Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Threatstobiodiversity
Uploaded by
api-235959158Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Threatstobiodiversity
Uploaded by
api-235959158Copyright:
Available Formats
Threats to Biodiversity: An Overview Guided Viewing Name: Selena Felix 1: Natural Capital: Forests Ecological Services Economic Services
Support energy flow and chemical cycling Reduce soil erosion Absorb and release water Purify water and air Influence local and regional Climate Store atmospheric carbon Economic Services Fuel wood Lumber Pulp to make paper Mining Livestock grazing Recreation Jobs
2: What are the 3 main types of forests? Old-growth forests, Second-growth forest, and tree plantation. 3: What are some of the problems associated with deforestation? Decreased soil fertility from erosion, runoff of eroded soil into aquatic systems and premature extinction of species with specialized niches. 4: What are the methods for harvesting trees? Selective cutting, clear cutiing, and strip cutting. 5: Clear-Cutting Forests Advantages Most Efficient Higher timber yields Maximum profits in shortest time Can reforest with fast- growing trees Short time to establish new stand of trees Needs less skill and planning Disadvantages Does considerable damage Destroys habitats Kills animals Reduces biodiversity Disrupts ecosystem processes Destroys and fragments wildlife habitats
6: What are some solutions for sustainable forestry? Identify and protect forest areas high in biodiversity Grow more timber on long rotations
Rely more on selective cutting and strip cutting Shift government subsidies from harvesting trees to planting trees Certify timber grown by sustainable methods Sharply reduce road building into uncut forest areas
7: What is the Healthy Forest Restoration Act? What are the PROS and CONS? A Healthy Forest Restoration Act is an act that allows timber companies to cut medium and large trees in 71% of the national forests. In return, must clear away smaller, more fire- prone trees and underbrush. Some forest scientists believe this could increase severe fires by removing fire resistant trees and leaving highly flammable slash. 8: Logging in National Forests Advantages Helps meet countrys timber needs Cut areas grow back Keeps lumber and paper prices down Provides jobs in nearby communities Promotes economic growth in nearby communities Disadvantages Provides only 4% of timber needs Ample private forest land to meet timber needs Has little effect on timber and paper prices Damages nearby rivers and fisheries Recreation in national forests provides more local jobs and income for local communities than logging
9: What are some causes of tropical deforestation? Subsidies, population growth and poverty. 10: Why should we care about the loss of tropical forests? About 2,100 of the 3,000 plants identified by the National Cancer Institution as sources of cancer fighting chemicals come from tropical forests. 11: Sustaining Tropical Forests Prevention Protect most diverse and endangered areas Restoration Reforestation
Educate settlers about sustainable agriculture and forestry Phase out subsidies that encourage unsustainable forest use Add subsidies that encourage sustainable
Rehabilitation of degraded areas
Concentrate farming and ranching on
forest use Protect forests with debt-for-nature swaps and conservation easements Certify sustainably grown timber Reduce illegal cutting Reduce poverty Slow population growth Slow population growth Reduce poverty Reduce illegal cutting Certify sustainably grown timber
already-cleared areas
12: Why are rangelands/grasslands so important? Soil formation Erosion control Nutrient cycling 13: How can we sustain rangeland productivity? What are some solutions to overgrazing? By controlling the number and distribution of livestock and by restoring degraded rangeland. Overgrazing occurs when too many animals graze for too long and exceed carrying capacity of a grassland area. 14: What is the 4 point strategy to restoring biodiversity worldwide? Map global ecosystems Locate and protect endangeredecosystems & species Restore as many degraded ecosystems as possible Make development biodiversity- friendly 15: What is a biodiversity hotspot? How many are there worldwide?6: What are the top 6 hotspots in the United States? A biodiversity hotspot is identified by ecologists as important and endangered centers of biodiversity. Worldwide there are 34 hotspots. 17: What are the five basic science-based principles for ecological restoration? Identify cause Stop abuse by eliminating or sharply reducing factors Reintroduce species if necessary Protect area from further degradation Use adaptive management to monitor 18: Define: Preservation: setting aside or protecting undisturbed natural areas from harmful human activities. Remediation: repairing an ecosystem that has been destroyed. Sustainability: ability of a system to survive for some specified time.
