Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fluid Mechanics
Uploaded by
shekhadaaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fluid Mechanics
Uploaded by
shekhadaaCopyright:
Available Formats
GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
B.E Semester: 3
Mechanical Engineering
Subject Code 130101
Subject Name Fluid Mechanics
Sr.No Course content
1. Fluids and Their Properties:
Fluids, Shear stress in a moving fluid, Difference between solid and fluid,
Newtonian and Non-Newtonian Fluid, Liquids and Gases, Molecular
structure of material, the continuum concept of a fluid, density, viscosity,
causes of viscosity in gases, causes of viscosity in a liquid, Surface tension,
capillary, vapor pressure, cavitation, compressibility and the bulk modulus,
Equation of states of a gas constant, Specific heats of a gas, Expansion of
a gas.
2. Pressures and Head:
Static’s of a fluid system, pressure, Pascal’s law of pressure at a point,
variation of pressure vertically in a fluid under gravity, equality of pressure
at the same level in a static fluid, general equation for the variation of
pressure due to gravity from a point to point in a static fluid, pressure and
head, the hydrostatic paradox, pressure measurements by manometers,
forced vortex
3. Static Forces on Surface and Buoyancy:
Action of fluid pressure on surface, resultant force and center of pressure
on a plane surface under uniform pressure, resultant force and center of
pressure on a plane surface immersed in a liquid, pressure diagrams,
forces on a curved surface due to hydrostatic pressure, buoyancy,
equilibrium of floating bodies, stability of a submerged body, stability of
floating bodies, determination of the metacentric height, determination of
the position of the metacentre relative to the center of buoyancy, periodic
time of oscillation.
4. Motion of Fluid Particles and Streams:
Fluid flow, different types of flow, frames of reference, real and ideal fluids,
analyzing fluid flow, motion of a fluid particle, acceleration of a fluid particle,
discharge and mean velocity, continuity of flow, continuity equations for 2-D
and 3-D flow in Cartesian coordinates of system.
5. The Energy Equation and its Application:
Momentum and fluid flow, Momentum equation for 2-D and 3-D flow along a
stream line, momentum correction factor, Euler’s equation of motion along a
stream line, Mechanical energy of a flowing fluid – Bernoulli’s theorem,
kinetic energy correction factor, pitot tube, determination of volumetric flow
rate via pitot tube, changes of pressure in tapering pipe, principle of venturi
meter, pipe orifices, Limitation on the velocity of flow in a pipeline, theory of
small orifices discharging to atmosphere, theory of large orifices,
Elementary theory of notches and weirs, flow in a curved path, pressure
gradient and change of total energy across the streamlines.
6. Two-Dimensional Ideal Fluid Flow:
Rotational and ir-rotational flow, circulation and vorticity, streamlines and
the stream functions, velocity potential and potential flow, relation between
stream function and velocity potential; flow nets, stream function and
velocity potential for uniform flow, vortex flow.
7. Dimensional Analysis And Similarities:
Dimensional analysis, dimensions and units, dimension reasoning,
dimensional quantities, Fundamental and derived units and dimensions,
dimensions of derivative and integrals, use of dimensional reasoning to
check calculations, units of derived quantities, conversion from one system
of unit to another, conversion of dimensional constants, dimensional
homogeneity, dimensional analysis using the indicial method- Rayleigh’s
method, dimensional analysis using group method-Buckingham Π theorem,
significance of dimensionless group, use of dimensionless groups in
experimental investigation, geometric similarity, dynamic similarity,
Kinematic similarity, Model testing-Model laws, Undistorted and Distorted
models.
8. Viscous Flow:
Reynolds number and Reynolds experiment, flow of viscous fluid through
circular pipe-HAGEN-POISEVILLE LAW, Flow of viscous fluid between two
parallel fixed plates, power absorbed in viscous flow through - journal ,Foot
step and Collar bearing , Movement of piston in dash pot, Methods of
Measurement of viscosity.
9. Compressible Fluid Flow :
Basic Thermodynamic relations, Basic thermodynamic processes, Basic
equations for one dimensional compression, stagnation properties,
pressure wave propagation and sound velocity, Flow through nozzles.
