Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Additional Mathematics Guide For O Levels
Uploaded by
Umair AhmedOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Additional Mathematics Guide For O Levels
Uploaded by
Umair AhmedCopyright:
Available Formats
New Additional Mathematics
Muhammad Hassan Nadeem
1. Sets
A null or empty set is donated by { } or . P = Q if they have the same elements. P Q, Q is subset of P. PQ, P is subset of R. PQ, Q is proper subset of P. PQ, P is proper subset of Q. PQ, Intersection of P and Q. PQ, union of P and Q. P compliment of P i.e. -P
2. Simultaneous Equations
2 4 = 2
3. Logarithms and Indices
Indices
1. 0 = 1 2. = 3. = 4. =
1
5. = +
6.
7. =
www.revision-notes.co.cc
New Additional Mathematics
Muhammad Hassan Nadeem
8. = 9.
Logarithms
1. = = 2. 1 = 0 3. = 1 5.
4. = +
=
1
1
6. = 7. =
8. = 9. =
log log
10. log = log log =
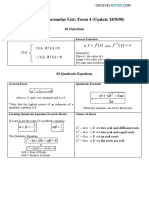
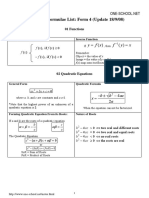
4. Quadratic Expressions and Equations
1. Sketching Graph
y-intercept
Put x=0
x-intercept
Put y=0
www.revision-notes.co.cc
New Additional Mathematics
Muhammad Hassan Nadeem
Turning point
Method 1 x-coordinate: = y-coordinate: = Method 2 Express = 2 + + as = 2 + by completing the square. The turning point is , .
2 4 2 4
2. Types of roots of + + = 2 4 0 : real roots 2 4 < 0 : no real roots 2 4 > 0 : distinct real roots 2 4 = 0 : equal, coincident or repeated real roots
5. Remainder Factor Theorems
Polynomials
1. ax 2 + bx + c is a polynomial of degree 2. 2. ax 3 + bx + c is a polynomial of degree 3.
Identities
= For all values of x
To find unknowns either substitute values of x, or equate coefficients of like powers of x.
www.revision-notes.co.cc
New Additional Mathematics
Muhammad Hassan Nadeem
Remainder theorem
If a polynomial f(x) is divided by (x-a), the remainder is f(a)
Factor Theorem
(x-a) is a factor of f(x) then f(a) = 0
Solution of cubic Equation
I. II. III. Obtain one factor (x-a) by trail and error method. Divide the cubic equation with a, by synthetic division to find the quadratic equation. Solve the quadratic equation to find remaining two factors of cubic equation.
For example: I. II. The equation 3 + 2 2 5 6 = 0 has (x-2) as one factor, found by trail and error method. Synthetic division will be done as follows:
III. IV. V.
The quadratics equation obtained is 2 + 4 + 3 = 0. Equation is solved by quadratic formula, X=-1 and X=-3. Answer would be (x-2)(x+1)(x+3).
6. Matrices
www.revision-notes.co.cc
New Additional Mathematics
Muhammad Hassan Nadeem
1. Order of a matrix
Order if matrix is stated as its number of rows x number of columns. For example, the matrix 5
2 has order 1 x 3.
