalDocument25 pagesGears FundamentalMOHD ZULHELMIE ZAINAL ABIDINNo ratings yet
- Gears SV New Curriculum LecDocument19 pagesGears SV New Curriculum Lectest 2No ratings yet
- Bevel GearsDocument4 pagesBevel GearsTomislav FilipovicNo ratings yet
- MODULE 6 - Spur GearDocument13 pagesMODULE 6 - Spur GearBoris PalaoNo ratings yet
- Spur and Gear Trains KOM PDFDocument18 pagesSpur and Gear Trains KOM PDFSam prabhakarNo ratings yet
- Gonowon 3c Gear NomenclatureDocument32 pagesGonowon 3c Gear NomenclatureSheena LaniogNo ratings yet
- DJJ 10033-Chapter 5.GEARDocument34 pagesDJJ 10033-Chapter 5.GEARStepianus JtNo ratings yet
- Involute Gear and Spline SoftwareDocument9 pagesInvolute Gear and Spline Softwaresumeetsaini88No ratings yet
- Gear Heel Pitch DiameterDocument5 pagesGear Heel Pitch DiameterMadnutsNo ratings yet
- Gear Geometry & Profile TheoryDocument24 pagesGear Geometry & Profile Theoryansh1983100% (2)
- Plate 3Document5 pagesPlate 3shaunmedina0006No ratings yet
- Design of GearsDocument94 pagesDesign of Gears60-Hafiz Muhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Bevel Gear Model-3Document1 pageBevel Gear Model-3vijay_khandgeNo ratings yet
- Gear & Design Gearbox DJSDocument12 pagesGear & Design Gearbox DJSAnonymous z4Fe39jNo ratings yet
- INVOLUTE SPUR GEARS TERMINOLOGY AND MESHINGDocument13 pagesINVOLUTE SPUR GEARS TERMINOLOGY AND MESHINGjiteshpaul100% (1)
- Unit-5 Gears and Gear Trains: Guru Nanak Institute of TechnologyDocument9 pagesUnit-5 Gears and Gear Trains: Guru Nanak Institute of TechnologyKonduru Vinay Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Metrology, Gear MeasurementDocument44 pagesMetrology, Gear MeasurementPiu Kundu100% (23)
- DJJ 10033-Chapter 5Document45 pagesDJJ 10033-Chapter 5Abbas SeuNo ratings yet
- CH08 2Document52 pagesCH08 2abdallah ghannamNo ratings yet
- Bevel Gear Model-2Document1 pageBevel Gear Model-2vijay_khandgeNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Spur GearDocument18 pagesParts of A Spur GearAnthony FajardoNo ratings yet
- Gear TerminologyDocument21 pagesGear TerminologyAns ahmed100% (1)
- Gear Pitch Surface DefinitionsDocument2 pagesGear Pitch Surface DefinitionsMari MuthuNo ratings yet
- Misalignment of The Exhaust Manifold and BellowsDocument5 pagesMisalignment of The Exhaust Manifold and BellowsAhmed NahrawyNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Trouble: CodesDocument17 pagesDiagnostic Trouble: CodesAhmed NahrawyNo ratings yet
- HydraulicPressureDrop PDFDocument1 pageHydraulicPressureDrop PDFAhmed NahrawyNo ratings yet
- AutomotiveDocument124 pagesAutomotiveAhmed Nahrawy100% (9)
- Failures of Cylinder Head Valves On G3500C and G3500E Generator Set Engines (1100, 1105, 1121)Document5 pagesFailures of Cylinder Head Valves On G3500C and G3500E Generator Set Engines (1100, 1105, 1121)Ahmed Nahrawy100% (1)
- Hydraulic Hints PDFDocument29 pagesHydraulic Hints PDFAhmed NahrawyNo ratings yet
- A CFD Study To Analyze The Aerodynamic Torque, Lift, and Drag Forces For A Butterfly Valve in The Mid-Stroke PositionDocument9 pagesA CFD Study To Analyze The Aerodynamic Torque, Lift, and Drag Forces For A Butterfly Valve in The Mid-Stroke PositionAhmed NahrawyNo ratings yet
- Valve Stem Projection - Measure/Record: Operation and Maintenance ManualDocument2 pagesValve Stem Projection - Measure/Record: Operation and Maintenance ManualAhmed NahrawyNo ratings yet
- Fuel Metering Valve Problem: TroubleshootingDocument2 pagesFuel Metering Valve Problem: TroubleshootingAhmed NahrawyNo ratings yet
- Creation and Control of Fluid FlowDocument42 pagesCreation and Control of Fluid FlowAhmed NahrawyNo ratings yet
- ITec - Hyundai Codigos OBD EspecificosDocument10 pagesITec - Hyundai Codigos OBD EspecificosMASTERTECH_01100% (1)
- ASME Pressure Transient Flow Forces (Manring and Zhang)Document5 pagesASME Pressure Transient Flow Forces (Manring and Zhang)Ahmed NahrawyNo ratings yet
- 966F Wheel Loader Electrical SystemDocument2 pages966F Wheel Loader Electrical SystemAhmed Nahrawy82% (11)
- Geotech 3-5 Reclaimer 26600112Document26 pagesGeotech 3-5 Reclaimer 26600112Ahmed NahrawyNo ratings yet
- 966F & 966F Series II Wheel Loaders Hydraulic SystemDocument2 pages966F & 966F Series II Wheel Loaders Hydraulic SystemAhmed Nahrawy100% (7)