10. Turbulent Flow:
Characteristics of diff. types of flow, expression for coefficient of friction -
Darchy Weichback Equation, moody diagram resistance of smooth and
rough pipes shear stress and velocity distribution in turbulent flow through
pipes.
Reference Books:
1. Fluid Mechanics and Fluid Power Engineering by D.S. Kumar, S.K.Kataria &
Sons
2. Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machines by R.K. Bansal, Laxmi Prakashan
3. Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machines by R.K. Rajput , S.Chand & Co.
4. Theory and Applications of Fluid Mechanics by K.Subramanya, TMH outline
series, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Ltd.
5. Fluid Mechanics by Frank .M. White, McGraw Hill Publishing Company Ltd.
6. Mechanics of Fluids by Shames, McGraw Hill Publishing Company Ltd.
You might also like
- Ace Tut 02 Turbulent BackstepDocument22 pagesAce Tut 02 Turbulent BackstepHilario de JesusNo ratings yet
- Vibration Analysis of Tapered BeamDocument51 pagesVibration Analysis of Tapered BeambiomechanicsNo ratings yet
- Combined PPT PSA Oxygen PlantDocument39 pagesCombined PPT PSA Oxygen Plantshivani50% (2)
- Sakhalin LNG-Train GenDocument54 pagesSakhalin LNG-Train GenRobert WatersNo ratings yet
- 01-Architecture & PlanningDocument29 pages01-Architecture & PlanningpragatinareshNo ratings yet
- STRESS-STRAINDocument14 pagesSTRESS-STRAINcikmonNo ratings yet
- Moment Connections Bolted WeltedDocument6 pagesMoment Connections Bolted WeltedRavirajsinh JadejaNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of G+6 Building in Different Seismic Zones of IndiaDocument12 pagesAnalysis and Design of G+6 Building in Different Seismic Zones of IndiaIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- 2017 FSAE Structural Equivalency Spreadsheet GuideDocument130 pages2017 FSAE Structural Equivalency Spreadsheet GuideTeddy TPNo ratings yet
- CE 809 - Lecture 1 - Formulation of Mathematical Model of SDF SystemsDocument29 pagesCE 809 - Lecture 1 - Formulation of Mathematical Model of SDF SystemsArslan UmarNo ratings yet
- 2015 - Finite Element Modelling of Debonding Failures in Steel Beams Flexurally Strengthened With CFRP Laminates - Teng Fernando Yu PDFDocument12 pages2015 - Finite Element Modelling of Debonding Failures in Steel Beams Flexurally Strengthened With CFRP Laminates - Teng Fernando Yu PDFvlad lupasteanuNo ratings yet
- Calculations of hoop bar diameter for columns according to ductile detailingDocument1 pageCalculations of hoop bar diameter for columns according to ductile detailingRahul AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Spreadsheet IndexDocument1 pageSpreadsheet IndexPrabhuNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods and Computer ProgrammingDocument19 pagesNumerical Methods and Computer ProgrammingSabby OnindoNo ratings yet
- Tnea 2022 Round 4 Voc + Gen + 7 5 Grand Analysis Ashwin RDocument44 pagesTnea 2022 Round 4 Voc + Gen + 7 5 Grand Analysis Ashwin RSai DhanushNo ratings yet
- CIV3506 2022 Assign2 Exemplary2Document33 pagesCIV3506 2022 Assign2 Exemplary2Neil WayneNo ratings yet
- Cash Memo For Mobile Shop in ExcelDocument1 pageCash Memo For Mobile Shop in Excelsrajece100% (1)
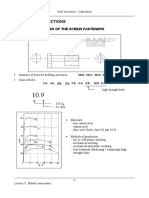
- Bolted Connections: 1.1 Range and Class of The Screw FastenersDocument8 pagesBolted Connections: 1.1 Range and Class of The Screw FastenersksNo ratings yet
- Calculate centroid and area of composite shapesDocument75 pagesCalculate centroid and area of composite shapesSarmad69No ratings yet
- Bell Crank Lever Dt. 14-07-2021Document4 pagesBell Crank Lever Dt. 14-07-2021AK kunduNo ratings yet
- Design of Ring Girder SupportDocument3 pagesDesign of Ring Girder Supportvishal guptaNo ratings yet
