Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 2 Assignment 01
Uploaded by
Jeff BrownOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 2 Assignment 01
Uploaded by
Jeff BrownCopyright:
Available Formats
Newtons Laws
Dalton Nielson Unit 2 Assignment 1
8. When your car moves along the highway at a constant velocity, the net force on it is zero. Why, then, do you continue running your engine? If you didnt continue running your engine you would lose the applied force and then all you have is friction and that would eventually stop the car.
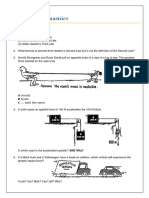
17. You hold an apple over your head. a. Identify all the forces acting on the apple and their reaction forces. When an apple falls there's only a few forces acting on that apple. The basic ones are gravity and air friction. The reaction force to the earth pulling the apple is the apple pulling the earth up with the SAME amount of force. The reaction force to air molecules hitting the apple is the apple exerting an equal and opposite force back on those air molecules. b. When you drop the apple, identify all the forces acting on it as it falls and the corresponding reaction forces. The forces that are acting on the apple as it falls would be gravity force and air resistance. 25. Suppose two carts, one twice as massive as the other, fly apart when the compressed spring that joins them is released. How fast does the heavier cart roll compared with the lighter cart? The heavier cart is moving at half the speed than the lighter cart. 33. Why is it that a cat that falls from the top of a 50 story building will hit a safety net below no faster than if it fell from the twentieth story? It is assumed that the cat reaches terminal velocity from the 20th floor before hitting the net, so therefore it doesnt matter how high the cat falls it will always reach terminal velocity at the 20 th story. 43. A stone is shown at rest on the ground. a. The vector shows the weight of the stone. Complete the vector diagram showing another vector that results in zero net force on the stone. Rock
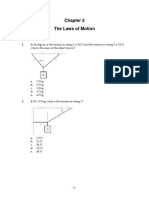
b. What is the conventional name of the vector you have drawn? Normal force 12. Forces of 3N and 4N act at right angles on a block of mass 5kg. Show that the resulting acceleration is 1 m/s2. 3N 5N 4N A2 + B = C2 5k F=ma
A2 + B 2 = C2
A2 + B2 = C 3 + 4 = 5N
2 2
5N = 5kg * a 5kg 5kg
5N = 1 m/s2 5kg
Define Angular speed (rotational speed) and tangential speed, and specify units for each. The definition of Angular speed is the change of direction per unit time, as of a target on a radar screen, without regard to the direction of the rotation axis; in other words, the magnitude of the angular velocity vector. Which is also known as angular rate.
You might also like
- 1 Motion Summary 2014Document58 pages1 Motion Summary 2014api-248740887No ratings yet
- Ding Thethe Effects of A ForceDocument18 pagesDing Thethe Effects of A Forcenik mohamad solehinNo ratings yet
- Additional Applications of Newton's Laws: Conceptual ProblemsDocument26 pagesAdditional Applications of Newton's Laws: Conceptual ProblemslizsatoshiNo ratings yet
- Formative Physics Forces AssessmentsDocument21 pagesFormative Physics Forces AssessmentsmoconnorusaNo ratings yet
- Force and Motion Grade 11 ChapterDocument88 pagesForce and Motion Grade 11 ChapterMundu Mustafa100% (1)
- As Topic 3 - Card 1 - Introduction To DynamicsDocument2 pagesAs Topic 3 - Card 1 - Introduction To DynamicsjordanlishuyangNo ratings yet
- Unit test physics friction forces Newton's lawsDocument8 pagesUnit test physics friction forces Newton's lawsDa babyNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws ExplainedDocument29 pagesNewton's Laws ExplainedCeline JamalNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Mechanics Revision SheetDocument7 pagesTopic 2 Mechanics Revision SheetJNo ratings yet
- Work Energy and Power MarkschemeDocument13 pagesWork Energy and Power MarkschemeMEXI EVYNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Problem Set 2016Document6 pagesTopic 2 Problem Set 2016ellie du123No ratings yet
