Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Path o Physio 123
Uploaded by
rjalavazo1989Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Path o Physio 123
Uploaded by
rjalavazo1989Copyright:
Available Formats
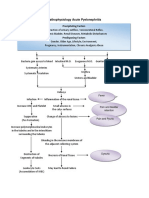
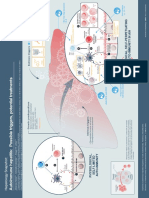
* Escherichia Coli
*Enterococuss Faecalis
*Kleibshiella
*Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
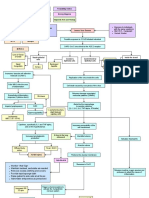
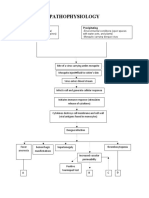
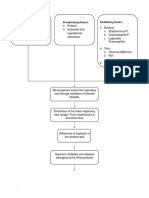
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
(Bacterial infection)
Ascends to the Kidney
Infection at : Renal Pelvis, Tubules and Interstitial Tissues of one or both Kidney
Release of Inflammatory Chemical Mediators
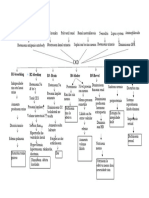
_
Chemotaxis Increased blood flow Increase capillary Release of cytokines
Permeability
Attraction of Increase blood cell Fluid Shift
Leukocytes Delivery
Production of Pain on lumbar Dysuria
Host cell produces
Swelling leukocytes area & abdomen
endogenous pyrogens
Diapedesis
Phagocytosis Pressure on nerves Leukocytosis
Accelerates set point
of
hypothalmic
Pus
thermo regulatory
Abscess
center
Pyuria
Stimulation of visceral afferent pathway
Vasoconstriction
Stimulation of medullary vomiting center
Fever
Nausea Vasodilation Increased
metabolism
Vomiting Increased
Oxygen demand
Cerebral vasodilation Flushed skin
Poor appetite
Headache Increase RR
Increase HR Malaise
Weight loss Increase vapor loss
Fatigue
Dehydration
Excessive thirst
Polyuria
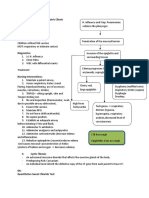
CHRONIC PYELONEPHRITIS
Persistent recurring infection
Progressive scarring of kidney
Renal failure
Septic shock
You might also like
- Updated FreebieDocument24 pagesUpdated FreebieHarshita AroraNo ratings yet
- Bhopal (M.P.) : Assignment OnDocument9 pagesBhopal (M.P.) : Assignment OnamitNo ratings yet
- First Page PDFDocument1 pageFirst Page PDFJordan BzNo ratings yet
- Liceo de Cagayan University: Acute AppendicitisDocument2 pagesLiceo de Cagayan University: Acute AppendicitisKylie AstrudNo ratings yet
- Pleurl Effusion Pathophysiology DiagramDocument2 pagesPleurl Effusion Pathophysiology DiagramAkiraMamo67% (3)
- Menigitis & EncephalitisDocument38 pagesMenigitis & EncephalitisKim GonzalesNo ratings yet
- GENERAL-PATHOPHYSIOLOGY-OF-LEPTOSPIROSIS-1 (AutoRecovered)Document14 pagesGENERAL-PATHOPHYSIOLOGY-OF-LEPTOSPIROSIS-1 (AutoRecovered)Lemuel GuevarraNo ratings yet
- The Patient and His Illness A. Pathophysiology (Book Based)Document5 pagesThe Patient and His Illness A. Pathophysiology (Book Based)Edmar Francis SabileNo ratings yet
- CBAHI StandardsDocument264 pagesCBAHI StandardsAnjo Cinco83% (30)
- Ventilation Cheat SheetDocument1 pageVentilation Cheat Sheetlizzy59683% (6)
- Pathophysiology Acute Pyelonephritis: Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Acute Pyelonephritis: Precipitating Factorsgodwinkent888No ratings yet
- Nursing Resignation LetterDocument1 pageNursing Resignation Letterrjalavazo19890% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Colon CancerDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Colon CancerJaymica Laggui DacquilNo ratings yet
- Copd PathoDocument2 pagesCopd PathoAlvin RamirezNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of AppendicitisDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of AppendicitisArvin Ian Penaflor100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective ThermoregulationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Ineffective Thermoregulationrjalavazo198979% (71)