- Civil Structural Calculations for Essar Oil Refinery ProjectDocument70 pagesCivil Structural Calculations for Essar Oil Refinery ProjectthakrarhitsNo ratings yet
- SimMan Tut 01 BackstepDocument20 pagesSimMan Tut 01 BackstepVenkata VasanthaNo ratings yet
- Flood GodavariDocument6 pagesFlood GodavarigangarajuNo ratings yet
- BITSF110 Course HandoutDocument3 pagesBITSF110 Course HandoutultimateNo ratings yet
- Ismc 250 Channel-Rolled Steel Beams (Indian Standard)Document3 pagesIsmc 250 Channel-Rolled Steel Beams (Indian Standard)keshabshrNo ratings yet
- Project Job Ref. Section Sheet No./rev. Calc. by Date CHK'D by Date App'd by DateDocument3 pagesProject Job Ref. Section Sheet No./rev. Calc. by Date CHK'D by Date App'd by DateAmanda SmithNo ratings yet
- Spring Constant For SoilDocument1 pageSpring Constant For Soilarman malikNo ratings yet
- Response Spectrum Analysis As Per Indian IS: 1893 (Part 1) - 2002Document15 pagesResponse Spectrum Analysis As Per Indian IS: 1893 (Part 1) - 2002Anonymous UibQYvc6No ratings yet
- Beams On Elastic FoundationDocument15 pagesBeams On Elastic FoundationIngeniero EstructuralNo ratings yet
- Design of reinforced rectangular beam as per IS 456-2000Document2 pagesDesign of reinforced rectangular beam as per IS 456-2000AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Types of Damping 1. Viscous DampingDocument6 pagesTypes of Damping 1. Viscous DampingZandro GagoteNo ratings yet
- M3D - SampleProblemSet ACI PDFDocument6 pagesM3D - SampleProblemSet ACI PDFasaisenthilNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis of Blast Resistant Structures in The Oil and Gas IndustryDocument15 pagesFinite Element Analysis of Blast Resistant Structures in The Oil and Gas IndustrySaliNo ratings yet
- Deflection ChecksDocument8 pagesDeflection Checksabhi aroteNo ratings yet
- Shear Force DiagramDocument13 pagesShear Force DiagramAhmed Mohamed Hassan100% (1)
- Combined Footing For 2 Columns-1Document32 pagesCombined Footing For 2 Columns-1Wanda BeasleyNo ratings yet
- MD 2Document33 pagesMD 2Wilfredo Nieves OsoriaNo ratings yet
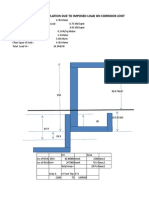
- Deflection Calculation Due To Imposed Load On Corridor JoistDocument14 pagesDeflection Calculation Due To Imposed Load On Corridor JoistranjitNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 SolutionDocument9 pagesAssignment 3 SolutionMurat BayrakNo ratings yet
- Plates - Shells - ResultsDocument4 pagesPlates - Shells - ResultsKamal RaoNo ratings yet
- 3.design For Flexure V1Document29 pages3.design For Flexure V1November RainNo ratings yet
- Fracture Mechanics NotesDocument16 pagesFracture Mechanics NotesHossam M ALrohilyNo ratings yet
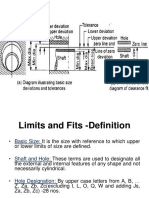
- Unit1 - Tolerance and Fits NumericalDocument16 pagesUnit1 - Tolerance and Fits NumericalnapatilNo ratings yet
- Specific StepsDocument26 pagesSpecific StepsAbdul Hamid BhattiNo ratings yet
- 220kv - NMC - Type Tower-CorrectedDocument19 pages220kv - NMC - Type Tower-Correctedpavan3961No ratings yet
- Dynamics Machine Vibration ProblemsDocument9 pagesDynamics Machine Vibration ProblemsnikhilasoknNo ratings yet
- Beam Columns Example - Is 800Document7 pagesBeam Columns Example - Is 800anil97232No ratings yet
- Relation Between Elastic ConstantsDocument5 pagesRelation Between Elastic Constantsnitin_johri100% (1)
- 498 Plate Girder CombinedDocument1 page498 Plate Girder CombinedYash DhabaliaNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Guide To Shear Force and Bending Moment Diagrams - Engineer4Free - The #1 Source For Free Engineering Tutorials PDFDocument4 pagesUltimate Guide To Shear Force and Bending Moment Diagrams - Engineer4Free - The #1 Source For Free Engineering Tutorials PDFSubhajyoti DasNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design UBC 1997Document1 pageSeismic Design UBC 1997Gaurav BhabadNo ratings yet