18: What are the eight priorities for protecting biodiversity? Take immediate action to preserve worlds biological hot spots Keep intact remaining old growth Complete mapping of worlds biodiversity for inventory and decision making Determine worlds marine hot spots Ensure that the full range of the earths ecosystems are included in global conservation strategy Make conservation profitable Initiate ecological restoration products to heal some of the damage done and increase share of earths land and water allotted to the rest of nature 19: Define: Reconciliation/Applied Ecology:Established and maintain new habitats to conserve species in places wher people live, work, and play. 20: Define: Background Extinction: Continuous, low level of extinction of species Extinction Rate: Expressed as a percentage or number of species that go extinct within a certain time period Mass Extinction: Extinction of many species in a relatively short amount of time 21: What are characteristics of vulnerable species? Specialized feeding habits Specialized feeding habits Low reproductive rate Large size Found only in one place or region 22: What is HIPPCO? HIPPCO is a way conservation biologists summarize the most important causes of premature extinction. 23: What can you do about invasive species? Do not allow wild animals to escape. 24: What are some characteristics of successful invader species? High reproductive rate Short generation time Pioneer species Long lived 25: How is pollution affecting species? They are killing species. 26: What is overexploitation? Over exploitation is the exploitation to the point of diminishing returns. 27: What is the U.S. Endangered Species Act? The U.S. Endangered Species Act is one of the worlds most far-reaching and controversial environmental laws from the 1973 U.S. 28: What is the CITIES Treaty? The CITIES Treaty is one of the most powerful treaties in the 1975 Convention on International Trade of
Endangered Species. 29: What can you do to help terrestrial biodiversity? What can you do to help protect species worldwide? Adopt a forest Plant trees and take care of them Recycle paper and buy recycled paper products Restore a nearby degraded forest or grassland Buy sustainable wood and wood products
You might also like
- Gel - RobberyDocument3 pagesGel - Robberyapi-235959158No ratings yet
- Apes Environmentalhistorylaw Presentationunit5Document5 pagesApes Environmentalhistorylaw Presentationunit5api-235959158No ratings yet
- Selena FelixDocument3 pagesSelena Felixapi-235959158No ratings yet
- Selena FelixDocument15 pagesSelena Felixapi-235959158No ratings yet
- Assignment 2 FingerprintsDocument5 pagesAssignment 2 Fingerprintsapi-235959158No ratings yet
- Untitleddocument 1Document4 pagesUntitleddocument 1api-235959158No ratings yet
- JJ Assignment 1Document3 pagesJJ Assignment 1api-235959158No ratings yet
- Immunology Page 2Document1 pageImmunology Page 2api-235959158No ratings yet
- PCR Lab Day 1Document1 pagePCR Lab Day 1api-235959158No ratings yet
- StopburningrainforestsforpalmoilDocument3 pagesStopburningrainforestsforpalmoilapi-235959158No ratings yet
- ApesDocument6 pagesApesapi-235959158No ratings yet
- MexicanfruitflyDocument2 pagesMexicanfruitflyapi-235959158No ratings yet
- PCR Lab Day 2Document1 pagePCR Lab Day 2api-235959158No ratings yet
- Immunology VocabularyDocument2 pagesImmunology Vocabularyapi-235959158No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 GuidedreadingworksheetforapesDocument7 pagesChapter 5 Guidedreadingworksheetforapesapi-235959158No ratings yet
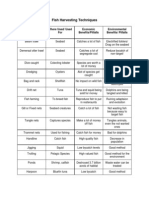
- FishharvestingtechniquesDocument2 pagesFishharvestingtechniquesapi-235959158No ratings yet
- PCR Flowchart SampleDocument3 pagesPCR Flowchart Sampleapi-236686558No ratings yet
- SomethingsfishylabDocument2 pagesSomethingsfishylabapi-235959158No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Study GuideDocument4 pagesUnit 3 Study Guideapi-235959158No ratings yet
- Flow Chart For JJDocument18 pagesFlow Chart For JJapi-235959158No ratings yet
- Biology Essentials-Populations Guided Viewing Worksheet: An Example of Each)Document2 pagesBiology Essentials-Populations Guided Viewing Worksheet: An Example of Each)api-235959158No ratings yet
- SelenaDocument11 pagesSelenaapi-235959158No ratings yet
- FoodforthoughtDocument5 pagesFoodforthoughtapi-235959158No ratings yet
- ApesDocument2 pagesApesapi-235959158No ratings yet
- Graph 1Document1 pageGraph 1api-235959158No ratings yet
