Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 PEAB ZC311 Assignment I
Uploaded by
M Helmy AdityaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1 PEAB ZC311 Assignment I
Uploaded by
M Helmy AdityaCopyright:
Available Formats
BIRLA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY & SCIENCE, PILANI B.
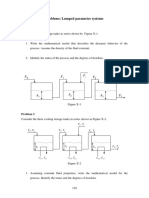
S Process Engineering (Aditya Birla Group - Cement Business) Second Semester 2010-2011 Course No. Course Title Component Questions: 1. A stream of warm water is produced in a steady flow mixing process by combining 1.0 kg s -1 of cool water at 298.15 K (25 C) with 0.8 kg s-1 of hot water at 348.15 K (75 C). During mixing, heat lost to the surrounding at rate of 30 kW. What is the temperature of the warm-water stream? Assume the specific heat of water constant at 4.18 kJ kg-1 K-1.
2. Gas is bled from a tank. Neglecting heat transfer between the gas and the tank, show that mass and energy balances produce the differential equation: dU dm = H ' U m Here, U and m refer to the gas remaining in the tank; H' is the specific enthalpy of the gas leaving the tank. Under what conditions can one assume H' = H 3. One mole of an ideal gas with Cp = (7/2)R and Cv = (512) R expands from P 1 = 8 bar and Tl = 600 K to P2 = 1 bar by each of the following paths: (a) Constant volume; (b) Constant temperature; (c) Adiabatically. Assuming mechanical reversibility, calculate W, Q, U, and H for each process. Sketch each path on a single P V diagram. 4. For methyl chloride at 373.15 K (100C) the second and third virial coefficients are: B = -242.5 cm3 mol-1 C = 25200 cm6 mol-2 Calculate the work of mechanically reversible, isothermal compression of 1 mol of methyl chloride from 1 bar to 55 bar at 373.15 K (100C). Base calculations on the following forms of the virial equation:
: PEAB ZC311 : Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics : Assignment 1
B C + V V2 (b) Z = 1 + B' P + C ' P 2
(a) Z = 1 + Where
C B2 B C' = ( RT ) 2 RT Why don't both equations give exactly the same result?
B' =
5. Estimate the volume occupied by 18 kg of ethylene (molecular weight = 28) at 328.15 K (55 C) and 35 bar using (a) Pitzers generalized correlation for second virial coefficient. (b) Redlich / Kwong (RK) equation 6. How much heat is required when 15 mol of 1-butene initially at 260 C is heated at atmospheric pressure to 1140.65 C.
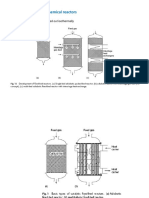
7. Determine the standard heat of each of the following reaction at 298.15 K (25C) and at 773.15 K (500C): 3NO2 (g) + H2O (l) + 2HNO3 (1) + NO (g) 8. With respect to 1 kg of liquid water: a. Initially at 273.15 K (0oC), it is heated to 373.15 K (100C) by contact with a heat reservoir at 373.15 K (100C). What is the entropy change of the water? Of the heat reservoir? What is Stotal? b. Initially at 273.15 K (0C), it is first heated to 323.15 K (50C) by contact with a heat reservoir at 323.15 K (50C) and then to 373.15 K (100C) by contact with a reservoir at 373.15 K (100C). What is Stotal? c. Explain how the water might be heated from 273.15 K (0C) to 373.15 K (100C) so that Stotal = 0. 9. Estimate the change in enthalpy and entropy when liquid ammonia at 270 K is compressed from its saturation pressure of 381 kPa to 1200 kPa. For saturated liquid ammonia at 270 K, V = 1.551 x m3 kg-1, and = 2.095 x l0-3 K-1. 10. One kilogram of water (Vl = 1003 cm3 kg-1) in a piston/cylinder device at 298.15 K (25C) and 1 bar is compressed in a mechanically reversible, isothermal process to 1500 bar. Determine Q, W, U, H, and S given that = 250 x l0-6 K-1 and = K =45 x l0-6 bar-1.