- Newton S Laws and FrictionDocument7 pagesNewton S Laws and Frictionapi-275290316No ratings yet
- Dynamics Test Physics 11 - SPH3U0 True/False and Multiple ChoiceDocument10 pagesDynamics Test Physics 11 - SPH3U0 True/False and Multiple Choiceyiyin97No ratings yet
- UNIT 3 - PhysicsDocument42 pagesUNIT 3 - PhysicsPpx XdNo ratings yet
- Chapter Questions Newton S LawsDocument8 pagesChapter Questions Newton S LawsJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- A Force That Opposes - Acts Parallel To The: Motion Surfaces in ContactDocument37 pagesA Force That Opposes - Acts Parallel To The: Motion Surfaces in ContactzainonayraNo ratings yet
- MidtermI 10ansDocument2 pagesMidtermI 10ansAlexNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Questions: Unit 1: Mechanics Chapter 9: Linear Momentum and CollisionsDocument22 pagesConceptual Questions: Unit 1: Mechanics Chapter 9: Linear Momentum and CollisionsEsther Kaye Joana PanaliganNo ratings yet
- Physics Unit 2 Practice Test Newton3Document4 pagesPhysics Unit 2 Practice Test Newton3Alejandro Bon50% (2)
- Work Power and Energy Test WPDocument6 pagesWork Power and Energy Test WPtabilinNo ratings yet
- Force of FrictionDocument30 pagesForce of FrictiongearnhaleNo ratings yet
- (1 Mark) : MarkschemeDocument29 pages(1 Mark) : MarkschemeAbdulaziz HalabiNo ratings yet
- Physics ProblemsDocument3 pagesPhysics ProblemsKenneth BailadorNo ratings yet
- Class Ix Physics 6 and 7 Slo Base Questions.-1Document20 pagesClass Ix Physics 6 and 7 Slo Base Questions.-1WaheedkhanNo ratings yet
- Newton S Laws Force Friction 291Document20 pagesNewton S Laws Force Friction 291Shorya KumarNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Solution Class 9 Chapter 9 PDFDocument8 pagesNCERT Exemplar Solution Class 9 Chapter 9 PDFvaishnavisingh 8BNo ratings yet
- Revision Assignment Force and PressureDocument14 pagesRevision Assignment Force and Pressurerajesh duaNo ratings yet
- 1d Forces Concepts Practice TestDocument9 pages1d Forces Concepts Practice TestNütella VallejosNo ratings yet
- 2aprob Sol 7Document7 pages2aprob Sol 7Gowrisankar RaoNo ratings yet
- Physics Problem SetDocument3 pagesPhysics Problem SetLilian GauiranNo ratings yet
- Physics Entrance Exam Review Questions A PDFDocument9 pagesPhysics Entrance Exam Review Questions A PDFsuan_143100% (6)
- g484 Module 1 4.1.1 Newtons LawsDocument10 pagesg484 Module 1 4.1.1 Newtons LawsOMEDINEDNo ratings yet
- 0307 ImpulseDocument4 pages0307 ImpulseimfizicsNo ratings yet
- Force AnalysisDocument152 pagesForce AnalysisWang Han Zhu100% (1)
- National Senior Certificate: Physical Sciences P1 (Physics) Half - Yearly Examinations JUNE 2020Document32 pagesNational Senior Certificate: Physical Sciences P1 (Physics) Half - Yearly Examinations JUNE 2020MfanafuthiNo ratings yet
- Linear Momentum and CollisionsDocument7 pagesLinear Momentum and CollisionsFaris AlasmariNo ratings yet
- Particle Dynamics (11th JK) WADocument48 pagesParticle Dynamics (11th JK) WAParijat SutradharNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Solution Class 9 Chapter 11 PDFDocument10 pagesNCERT Exemplar Solution Class 9 Chapter 11 PDFvaishnavisingh 8BNo ratings yet
- Chapter ForceDocument8 pagesChapter ForcenilimaNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument8 pagesNewton's Laws of MotionRoda Gayle RañadaNo ratings yet
- WorkEnergyOCQ Cabral Espiritu Franco VermanaogDocument5 pagesWorkEnergyOCQ Cabral Espiritu Franco VermanaogHanz EspirituNo ratings yet
- Work Energy and Power Practice WorksheetDocument13 pagesWork Energy and Power Practice Worksheet윤영석No ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument43 pagesNewton's Laws of MotionJhulia IlogonNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Dynamics Chapter ReviewDocument11 pagesModule 2 Dynamics Chapter ReviewAmelia RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- WTS Mechanics Crossnight PDFDocument31 pagesWTS Mechanics Crossnight PDFBontle PrincessNo ratings yet