- 966F Wheel Loader Electrical SystemDocument2 pages966F Wheel Loader Electrical SystemAhmed Nahrawy82% (11)
- ANSYS CFD-Post TutorialsDocument78 pagesANSYS CFD-Post Tutorialsstaedtlerp50% (2)
- WTL - 950HDocument13 pagesWTL - 950HAhmed Nahrawy100% (2)
- Methods of Producing Low Temperatures: LessonDocument14 pagesMethods of Producing Low Temperatures: Lessoncaptainhass100% (1)
- RAC Lecture 11Document22 pagesRAC Lecture 11api-3734466100% (2)
- Bearing Failure ModesDocument13 pagesBearing Failure ModesmayureshrmahajanNo ratings yet
- ScrapersDocument2 pagesScrapersAhmed NahrawyNo ratings yet
- LTS PlantDocument2 pagesLTS PlantAhmed NahrawyNo ratings yet
- Industrial Analog ControllersDocument9 pagesIndustrial Analog ControllersAhmed NahrawyNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Construction PDFDocument3 pagesPipeline Construction PDFAhmed Nahrawy100% (1)
- Well TestingDocument25 pagesWell TestingAhmed Nahrawy100% (3)
- SS QST30 PDFDocument4 pagesSS QST30 PDFRicardo DiasNo ratings yet
- K Value of FittingsDocument4 pagesK Value of FittingsJoydip Misra100% (6)
- Presentation System Curve - Grad - Pipeline CourseDocument32 pagesPresentation System Curve - Grad - Pipeline CourseAhmed NahrawyNo ratings yet
- Michelson Interferometer Na Lamp-1Document11 pagesMichelson Interferometer Na Lamp-1SOHINI KAYALNo ratings yet
- Carimin Acacia Stability-Onhire Loading JerunDocument6 pagesCarimin Acacia Stability-Onhire Loading Jerunh2sbnj86b4No ratings yet
- Consolidation: By. Rajesh S.GujarDocument33 pagesConsolidation: By. Rajesh S.Gujardarshan_dave17No ratings yet
- SDCK CD Ies 01 (Rev B)Document125 pagesSDCK CD Ies 01 (Rev B)Narada HerathNo ratings yet
- Apache Oozie - A workflow scheduler to manage Hadoop jobsDocument5 pagesApache Oozie - A workflow scheduler to manage Hadoop jobsarjuncchaudharyNo ratings yet
- Motores SumergiblesDocument68 pagesMotores SumergiblescyberespiaNo ratings yet
- Calculate heating and cooling loads for buildingsDocument8 pagesCalculate heating and cooling loads for buildingsdpadrianNo ratings yet
- How rock layers are formedDocument3 pagesHow rock layers are formedAlemar AllecerNo ratings yet
- Rockaway Beach Branch Community Impact StudyDocument98 pagesRockaway Beach Branch Community Impact StudyHanaRAlbertsNo ratings yet
- Odv-065r18ejj-G DS 2-0-3Document1 pageOdv-065r18ejj-G DS 2-0-3Евгений Переверзев0% (1)
- Townsend DischargeDocument6 pagesTownsend DischargeGordon DuffNo ratings yet
- Picador Vegetales HCM450Document20 pagesPicador Vegetales HCM450javier vilchez romeroNo ratings yet
- Pull Test Procedure - Chile Cabildo & Villa Seca 3MW-SkyLineDocument7 pagesPull Test Procedure - Chile Cabildo & Villa Seca 3MW-SkyLinecnuneza4No ratings yet
- Previews AGA XQ9902 PreDocument6 pagesPreviews AGA XQ9902 PreAldrin HernandezNo ratings yet
- The Shand CCS Feasibility Study Public ReportDocument124 pagesThe Shand CCS Feasibility Study Public ReportSai RuthvikNo ratings yet
- Estimating/ Construction Planning/ Scheduling and Programming/ Feasibility Project StudiesDocument4 pagesEstimating/ Construction Planning/ Scheduling and Programming/ Feasibility Project StudiesVholts Villa VitugNo ratings yet
- Minor Project Report On Efficiency Improvement of A Combined Cycle Power PlantDocument40 pagesMinor Project Report On Efficiency Improvement of A Combined Cycle Power PlantArpit Garg100% (1)
- Antena Eh para 10 MetrosDocument3 pagesAntena Eh para 10 Metros10sd156No ratings yet
- An Algorithm For Minimax Solution of Overdetennined Systems of Non-Linear EquationsDocument8 pagesAn Algorithm For Minimax Solution of Overdetennined Systems of Non-Linear EquationsDewi FitriyaniNo ratings yet
- Ford Essex V6 EngineDocument8 pagesFord Essex V6 EngineJoakamaster 16No ratings yet
- IEEE STD C37.30.1 Estandar de Requisitos para Interruptores de Aire de AV AC para Nivelesmayores A 1000VDocument104 pagesIEEE STD C37.30.1 Estandar de Requisitos para Interruptores de Aire de AV AC para Nivelesmayores A 1000Valex100% (4)
- GaN technology powers bright LEDsDocument13 pagesGaN technology powers bright LEDsluciowwNo ratings yet
- Magnum 3904 DatasheetDocument3 pagesMagnum 3904 DatasheetbobNo ratings yet
- Strength of Pressure Vessels With Ellipsoidal HeadsDocument8 pagesStrength of Pressure Vessels With Ellipsoidal Headsنصرالدين ادريسNo ratings yet