- Obesity Epidemiology PDFDocument513 pagesObesity Epidemiology PDFMelodic Dubz100% (1)
- Respiratory Disorders of Pediatric Clients-1Document10 pagesRespiratory Disorders of Pediatric Clients-1Genalyn PenuagaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal BTKV Herman 1Document11 pagesJurnal BTKV Herman 1Elyas MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument6 pagesPeptic Ulcer DiseaseBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Application LetterDocument1 pageNursing Application Letterrjalavazo1989100% (3)
- 09.Project-Hospital Management SystemDocument37 pages09.Project-Hospital Management Systemzahidrafique0% (1)
- Evaluation Tool in NursingDocument17 pagesEvaluation Tool in Nursingrjalavazo1989No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology EclampsiaDocument5 pagesPathophysiology EclampsiaYael EzraNo ratings yet
- PathoDocument7 pagesPathoAnonymous 87fNoO2fhVNo ratings yet
- Medical and Surgical NursingDocument9 pagesMedical and Surgical NursingWilmaBongotanPadawilNo ratings yet
- NURSE Criminal and Civil Case Research..Document7 pagesNURSE Criminal and Civil Case Research..rjalavazo198950% (2)
- Anatomy and Physiology-AppendicitisDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology-AppendicitisMaria Socorro Sismundo DavidNo ratings yet
- Signs and Symptoms:Flank Sample Nursing Diagnosis: Acute PyelonephritisDocument3 pagesSigns and Symptoms:Flank Sample Nursing Diagnosis: Acute PyelonephritisjohndelfinmNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever Pathophysiology: Precipitating Factors Predisposing FactorsDocument2 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic Fever Pathophysiology: Precipitating Factors Predisposing FactorsAl-Mujib TanogNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology - PyelonephritisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology - PyelonephritisFrancis Kevin Sagudo92% (13)
- Group 3 BSN3D CapDocument6 pagesGroup 3 BSN3D CapJingky AnquillanoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Lower Urinary Tract InfectionDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Lower Urinary Tract InfectionSTORAGE FILENo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology 1Document5 pagesPathophysiology 1Genevive Alcantara MartinNo ratings yet
- Patophy of PudDocument4 pagesPatophy of PudClarence BravioNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Pathophysiology (Book Based) : Non-Modifiable: ModifiableDocument2 pagesPneumonia Pathophysiology (Book Based) : Non-Modifiable: ModifiableYVETTE CLAIRE BORRESNo ratings yet
- Complications: Acute PancreatitisDocument2 pagesComplications: Acute PancreatitisNikey LimNo ratings yet
- 2.7 WOC of Intra DyalisisDocument2 pages2.7 WOC of Intra Dyalisisvictor zhefaNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument1 pagePa Tho Physiologymac0422No ratings yet
- Parapneumonic EffusionDocument1 pageParapneumonic EffusionValerie Anne BebitaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisMay RodeoNo ratings yet
- ECHAVEZ, Hazel Marie Section 2-H Patho B CPC #1: MyopericarditisDocument1 pageECHAVEZ, Hazel Marie Section 2-H Patho B CPC #1: MyopericarditisHazel Marie EchavezNo ratings yet
- V. B.1. Pathopysiology DiagramDocument4 pagesV. B.1. Pathopysiology DiagrambezaleeljonelNo ratings yet
- Chole CystitisDocument3 pagesChole CystitisJanine Mae MacaraigNo ratings yet
