Professional Documents
Culture Documents
01 3 2 PDF
Uploaded by
ak1828Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
01 3 2 PDF
Uploaded by
ak1828Copyright:
Available Formats
ABU Technical Committee 2006 Annual Meeting 2-5 November 2006 Beijing Doc T-6/44-3
DEVELOPMENT AND EXPANSION OF HELICOPTER HDTV CONTRIBUTION SYSTEM
EIICHI MATSUO NEWS ENGINEERING DIVISION ENGINEERING ADMINISTRATION DEPARTMENT NIPPON HOSO KYOKAI, JAPAN
Presented at ABU Technical Committee 2006 Annual Meeting in Beijing
Development and expansion of helicopter HDTV contribution system
Eiichi Matsuo News Engineering Division Engineering Administration Department NHK, Japan
1. Introduction NHK maintains helicopters at eleven (11) locations around Japan for aerial news coverage of emergencies such as earthquakes. In order to equip helicopters with HDTV equipment, it was necessary to overcome limitations relating to weight, space, and power supply. But NHK improved its technology to deduce the power consumption, size and weight of HDTV equipment, NHK has a plan to have all its helicopters fitted with HDTV video systems until December this year. This report presents an outline of NHKs work in the development and implementing its HDTV video system for helicopters. 2. Features of News Helicopters equipped HDTV 2.1 Helicopters NHK uses two models of helicopters for HDTV reporting. These were selected through a comprehensive evaluation of characteristics including safety, body size, carrying capacity (number of passengers), space, and power supply. Medium Twin Helicopter AS365N2 (Eurocopter) This model features a long flying range, and is usually based in Tokyo, Osaka, and other major Japanese cities. Light Twin Helicopter EC135T2 (Eurocopter) This model is relatively quiet, and is useful where maneuverability is important. It is usually based in regional cities
Picture1; Medium Twin Helicopter (AS365N2)
Picture2; Light Twin Helicopter (EC135T2)
2.2 HDTV Reporting Functions The main functions of the HDTV systems fitted in the HDTV news helicopters are as follows. HDTV Video Capture The video camera fitted in the helicopters is equipped with a function that suppresses shaking due to the vibration of the helicopters, thereby enabling capture of stable HDTV video images.
1
Presented at ABU Technical Committee 2006 Annual Meeting in Beijing
HDTV VTR Recording This function enables video captured from the camera and video transmitted from the ground to be recorded in HDTV format. HDTV/SDTV Signal Transmission This function enables HDTV and SDTV signals to be transmitted to terrestrial base station of micro wave. HDTV/SDTV Signal Reception This function enables HDTV and SDTV signals to be received from an ENG vehicle on the ground. 3. Main Reporting Facilities An outline of the helicopter reporting system is given in Fig. 1. This is the simplest possible system, allowing operation only by a camera operator.
Video and Audio system
ICS (Inter-Communication System) Video: HD SDI Router Audio: Audio Switcher and Inter-Communication
Wireless Communication
VHF: communication UHF: transmitting data
UHF VHF
HDTV Anti-vibration camera
Disaster area Receiving signal (HDTV /SDTV )
Microwave
(HDTV/SDTV)
NH K
Base Station
Rear Transmission Antenna
ENG Vehicle
Front Transmission Antenna
Figure1;
News helicopter system
3.1 HDTV anti-vibration Camera In order to allow capture of steady video images unaffected by the effects of helicopter vibration, the HDTV camera installed in the helicopter is equipped with a function that prevents shaking due to vibration (anti-vibration function). For safety reasons, the camera itself is fixed outside the helicopter, and controlled from inside using a remote controller. (See picture3) The cameraman operates the camera using a joystick on the control panel inside the helicopter, to control panning, tilting, etc. of the camera. (See picture4.) The camera system features an anti-vibration camera platform that uses an optical gyroscope, and a discrete 2.2-million-pixel FIT-type 3-CCD imaging device with 40X optical zoom HDTV lens. These elements combine to enable the capture of stable, high-definition, high-magnification video images.