2. Equality Two matrices are equal if they are of the same order and if their corresponding elements are equal.
3. Addition
To add two matrices, we add their corresponding elements. For example,
6 3
2 4 + 5 4
2 2 = 1 7
0 . 6
4. Subtraction
To subtract two matrices, we subtract their corresponding elements. For example,
6 9
3 14
5 2 5 4
7 20
4 5 = 12 1
4 6
0 . 6
5. Scalar multiplication
To multiply a matrix by k, we multiply each element by k. For example,
2 3
4 2 = 1 3
2 6 4 or 3 = . 4 12
6. Matrix multiplication To multiply two matrices, column of the first matrix must be equal to the row of the second matrix. The product will have order row of first matrix X column of second matrix. 2 4 3 2 1 4 For example: 1 3 = 1 5 2 7 2 1 To get the first row of product do following:
www.revision-notes.co.cc
New Additional Mathematics
Muhammad Hassan Nadeem
a = (2 x 3) + (4 X 1) = 10 (1st row of first, 1st column of second) b = (2 x 2) + (4 x 5) = 24 (1st row of first, 2st column of second) c = (2 x 1) + (4 x 2) = 10 (1st row of first, 3st column of second) d = (2 x 4) + (4 x 7) = 36 (1st row of first, 4st column of second) e = (1 x 3) + (3 x 1) = 6 (2st row of first, 1st column of second) f = (1 x 2) + (3 x 5) = 17 (2st row of first, 2st column of second) g = (1 x 1) + (3 x 2) = 7 (2st row of first, 3st column of second) h = (1 x 4) + (3 x 7) = 25 (2st row of first, 4st column of second) i = (2 x 3) + (-1 x 1) = 5 (3st row of first, 1st column of second) j = (2 x 2) + (-1 x 5) = -1 (3st row of first, 2st column of second) k = (2 x 1) + (-1 x 2) = 0 (3st row of first, 3st column of second) l = (2 x 4) + (-1 x 7) = 1 (3st row of first, 4st column of second) 7. 2 x2 Matrices 1 0 is called identity matrix. When it is multiplied with any 0 1 matrix X the answer will be X. b. Determinant of matrix will be = = c. Adjoint of matrix will be = d. Inverse of non-singular matrix (determinant is 0) will be : 1 = a. The matrix
8. Solving simultaneous linear equations by a matrix method
+ = + = 1 = =
7. Coordinate Geometry
www.revision-notes.co.cc
New Additional Mathematics
Muhammad Hassan Nadeem
Formulas = 2 1
2
+ 2 1
= Parallelogram
1 + 2 1 + 2 , 2 2
If ABCD is a parallelogram then diagonals AC and BD have a common midpoint. Equation of Straight line To find the equation of a line of best fit, you need the gradient(m) of the line, and the y-intercept(c) of the line. The gradient can be found by taking any two points on the line and using the following formula: = = 2 1 2 1
The y-intercept is the y-coordinate of the point at which the line crosses the yaxis (it may need to be extended). This will give the following equation: = + Where y and x are the variables, m is the gradient and c is the y-intercept. Equation of parallel lines Parallel line have equal gradient. If lines = 1 1 and = 2 2 are parallel then 1 = 2 Equations of perpendicular line If lines = 1 1 and = 2 2 are perpendicular then 1 = Perpendicular bisector
1 2
and 2 =
1 1
www.revision-notes.co.cc
New Additional Mathematics
Muhammad Hassan Nadeem
The line that passes through the midpoint of A and B, and perpendicular bisector of AB. For any point P on the line, PA = PB
Points of Intersection The coordinates of point of intersection of a line and a non-parallel line or a curve can be obtained by solving their equations simultaneously.
8. Linear Law
To apply the linear law for a non-linear equation in variables x and y, express the equation in the form = + Where X and Y are expressions in x and/or y.
9. Functions
Page 196
10. Trigonometric Functions
www.revision-notes.co.cc
New Additional Mathematics
Muhammad Hassan Nadeem
+ 90
Sin 2
180
All 1
0,360
Tan 3
270
is always acute.
Cos 4
Basics
sin = cos = tan = tan =
sin
cosec = sec = cot =
cos 1 sin 1
cos 1 tan
www.revision-notes.co.cc
New Additional Mathematics
Muhammad Hassan Nadeem
Rule 1
sin(90 ) = cos cos 90 = sin tan 90 =
1 tan
= cot
Rule 2
sin(180 ) = + sin cos 180 = cos tan 180 = tan
Rule 3
sin(180 + ) = sin cos 180 + = cos tan 180 + = +tan
Rule 4
sin(360 ) = sin cos 360 = +cos tan 360 = tan
Rule 5
sin( ) = sin cos = +cos tan = tan
www.revision-notes.co.cc
New Additional Mathematics
Muhammad Hassan Nadeem
Trigonometric Ratios of Some Special Angles
cos 45 = sin 45 = 1 2 1 cos 60 = sin 60 = 1 2 cos 30 = 3 2 1 sin 30 = 2 1 tan 30 3
2 tan 45 = 1
3 2 tan 60 = 3
11. Simple Trigonometric Identities
Trigonometric Identities
sin2 + cos 2 = 1 1 + tan2 = sec 2 1 + cot 2 = cosec 2
12. Circular Measure
Relation between Radian and Degree
2 3 2
= 90 = 270
= 180 2 = 360
= where s is arc length, r is radius and is angle of sector is radians = = 2
2 2 1 1
where A is Area of sector =
www.revision-notes.co.cc
New Additional Mathematics
Muhammad Hassan Nadeem
13. Permutation and Combination
! = 1 2 3 2 1 0! = 1 ! = 1 !