- Convert MefsDocument3 pagesConvert MefssaghfadNo ratings yet
- WORK, POWER AND ENERGY: KEY CONCEPTSDocument7 pagesWORK, POWER AND ENERGY: KEY CONCEPTSGrace Adrianne BacayNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy & Power Practice QuizDocument3 pagesWork, Energy & Power Practice QuizJohn Mark CabicunganNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Class XI Work Power EnergyDocument4 pagesWorksheet Class XI Work Power Energyroythomasc100% (2)
- Laws of Motion Set-1 Chapter-5Document20 pagesLaws of Motion Set-1 Chapter-5Sourish MaitraNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motioin Cbse Questons PDFDocument63 pagesLaws of Motioin Cbse Questons PDFRazeem AhmadNo ratings yet
- Hindusthan College of Engineering and Technology: (An Autonomous Institution, Affiliated To Anna University, Chennai)Document15 pagesHindusthan College of Engineering and Technology: (An Autonomous Institution, Affiliated To Anna University, Chennai)VEERAMANIKANDANNo ratings yet
- Work Power Energy QuestionsDocument17 pagesWork Power Energy QuestionsAnupam MNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument5 pagesPhysicsBacillus SubtilisNo ratings yet
- MomentumDocument64 pagesMomentumjoe doeNo ratings yet
- MotionDocument17 pagesMotionJohnNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Physics 3Document2 pagesPhysics 3Jeff BrownNo ratings yet
- Examining group data in coming weeksDocument1 pageExamining group data in coming weeksJeff BrownNo ratings yet
- Research Paper FinalDocument2 pagesResearch Paper FinalJeff BrownNo ratings yet
- Carrier Recovery: A Carrier Recovery System Is A Term Used For The Circuit That EstimatesDocument3 pagesCarrier Recovery: A Carrier Recovery System Is A Term Used For The Circuit That EstimatesJeff BrownNo ratings yet
- Physics 2Document3 pagesPhysics 2Jeff BrownNo ratings yet
- Jeff Brown Strategies For The Technical Professional Mr. Harr's Class 11/26/13 Unit 10-Assignment 1Document7 pagesJeff Brown Strategies For The Technical Professional Mr. Harr's Class 11/26/13 Unit 10-Assignment 1Jeff BrownNo ratings yet
- Analog Electrical Multiple Choice TestDocument8 pagesAnalog Electrical Multiple Choice TestJeff BrownNo ratings yet
- Elevator Exam 01Document6 pagesElevator Exam 01Jeff BrownNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Assignment 1 - Intercultural Conflict Analysis: Jeff Brown Michelle Pultorak's Class CO2520T July 20, 2013Document3 pagesUnit 5 Assignment 1 - Intercultural Conflict Analysis: Jeff Brown Michelle Pultorak's Class CO2520T July 20, 2013Jeff BrownNo ratings yet
- 06 5-2 Ethics StatementDocument2 pages06 5-2 Ethics StatementJeff BrownNo ratings yet
- Difficult PeopleDocument15 pagesDifficult PeopleJeff Brown100% (1)
- 12 Unit 7-2 Ethics StatementDocument2 pages12 Unit 7-2 Ethics StatementJeff BrownNo ratings yet
- 13 Unit 8 AssignmentDocument3 pages13 Unit 8 AssignmentJeff BrownNo ratings yet
- 14 Unit 8 EthicsDocument2 pages14 Unit 8 EthicsJeff BrownNo ratings yet
- 08 Unit 6 StuffDocument2 pages08 Unit 6 StuffJeff BrownNo ratings yet
- 09 Unit 6-2 Ethics StatementDocument2 pages09 Unit 6-2 Ethics StatementJeff BrownNo ratings yet
- Jeff Brown Michelle Pultorak's Class CO2520T July 20, 2013Document3 pagesJeff Brown Michelle Pultorak's Class CO2520T July 20, 2013Jeff BrownNo ratings yet
- Human Communications Class NotesDocument2 pagesHuman Communications Class NotesJeff BrownNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Assignment 1 - Intercultural Conflict Analysis: Jeff Brown Michelle Pultorak's Class CO2520T July 20, 2013Document3 pagesUnit 5 Assignment 1 - Intercultural Conflict Analysis: Jeff Brown Michelle Pultorak's Class CO2520T July 20, 2013Jeff BrownNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Homework Assignment Problems: Jeff Brown Microprocessing Mr. Hamza 08-01-13Document2 pagesUnit 7 Homework Assignment Problems: Jeff Brown Microprocessing Mr. Hamza 08-01-13Jeff BrownNo ratings yet