ALL THE BEST
You might also like
- Che 456 Spring 2011 Major 2 Styrene Production BackgroundDocument6 pagesChe 456 Spring 2011 Major 2 Styrene Production Backgroundyamel huaira taipeNo ratings yet
- Reactor ModelDocument12 pagesReactor ModelTanuja ThanuNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger DesignDocument19 pagesHeat Exchanger DesignRankhamb ShubhamNo ratings yet
- Condution Holman 10th-Ed PDFDocument167 pagesCondution Holman 10th-Ed PDFLizbeth Abril100% (1)
- Wacker Process Slides 2008Document5 pagesWacker Process Slides 2008Zakariya AdamNo ratings yet
- Ethylene Oxide and Ethanol Amines Production ProcessesDocument7 pagesEthylene Oxide and Ethanol Amines Production Processesمحمود محمدNo ratings yet
- EnnnDocument9 pagesEnnnSajid AliNo ratings yet
- PFD SUPER FINAL Production of Phenol PDFDocument1 pagePFD SUPER FINAL Production of Phenol PDFJohn Philip AyoNo ratings yet
- Dee CDocument15 pagesDee CAnderson David ValenciaNo ratings yet
- A Kinetic Model of Steady State Ethylene Epoxidation Over A Supported Silver CatalystDocument17 pagesA Kinetic Model of Steady State Ethylene Epoxidation Over A Supported Silver CatalystFrank LordNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Networks: (Continued) Slide-2Document44 pagesHeat Exchanger Networks: (Continued) Slide-2Adheep DasNo ratings yet
- The Dehydrogenation of Isopropanol To Form Hydrogen GasDocument31 pagesThe Dehydrogenation of Isopropanol To Form Hydrogen GasEdidiong AsuquoNo ratings yet
- Alkylation Process OverviewDocument7 pagesAlkylation Process OverviewVasthadu Vasu Khanan DLNo ratings yet
- Cumene BDocument6 pagesCumene BimanchenNo ratings yet
- Flash Drum Design Che 4253 - Design I CheDocument5 pagesFlash Drum Design Che 4253 - Design I CheDiliniNo ratings yet
- RCMDocument15 pagesRCMAdzamNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4a – Pressure Drop in Packed ColumnsDocument21 pagesExperiment 4a – Pressure Drop in Packed ColumnsMohamad Samer KansouNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Objective Type Questions Matls of ConstructionDocument14 pagesChemical Engineering Objective Type Questions Matls of ConstructiongshdavidNo ratings yet
- Energy Transport Notes 2Document102 pagesEnergy Transport Notes 2Faisal MumtazNo ratings yet
- Thus, This Term Actually Means A in A Constant-Volume System The Measure of Reaction Rate of Component I BecomesDocument23 pagesThus, This Term Actually Means A in A Constant-Volume System The Measure of Reaction Rate of Component I Becomesalice Annabelle100% (1)
- First Order SystemDocument21 pagesFirst Order SystemNiranjan BeheraNo ratings yet
- Reaction Kinectis and Reactor DesignDocument41 pagesReaction Kinectis and Reactor DesignReeve Tang CsvNo ratings yet
- Highly selective MEG process via ethylene carbonateDocument5 pagesHighly selective MEG process via ethylene carbonateirfanNo ratings yet
- Prob 01Document12 pagesProb 01Ahmad SayyedahmadNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer OperationsDocument77 pagesMass Transfer OperationsNhã UyênNo ratings yet
- QDocument1 pageQSSLabNo ratings yet
- Evaporation: Kevin A. OlegarioDocument6 pagesEvaporation: Kevin A. OlegarioKitty VNo ratings yet
- Crystallizer Thickness CalculationDocument8 pagesCrystallizer Thickness CalculationAmritRoshniKaurNo ratings yet