- DOM-I-Force Analysis PDFDocument26 pagesDOM-I-Force Analysis PDFNaveenKrishNo ratings yet
- Ib RCC StructuresDocument12 pagesIb RCC StructuresRaj BakhtaniNo ratings yet
- Transverse Shear-Build Up SectionsDocument8 pagesTransverse Shear-Build Up SectionsKavish DayaNo ratings yet
- Rillej: Portlan'D Cement AssociationDocument328 pagesRillej: Portlan'D Cement AssociationCarlos PEREZ NEYRANo ratings yet
- Tower Design SheetDocument41 pagesTower Design Sheet14pcashNo ratings yet
- Design of lacing face to face for ISMC 300 columnDocument3 pagesDesign of lacing face to face for ISMC 300 columnkiranNo ratings yet
- SOM All Chapters With TimingsDocument376 pagesSOM All Chapters With TimingsSUMIT SUMANNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument2 pagesFluid MechanicsDax ShuklaNo ratings yet
- (Theme Based Painting) : Tech Aeon - 2016Document1 page(Theme Based Painting) : Tech Aeon - 2016shekhadaaNo ratings yet
- PPE Syllabus 2171910Document3 pagesPPE Syllabus 2171910shekhadaaNo ratings yet
- (Theme Based Painting) : Tech Aeon - 2016Document1 page(Theme Based Painting) : Tech Aeon - 2016shekhadaaNo ratings yet
- Power Engineering Experiments for Various BranchesDocument1 pagePower Engineering Experiments for Various BranchesshekhadaaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Processes - IDocument2 pagesManufacturing Processes - IshekhadaaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument5 pagesMultiple Choice QuestionsshekhadaaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics Scales and MeasurementsDocument1 pageEngineering Graphics Scales and MeasurementsshekhadaaNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods in Geophysics: Implicit Methods ExplainedDocument30 pagesNumerical Methods in Geophysics: Implicit Methods ExplainedshekhadaaNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument2 pagesFluid Mechanicsshekhadaa100% (1)
- 2015 Summer OldDocument1 page2015 Summer OldshekhadaaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines and ElectronicsDocument2 pagesElectrical Machines and Electronicsrathorsumit2006No ratings yet
- Four stroke engine working cycle revolutions crankshaftDocument17 pagesFour stroke engine working cycle revolutions crankshaftshekhadaaNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument2 pagesFluid Mechanicsshekhadaa100% (1)
- Monitoring System List of QuestionsDocument8 pagesMonitoring System List of QuestionsshekhadaaNo ratings yet
- Machine Design IDocument2 pagesMachine Design IBhavesh PipaliyaNo ratings yet
- Acadamic PlannigDocument2 pagesAcadamic PlannigshekhadaaNo ratings yet
- Ma 813Document75 pagesMa 813shekhadaaNo ratings yet
- BE SEM-I Teaching Scheme & Subject Code (Old) - All BranchDocument1 pageBE SEM-I Teaching Scheme & Subject Code (Old) - All BranchshekhadaaNo ratings yet
- Questions BankDocument12 pagesQuestions BankshekhadaaNo ratings yet
- MarypskDocument3 pagesMarypskshekhadaaNo ratings yet
- Automobile EngineeringDocument4 pagesAutomobile EngineeringRita KalaniNo ratings yet
- Noble Workshop On Effective Teaching MethodologyDocument2 pagesNoble Workshop On Effective Teaching MethodologyshekhadaaNo ratings yet
- Material Science & MetallurgyDocument2 pagesMaterial Science & Metallurgyshekhadaa60% (5)
- RackDocument16 pagesRackshekhadaaNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning (Web Course)Document2 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioning (Web Course)ShivangAggarwalNo ratings yet
- MechanicalDocument2 pagesMechanicaljvc_84No ratings yet
- Manufacturing Processes - IDocument2 pagesManufacturing Processes - IshekhadaaNo ratings yet