- Preeclampsia PathophysioDocument5 pagesPreeclampsia PathophysioStephen S. PadayhagNo ratings yet
- Predisposing Factors Disease Precipitating Factors: LegendDocument3 pagesPredisposing Factors Disease Precipitating Factors: LegendSOPHIA LOISE TEJANO FULACHENo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Predisposing PrecipitatingDocument3 pagesPathophysiology: Predisposing PrecipitatinggizelleNo ratings yet
- DP - DM EncepaDocument2 pagesDP - DM EncepaimnotdatsunnyNo ratings yet
- Pathophy DMDocument1 pagePathophy DMCarmella CaritosNo ratings yet
- Definition of TermsDocument5 pagesDefinition of TermsLou KristofferNo ratings yet
- Pathopysiology (UTI)Document1 pagePathopysiology (UTI)Baji ۦۦNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of Typhoid Fever Client BasedrtyytyttyDocument3 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Typhoid Fever Client Basedrtyytyttyangeliejoy_1109No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Diet Stress Hereditary AgeDocument2 pagesPathophysiology: Diet Stress Hereditary AgeChucky VergaraNo ratings yet
- PathyDocument3 pagesPathyTRIXY MAE HORTILLANO100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisIra Velle ViosNo ratings yet
- Case Report (Peptic Ulcer Disease) : Saint Louis University School of Nursing Bonifacio Street, Baguio CityDocument5 pagesCase Report (Peptic Ulcer Disease) : Saint Louis University School of Nursing Bonifacio Street, Baguio CityCarren_Louise__8090100% (8)
- Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors: Contributing FactorsDocument6 pagesPredisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors: Contributing FactorsKen SimonNo ratings yet
- Hypovolemic Shock PathophysiologyDocument8 pagesHypovolemic Shock PathophysiologyKAYCEENo ratings yet
- Pathway PneumoniaDocument1 pagePathway PneumoniaFairuzNo ratings yet
- Pathway LosDocument1 pagePathway LosGracianoNo ratings yet
- Pathway CKDDocument2 pagesPathway CKDWijayea PunkrockNo ratings yet
- Trans Hepatobiliary SystemDocument5 pagesTrans Hepatobiliary SystemJulie CatianNo ratings yet
- Path o PhysiologyDocument9 pagesPath o PhysiologyKyle Ü D. CunanersNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of Broncho PneumoniaDocument1 pagePa Tho Physiology of Broncho PneumoniaPong's Teodoro SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Diagram For Patho HE and AGDocument3 pagesDiagram For Patho HE and AGDaniel Andre S. SomorayNo ratings yet
- Not Activity No. 7Document12 pagesNot Activity No. 7Patricia Marie Laman YadaoNo ratings yet
- Modifiable Risk Factors: Non-Modifiable Risk Factors:: IV. Pathophysiology of Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument5 pagesModifiable Risk Factors: Non-Modifiable Risk Factors:: IV. Pathophysiology of Chronic Kidney DiseaseSteffi MurielNo ratings yet
- Liver CirrhosisDocument44 pagesLiver CirrhosisaboubakarylwabukobaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Appendicitis: Vague, Dull, Diffuse Pain in The Midabdomen or EpigastriumDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Appendicitis: Vague, Dull, Diffuse Pain in The Midabdomen or EpigastriumGinoTevesNo ratings yet
- The Dog's Medical Dictionary: An encyclopædia of the diseases, their diagnosis & treatment, and the physical development of the dogFrom EverandThe Dog's Medical Dictionary: An encyclopædia of the diseases, their diagnosis & treatment, and the physical development of the dogNo ratings yet
