Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tachycardia Algorythm
Uploaded by
UZNAPM0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
204 views1 pageAlgorythm detailing step by step the management of tachycardia
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAlgorythm detailing step by step the management of tachycardia
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
204 views1 pageTachycardia Algorythm
Uploaded by
UZNAPMAlgorythm detailing step by step the management of tachycardia
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
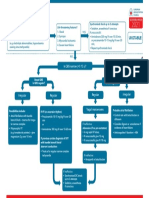
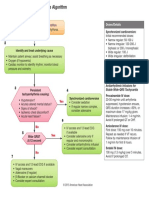
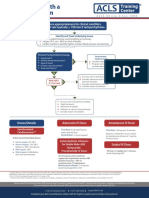
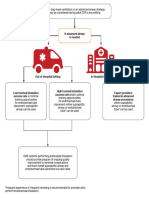
Resuscitation Council (UK)
• Support ABCs: give oxygen; cannulate a vein
• Monitor ECG, BP, SpO2
Adult tachycardia algorithm • Record 12-lead ECG if possible; if not, record rhythm strip
(with pulse) • Identify and treat reversible causes (e.g. electrolyte abnormalities)
Synchronised DC Shock * Unstable
Is patient stable?
Up to 3 attempts
Signs of instability include:
1. Reduced conscious level 2. Chest pain
3. Systolic BP < 90 mmHg 4. Heart failure
• Amiodarone 300 mg IV over 10-20 min (Rate-related symptoms uncommon at less than 150 beats min-1)
and repeat shock; followed by:
• Amiodarone 900 mg over 24 h Stable
Is QRS narrow (< 0.12 sec)?
Broad Narrow
Broad QRS Narrow QRS
Is QRS regular? Is rhythm regular?
Regular Irregular
Irregular Regular • Use vagal manoeuvres Irregular Narrow Complex
• Adenosine 6 mg rapid IV bolus; Tachycardia
Seek expert help if unsuccessful give 12 mg;
Probable atrial fibrillation
if unsuccessful give further 12 mg.
Control rate with:
• Monitor ECG continuously
Possibilities include: If Ventricular Tachycardia • β-Blocker IV or digoxin IV
• AF with bundle branch block (or uncertain rhythm): If onset < 48 h consider:
treat as for narrow complex • Amiodarone 300 mg IV • Amiodarone 300 mg IV 20-60 min;
• Pre-excited AF over 20-60 min; Normal sinus rhythm restored? then 900 mg over 24 h
consider amiodarone then 900 mg over 24 h
• Polymorphic VT (e.g.
torsade de pointes - give
If previously confirmed SVT Yes No
with bundle branch block:
magnesium 2 g over 10 min)
• Give adenosine as for regular Probable re-entry PSVT:
narrow complex tachycardia Seek expert help
* Attempted electrical cardioversion is
• Record 12-lead ECG in sinus
always undertaken under sedation
rhythm
or general anaesthesia • If recurs, give adenosine again &
consider choice of anti-arrhythmic Possible atrial flutter
prophylaxis • Control rate (e.g. β-Blocker)
You might also like
- ALS Algorithms LS Tachycardia 2.0Document1 pageALS Algorithms LS Tachycardia 2.0Lucian Alin DinuNo ratings yet
- 5.ALS Algorithms TachycardiaDocument1 page5.ALS Algorithms TachycardiaMassimo Di BenedettoNo ratings yet
- Adult Tachycardia (With Pulse) AlgorithmDocument1 pageAdult Tachycardia (With Pulse) AlgorithmJames ChoiNo ratings yet