= =
! ! ! ! !
14. Binomial Theorem
+
2 2 3 3 1 = + 1 + 2 + 3 + +
+1 =
15. Differentiation
= 1 + = 1 + 1 = 1 = +
www.revision-notes.co.cc
New Additional Mathematics
Muhammad Hassan Nadeem
= 2 Where v and u are two functions Gradient of a curve at any point P(x,y) is
at x
16. Rate of Change
The rate of change of a variable x with respect to time is = = 100%
+ = + +
17. Higher Derivative
= 0 when x =a then point (a, f(a)) is a stationary point. = 0 and
2 2
0 when x =a then point (a, f(a)) is a turning point.
For a turning point T
I.
If
2 2
> 0, then T is a minimum point.
www.revision-notes.co.cc
New Additional Mathematics
Muhammad Hassan Nadeem
II.
If
2 2
< 0, then T is a maximum point.
18. Derivative of Trigonometric Functions
sin = cos cos = sin tan = sec 2
sinn = sinn 1 cos cos n = cos n 1 sin tann = tann 1 sec 2
19. Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
= + = +
www.revision-notes.co.cc
New Additional Mathematics
Muhammad Hassan Nadeem
A curve defined by y=ln(ax+b) has a domain ax+b>0 and the curve cuts the xaxis at the point where ax+b=1 1 = 1 ln = + = +
20. Integration
= = 1 2 + = 2
1 = 2 + 2
+1 = + + 1
+1 +1 = + + + 1 + 1
+ +1 ( + ) = + ( + 1)
= ()
= ()
www.revision-notes.co.cc
New Additional Mathematics
Muhammad Hassan Nadeem
= 0
sin = cos cos = sin tan = sec 2
cos = sin + sin = cos + 2 = +
1 sin( + ) = cos( + ) 1 cos( + ) = sin( + ) 1 tan( + ) = sec 2 ( + )
cos( + ) =
1 sin( + ) +
1 sin( + ) = cos( + ) + 2 ( + ) = 1 ( + ) +
= =
= + = +
www.revision-notes.co.cc
New Additional Mathematics
Muhammad Hassan Nadeem
21. Applications of Integration
For a region R above the x-axis, enclosed by the curve y=f(x), the x-axis and the lines x=a and x=b, the area R is:
For a region R below the x-axis, enclosed by the curve y=f(x), the x-axis and the lines x=a and x=b, the area R is:
For a region R enclosed by the curves y=f(x) and y=g(x) and the lines x=a and x=b, the area R is:
()
www.revision-notes.co.cc
New Additional Mathematics
Muhammad Hassan Nadeem
22. Kinematics
= = = = =
= + 1 = + 2 2 = 1 + 2
2 = 2 + 2
23. Vectors
If = then = 2 + 2 = and k > 0 a and b are in the same direction = and k < 0 a and b are opposite in direction Vectors expressed in terms of two parallel vectors a and b: + = + p = r and q = s
www.revision-notes.co.cc
New Additional Mathematics
Muhammad Hassan Nadeem
If A, B and C are collinear points AB=kBC If P has coordinates (x, y) in a Cartesian plane, then the position vector of P is = + where i and j are unit vectors in the positive direction along the x-axis and the yaxis respectively. Unit vector is the direction of is 1 + 2 + 2 1 2 + 2
24. Relative velocity
www.revision-notes.co.cc
You might also like
- (Cambridge IGCSE ADD - MATHS PDFDocument348 pages(Cambridge IGCSE ADD - MATHS PDFUmam Rafique100% (19)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- O Level Mathematics Revision Notes (SEAB) PDFDocument184 pagesO Level Mathematics Revision Notes (SEAB) PDFBilal Akram90% (10)
- Solving Quadratic EquationDocument41 pagesSolving Quadratic EquationMarites BalmasNo ratings yet
- O Level Maths Notes, PDFDocument67 pagesO Level Maths Notes, PDFMahad Imran85% (181)
- Additional Maths Resource Pack2Document46 pagesAdditional Maths Resource Pack2Shaamini100% (6)
- MATHS Olevels NotesDocument18 pagesMATHS Olevels NotesMahad Imran100% (8)
- Ad Maths Formula ListDocument16 pagesAd Maths Formula ListZareena CarrimNo ratings yet
- LEG O Level Additional MathsDocument175 pagesLEG O Level Additional MathsMuhammed Ali90% (10)