Presented at ABU Technical Committee 2006 Annual Meeting in Beijing
Picture3; HDTV anti-vibration Camera
Picture4; Operation inside helicopter
3.2 HDTV VTR The VTR system incorporates a compact HDTV VTR that can be used for recording and playing back video. When the helicopter flies out of the area of transmission coverage , the video can be temporarily recorded to the VTR. Then, after the helicopter moves into an area where transmission is possible, the recorded video can be played back and transmitted to the receiver. 3.3 Video and audio system
(a) ICS (Intercommunication System) The video and audio systems of the helicopter are integrated in an ICS. Video signals are carried over an HD SDI interface, using an 8x8 HDTV matrix switcher, which provides the necessary and sufficient capabilities for reporting. In addition, direct switching from the air enables live broadcasts from the helicopter. Audio signal resource lines can be switched by pushing a button, to carry audio for different configurations, such as reporter + guest , reporter + VE (video engineer) , or camera operator , thereby enabling flexible operation to suit the makeup of the helicopter crew. The compact system ICS even incorporates a wireless capability for contact and communication between the people on board the helicopter. (b) Up/down converter The entire in-helicopter video system is HDTV-based, so SDTV video is up-converted and handled as a HDTV signal. In addition, by down-converting the output of the HDTV MTX to SDTV, the system is capable of transmitting both HDTV and SDTV video. 3.4 Transmission system Video images taken from the helicopter at the report scene are transmitted to the TV broadcast station via a terrestrial base stations. A diagram outlining the transmission network is shown in the figure below.
Presented at ABU Technical Committee 2006 Annual Meeting in Beijing
HDTV Helicopter
Base Station
Base station
HDTV-ENG Vehicle
Figure2; Microwave Link Network
Broadcast Station
Next, we will explain the transmission system of the helicopter. The helicopter system is equipped with a variety of functions to enable live broadcast from the report scene. (a)Video transmission system Transmission of video signals is achieved using an FPU transmitter and ADS (Antenna Directional System). (1) Transmitter The system uses a 7GHz-band microwave transmitter, capable of transmitting both HDTV (*QAM modulation) and SDTV (FM) video signals, over approximately the same range for each. * QAM : Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (2) ADS (Antenna Directional System) In order to transmit video from the helicopter, it is necessary to use a parabolic antenna for microwave transmission, oriented in the direction of the ground base station. In order to allow operation by a camera operator , the antenna automatically adjusts itself to the direction of the ground base station. This automatic direction finding is achieved principally through two functions, as described below. Antenna switching function Since the transmission of video may be blocked by the helicopter itself, depending on the relative orientation of the terrestrial base station and helicopter, two transmission antennas are installed on each helicopterat left and right on the Medium Twin Helicopter; at front and back on the Light Twin Helicopter. There is mechanism to ensure that when the direction of the helicopter changes, there is automatic switching to the other antenna, which is directed in the approximate direction of the terrestrial base station.
Presented at ABU Technical Committee 2006 Annual Meeting in Beijing
Left Antenna Switching Point Right Antenna Switching Point
Figure3; Antenna switching function Automatic tracking system This function ensures that the direction of the helicopters parabolic transmission antenna is automatically adjusted to remain oriented towards the terrestrial base station. (1) WB (wide band width) command tracking Helicopter : Receives a UHF WB wireless signal indicating the angle of the base station antenna, then calculates the bearings of the base station and adjusts antenna direction accordingly Base station : Antenna automatically adjusts to the direction of maximum received signal strength
Helicopter
Transmission Antenna Adjusting to base station based on data of UHF-WB Receiving Antenna Automatically adjusted to the direction of maximum received signal strength
UHF-WB wireless signal Transmitting the angle of the base station antenna
Base station
Figure4; UHF WB command tracking (2) GPS tracking Helicopter: Calculates and adjusts antenna direction from helicopters GPS data and latitude and longitude of the base station. The latitude and longitude of the base station must be set in the helicopter before the flight. Base station: Antenna is automatically adjusted based on position data received from helicopter via UHF narrow band width.
