Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ir 2104
Uploaded by
Néstor BernalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ir 2104
Uploaded by
Néstor BernalCopyright:
Available Formats
Data Sheet No.
PD60046-S
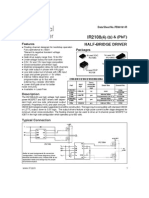
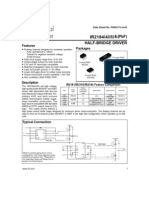
IR2104(S) & (PbF)
HALF-BRIDGE DRIVER
Features
Floating channel designed for bootstrap operation
Fully operational to +600V Tolerant to negative transient voltage dV/dt immune Gate drive supply range from 10 to 20V Undervoltage lockout 3.3V, 5V and 15V input logic compatible Cross-conduction prevention logic Internally set deadtime High side output in phase with input Shut down input turns off both channels Matched propagation delay for both channels Also available LEAD-FREE
Product Summary
VOFFSET IO+/VOUT ton/off (typ.) Deadtime (typ.) 600V max. 130 mA / 270 mA 10 - 20V 680 & 150 ns 520 ns
Packages
Description
The IR2104(S) are high voltage, high speed power 8 Lead SOIC MOSFET and IGBT drivers with dependent high and low 8 Lead PDIP IR2104S side referenced output channels. Proprietary HVIC and IR2104 latch immune CMOS technologies enable ruggedized monolithic construction. The logic input is compatible with standard CMOS or LSTTL output, down to 3.3V logic. The output drivers feature a high pulse current buffer stage designed for minimum driver cross-conduction. The floating channel can be used to drive an N-channel power MOSFET or IGBT in the high side configuration which operates from 10 to 600 volts.
Typical Connection
up to 600V VCC
VCC
IN SD
VB HO VS LO
TO LOAD
IN SD COM
(Refer to Lead Assignment for correct pin configuration) This/These diagram(s) show electrical connections only. Please refer to our Application Notes and DesignTips for proper circuit board layout.
www.irf.com
IR2104(S) & (PbF)
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Absolute maximum ratings indicate sustained limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. All voltage parameters are absolute voltages referenced to COM. The thermal resistance and power dissipation ratings are measured under board mounted and still air conditions.
Symbol
VB VS VHO VCC VLO VIN dVs/dt PD RthJA TJ TS TL
Definition
High side floating absolute voltage High side floating supply offset voltage High side floating output voltage Low side and logic fixed supply voltage Low side output voltage Logic input voltage (IN & SD ) Allowable offset supply voltage transient Package power dissipation @ TA +25C Thermal resistance, junction to ambient Junction temperature Storage temperature Lead temperature (soldering, 10 seconds) (8 lead PDIP) (8 lead SOIC) (8 lead PDIP) (8 lead SOIC)
Min.
-0.3 VB - 25 VS - 0.3 -0.3 -0.3 -0.3 -55
Max.
625 VB + 0.3 VB + 0.3 25 VCC + 0.3 VCC + 0.3 50 1.0 0.625 125 200 150 150 300
Units
V/ns W C/W
Recommended Operating Conditions
The Input/Output logic timing diagram is shown in Figure 1. For proper operation the device should be used within the recommended conditions. The VS offset rating is tested with all supplies biased at 15V differential.
Symbol
VB VS VHO VCC VLO VIN TA
Definition
High side floating supply absolute voltage High side floating supply offset voltage High side floating output voltage Low side and logic fixed supply voltage Low side output voltage Logic input voltage (IN & SD ) Ambient temperature
Min.
VS + 10 Note 1 VS 10 0 0 -40
Max.
VS + 20 600 VB 20 VCC VCC 125
Units
Note 1: Logic operational for VS of -5 to +600V. Logic state held for VS of -5V to -VBS. (Please refer to the Design Tip DT97-3 for more details).
www.irf.com
IR2104(S) & (PbF)
Dynamic Electrical Characteristics
VBIAS (VCC, VBS) = 15V, CL = 1000 pF and TA = 25C unless otherwise specified.
Symbol
ton toff tsd tr tf DT MT
Definition
Turn-on propagation delay Turn-off propagation delay Shutdown propagation delay Turn-on rise time Turn-off fall time Deadtime, LS turn-off to HS turn-on & HS turn-on to LS turn-off Delay matching, HS & LS turn-on/off
Min. Typ. Max. Units Test Conditions
400 680 150 160 100 50 520 820 220 220 170 90 650 60 ns VS = 0V VS = 600V
Static Electrical Characteristics
VBIAS (VCC, VBS) = 15V and TA = 25C unless otherwise specified. The VIN, VTH and IIN parameters are referenced to COM. The VO and IO parameters are referenced to COM and are applicable to the respective output leads: HO or LO.