- Edexcel IGCSE Vector NotesDocument40 pagesEdexcel IGCSE Vector NotesÅzmâñ KhäñNo ratings yet
- Igcse Additional Mathematics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesIgcse Additional Mathematics Formula SheetDinanAlasad71% (17)
- Additional Maths Revision NotesDocument84 pagesAdditional Maths Revision NotesEmmanuel Light50% (6)
- Maths IGCSE Quick RevisionDocument6 pagesMaths IGCSE Quick RevisionMahmoudsamir El Shazly100% (1)
- IGCSE Maths Past Examination Papers Classified by TopicDocument82 pagesIGCSE Maths Past Examination Papers Classified by TopicDinanAlasad74% (92)
- O-Level Physics NotesDocument58 pagesO-Level Physics NotesAnonymous UjF5VlVtm100% (2)
- Curved BeamDocument85 pagesCurved Beamanon_651663167No ratings yet
- What Is ModernityDocument20 pagesWhat Is ModernityUmair AhmedNo ratings yet
- A Level Maths P 3 NotesDocument14 pagesA Level Maths P 3 Notesoalevels78% (9)
- Extended IGCSE Maths Revision NotesDocument52 pagesExtended IGCSE Maths Revision Notesliberto2160% (5)
- IGCSE Math (Worked Answers)Document22 pagesIGCSE Math (Worked Answers)Amnah Riyaz100% (1)
- Topical Revision Notes Additional Mathematics O Level PDFDocument186 pagesTopical Revision Notes Additional Mathematics O Level PDFShamvil Raza100% (5)
- Add MathsDocument40 pagesAdd MathsJoseph TingNo ratings yet
- DLP Additional Mathematics Form 4Document324 pagesDLP Additional Mathematics Form 4Curtis Chong100% (4)
- BS 4999-0 General RequirementsDocument8 pagesBS 4999-0 General RequirementsUmair Ahmed100% (1)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Math Quest Math Methods VCE 12 (2016 Edition)Document542 pagesMath Quest Math Methods VCE 12 (2016 Edition)NhiNo ratings yet
- HSC 3U Maths FormulaeDocument7 pagesHSC 3U Maths FormulaeHotz InatorNo ratings yet
- Revision Checklist For O Level Physics 5054 FINALDocument24 pagesRevision Checklist For O Level Physics 5054 FINALYenny Tiga100% (3)
- Week 1 - PPT 1 - AMG 211 (Basic Algebraic Operations To Equations and Inequalities)Document36 pagesWeek 1 - PPT 1 - AMG 211 (Basic Algebraic Operations To Equations and Inequalities)not funny didn't laughNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Alevel Paper-3 Topical Past PDFDocument16 pagesMathematics Alevel Paper-3 Topical Past PDFRiyaansh Mittal0% (1)
- Mathematics A Level P 1 Topical Past Pap PDFDocument19 pagesMathematics A Level P 1 Topical Past Pap PDFIqra Hameed Khan50% (4)
- BITS Pilani: Instructor in Charge-Dr. Kalyana Rama J SDocument23 pagesBITS Pilani: Instructor in Charge-Dr. Kalyana Rama J SSaiteja SistlaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Notes PDFDocument12 pagesMathematics Notes PDFrawan100% (1)
- Longman Additional Mathematics For A Level (Advanced Level)Document536 pagesLongman Additional Mathematics For A Level (Advanced Level)akakios033% (3)
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- JKR Astro Research Foundatioin Vimsottari Dasa SystemDocument6 pagesJKR Astro Research Foundatioin Vimsottari Dasa SystemjeydownloadNo ratings yet
- Maths p1Document31 pagesMaths p1Kamran Khan50% (2)
- Formulation of Soap PDFDocument4 pagesFormulation of Soap PDFNelson StangNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Penetration TestDocument5 pagesPenetration TestU Mad BRoNo ratings yet
- Heidegger-The Age of The World-PictureDocument16 pagesHeidegger-The Age of The World-PictureAlexandra Seidenshaw100% (4)
- B 29 - 14Document4 pagesB 29 - 14ruben carcamoNo ratings yet