- Vapor-Liquid Equilibria. Ethylene Oxide - Acetaldehyde and Ethylene Oxide - Water SystemsDocument5 pagesVapor-Liquid Equilibria. Ethylene Oxide - Acetaldehyde and Ethylene Oxide - Water SystemsGie0% (1)
- Plant Design of Acetone ProductionDocument20 pagesPlant Design of Acetone ProductionMary Grace VelitarioNo ratings yet
- Homework 2: U KQ Where:u Btu H FT Q FT H K ConstantDocument6 pagesHomework 2: U KQ Where:u Btu H FT Q FT H K ConstantkatelynNo ratings yet
- Project Review On Production of AcroleinDocument19 pagesProject Review On Production of Acroleinasrahaman9No ratings yet
- Designing Reactive Distillation Processes With Improved EfficiencyDocument295 pagesDesigning Reactive Distillation Processes With Improved EfficiencyAseem KashyapNo ratings yet
- Adipic AcidDocument7 pagesAdipic AcidsadiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9.6 QuizDocument2 pagesChapter 9.6 QuizspeedkillzNo ratings yet
- Advanced Distillation Technology: A Basic Guide to Process Simulation and the Latest TechniquesDocument19 pagesAdvanced Distillation Technology: A Basic Guide to Process Simulation and the Latest TechniquesWawan Swaiper Cool100% (1)
- Energy balance on chemical reactorsDocument41 pagesEnergy balance on chemical reactorsHotib PerwiraNo ratings yet
- Allyl BDocument9 pagesAllyl BDemet AcargilNo ratings yet
- Methane Steam ReformingDocument8 pagesMethane Steam ReformingPanda BoyNo ratings yet
- CP302 Mass Transfer Principles: Diffusion in SolidsDocument38 pagesCP302 Mass Transfer Principles: Diffusion in SolidsDeneshVijayNo ratings yet
- Producing Ethyl Chloride in iCONDocument19 pagesProducing Ethyl Chloride in iCONlynNo ratings yet
- Production of 20,000 MTBE from Methanol and Butylene via Catalytic ConversionDocument177 pagesProduction of 20,000 MTBE from Methanol and Butylene via Catalytic ConversioniffatNo ratings yet
- Material and Balance For Sohio Process That Produce AcrytonitrileDocument2 pagesMaterial and Balance For Sohio Process That Produce Acrytonitrileafnan_lion940% (1)
- Styrene From Ethane and BenzeneDocument6 pagesStyrene From Ethane and BenzeneAmy Puah100% (2)
- Cooling Towers Information PackageDocument25 pagesCooling Towers Information Packagemdawg467No ratings yet
- Church 1951Document8 pagesChurch 1951Evan DulayNo ratings yet
- N-Butane To Maleic AnhydrideDocument6 pagesN-Butane To Maleic AnhydrideNomeacuerdo Yo MismoNo ratings yet
- 8 3 Packed Bed ReactorsDocument20 pages8 3 Packed Bed ReactorsridhajamelNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Studies of Ketazine Formation PDFDocument6 pagesKinetic Studies of Ketazine Formation PDFkamesh_che009100% (1)
- Acetone PDFDocument118 pagesAcetone PDFNhn Neen100% (1)
- Column Design PDFDocument2 pagesColumn Design PDFRobin0% (1)
- Overall Flowsheet Simulation Benzene Cyclohexane TW6Document7 pagesOverall Flowsheet Simulation Benzene Cyclohexane TW6Mitesh ParmarNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer Lecture Slides Diffusion Gases Convection Frame ReferenceDocument24 pagesMass Transfer Lecture Slides Diffusion Gases Convection Frame ReferenceaaaNo ratings yet
- Process Description DmeDocument3 pagesProcess Description DmeFirdaus YahyaNo ratings yet
- Hydrogenation of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters To FattyDocument9 pagesHydrogenation of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters To FattyYulius Harmawan Setya PratamaNo ratings yet