- Steam System DesignDocument74 pagesSteam System DesignIshan RanganathNo ratings yet
- RCC BEAM DESIGN AND SERVICEABILITYDocument15 pagesRCC BEAM DESIGN AND SERVICEABILITYprashmceNo ratings yet
- NUSTian Final July SeptDocument36 pagesNUSTian Final July SeptAdeel KhanNo ratings yet
- How Do We Classify An Antipumping Relay?: What Will Happen If Antipumping Relay Circuit Is Not Present?Document6 pagesHow Do We Classify An Antipumping Relay?: What Will Happen If Antipumping Relay Circuit Is Not Present?joseNo ratings yet
- How to Operate AAS with SignPal & PhotoPRINTDocument25 pagesHow to Operate AAS with SignPal & PhotoPRINTLucian DogariuNo ratings yet
- Kepb003404 PDFDocument472 pagesKepb003404 PDFELIAS100% (1)
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsFrom EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Petroleum Process SafetyFrom EverandIntroduction to Petroleum Process SafetyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Guidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisFrom EverandGuidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersFrom EverandA Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Trevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationFrom EverandTrevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsFrom EverandGuidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsNo ratings yet
- Chemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesFrom EverandChemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (14)
- Guidelines for Implementing Process Safety ManagementFrom EverandGuidelines for Implementing Process Safety ManagementNo ratings yet
- A Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesFrom EverandA Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Incidents That Define Process SafetyFrom EverandIncidents That Define Process SafetyNo ratings yet
- Inherently Safer Chemical Processes: A Life Cycle ApproachFrom EverandInherently Safer Chemical Processes: A Life Cycle ApproachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Rules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersFrom EverandRules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- Safety Fundamentals and Best Practices in Construction IndustryFrom EverandSafety Fundamentals and Best Practices in Construction IndustryNo ratings yet
- Radium Girls: Women and Industrial Health Reform, 1910-1935From EverandRadium Girls: Women and Industrial Health Reform, 1910-1935Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Practical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsFrom EverandPractical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- The Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeFrom EverandThe Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- 3D Printing of Concrete: State of the Art and Challenges of the Digital Construction RevolutionFrom Everand3D Printing of Concrete: State of the Art and Challenges of the Digital Construction RevolutionArnaud PerrotNo ratings yet
- Nutritional and Therapeutic Interventions for Diabetes and Metabolic SyndromeFrom EverandNutritional and Therapeutic Interventions for Diabetes and Metabolic SyndromeNo ratings yet
- Exercise, Sport, and Bioanalytical Chemistry: Principles and PracticeFrom EverandExercise, Sport, and Bioanalytical Chemistry: Principles and PracticeNo ratings yet
- Fire Fighting Pumping Systems at Industrial FacilitiesFrom EverandFire Fighting Pumping Systems at Industrial FacilitiesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Safety and Intelligent Transport Systems Development in the People’s Republic of ChinaFrom EverandSafety and Intelligent Transport Systems Development in the People’s Republic of ChinaNo ratings yet
- Safety Critical Systems Handbook: A Straight forward Guide to Functional Safety, IEC 61508 (2010 EDITION) and Related Standards, Including Process IEC 61511 and Machinery IEC 62061 and ISO 13849From EverandSafety Critical Systems Handbook: A Straight forward Guide to Functional Safety, IEC 61508 (2010 EDITION) and Related Standards, Including Process IEC 61511 and Machinery IEC 62061 and ISO 13849Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Fire Protection Engineering in Building DesignFrom EverandFire Protection Engineering in Building DesignRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)