- Ecgs and Acute Cardiac Events: Yuniardi Alriyanto, MD Doris Sylvanus Hospital PalangkarayaDocument47 pagesEcgs and Acute Cardiac Events: Yuniardi Alriyanto, MD Doris Sylvanus Hospital PalangkarayaAuliaRusdiAllmuttaqienNo ratings yet
- G2015 Adult Tachycardia PDFDocument1 pageG2015 Adult Tachycardia PDFPlabber JuneNo ratings yet
- G2015 Adult Tachycardia PDFDocument1 pageG2015 Adult Tachycardia PDFibbs91No ratings yet
- Tachycardia Algorithm 2021Document1 pageTachycardia Algorithm 2021Ravin DebieNo ratings yet
- Managemen Disritmia: Dr. Rofika Hanifa, SPPDDocument20 pagesManagemen Disritmia: Dr. Rofika Hanifa, SPPDavivlabirdNo ratings yet
- 2010 Integrated Updated Circulation ACLS Tachycardia AlgorithmDocument1 page2010 Integrated Updated Circulation ACLS Tachycardia AlgorithmRyggie ComelonNo ratings yet
- Algo Tachycardia PDFDocument1 pageAlgo Tachycardia PDFYudhistira AdiNo ratings yet
- Assess Appropriateness For Clinical Condition. Heart Rate Typically 150/min If TachyarrhythmiaDocument1 pageAssess Appropriateness For Clinical Condition. Heart Rate Typically 150/min If TachyarrhythmiaSiti Nur R Firda FauziyahNo ratings yet
- AdultTachycardiaWithPulse AlgorithmDocument1 pageAdultTachycardiaWithPulse AlgorithmIsmail SlimNo ratings yet
- Adult Tachycardia Algorithm: (With Pulse)Document1 pageAdult Tachycardia Algorithm: (With Pulse)ITSimplyNo ratings yet
- AlgorithmACLS Tachycardia 200612Document1 pageAlgorithmACLS Tachycardia 200612must dietNo ratings yet
- Adult Tachycardia With A Pulse Algorithm: Doses/DetailsDocument1 pageAdult Tachycardia With A Pulse Algorithm: Doses/DetailsZakiyahulfahdwNo ratings yet
- Adult Tachycardia With A Pulse Algorithm: Doses/DetailsDocument1 pageAdult Tachycardia With A Pulse Algorithm: Doses/DetailsAlexis HospitalNo ratings yet
- Advanced Cardiac Life SupportDocument37 pagesAdvanced Cardiac Life SupportRoy Acosta GumbanNo ratings yet
- Website Tachycardia Algorithm DiagramDocument1 pageWebsite Tachycardia Algorithm Diagramcolette zgheibNo ratings yet
- .JPG 958×1,280 PixelsDocument1 page.JPG 958×1,280 Pixelsyordanos getachewNo ratings yet
- Tachycardia With A Pulse Algorithm: Assess Appropriateness For Clinical ConditionDocument1 pageTachycardia With A Pulse Algorithm: Assess Appropriateness For Clinical ConditionDendy Frannuzul RamadhanNo ratings yet
- AlgorithmACLStachycardiawithapulse PDFDocument1 pageAlgorithmACLStachycardiawithapulse PDFDendy Frannuzul RamadhanNo ratings yet
- AlgorithmACLS Tachycardia 200612Document1 pageAlgorithmACLS Tachycardia 200612YassarNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Tachycardia With A Pulse Algorithm: Yes NoDocument1 pagePediatric Tachycardia With A Pulse Algorithm: Yes NoRatna TambaNo ratings yet
- Peri-Arrest ArrythmiaDocument14 pagesPeri-Arrest Arrythmiamohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- Adult Tachycardia Algorithm: (With Pulse)Document1 pageAdult Tachycardia Algorithm: (With Pulse)ITSimplyNo ratings yet
- Bra Dal GoDocument1 pageBra Dal Gozacklim_2000No ratings yet
- Pals TachycardiaDocument1 pagePals TachycardiadarlingcarvajalduqueNo ratings yet