- 02 Unit 8 AssignmentDocument4 pages02 Unit 8 AssignmentJeff BrownNo ratings yet
- 03 Unit 9 AssignmentDocument1 page03 Unit 9 AssignmentJeff Brown0% (1)
- Unit 1-1 Field ExperienceDocument3 pagesUnit 1-1 Field ExperienceJeff BrownNo ratings yet
- Unit 4-2 Ethics StatementDocument2 pagesUnit 4-2 Ethics StatementJeff BrownNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Assignment 1Document1 pageUnit 3 Assignment 1Jeff BrownNo ratings yet
- Societal FactorsDocument3 pagesSocietal FactorsJeff BrownNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 1Document2 pagesUnit 2 1Jeff BrownNo ratings yet
- Models of CommunicationDocument2 pagesModels of CommunicationJeff BrownNo ratings yet
- Brand Me - My Self AssesmentDocument1 pageBrand Me - My Self AssesmentJeff BrownNo ratings yet
- Addu High School Physics Worksheet on Quantities and UnitsDocument3 pagesAddu High School Physics Worksheet on Quantities and UnitsDhanBahadurNo ratings yet
- Mixing Time of Refining Vessels Stirred by Gas InjectionDocument8 pagesMixing Time of Refining Vessels Stirred by Gas InjectionПетр СамосийNo ratings yet
- Physics 10 Reviewer Question SheetDocument5 pagesPhysics 10 Reviewer Question SheetAntonette TabilNo ratings yet
- Example PPPDocument3 pagesExample PPPAliNo ratings yet
- Application of DifferentiationDocument4 pagesApplication of Differentiationapi-127466285No ratings yet
- Physics All You WantDocument232 pagesPhysics All You Wanttapiwa nzvatuNo ratings yet
- 3rd Monthly TestDocument3 pages3rd Monthly TestRowena Sta MariaNo ratings yet
- Special Theory of Relativity by UgarovDocument410 pagesSpecial Theory of Relativity by UgarovRodrigo Mario Calle HuamaniNo ratings yet
- Balls Take High and Low TracksDocument11 pagesBalls Take High and Low Trackspalparas100% (2)
- PM TB Solutions C02Document10 pagesPM TB Solutions C02Vishwajeet Ujhoodha86% (14)
- 100 Laws of Motion Practice QuestionsDocument33 pages100 Laws of Motion Practice QuestionsLyn RegaladoNo ratings yet
- Simulation of The Coating Process: Josef DembickýDocument5 pagesSimulation of The Coating Process: Josef DembickýGizem CaliskanNo ratings yet
- LECTURE (NOTE) - Module 01 - MeasurementDocument86 pagesLECTURE (NOTE) - Module 01 - Measurement821A 45RajNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight Line - Practice Sheet - Arjuna JEE 4.0 2024Document4 pagesMotion in A Straight Line - Practice Sheet - Arjuna JEE 4.0 2024Kanishq SarkarNo ratings yet
- 16716apni KakshaDocument30 pages16716apni Kaksha06 boymaxxNo ratings yet
- Physics: 1. Measurements and UnitsDocument43 pagesPhysics: 1. Measurements and UnitsMadhuri Devi100% (1)
- Traffic-Flow Modelos Matemáticos HabermanDocument137 pagesTraffic-Flow Modelos Matemáticos HabermanLuis AngelesNo ratings yet
- Mass and Inertia: Dynamics 1Document11 pagesMass and Inertia: Dynamics 1Joe West100% (2)
- 1-15-15 Kinematics AP1 - Review SetDocument8 pages1-15-15 Kinematics AP1 - Review SetLudwig Van Beethoven100% (1)
- Solving Problems Involving Speed and VelocityDocument3 pagesSolving Problems Involving Speed and VelocityAida GanaNo ratings yet
- Mastering Physics AnswersDocument144 pagesMastering Physics Answerscuriousbookworm100% (2)
- IIT Ashram: Part (A) : PhysicsDocument5 pagesIIT Ashram: Part (A) : PhysicsPujan ShahNo ratings yet
- 1-D Kinematics Test ReviewDocument2 pages1-D Kinematics Test ReviewKaitlynNo ratings yet
- Bending of Uniformly Cantilever Rectangular Plates PDFDocument13 pagesBending of Uniformly Cantilever Rectangular Plates PDFJacopo Svetoni0% (1)
- Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesLesson PlanMuhammad ZahiruddinNo ratings yet
- Particle Dynamics SheetDocument27 pagesParticle Dynamics SheetAkhilesh SoniNo ratings yet
- Physical-Science-Q4-Week-7_v2_Document21 pagesPhysical-Science-Q4-Week-7_v2_janethbiapasagdanNo ratings yet
- ECV 302 HYDRAULICS I - CAT 1 - Model Answers PDFDocument5 pagesECV 302 HYDRAULICS I - CAT 1 - Model Answers PDFPaulpablo ZaireNo ratings yet
- MCV4U - Unit 2 - Version ADocument53 pagesMCV4U - Unit 2 - Version AhayatNo ratings yet