- Continuous Regenerative (Moving Bed) CCR PlatformingDocument4 pagesContinuous Regenerative (Moving Bed) CCR PlatformingAnnissa Nur HidayatiNo ratings yet
- International Thermodynamic Tables of the Fluid State: Propylene (Propene)From EverandInternational Thermodynamic Tables of the Fluid State: Propylene (Propene)No ratings yet
- Crude Ratio GAP 2016Document9 pagesCrude Ratio GAP 2016M Helmy AdityaNo ratings yet
- Additive 213Document12 pagesAdditive 213M Helmy AdityaNo ratings yet
- Cascade ControlDocument7 pagesCascade ControlM Helmy AdityaNo ratings yet
- Game Data File ListDocument512 pagesGame Data File Listrahman_alfarisiNo ratings yet
- ASIO4ALL v2 Instruction ManualDocument11 pagesASIO4ALL v2 Instruction ManualDanny_Grafix_1728No ratings yet
- Examples of Third Order ReactingDocument1 pageExamples of Third Order ReactingM Helmy AdityaNo ratings yet
- Examples of Third Order ReactingDocument1 pageExamples of Third Order ReactingM Helmy AdityaNo ratings yet
- Nitroguanidine: Guanidine, NitroDocument1 pageNitroguanidine: Guanidine, NitroM Helmy AdityaNo ratings yet
- ProblemDocument18 pagesProblemM Helmy AdityaNo ratings yet
- Pengenalan Teknik KimiaDocument7 pagesPengenalan Teknik KimiaM Helmy AdityaNo ratings yet
- Pemrograman Komputer PDFDocument2 pagesPemrograman Komputer PDFCornelius YudhaNo ratings yet
- Al-Q AQO IBD AKH TRH KEM: Nilai Raport SMT 1 Kelas X Ap1 TAHUN 2013/2014Document3 pagesAl-Q AQO IBD AKH TRH KEM: Nilai Raport SMT 1 Kelas X Ap1 TAHUN 2013/2014M Helmy AdityaNo ratings yet
- Jadwal Gasal 2014-2015Document4 pagesJadwal Gasal 2014-2015M Helmy AdityaNo ratings yet
- Machine Elements w2-w3Document63 pagesMachine Elements w2-w3M Helmy AdityaNo ratings yet
- Pengenalan Teknik KimiaDocument7 pagesPengenalan Teknik KimiaM Helmy AdityaNo ratings yet
- 2nd AssignmentDocument1 page2nd AssignmentM Helmy AdityaNo ratings yet
- Lamp Penerima Beasiswa BI 2014Document1 pageLamp Penerima Beasiswa BI 2014M Helmy AdityaNo ratings yet
- CO2 DataDocument154 pagesCO2 DataM Helmy AdityaNo ratings yet
- SSH Gratis 1 BLNDocument1 pageSSH Gratis 1 BLNM Helmy AdityaNo ratings yet
- Tugas OTK 3 Menghitung T bubble point dan T dew point LPGDocument3 pagesTugas OTK 3 Menghitung T bubble point dan T dew point LPGM Helmy AdityaNo ratings yet
- HitunganDocument2 pagesHitunganM Helmy AdityaNo ratings yet
- Matlab Guide BookDocument26 pagesMatlab Guide BookKingchemNo ratings yet
- DapusDocument1 pageDapusM Helmy AdityaNo ratings yet
- Contoh Pidato Kemerdekaan Bhs InggrisDocument1 pageContoh Pidato Kemerdekaan Bhs InggrisM Helmy AdityaNo ratings yet
- Pressure Drop in Pipe Fittings and ValvesDocument16 pagesPressure Drop in Pipe Fittings and ValvesM Helmy AdityaNo ratings yet
- Particle Mechanics II Sample QuestionsDocument49 pagesParticle Mechanics II Sample QuestionsPaYee Biongcog - Manalo45% (11)
- Chapter 1 Short 1 ChemistryDocument12 pagesChapter 1 Short 1 ChemistryvaibhavikamatarNo ratings yet
- Fine and Extra-Fine Vibrating Mill GrindingDocument5 pagesFine and Extra-Fine Vibrating Mill GrindingdearistyaNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Biology F4Document12 pagesTest 1 Biology F4Nurfatin JamaludinNo ratings yet