- Chapt-17 Compass ErrorDocument4 pagesChapt-17 Compass ErrorShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Maths NotesDocument2 pagesIGCSE Maths Notesudinaksimple29% (7)
- Merged Modules MATHS For IGCSEDocument143 pagesMerged Modules MATHS For IGCSElittlegus100% (2)
- SPM Add Maths Formula List Form4 PDFDocument16 pagesSPM Add Maths Formula List Form4 PDFNicholas Rogers80% (5)
- 5 CIE IGCSE Additional Mathematics Paper 2 Topical Past Paper Factors of PolynomialsDocument15 pages5 CIE IGCSE Additional Mathematics Paper 2 Topical Past Paper Factors of PolynomialsAng Kai Jun100% (1)
- SPM Add Maths Formula List Form4Document16 pagesSPM Add Maths Formula List Form4Alvin HonNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationsDocument39 pagesQuadratic Equationsthinkiit100% (2)
- LESSON 4 CAL 2 IntegralsDocument40 pagesLESSON 4 CAL 2 IntegralsZero DragneelNo ratings yet
- MC Ty Trigids 2009 1Document9 pagesMC Ty Trigids 2009 1Kurniawan SusiloNo ratings yet
- Math Question Papers For Class 12Document155 pagesMath Question Papers For Class 12GopalSharma100% (1)
- Coplex Number FormulasDocument7 pagesCoplex Number FormulasMohan KhedkarNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics - List of Formulae (Form 4)Document19 pagesAdditional Mathematics - List of Formulae (Form 4)Syazleen Nabilah AkmalNo ratings yet
- Maths Concepts and Formulae: y FX F y XDocument16 pagesMaths Concepts and Formulae: y FX F y XAt TanwiNo ratings yet
- A-Math Formula List - Additional Math (4047) Updated 6th Apr 2015 PDFDocument12 pagesA-Math Formula List - Additional Math (4047) Updated 6th Apr 2015 PDFilluminatehNo ratings yet
- Unit I Mathematical Tools 1.1 Basic Mathematics For Physics: I. Quadratic Equation and Its SolutionDocument16 pagesUnit I Mathematical Tools 1.1 Basic Mathematics For Physics: I. Quadratic Equation and Its SolutionJit AggNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - 11th ClassDocument9 pagesMathematics - 11th ClasspaupermNo ratings yet
- Notes MathDocument4 pagesNotes MathNaveed Atta UllahNo ratings yet
- HSN Course SummaryDocument26 pagesHSN Course SummaryQwaAlmanlawiNo ratings yet
- Essential Formulae: Number and AlgebraDocument7 pagesEssential Formulae: Number and AlgebraShinigami01001No ratings yet
- Basic Maths FormulaeDocument10 pagesBasic Maths FormulaeAns DevNo ratings yet
- Maths Model Test Paper For Summative Assessment - 1Document13 pagesMaths Model Test Paper For Summative Assessment - 1Apex InstituteNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions Lecture 23 To 45Document27 pagesPractice Questions Lecture 23 To 45Ali Qasim JafferyNo ratings yet
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Green Ship Recycling - Basel Action NetworkDocument7 pagesGreen Ship Recycling - Basel Action NetworkUmair AhmedNo ratings yet
- P AimsDocument4 pagesP AimsUmair AhmedNo ratings yet
- Technical Note - Friction Factor Diagrams For Pipe FlowDocument16 pagesTechnical Note - Friction Factor Diagrams For Pipe Flowjaskaran singhNo ratings yet
- Present Tense - 1Document1 pagePresent Tense - 1Barbara WilgerNo ratings yet
- Physics DefinitionDocument3 pagesPhysics DefinitionUmair AhmedNo ratings yet
- Dkvm-2 Manual v1.2Document28 pagesDkvm-2 Manual v1.2edordonezNo ratings yet
- 10 Secrets High School Test PDFDocument171 pages10 Secrets High School Test PDFOlimpiu AntNo ratings yet
- Biomedical StatisticsDocument78 pagesBiomedical StatisticsUmair AhmedNo ratings yet
- Geography TopicalDocument15 pagesGeography TopicalUmair Ahmed20% (5)
- Biomedical StatisticsDocument78 pagesBiomedical StatisticsUmair AhmedNo ratings yet