- Sweet and Sour Gas Injection As An Enhanced Oil Recovery Method in Abu Dhabi Offshore Oil FieldsDocument7 pagesSweet and Sour Gas Injection As An Enhanced Oil Recovery Method in Abu Dhabi Offshore Oil FieldsKARARNo ratings yet
- 3 - 5 Gas Condensate Reservoirs - Aug06Document10 pages3 - 5 Gas Condensate Reservoirs - Aug06Ashraf SeragNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 Atomic Structure and Electron ConfigurationDocument44 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 Atomic Structure and Electron ConfigurationMaria AnnaNo ratings yet
- LNG R&D For The Liquefaction and Regasification Processes: 1.theme DescriptionDocument9 pagesLNG R&D For The Liquefaction and Regasification Processes: 1.theme DescriptionVikas PatelNo ratings yet
- 11.boiler Water ChemistryDocument9 pages11.boiler Water Chemistrykcp1986No ratings yet
- Liquid-Liquid Extraction (LLE)Document28 pagesLiquid-Liquid Extraction (LLE)IrMuhammadFaizNo ratings yet
- Volumetric Properties of Pure Fluids: Chapter 3 Smith and Van NessDocument60 pagesVolumetric Properties of Pure Fluids: Chapter 3 Smith and Van NessKush PatelNo ratings yet
- Caustic Recovery PlantDocument8 pagesCaustic Recovery PlantarjmandquestNo ratings yet
- Lakhmir Singh Solutions For Class 9 Feb22 Chemistry Chapter 4 Structure of AtomDocument14 pagesLakhmir Singh Solutions For Class 9 Feb22 Chemistry Chapter 4 Structure of AtomDarshilNo ratings yet
- Ref BasicsDocument15 pagesRef BasicsManasvini KarthihaNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Dew Point of Flue Gas 4x135 MW Jindal, AngulDocument2 pagesCalculation of Dew Point of Flue Gas 4x135 MW Jindal, AngulAshitava SenNo ratings yet
- Bubble Coalescence Inhibition Depends on Electrolyte Concentration and Bubble SizeDocument8 pagesBubble Coalescence Inhibition Depends on Electrolyte Concentration and Bubble SizeJose Luis Barrientos RiosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document58 pagesLecture 2Meej AustriaNo ratings yet
- VenturimeterDocument8 pagesVenturimeterAbhishek Kandoi100% (1)
- PHY4221 (2020) Assignment 2Document2 pagesPHY4221 (2020) Assignment 2MainzaNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Dust Suppression System WiDocument3 pagesEstimation of Dust Suppression System WiRopafadzo ChihuriNo ratings yet
- Instrument tag nos. from Scope of Work compression trainsDocument39 pagesInstrument tag nos. from Scope of Work compression trainsPrathamesh OmtechNo ratings yet
- Advanced Application of Micropasma WeldingDocument12 pagesAdvanced Application of Micropasma WeldingKonstantin MarjanuczNo ratings yet
- Vacuum Evaporators Mateo Torres.Document11 pagesVacuum Evaporators Mateo Torres.Jakson Mateo Torres GuerraNo ratings yet
- Gases and Chem Rexn MCQDocument5 pagesGases and Chem Rexn MCQAlfredo L. CariasoNo ratings yet
- Determination of VLP by Choke and Bottom Hole ParametersDocument14 pagesDetermination of VLP by Choke and Bottom Hole ParametersRaghadaNo ratings yet
- VLE Calculations for Distillation DesignDocument4 pagesVLE Calculations for Distillation Designsandeep lal0% (1)
- Atmospheric Distillation UnitDocument5 pagesAtmospheric Distillation UnitMukund KsNo ratings yet
- RAC Assignment 2011-12-2Document4 pagesRAC Assignment 2011-12-2Tochi Krishna AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Calculation - Horizontal Pressure VesselDocument30 pagesCalculation - Horizontal Pressure VesselVlanic StudioNo ratings yet
- REVIEWDocument14 pagesREVIEWerlifieNo ratings yet
- Properties of Three States of Matter (Lesson Plan)Document6 pagesProperties of Three States of Matter (Lesson Plan)LIZA MARIE GONZALESNo ratings yet
- Separator Design-1Document12 pagesSeparator Design-1vela vanNo ratings yet