Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Microprocessor Information Transfer Instruction Flow: Electrical and Electronic Engineering
Uploaded by
Enock Omari0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesnice
Original Title
Instruction Cycle
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentnice
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesMicroprocessor Information Transfer Instruction Flow: Electrical and Electronic Engineering
Uploaded by
Enock Omarinice
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
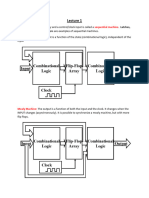
ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING
Microprocessor Information Transfer
Instruction Flow
The following sequence of events takes place:
Next address contents are fetched from the program counter and temporarily stored in
the memory address register (MAR! This to let the program memory have time to
locally decode the address! "atches can also #e used to introduce a #uffer #etween the
two devices!
$pdated address is put on the address #us and sent to program memory
%n the selected chip& the local address is decoded and the circuitry activated to allow
information stored in the location to #e accessed!
'hen appropriate R(A) signal is sent from timing and control to the memory& the
instruction #its from the location are put on the data #us and sent to the memory data
register in the microprocessor! This action helps in the decoding process!
%nstruction word is transferred to instruction register where it is held usually until the
end of the machine cycle or instruction cycle!
%nstruction is decoded into appropriate electrical signals and under timing and control&
appropriate commands are executed #y the various functional #locks of the
microprocessor and different su#*systems of the microcomputer system
The program counter is incremented
Data Flow
+or data word retrieval& the source could #e either the data memory or one of the %,- devices
or vice versa
The address of the data memory or %,- device must first #e sent out #y the ./$ from
the address register!
The point of entry and exit from the microprocessor is mostly the accumulator
The operation
All data words that are specified in a particular instruction take place in the execution
su#*cycle!
You might also like
- Data Transfer SchemeDocument20 pagesData Transfer SchemeJohn PaulNo ratings yet
- Purpose and Function of The CPUDocument16 pagesPurpose and Function of The CPUsophiegcseNo ratings yet
- CS2253 Computer Organization and Architecture Lecture NotesDocument181 pagesCS2253 Computer Organization and Architecture Lecture NotesRoselene RebeccaNo ratings yet
- Answers To Chapter 3 Activities and QuestionsDocument14 pagesAnswers To Chapter 3 Activities and QuestionsKurt HaanNo ratings yet
- 8085 Interrupt PDFDocument67 pages8085 Interrupt PDFDeepika Agrawal100% (1)
- The Basic Structure and Functional Units of a Computer SystemDocument180 pagesThe Basic Structure and Functional Units of a Computer SystemAltafAhmed2706No ratings yet
- Vtu 4TH Sem Cse Computer Organization Notes 10CS46Document75 pagesVtu 4TH Sem Cse Computer Organization Notes 10CS46EKTHATIGER633590100% (12)
- Module 1Document36 pagesModule 1shruthi p rNo ratings yet
- 28-5-I O Fundamentals Handshaking, Buffering-20!10!2021 (20-Oct-2021) Material I 20-10-2021 Unit-5-Lecture1Document15 pages28-5-I O Fundamentals Handshaking, Buffering-20!10!2021 (20-Oct-2021) Material I 20-10-2021 Unit-5-Lecture1Mudit Jain100% (1)
- Co Notes Module 1Document42 pagesCo Notes Module 1Vinyas M SNo ratings yet
- (New) Coa Unit1Document76 pages(New) Coa Unit1Adolf HitlerNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems: Hardware (Book No. 1 Chapter 2)Document82 pagesComputer Systems: Hardware (Book No. 1 Chapter 2)Belat CruzNo ratings yet