Presented at ABU Technical Committee 2006 Annual Meeting in Beijing
Detector for Searching Tx Direction
Receiving Antenna
Receiving Process Searching Tx position based on microwave strength Receiving antenna automatically adjusted to Tx position
Tx
Figure5; GPS tracking (b) Video receiving system By using a helicopter as a relay point , a helicopter are able to receive microwaves from an ENG vehicle on the ground. (1) Receiver The system uses a microwave receiver, capable of receiving both HDTV (QAM/*OFDM modulation) and SDTV (FM) video signals. * OFDM : Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (2) DFR ( Direction Finding Receiver ) A detection antenna detects the arrival direction of the microwaves, and the receiving antenna is then automatically adjusted to the point of transmission on the ground.
Detector for Searching Tx Direction
Receiving Antenna
Receiving Process Searching Tx position based on microwave strength Receiving antenna automatically adjusted to Tx position
Tx
Figure6; DFR system
Presented at ABU Technical Committee 2006 Annual Meeting in Beijing
4. Summary This report provides an introduction to NHKs development and implementation of a HDTV reporting system for its news helicopters. Until December 2006, NHK has a plan to install HDTV video system to all helicopters. These systems will make it possible for NHK to deliver live broadcast coverage of earthquakes, accidents, and other emergency situations in HDTV video, from anywhere in Japan within a short time. (See figure.) Through the safe and accurate reporting of its HDTV-equipped helicopters, NHK hopes to continue making a contribution to public broadcasting by helping to save lives and property.
Figure7; NHK helicopter base
Presented at ABU Technical Committee 2006 Annual Meeting in Beijing
You might also like
- Radio Handbook 19 1975Document975 pagesRadio Handbook 19 1975Hsu100% (4)
- Uav Monopulse AntennaDocument7 pagesUav Monopulse AntennaognianovNo ratings yet
- Satellite Television: Analogue and Digital Reception TechniquesFrom EverandSatellite Television: Analogue and Digital Reception TechniquesRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- 004-Fligh System Implementation in A UAVDocument51 pages004-Fligh System Implementation in A UAVAria IraniNo ratings yet
- Training Report FinalDocument44 pagesTraining Report FinalShruti GuptaNo ratings yet
- CCTV System StandardsDocument17 pagesCCTV System StandardsCyrene MamaradloNo ratings yet
- SWP Radio Frequency Transmitting ApparatusDocument17 pagesSWP Radio Frequency Transmitting ApparatusChristian BarNo ratings yet
- Principles of Communication Workbook p2Document68 pagesPrinciples of Communication Workbook p2Shaina MabborangNo ratings yet
- Wireless Video Surveillance Project by Alcon C4UDocument15 pagesWireless Video Surveillance Project by Alcon C4UBobanNo ratings yet
- Media and Technology - Behind The ScenesDocument41 pagesMedia and Technology - Behind The Scenesfantacy singhNo ratings yet
- IPTV Applications Using GPON v3Document23 pagesIPTV Applications Using GPON v3Amelies Estrada ValsNo ratings yet
- Referensi Antena VSAT GyroDocument2 pagesReferensi Antena VSAT GyrowidysulistiantoNo ratings yet
- 240-Bishop-Remote Control Handbook PDFDocument233 pages240-Bishop-Remote Control Handbook PDFSantiago PatitucciNo ratings yet