- TachycardiaDocument7 pagesTachycardiaArvind SahniNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmia Types and ManagementDocument43 pagesArrhythmia Types and ManagementKaleb DemisseNo ratings yet
- ACLS Tachycardia Algorithm For Managing Stable TachycardiaDocument4 pagesACLS Tachycardia Algorithm For Managing Stable TachycardiaLady MuffinsNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument7 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromePuskesmas Pinang JayaNo ratings yet
- EKG Rhythms: SVT, Atrial Fibrillation, AV Blocks (39Document10 pagesEKG Rhythms: SVT, Atrial Fibrillation, AV Blocks (39Saidel ElizondoNo ratings yet
- Hippo EM Board Review - Bradycardia- A Simplified Approach Written Summary 2Document10 pagesHippo EM Board Review - Bradycardia- A Simplified Approach Written Summary 2alexandertorresreyNo ratings yet
- Tachycardia AlgorithmDocument1 pageTachycardia AlgorithmGideon BahuleNo ratings yet
- Bradycardia and TachycardiaDocument66 pagesBradycardia and TachycardiaKarissaNo ratings yet
- Algo Pals TachycardiaDocument1 pageAlgo Pals TachycardiaArdie FratamaNo ratings yet
- ACLS Study Guide 2016: Essentials for Passing ExamDocument2 pagesACLS Study Guide 2016: Essentials for Passing Examnova939100% (2)
- MCEM B CVS TachycardiaDocument12 pagesMCEM B CVS TachycardiaRajin MaahiNo ratings yet
- Medicine II Arrhythmia LectureDocument14 pagesMedicine II Arrhythmia LectureAbigael SantosNo ratings yet
- Algoritmos AHA ACLS AdultoDocument4 pagesAlgoritmos AHA ACLS AdultoChristianFelipePorrasCastroNo ratings yet
- Periarestne AritmijeDocument10 pagesPeriarestne AritmijeMustafa ŠabićNo ratings yet
- Onlinemeded Notes CardioDocument1 pageOnlinemeded Notes CardioCourtney HolbrookNo ratings yet
- Obat-Obatan Dalam Bantuan Hidup LanjutDocument16 pagesObat-Obatan Dalam Bantuan Hidup LanjutTheresia SihotangNo ratings yet
- Nursing CS Treatment-Of-Atrial-Dysrhythmias 02Document1 pageNursing CS Treatment-Of-Atrial-Dysrhythmias 02frankshro156No ratings yet
- TachycardiaDocument12 pagesTachycardiaPuskesmas Pinang JayaNo ratings yet
- Antiarrythmic Agents: Antiarrythmic Drugs For HorsesDocument3 pagesAntiarrythmic Agents: Antiarrythmic Drugs For HorsesMageja TatendaNo ratings yet
- AlgorithmsDocument16 pagesAlgorithmsirish laglevaNo ratings yet
- 26) Approach To Pediatric ArrhythmiasDocument44 pages26) Approach To Pediatric ArrhythmiasJude AlyousefNo ratings yet
- Tatalaksana ArrthytmiaDocument55 pagesTatalaksana ArrthytmiaJanstine FirstiandyNo ratings yet
- K31a - Electrophysiology and Cardiac Arrhytmia EmergencyDocument46 pagesK31a - Electrophysiology and Cardiac Arrhytmia EmergencyXeniel AlastairNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmias EmergencyDocument10 pagesArrhythmias EmergencyNITACORDEIRONo ratings yet
- U.M.F. "Gr. T. Popa" Ia Ş IDocument37 pagesU.M.F. "Gr. T. Popa" Ia Ş Ij.doe.hex_87No ratings yet
- Emergency Department STEMI Algorithm GuideDocument1 pageEmergency Department STEMI Algorithm GuideOgizWaraNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmias: Clinical DiagnosisDocument4 pagesArrhythmias: Clinical DiagnosispaveethrahNo ratings yet