- Coa 1Document133 pagesCoa 1Vis KosNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Memory and I/O Interfacing GuideDocument20 pagesMicroprocessor Memory and I/O Interfacing GuideAVCCE PRONo ratings yet
- Hardwired and Microprogrammed Control Unit OrganizationDocument40 pagesHardwired and Microprogrammed Control Unit OrganizationShivani GargNo ratings yet
- Computing Systems OrganizationDocument22 pagesComputing Systems Organizationifti_scriNo ratings yet
- Arm ProgrammingDocument84 pagesArm ProgrammingmnmnNo ratings yet
- HardwareDocument17 pagesHardwareSLADIFYNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Basic Structure of ComputersDocument76 pagesModule 3 Basic Structure of ComputersMadhuNo ratings yet
- Processor ArchitectureDocument39 pagesProcessor ArchitectureSudheerNo ratings yet
- MT ConnectDocument61 pagesMT ConnectMagesh SundaramNo ratings yet
- Chp3.2 controlUnitInstructionSetDocument4 pagesChp3.2 controlUnitInstructionSetheyfiez12No ratings yet
- LU17 18 CISC MicroprogrammingDocument14 pagesLU17 18 CISC MicroprogrammingMani Bharathi VNo ratings yet
- 15 - Control Unit Part 2Document77 pages15 - Control Unit Part 2Divya ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document20 pagesChapter 2esubalew sintieNo ratings yet
- COMP 231 Microprocessor and Assembly LanguageDocument55 pagesCOMP 231 Microprocessor and Assembly LanguageAanchalAdhikariNo ratings yet
- Timing and ControlDocument40 pagesTiming and Controlrohitpulana9090No ratings yet
- William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8 EditionDocument59 pagesWilliam Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8 EditionjumarNo ratings yet
- Computer OrgnisationDocument138 pagesComputer OrgnisationmadhuNo ratings yet
- COMPUTER SYSTEM ORGANIZATIONDocument45 pagesCOMPUTER SYSTEM ORGANIZATIONRa-ed Figueroa100% (1)
- Basic Operational ConceptsDocument4 pagesBasic Operational ConceptsmenakadevieceNo ratings yet
- As Computer Science CH4Document4 pagesAs Computer Science CH4Ahmed RazaNo ratings yet
- Coa Mod 1Document77 pagesCoa Mod 1thomsondevassykuttyNo ratings yet
- Cau Hoi Ve MT - TA Chuyen NganhDocument36 pagesCau Hoi Ve MT - TA Chuyen Nganhat7aNo ratings yet
- MICROPROCESSOR UNIT I SYLLABUSDocument54 pagesMICROPROCESSOR UNIT I SYLLABUSNikhil DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- COD Unit 2 PDFDocument49 pagesCOD Unit 2 PDFYash Gupta MauryaNo ratings yet
- Cod Unit 2Document44 pagesCod Unit 2anilNo ratings yet
- Computer OrganizationDocument150 pagesComputer OrganizationT Syam KumarNo ratings yet
- computer Arch notesDocument9 pagescomputer Arch noteszomukozaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ComputerDocument47 pagesIntroduction To ComputerPradhyumn ShetTilveNo ratings yet
- A Smart GSM Based Embedded Solution For Continuous Remote Monitoring of Cardiac PatientsDocument24 pagesA Smart GSM Based Embedded Solution For Continuous Remote Monitoring of Cardiac PatientsG NAVEEN KUMARNo ratings yet
- Subject: Computer Organization Sub Code: 21Cs34 Semester: 3Document43 pagesSubject: Computer Organization Sub Code: 21Cs34 Semester: 3Shanthi.VNo ratings yet
- Memory OperationsDocument10 pagesMemory OperationsJEEVANANTHAM GNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor OperationDocument6 pagesMicroprocessor Operationrooopes5No ratings yet
- Co Module1 Notes 21schemeDocument14 pagesCo Module1 Notes 21schemeShivam KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii - IiDocument34 pagesUnit Iii - Iiy22cd125No ratings yet
- Modern SCADA Systems GuideDocument48 pagesModern SCADA Systems GuideBagusaryowibowo WibowoNo ratings yet
- Module 3 HalfDocument8 pagesModule 3 HalfShivani AppiNo ratings yet