- Acu 5000 Antenna Control UnitDocument2 pagesAcu 5000 Antenna Control UnitCarlosNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Report Bel Bharat ElectronicsDocument40 pagesSummer Training Report Bel Bharat ElectronicsHarish Kr SinghNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Wireless Video CameraDocument25 pagesIntelligent Wireless Video CameraSaiprasanna Lakshmi73% (11)
- 1.basics of CommunicationDocument24 pages1.basics of CommunicationrizwanwarNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Communication Systems ChapterDocument10 pagesIntroduction to Communication Systems ChapterCedric Bernard100% (1)
- About HartDocument154 pagesAbout Hartapi-3725139100% (1)
- DoordarshanDocument31 pagesDoordarshandeepak113311No ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Payload Camera Control System For Unmanned Aerial VehicleDocument7 pagesDesign and Implementation of Payload Camera Control System For Unmanned Aerial VehicleEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- SPECIFICATIONS FOR FIBER OPTIC CABLE AND TRAFFIC CCTV INSTALLATIONDocument8 pagesSPECIFICATIONS FOR FIBER OPTIC CABLE AND TRAFFIC CCTV INSTALLATIONjdpdeleonNo ratings yet
- Flight Control Systems For A Station Keeping Hovering UAV: Bill Pisano March 16, 2005Document9 pagesFlight Control Systems For A Station Keeping Hovering UAV: Bill Pisano March 16, 2005lgrome73No ratings yet
- 27 41 32 Ip-Based Television System (Iptv)Document30 pages27 41 32 Ip-Based Television System (Iptv)Mohamed Abou El hassanNo ratings yet
- Development of A Low-Cost Embedded Flight Controller For QuadcopterDocument6 pagesDevelopment of A Low-Cost Embedded Flight Controller For Quadcopter029Muhammad Robith Fikris SholihNo ratings yet
- Boeing Flight Deck Entry Video Surveillance SystemDocument4 pagesBoeing Flight Deck Entry Video Surveillance SystemWinaldo Satryadi ManurungNo ratings yet
- A E Specification 1080P IR PTZ NETWORKCAMERA DHSD49225XAHNR 001Document10 pagesA E Specification 1080P IR PTZ NETWORKCAMERA DHSD49225XAHNR 001Chechomaxx MaxxNo ratings yet
- Summer Training ReschedulingDocument4 pagesSummer Training ReschedulingYash VardhanNo ratings yet
- DRAFTDocument6 pagesDRAFTEmad Al-RowaishedNo ratings yet
- Camera System RequirementsDocument5 pagesCamera System RequirementsmohdNo ratings yet
- 4 Weeks Training in Doordarshan LucknowDocument25 pages4 Weeks Training in Doordarshan LucknowAmresh ChandraNo ratings yet
- Electrical Spec.'S CCTV System 16782-1Document12 pagesElectrical Spec.'S CCTV System 16782-1Waleed Abd El-HamiedNo ratings yet
- Cd-5-Doc Quadcopter Batch No 30 PDFDocument51 pagesCd-5-Doc Quadcopter Batch No 30 PDFjunaid 786No ratings yet
- Environment MonitoringDocument4 pagesEnvironment MonitoringrandyzzzNo ratings yet
- Training From Doordarshan, BhopalDocument25 pagesTraining From Doordarshan, BhopalRahul MishraNo ratings yet
- A e Specification Pro Network Video Recorder Dhi-Nvr5416 5432 5464-16p-4ks2 v001 001Document7 pagesA e Specification Pro Network Video Recorder Dhi-Nvr5416 5432 5464-16p-4ks2 v001 001Saeed JavaidNo ratings yet
- Drone FeasibilityDocument30 pagesDrone FeasibilityAbhishek PatiyalNo ratings yet
- GPS Perf StdsDocument6 pagesGPS Perf StdsspirittosoulNo ratings yet