- Cardiology Notes USMLE Step CKDocument135 pagesCardiology Notes USMLE Step CKArianna BetancourtNo ratings yet
- E Class Coupe Cabriolet 2 PDFDocument67 pagesE Class Coupe Cabriolet 2 PDFUZNAPMNo ratings yet
- E Class Coupe Cabriolet 2 PDFDocument67 pagesE Class Coupe Cabriolet 2 PDFUZNAPMNo ratings yet
- LiabilitiesDocument68 pagesLiabilitiesUZNAPMNo ratings yet
- Fiesta EBrochure Feb 2014Document39 pagesFiesta EBrochure Feb 2014UZNAPMNo ratings yet
- C Class Estate PDFDocument13 pagesC Class Estate PDFUZNAPMNo ratings yet
- New S-MAX EbrochureDocument26 pagesNew S-MAX EbrochureshuusakuNo ratings yet
- Cla Class PDFDocument68 pagesCla Class PDFUZNAPMNo ratings yet
- C Class Saloon PDFDocument51 pagesC Class Saloon PDFUZNAPMNo ratings yet
- Nuevo Mapa Del MundoDocument1 pageNuevo Mapa Del MundoverarexNo ratings yet
- 2402 Know Your Prostate IfmDocument15 pages2402 Know Your Prostate IfmUZNAPMNo ratings yet
- Fiat Panda Lug2013Document32 pagesFiat Panda Lug2013UZNAPMNo ratings yet
- New S-MAX EbrochureDocument26 pagesNew S-MAX EbrochureshuusakuNo ratings yet
- Ranger EBrochure (24 April 2013)Document23 pagesRanger EBrochure (24 April 2013)UZNAPMNo ratings yet
- Kuga EBrochureDocument33 pagesKuga EBrochureUZNAPMNo ratings yet
- Ka EBrochureDocument28 pagesKa EBrochureUZNAPMNo ratings yet
- Focus EBrochure (December 2013)Document32 pagesFocus EBrochure (December 2013)UZNAPMNo ratings yet
- New 2013 EcoSport BrochureDocument7 pagesNew 2013 EcoSport BrochureUZNAPMNo ratings yet
- BMAX Ebrochure (April 2014)Document33 pagesBMAX Ebrochure (April 2014)UZNAPMNo ratings yet
- Renault ZoeDocument16 pagesRenault ZoeUZNAPM100% (2)
- Scenic Family RenaultDocument20 pagesScenic Family RenaultUZNAPMNo ratings yet
- Nuevo Mapa Del MundoDocument1 pageNuevo Mapa Del MundoverarexNo ratings yet
- Newly Diagnosed BookletDocument44 pagesNewly Diagnosed BookletUZNAPMNo ratings yet
- Renault TwizyDocument16 pagesRenault TwizyUZNAPMNo ratings yet
- Renault SportDocument32 pagesRenault SportUZNAPMNo ratings yet
- Megane Coupe CabDocument12 pagesMegane Coupe CabUZNAPMNo ratings yet
- Twingo RenaultDocument12 pagesTwingo RenaultUZNAPMNo ratings yet
- Planning For Business Growth GuideDocument71 pagesPlanning For Business Growth GuideUZNAPMNo ratings yet
- New ClioDocument24 pagesNew ClioUZNAPMNo ratings yet
- Megane Hatch and Sport Tour ErDocument20 pagesMegane Hatch and Sport Tour ErUZNAPMNo ratings yet
- Spindle Cell TumorsDocument138 pagesSpindle Cell TumorsMadhura ShekatkarNo ratings yet
- Covid-19 PCR Test ReportDocument1 pageCovid-19 PCR Test ReportPriyank MardaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Tyna MooreDocument91 pagesDr. Tyna MooreCaroline AloulNo ratings yet
- Case Study PedsDocument11 pagesCase Study PedsGenesis Bicera100% (1)
- Telaah Kritis Artikel Terapi PZ 2020Document7 pagesTelaah Kritis Artikel Terapi PZ 2020dewi arifahniNo ratings yet
- Patho Physiology: Pathophysiology of Myelomeningocele and HydrocephalusDocument3 pagesPatho Physiology: Pathophysiology of Myelomeningocele and Hydrocephalusjettski_10No ratings yet