- Module 3, Notes PDFDocument17 pagesModule 3, Notes PDFShankar MNo ratings yet
- Input Output OrganizationDocument15 pagesInput Output OrganizationRaman Ray 105No ratings yet
- External Devices and IO ModuleDocument7 pagesExternal Devices and IO Modulekanaksanket100% (5)
- 08 - The Processor - Students VersionDocument9 pages08 - The Processor - Students Versionfghf1No ratings yet
- HardwareDocument21 pagesHardwareSimranNo ratings yet
- Ae 773 Applied MechatronicsDocument73 pagesAe 773 Applied Mechatronicsarun_21861208No ratings yet
- Chp6 Interrupt - StackDocument12 pagesChp6 Interrupt - StackNur AfiqahNo ratings yet
- Basic Computer Organization: Unit - 1Document9 pagesBasic Computer Organization: Unit - 1theresa.painterNo ratings yet
- CH17Document4 pagesCH17anon_45056233No ratings yet
- Practical Data Acquisition for Instrumentation and Control SystemsFrom EverandPractical Data Acquisition for Instrumentation and Control SystemsNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics, Computer Architecture and Microprocessor Design PrinciplesFrom EverandDigital Electronics, Computer Architecture and Microprocessor Design PrinciplesNo ratings yet
- Debt Collection Proposal: Prepared For: Prepared byDocument8 pagesDebt Collection Proposal: Prepared For: Prepared byEnock OmariNo ratings yet
- Generic Project Proposal TemplateDocument9 pagesGeneric Project Proposal TemplateCikaNo ratings yet
- Diceman Solutions MovDocument1 pageDiceman Solutions MovEnock OmariNo ratings yet
- Wien Bridge.Document11 pagesWien Bridge.Enock OmariNo ratings yet
- EEE 2215 Electromagnetics I CAT 2&3 2012-2013Document2 pagesEEE 2215 Electromagnetics I CAT 2&3 2012-2013Enock OmariNo ratings yet
- Student ProjectsDocument27 pagesStudent ProjectsVishal Shah100% (1)
- Lag-Lead Compensator Design for Frequency Response SpecsDocument3 pagesLag-Lead Compensator Design for Frequency Response SpecsEnock OmariNo ratings yet
- MTS86C DebuggingDocument8 pagesMTS86C DebuggingEnock OmariNo ratings yet
- Eee 2202 AssignmentDocument2 pagesEee 2202 AssignmentEnock OmariNo ratings yet
- Cancer Testing and PreventionDocument68 pagesCancer Testing and PreventionEnock OmariNo ratings yet
- Eee 2202 AssignmentDocument2 pagesEee 2202 AssignmentEnock OmariNo ratings yet
- FRICTION LOSSES IN PIPESDocument10 pagesFRICTION LOSSES IN PIPESEnock OmariNo ratings yet
- 8086 Instr FormatDocument4 pages8086 Instr FormatEnock OmariNo ratings yet
- Programming Intel 8086Document2 pagesProgramming Intel 8086Enock OmariNo ratings yet
- ICS 2206 Database System JujaDocument61 pagesICS 2206 Database System JujaEnock OmariNo ratings yet
- Ccna 1Document13 pagesCcna 1Amilcar Fernando Ferreira MartinsNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor IntroDocument12 pagesMicroprocessor IntroEnock OmariNo ratings yet
- Memory MappingDocument7 pagesMemory MappingEnock OmariNo ratings yet
- How Laser Printers WorkDocument7 pagesHow Laser Printers WorkPradeepNo ratings yet
- Programming Intel 8086Document2 pagesProgramming Intel 8086Enock OmariNo ratings yet
- Intel 8086 MicroprocessorDocument3 pagesIntel 8086 MicroprocessorEnock OmariNo ratings yet
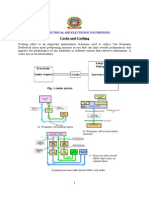
- ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Cache CachingDocument15 pagesELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Cache CachingEnock OmariNo ratings yet
- Assembler Exercise1Document3 pagesAssembler Exercise1Enock OmariNo ratings yet
- 2D ArraysDocument32 pages2D ArraysEnock OmariNo ratings yet
- System Development: EditorDocument6 pagesSystem Development: EditorEnock OmariNo ratings yet
- Logic Gates & Com Bi National Logic DesignDocument64 pagesLogic Gates & Com Bi National Logic DesignEnock Omari100% (1)