- Television and DisplayDocument36 pagesTelevision and DisplayEbenezer HauleNo ratings yet
- Television and Video Engineering Lab Manual PDFDocument77 pagesTelevision and Video Engineering Lab Manual PDFtariq76100% (2)
- Ho So Thau May Phat Analog Co The Nang Cap Len T2 Cua DD India T1 2013Document69 pagesHo So Thau May Phat Analog Co The Nang Cap Len T2 Cua DD India T1 2013Mau PhamNo ratings yet
- A Vision-Based Automatic Landing Method For Fixed Wing UAVsDocument15 pagesA Vision-Based Automatic Landing Method For Fixed Wing UAVsAli YasinNo ratings yet
- BY Harshitha.S (1VI07TE022) Priyanka.N (1VI07TE038) Varun.K.P (1VI05TE058)Document47 pagesBY Harshitha.S (1VI07TE022) Priyanka.N (1VI07TE038) Varun.K.P (1VI05TE058)Kavya NarayanNo ratings yet
- Mobile Satellite Communication System for HelicoptersDocument17 pagesMobile Satellite Communication System for HelicoptersBrad CowanNo ratings yet
- CoEP Satellite Initiative GS PDFDocument10 pagesCoEP Satellite Initiative GS PDFmikedelta28No ratings yet
- Robotics Helicopter Control and Its Applications in EngineeringDocument6 pagesRobotics Helicopter Control and Its Applications in EngineeringInternational Journal of computational Engineering research (IJCER)No ratings yet
- A E Specification EnUS 2267330955Document4 pagesA E Specification EnUS 2267330955Rahadhian Kartikayudha NingratNo ratings yet
- Cohu Electronics 6960 Dual Head Positioning SystemDocument8 pagesCohu Electronics 6960 Dual Head Positioning SystemDian PurwantoNo ratings yet
- Advanced - Compact - Test - Range For Both Radome and Antenna MeasurementDocument4 pagesAdvanced - Compact - Test - Range For Both Radome and Antenna MeasurementNguyen Ba DungNo ratings yet
- Final Tor CCTV 1Document17 pagesFinal Tor CCTV 1AbeyMulugetaNo ratings yet
- Annexure-VI Visual Monitoring System For Watch and Ward of Substation Premises - Rev02Document8 pagesAnnexure-VI Visual Monitoring System For Watch and Ward of Substation Premises - Rev02gaurang1111No ratings yet
- ShrishtibeltrpDocument40 pagesShrishtibeltrpShrishti ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- 2nd AIP - BS - BRI - CGCL - 010609Document33 pages2nd AIP - BS - BRI - CGCL - 010609yiuloi997023No ratings yet
- Autonomous Hovering of A Vision/IMU Guided QuadrotorDocument6 pagesAutonomous Hovering of A Vision/IMU Guided QuadrotorKok Kai YitNo ratings yet
- Audio Video Wireless Transmitter ProjectDocument20 pagesAudio Video Wireless Transmitter ProjectkelvinbelushiNo ratings yet
- Communication System For On Board Data Telemetry To Ground.Document26 pagesCommunication System For On Board Data Telemetry To Ground.Engr Waqar Ahmed RajputNo ratings yet
- 6 Weeks Training in Doordarshan JalandharDocument25 pages6 Weeks Training in Doordarshan Jalandharrenusahu66No ratings yet
- UAV ReportDocument34 pagesUAV ReportJAYAPRABHAKARAN N NNo ratings yet
- REPORT ON INDUSTRIAL TRAINING AT DDK LUCKNOWDocument30 pagesREPORT ON INDUSTRIAL TRAINING AT DDK LUCKNOWSunil PandeyNo ratings yet
- Mobile 3D Mapping With A Low-Cost UAV SystemDocument6 pagesMobile 3D Mapping With A Low-Cost UAV SystemGANESHNo ratings yet
- MSC 86Document22 pagesMSC 86SandraNo ratings yet
- Product Guide SpecificationDocument6 pagesProduct Guide SpecificationgutierkNo ratings yet
- Audio Video Intercom SpecificationDocument7 pagesAudio Video Intercom SpecificationvicopihueNo ratings yet