- Aj CSF - Rhinorrhea - + - Nasal - Foreign - Body - + - Myiasis - + - ChoanalDocument63 pagesAj CSF - Rhinorrhea - + - Nasal - Foreign - Body - + - Myiasis - + - ChoanalTradigrade PukarNo ratings yet
- Transfusion - March April 1966 - Allen - Choice of Blood For Exchange TransfusionDocument3 pagesTransfusion - March April 1966 - Allen - Choice of Blood For Exchange TransfusionDR. KHANNo ratings yet
- 7 Gastroenteritis Nursing Care Plans - NurseslabsDocument8 pages7 Gastroenteritis Nursing Care Plans - NurseslabsHikaru Takishima91% (23)
- Preeclampsia With HELLP SyndromeDocument8 pagesPreeclampsia With HELLP SyndromeWely Tiffani YpNo ratings yet
- Patient Information From Your Surgeon & Sages Laparoscopic Gallbladder RemovalDocument5 pagesPatient Information From Your Surgeon & Sages Laparoscopic Gallbladder RemovalolarrozaNo ratings yet
- Reye SyndromeDocument15 pagesReye Syndromezeeky35No ratings yet
- Heart & Neck Vessel AssessmentDocument46 pagesHeart & Neck Vessel AssessmentLouise Nathalia VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Hypertension in Pregnancy (Pogs-Cpg)Document55 pagesHypertension in Pregnancy (Pogs-Cpg)Philip Piolo Fuego67% (3)
- Clnical MedicineDocument42 pagesClnical Medicineahmed mokhtarNo ratings yet
- RANZCO 2012 PosterDocument7 pagesRANZCO 2012 PosterGray Design GroupNo ratings yet
- Common Retinal Diseases: FloatersDocument7 pagesCommon Retinal Diseases: FloatersDan-Dan Irika CentinoNo ratings yet
- 2020 MTE GIVD Classification 2020 05 20Document14 pages2020 MTE GIVD Classification 2020 05 20Dr.Sivakumar SelvarajNo ratings yet
- Resolution NoDocument8 pagesResolution NoRAFAEL NOEL PANGGATNo ratings yet
- Lipoma ExcisionDocument4 pagesLipoma ExcisionNikolaus TalloNo ratings yet
- RESEARCH 1 Fi 2Document20 pagesRESEARCH 1 Fi 2Alondra SagarioNo ratings yet
- Patient-Nurse DialogueDocument3 pagesPatient-Nurse Dialogueristy dian puspitaNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument5 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentMonirul Islam MilonNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure BrochureDocument2 pagesHeart Failure Brochureapi-251155476No ratings yet
- Plabable Gems Endocrine PDF P7aDocument44 pagesPlabable Gems Endocrine PDF P7aayşenur sevinçNo ratings yet
- PPPVD Fecal Scoring Chart UPDATE EN FINALDocument2 pagesPPPVD Fecal Scoring Chart UPDATE EN FINALJon DoughballNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia in Children - Classification, Clinical Features, and Diagnosis - UpToDateDocument20 pagesAutoimmune Hemolytic Anemia in Children - Classification, Clinical Features, and Diagnosis - UpToDateNedelcu Miruna100% (1)
- Askep Pada Acute Coronary Syndrome AcsDocument62 pagesAskep Pada Acute Coronary Syndrome Acsdefi rhNo ratings yet
- MouthDocument12 pagesMouthRodolfo MartinezNo ratings yet
- Archive: Enterotoxemia (Overeating Disease) in Sheep and GoatsDocument4 pagesArchive: Enterotoxemia (Overeating Disease) in Sheep and GoatsErnesto VersailleNo ratings yet