- Grain Size Vs Heat TreatmentDocument24 pagesGrain Size Vs Heat TreatmentRyan ChenNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv Photochemistry and Spectroscopy: Part A 1. Define PhotochemistryDocument18 pagesUnit Iv Photochemistry and Spectroscopy: Part A 1. Define PhotochemistryKrithigasri MurugesanNo ratings yet
- Mixing Weld and Bolt Part1Document3 pagesMixing Weld and Bolt Part1ihpeterNo ratings yet
- Wear Plate SpecsDocument4 pagesWear Plate SpecsJuan Carlos EspinozaNo ratings yet
- 005 Hydrogenics Denis Thomas - Electrolyzer Technology of BioCat ProjectDocument26 pages005 Hydrogenics Denis Thomas - Electrolyzer Technology of BioCat ProjectgmolguinpNo ratings yet
- Quick Coupling Products Distribution: Catalogue 3800-DS/UKDocument68 pagesQuick Coupling Products Distribution: Catalogue 3800-DS/UKhoussem houssemNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Cesium Octacyanomolybdate (V) - and Cesium Cyanotungstate (V) Dihydrate: A More Successful Method OctaDocument3 pagesSynthesis of Cesium Octacyanomolybdate (V) - and Cesium Cyanotungstate (V) Dihydrate: A More Successful Method OctaDabasish DekaNo ratings yet
- SRISAI PUBLIC SCHOOL CLASS X CHAPTER 1 PERIODIC TABLEDocument3 pagesSRISAI PUBLIC SCHOOL CLASS X CHAPTER 1 PERIODIC TABLENaga VikramNo ratings yet
- Tamseal Admix: Description Technical DataDocument2 pagesTamseal Admix: Description Technical DataJoyce Agustine Glory LNo ratings yet
- Mooring Line Management SNAME 1994Document8 pagesMooring Line Management SNAME 1994Peyman MznNo ratings yet
- MCQ - Question-Paper-11 PDFDocument16 pagesMCQ - Question-Paper-11 PDFMuhammad TauseefNo ratings yet
- VTP & VPC: Vertical Turbine Wet Pit and Double Casing Pumps Maintenance ChecklistDocument2 pagesVTP & VPC: Vertical Turbine Wet Pit and Double Casing Pumps Maintenance Checklistsathiyam2kNo ratings yet
- Santoprene™ 101-64: Thermoplastic VulcanizateDocument4 pagesSantoprene™ 101-64: Thermoplastic VulcanizateMohitNo ratings yet
- Astm D 4176 PDFDocument4 pagesAstm D 4176 PDFAlexander Amado QuinteroNo ratings yet
- MSDS - TD - OIL - 22 For Chimpo GearboxDocument7 pagesMSDS - TD - OIL - 22 For Chimpo GearboxKritbordin RintaNo ratings yet
- Sodium Carbonate Production from Trona OreDocument17 pagesSodium Carbonate Production from Trona OreVaanNo ratings yet
- CH 13Document69 pagesCH 13pwmvsi100% (2)
- Dust Collection ChecklistDocument4 pagesDust Collection ChecklistbroedenNo ratings yet
- Research Paper March 10 2019Document12 pagesResearch Paper March 10 2019vincent jancarlo ricarteNo ratings yet
- Spent Coffee Grounds Heat Coffee RoastingDocument15 pagesSpent Coffee Grounds Heat Coffee RoastingMJundiNo ratings yet
- Main Pump PDFDocument36 pagesMain Pump PDFElia MekdadNo ratings yet
- Vessel Drum Sew DWGDocument2 pagesVessel Drum Sew DWGSANGEETHANo ratings yet
- BlowersDocument65 pagesBlowersmartin.rubenNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-College 3Document10 pagesChemistry-College 3Subhabrata MabhaiNo ratings yet
- 13 Fluid and Electrolyte Balance محاضرةDocument69 pages13 Fluid and Electrolyte Balance محاضرةRasheed SadekNo ratings yet
- Studies On Degradation of Synthetic Polymer Nylon 6 by FungusDocument8 pagesStudies On Degradation of Synthetic Polymer Nylon 6 by FungusTiten PinastiNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Phase EquilibriaDocument53 pagesIntroduction to Phase EquilibriaEko Putra BayuNo ratings yet