- DSTBDTH PDFDocument6 pagesDSTBDTH PDFwenv_gunturwssNo ratings yet
- HELINA MISSILE GUIDANCE SYSTEMDocument10 pagesHELINA MISSILE GUIDANCE SYSTEMsaurabh07tripathiNo ratings yet
- 102RRo76Q5s1R1120 PDFDocument5 pages102RRo76Q5s1R1120 PDFPallavi PatilNo ratings yet
- IPTV Delivery Networks: Next Generation Architectures for Live and Video-on-Demand ServicesFrom EverandIPTV Delivery Networks: Next Generation Architectures for Live and Video-on-Demand ServicesSuliman Mohamed FatiNo ratings yet
- RX8000 7-1-4 ExternalDocument113 pagesRX8000 7-1-4 Externalak1828No ratings yet
- RX8000 7-1-4 ExternalDocument113 pagesRX8000 7-1-4 Externalak1828No ratings yet
- User Manual Titan MuxDocument81 pagesUser Manual Titan Muxak1828100% (1)
- Tech 3335Document68 pagesTech 3335ak1828No ratings yet
- TDC RN 0000 V2.13.3Document41 pagesTDC RN 0000 V2.13.3ak1828No ratings yet
- Datasheet tvg420Document2 pagesDatasheet tvg420ak1828No ratings yet
- TT1260 User GuideDocument30 pagesTT1260 User Guideak1828No ratings yet
- Ncompass DatasheetDocument4 pagesNcompass Datasheetak1828No ratings yet
- DRD700 ManualDocument26 pagesDRD700 Manualak1828No ratings yet
- Titan MUX User Manual 1 5Document158 pagesTitan MUX User Manual 1 5ak1828No ratings yet
- Tech 3335Document68 pagesTech 3335ak1828No ratings yet
- Earth Station Antenna Products and SystemsDocument40 pagesEarth Station Antenna Products and Systemsak1828No ratings yet
- DVB Subtitling: DVB Stands For Digital Video Broadcasting, and This Technology Relies OnDocument3 pagesDVB Subtitling: DVB Stands For Digital Video Broadcasting, and This Technology Relies Onak1828No ratings yet
- User Guide: RX1290 Multi-Format Receiver Software Version 3.0.0Document24 pagesUser Guide: RX1290 Multi-Format Receiver Software Version 3.0.0ak1828No ratings yet
- R Rec BT.656 5 200712 I!!pdf eDocument16 pagesR Rec BT.656 5 200712 I!!pdf eRenzo SattiNo ratings yet
- Transmission (Uni) and Production Facilities (Oss) Rate Card AUGUST 2014Document17 pagesTransmission (Uni) and Production Facilities (Oss) Rate Card AUGUST 2014ak1828No ratings yet
- Coax ConnectorDocument170 pagesCoax Connectorak1828No ratings yet
- SAYC - OKbridge Version, Part 1Document19 pagesSAYC - OKbridge Version, Part 1Ionut VasilescuNo ratings yet
- White Paper DVB SubtitlingDocument9 pagesWhite Paper DVB Subtitlingak1828No ratings yet
- DTH v1.7 Tranmission Rules PDFDocument30 pagesDTH v1.7 Tranmission Rules PDFak1828No ratings yet
- Ibc2006 Iptv Integrating DVB-C and Docsisworks For Cable Iptv eBook-EenDocument14 pagesIbc2006 Iptv Integrating DVB-C and Docsisworks For Cable Iptv eBook-Eenak1828No ratings yet
- HEVC: The Path To Better Pictures: White PaperDocument8 pagesHEVC: The Path To Better Pictures: White Paperak1828No ratings yet
- 37W-29687-0 802.11 - WiFi - Poster - LRDocument2 pages37W-29687-0 802.11 - WiFi - Poster - LRak1828No ratings yet
- HEVC: The Path To Better Pictures: White PaperDocument8 pagesHEVC: The Path To Better Pictures: White Paperak1828No ratings yet
- Datasheet tvg420Document2 pagesDatasheet tvg420ak1828No ratings yet
- COLETA Contract Levels Table - HCP Points for Trump and Notrump ContractsDocument1 pageCOLETA Contract Levels Table - HCP Points for Trump and Notrump Contractsak1828No ratings yet