- Apes-Terrestrial Biomes ReviewDocument6 pagesApes-Terrestrial Biomes Reviewapi-235959158No ratings yet
- Saltwater (Control) : 0 Sec 30 Sec 1 Min I Min 30 Sec 2 MinDocument5 pagesSaltwater (Control) : 0 Sec 30 Sec 1 Min I Min 30 Sec 2 Minapi-235959158No ratings yet
- Selena FelixDocument8 pagesSelena Felixapi-235959158No ratings yet
- Apesstudyguide AquaticecosystemsDocument6 pagesApesstudyguide Aquaticecosystemsapi-235959158No ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Clei 4 Talleres de InvestigacionDocument15 pagesClei 4 Talleres de InvestigacionDaniel ReyesNo ratings yet
- An Ethnobotanical Study of Medicinal Plants Used in Ethiopia PDFDocument23 pagesAn Ethnobotanical Study of Medicinal Plants Used in Ethiopia PDFFelix QuivioNo ratings yet
- 171 PDFDocument242 pages171 PDFSantosh PatilNo ratings yet
- Private Data and Public ValueDocument216 pagesPrivate Data and Public Valueselar89No ratings yet
- Decolonizing Nature: Making The World Matter: T. J. DemosDocument6 pagesDecolonizing Nature: Making The World Matter: T. J. DemosMichal Mukti KrawczykNo ratings yet
- Environmental ScienceDocument29 pagesEnvironmental ScienceMark Cedric BundalianNo ratings yet
- Excessive Deforestation of Gishwati Mountainous Forest & Biodiversity ChangesDocument3 pagesExcessive Deforestation of Gishwati Mountainous Forest & Biodiversity ChangesDUSABEMARIYANo ratings yet
- Environmental Impacts of Tourism in Kullu-Manali Complex in North Western Himalaya, India. Part 1: The Adverse ImpactsDocument17 pagesEnvironmental Impacts of Tourism in Kullu-Manali Complex in North Western Himalaya, India. Part 1: The Adverse ImpactsTimothy MasonNo ratings yet
- Test 09Document10 pagesTest 09Đàm Mạnh QuânNo ratings yet
- The Lorax Tasia RasmussenDocument5 pagesThe Lorax Tasia Rasmussenapi-252001729No ratings yet
- Minerals OlevelDocument7 pagesMinerals OlevelOmer NaseemNo ratings yet
- Outside The Box - Charlotte Kendra G. Castillo Purdue University Purdue Climate Change Research CenterDocument27 pagesOutside The Box - Charlotte Kendra G. Castillo Purdue University Purdue Climate Change Research CenterMatthew CuaNo ratings yet
- Don't Know What It IsDocument531 pagesDon't Know What It Isনুরুন নবী খোকনNo ratings yet
- Environmental ScienceDocument44 pagesEnvironmental ScienceprusothmahaNo ratings yet
- The Environment Vocabulary Practice - 80587Document2 pagesThe Environment Vocabulary Practice - 80587Elena ContrasNo ratings yet
- Ibps Practice For All SubjectDocument26 pagesIbps Practice For All SubjectÃrpit MadankarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Environmental Problems in The PhilippinesDocument16 pagesLesson 3 Environmental Problems in The PhilippinesLayla GreenflashNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Packet 20-21 PT 2Document21 pagesUnit 5 Packet 20-21 PT 2api-589327328No ratings yet
- Natural Resource Valuation and Policy in Brazil CompressDocument277 pagesNatural Resource Valuation and Policy in Brazil CompressAndrePauloMSNo ratings yet
- Bba-1 E.V.SDocument68 pagesBba-1 E.V.Sasra0% (1)
- Environmental Issues: Climate ChangeDocument2 pagesEnvironmental Issues: Climate ChangeNavendu ShekharNo ratings yet
- PGDELP May 20-21 Exam PaperDocument2 pagesPGDELP May 20-21 Exam PaperAyon Mohon GhoshNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4 Population & The Environment: SPEAKING Describing Cause and EffectDocument3 pagesUNIT 4 Population & The Environment: SPEAKING Describing Cause and EffectEdu Lamas GallegoNo ratings yet
- Examen Anglais Science Humaines 2022 Session Normale SujetDocument6 pagesExamen Anglais Science Humaines 2022 Session Normale Sujetitsmeselenophile xNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle-Definition - Explanation - DiagramDocument4 pagesCarbon Cycle-Definition - Explanation - Diagramjarina jeydNo ratings yet
- Challenges For Vulnerability Reduction in Brazil - Insights From The PAR FrameworkDocument43 pagesChallenges For Vulnerability Reduction in Brazil - Insights From The PAR FrameworkjoaojosevieiraNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science and Policy: Mark HironsDocument8 pagesEnvironmental Science and Policy: Mark HironsFadlun Chairunnisa NahumaruryNo ratings yet
- Summary 2021 - NAM DINHDocument7 pagesSummary 2021 - NAM DINHTrần LộcNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 - BT MLH Lop 12 - KeyDocument6 pagesUnit 10 - BT MLH Lop 12 - KeyThao NguyenNo ratings yet
- Methods To Estimate Above Ground BiomassDocument7 pagesMethods To Estimate Above Ground BiomassMiguel ParejoNo ratings yet