- Nursing Curiculum Vitae - Rjay100Document3 pagesNursing Curiculum Vitae - Rjay100rjalavazo1989No ratings yet
- Urine Analysis 1429 - RH - FinalDocument3 pagesUrine Analysis 1429 - RH - Finalrjalavazo1989No ratings yet
- Acute Pepetic UlcerDocument1 pageAcute Pepetic Ulcerrjalavazo1989No ratings yet
- ZegenDocument2 pagesZegenianecunar100% (3)
- Acute Pepetic UlcerDocument1 pageAcute Pepetic Ulcerrjalavazo1989No ratings yet
- NCP M7Document3 pagesNCP M7rjalavazo1989No ratings yet
- Science Form 3 PPTnewDocument9 pagesScience Form 3 PPTnewRedzuan SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Davao Doctors College General Malvar Street, Davao City Nursing ProgramDocument5 pagesDavao Doctors College General Malvar Street, Davao City Nursing ProgramJhoneric Vencer EscultorNo ratings yet
- What Are NightmaresDocument2 pagesWhat Are NightmaresCharlie BalucanNo ratings yet
- Nso EgdDocument3 pagesNso Egdtry dokkNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Resuscitation: Presented By: Dr. Harish Uppala Chairperson: Dr. Kousalya Moderator: Dr. HemnathDocument23 pagesNeonatal Resuscitation: Presented By: Dr. Harish Uppala Chairperson: Dr. Kousalya Moderator: Dr. HemnathPraveen RamasamyNo ratings yet
- 26 - Nonsurgical Treatment of Peyronies DiseaseDocument4 pages26 - Nonsurgical Treatment of Peyronies DiseaseNunuh SulaemanNo ratings yet
- Clark 2004Document18 pagesClark 2004Joo XanderNo ratings yet
- Efektivitas Pemberian Ikan Gabus Kukus Terhadap Penyembuhan Laserasi Perineum Pada Ibu PostpartumDocument9 pagesEfektivitas Pemberian Ikan Gabus Kukus Terhadap Penyembuhan Laserasi Perineum Pada Ibu Postpartumjulimarni13No ratings yet
- Viral Skin InfectionsDocument28 pagesViral Skin Infectionstolesadereje73No ratings yet
- Historical and Contemporary Perspectives, Issues of Maternal and Child HealthDocument96 pagesHistorical and Contemporary Perspectives, Issues of Maternal and Child HealthBindu Philip100% (1)
- Compendium of Instructions - Covid19Document472 pagesCompendium of Instructions - Covid19Ramesh Babu TatapudiNo ratings yet
- Ijcem0006 0358Document9 pagesIjcem0006 0358najwaNo ratings yet
- Cervical Spine Injury: Julie C. LeonardDocument15 pagesCervical Spine Injury: Julie C. LeonardCamilla CristinaNo ratings yet
- The Challenge of Epidemiology Issues and Selected Readings Who Paho BookDocument1,045 pagesThe Challenge of Epidemiology Issues and Selected Readings Who Paho Bookkareem79No ratings yet
- Albendazole - Drug Information PDFDocument7 pagesAlbendazole - Drug Information PDFjjjkkNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems ADocument2 pagesPractice Problems ACrystal LynaeNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis Autoinmune 2020Document3 pagesHepatitis Autoinmune 2020Clemente PonceNo ratings yet
- Y10 Chapter+13 ExcretionDocument67 pagesY10 Chapter+13 ExcretionLOW YUEBEI RIJNo ratings yet
- Grams Stain-Kit: CompositionDocument3 pagesGrams Stain-Kit: Compositionhamza hamzaNo ratings yet
- Print - Chapter 14. Ammonia and UreaDocument9 pagesPrint - Chapter 14. Ammonia and UreabelaginaNo ratings yet
- The Control and Prevention of MRSA in Hospitals and in The CommunityDocument41 pagesThe Control and Prevention of MRSA in Hospitals and in The CommunityDimas RfNo ratings yet
- Vein Artery Capillary: Thin Wall Wide Lumen Valve Thick Wall Narrow Lumen One Cell Thick WallDocument1 pageVein Artery Capillary: Thin Wall Wide Lumen Valve Thick Wall Narrow Lumen One Cell Thick WallHuiso RohNo ratings yet