- ACG Guideline EsophagealEosinophilia and EoE May 2013Document14 pagesACG Guideline EsophagealEosinophilia and EoE May 2013nimasolhjooNo ratings yet
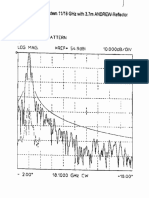
- 3.7m K Band Pattern-1Document6 pages3.7m K Band Pattern-1ak1828No ratings yet
- Single Fpga Implementation of A Digital Modulator For DVB-SDocument5 pagesSingle Fpga Implementation of A Digital Modulator For DVB-Sak1828No ratings yet
- DVB CookDocument13 pagesDVB CookBoris VianNo ratings yet
- HJGHJGDocument205 pagesHJGHJGtrsghstrhsNo ratings yet
- ESP32-RFID-Live-MySQLDocument14 pagesESP32-RFID-Live-MySQLTaoufik Zaim100% (1)
- All The Way With QRPDocument3 pagesAll The Way With QRPBenjamin DoverNo ratings yet
- AMEBA DARPA-SN-17-12 ProposersDay For Posting 16dec2016Document4 pagesAMEBA DARPA-SN-17-12 ProposersDay For Posting 16dec2016Steve AbonyiNo ratings yet
- FM System: CatalogDocument25 pagesFM System: CatalogGurmesa BatiNo ratings yet
- RC CarDocument16 pagesRC CarKanaka H KNo ratings yet
- Secured Wireless Communication Between Remote Army StationsDocument6 pagesSecured Wireless Communication Between Remote Army StationsPujitha NekkalaNo ratings yet
- United States Patent: Patent Number: Heberle Date of Patent: SepDocument10 pagesUnited States Patent: Patent Number: Heberle Date of Patent: SepcharitablegrinderNo ratings yet
- Cobra 19 DX 4Document11 pagesCobra 19 DX 4José Roberto Rodrigues Cândido de AraujoNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.6: Title: Aim: Equipment: Antenna Trainer KitDocument4 pagesExperiment No.6: Title: Aim: Equipment: Antenna Trainer KitMahesh Manikrao KumbharNo ratings yet
- TX 433Document8 pagesTX 433Sai PrintersNo ratings yet
- Amplitude Modulation ExplainedDocument62 pagesAmplitude Modulation ExplainedShikhar AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 12 Com123n TXDocument7 pages12 Com123n TXCauVong JustinNo ratings yet
- Pressure Calibration: Applications SolutionsDocument32 pagesPressure Calibration: Applications SolutionscarlosmarciosfreitasNo ratings yet
- Multipurpose Smart Glove A Personal Assistant For Differently AbledDocument61 pagesMultipurpose Smart Glove A Personal Assistant For Differently AbledTanyaGargNo ratings yet
- 9500 MPR-A Radio User Guide: PrintDocument5 pages9500 MPR-A Radio User Guide: PrintGeorge KirollosNo ratings yet
- A High Performance RF Transceiver ImplementationDocument5 pagesA High Performance RF Transceiver ImplementationSid DuttaNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On Cell Phone Detector-1Document4 pagesA Project Report On Cell Phone Detector-1Pranav BahalkarNo ratings yet
- Experimental Evaluation of Impulsive Ultrasonic Intra-Body Communications For Implantable Biomedical DevicesDocument14 pagesExperimental Evaluation of Impulsive Ultrasonic Intra-Body Communications For Implantable Biomedical DevicesGeneration GenerationNo ratings yet
- Trends in Satellite TechnologyDocument14 pagesTrends in Satellite TechnologyDr. Surendra PalNo ratings yet
- User Manual: Manufactured by ItalyDocument24 pagesUser Manual: Manufactured by ItalyQuive CarlosNo ratings yet
- HBS-730 Bluetooth Stereo Headset: User ManualDocument19 pagesHBS-730 Bluetooth Stereo Headset: User ManualcaddyNo ratings yet
- Radar-Theory-đã chuyển đổiDocument288 pagesRadar-Theory-đã chuyển đổiDat TrongNo ratings yet