- Interacting Two Matlab Guis ProgramaticallyDocument7 pagesInteracting Two Matlab Guis ProgramaticallyUmair AhmedNo ratings yet
- Work OrderDocument1 pageWork OrderUmair AhmedNo ratings yet
- Turtles Have No TeethDocument2 pagesTurtles Have No TeethUmair AhmedNo ratings yet
- Computer March 2012Document5 pagesComputer March 2012Umair AhmedNo ratings yet
- Critical Vulnerables FoundDocument2 pagesCritical Vulnerables FoundUmair AhmedNo ratings yet
- Grignard ReactionDocument1 pageGrignard ReactionSulaiman Al Shidhani100% (2)
- PHYS132 Formula SheetDocument12 pagesPHYS132 Formula SheetMuhammad IshtiaqNo ratings yet
- Env68 8 06 06 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 8 06 06 KCapi-367296283No ratings yet
- Max - Maier - Applications of Stimulated Raman Scattering PDFDocument23 pagesMax - Maier - Applications of Stimulated Raman Scattering PDFAkriti SinghNo ratings yet
- Axisymm TutorialDocument15 pagesAxisymm Tutorialmudur6No ratings yet
- Term PaperDocument6 pagesTerm PaperNorshida CalibiNo ratings yet
- WS 1 Nelson Vaugh RotorDocument24 pagesWS 1 Nelson Vaugh RotorrgruizNo ratings yet
- Point Group PDFDocument46 pagesPoint Group PDFDharamsingh WaskaleNo ratings yet
- The Tips For Operation and Maintenance Belt Filter Press For Sludge DewateringDocument1 pageThe Tips For Operation and Maintenance Belt Filter Press For Sludge DewateringFuad NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Indian Standard: Ceramic Tiles - Methods of Test, Sampl G and Basis For AcceptanceDocument47 pagesIndian Standard: Ceramic Tiles - Methods of Test, Sampl G and Basis For AcceptanceUppala Krishna ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Turbo Machinery Validation Against Experimental ResultsDocument13 pagesOptimization of Turbo Machinery Validation Against Experimental ResultsSrinivasNo ratings yet
- Medical Image Retrieval With Probabilistic Multi-Class Support Vector Machine Classifiers and Adaptive Similarity FusionDocument14 pagesMedical Image Retrieval With Probabilistic Multi-Class Support Vector Machine Classifiers and Adaptive Similarity FusionDuraiPandyNo ratings yet
- SM Lab (Tension Test)Document15 pagesSM Lab (Tension Test)sushilkumar100% (1)
- Lock ShimDocument3 pagesLock ShimJulie WeiNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 PDFDocument12 pagesExercise 1 PDFAnjali GuptaNo ratings yet
- 15 04 0662-02-004a Channel Model Final Report r1Document40 pages15 04 0662-02-004a Channel Model Final Report r1Alex Samuel Ludeña HuamaniNo ratings yet
- Elma O. Camiom-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesElma O. Camiom-WPS OfficeElma Ortega CamionNo ratings yet
- Control Valve Inspection RequirementDocument1 pageControl Valve Inspection RequirementGeekyard Geeks GNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document1 pageTutorial 5SHOURYA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Approximate Calculation of "Ground Reaction" When A Ship Is Aground Over Quite A Distance of Its Flat-Bottom and Is Not Heavily TrimmedDocument2 pagesApproximate Calculation of "Ground Reaction" When A Ship Is Aground Over Quite A Distance of Its Flat-Bottom and Is Not Heavily Trimmedmyusuf_engineerNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Joint Forces IIDocument5 pagesLecture 8 Joint Forces IIVenkatNo ratings yet
- Class IX: Science Chapter 11: Work and Energy Chapter Notes Key LearningDocument2 pagesClass IX: Science Chapter 11: Work and Energy Chapter Notes Key LearningMohanNayakNo ratings yet