Symbol
VIH VIL VSD,TH+ VSD,THVOH VOL ILK IQBS IQCC IIN+ IINVCCUV+ VCCUVIO+ IO-
Definition
Logic 1 (HO) & Logic 0 (LO) input voltage Logic 0 (HO) & Logic 1 (LO) input voltage SD input positive going threshold SD input negative going threshold High level output voltage, VBIAS - VO Low level output voltage, VO Offset supply leakage current Quiescent VBS supply current Quiescent VCC supply current Logic 1 input bias current Logic 0 input bias current VCC supply undervoltage positive going threshold VCC supply undervoltage negative going threshold Output high short circuit pulsed current Output low short circuit pulsed current
Min. Typ. Max. Units Test Conditions
3 3 8 7.4 130 270 30 150 3 8.9 8.2 210 360 0.8 0.8 100 100 50 55 270 10 1 9.8 V 9 mA VO = 0V PW 10 s VO = 15V PW 10 s A mV V VCC = 10V to 20V VCC = 10V to 20V VCC = 10V to 20V VCC = 10V to 20V IO = 0A IO = 0A VB = VS = 600V VIN = 0V or 5V VIN = 0V or 5V VIN = 5V VIN = 0V
www.irf.com
IR2104(S) & (PbF)
Functional Block Diagram
VB
HV LEVEL SHIFT
Q PULSE FILTER R S VS HO
IN PULSE GEN
DEAD TIME & SHOOT-THROUGH PREVENTION
UV DETECT VCC
SD
LO
COM
Lead Definitions
Symbol Description
IN Logic input for high and low side gate driver outputs (HO and LO), in phase with HO Logic input for shutdown High side floating supply High side gate drive output High side floating supply return Low side and logic fixed supply Low side gate drive output Low side return
SD VB
HO VS VCC LO COM
Lead Assignments
1 2 3 4 VCC IN SD COM VB HO VS LO
8
7 6 5
1 2 3 4
VCC IN SD COM
VB HO VS LO
8
7 6 5
8 Lead PDIP
8 Lead SOIC
IR2104 4
IR2104S www.irf.com
IR2104(S) & (PbF)
IN
IN(LO)
50% 50%
SD
IN(HO)
ton tr 90% toff 90% tf
HO LO
LO HO
Figure 1. Input/Output Timing Diagram
10%
10%
Figure 2. Switching Time Waveform Definitions
50%
50%
SD
50%
IN
tsd
90%
HO LO
90%
HO
DT
10% DT
LO
Figure 3. Shutdown Waveform Definitions
90%
10%
Figure 4. Deadtime Waveform Definitions
IN (LO)
50% 50%
IN (HO)
LO
HO
10%
MT 90%
MT
LO
HO
Figure 5. Delay Matching Waveform Definitions
www.irf.com
IR2104(S) & (PbF)
1 40 0 T urn -O n D e l ay T i m e (n s)
Turn-On Delay Time (ns)
1400 1200 1000 800 600 400 200 0 10 12 14 16 18 20 Typ. Max.
1 20 0 1 00 0
M a x.
8 00 6 00 4 00 2 00 0 -50 -25 0 25 50 75 1 00 1 25
Temperature (C)
T yp .
VBIAS Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 6A. Turn-On Time vs Temperature
Figure 6B. Turn-On Time vs Supply Voltage
1000 Max . Turn-On Delay Time (ns)
Turn-Off Delay Time (ns)
5 00 4 00 3 00 2 00 1 00 T yp . 0 M ax .
800 600 Typ. 400 200 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
-50
-25
25
50
75
1 00
1 25
Input Voltage (V)
Temperature (C)
Figure 6C. Turn-On Time vs Input Voltage
Figure 7A. Turn-Off Time vs Temperature
500
1000 Turn-Off Delay Time (ns 800 600 400 200 Typ 0
10 12 14 16 18 20
Turn-Off Delay Time (ns)
400 300 200 Typ. 100 0 Max.
Ma x .
10
12 14
16 18
20
VBIAS Supply Voltage (V)
Input Voltage (V)
Figure 7B. Turn-Off Time vs Supply Voltage
Figure 7C. Turn-Off Time vs Input Voltage
www.irf.com
IR2104(S) & (PbF)
500
Shutdown Delay Time (ns)
500
Shutdown Delay Time (ns)
400 300 200 100 0 -5 0 -2 5 0 25 50 75 100 125 M ax.
400 300 200 Typ. 100 0 10 12 14 16 18 20 Max.
T y p.
Temperature (C)
VBIAS Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 8A. Shutdown Time vs Temperature
Figure 8B. Shutdown Time vs Voltage
500
500
Turn-On Rise Time (ns)
400 300 200 100 Typ. 0 -5 0 -2 5 0 25 50 75 100 125
Turn-On Rise Time (ns)
400 300 M ax. 200 100 Typ. 0 10 12 14 16 18 20
M ax.
Temperature (C)
VBIAS Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 9A. Turn-On Rise Time vs Temperature
20 0
Figure 9B. Turn-On Rise Time vs Voltage
200
Turn-Off Fall Time (ns)
Turn-Off Fall Time (ns)
15 0
150 M ax. 100
10 0 M ax. 50 Ty p. 0 -50 -25 0 25 50 75 10 0 12 5
50 Typ. 0 10 12 14 16 18 20
Temperature (C)
VBIAS Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 10A. Turn-Off Fall Time vs Temperature
Figure 10B. Turn-Off Fall Time vs Voltage
www.irf.com
IR2104(S) & (PbF)
1400 1200 1400 1200
Deadtime (ns)
1000 800 600 400 200 0 -5 0 -2 5 0 25 50 75 100 125 Typ. Mi n. M ax.
Deadtime (ns)
1000 M ax. 800 600 Typ. 400 Mi n. 200 0 10 12 14 16 18 20
Temperature (C)
VBIAS Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 11A. Deadtime vs Temperature
8 7 I nput V ol tag e (V ) 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 -50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
Temperature (C)
Figure 11B. Deadtime vs Voltage
8 7 I n pu t V ol ta g e (V ) 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 10 12 14 16 18 20
Vcc Supply Voltage (V)
Mi n.
Mi n.
Figure 12A. Logic "1" (HO) & Logic 0 (LO) & Inactive SD Input Voltage vs Temperature
4 3.2 2.4 1.6 Max . 0.8 0 -50
Figure 12B. Logic "1" (HO) & Logic 0 (LO) & Inactive SD Input Voltage vs Voltage
4 3 .2 I nputV ol ta g e (V ) 2 .4 1 .6 M ax. 0 .8 0
Input Voltage (V)
-25
25
50
75
100
125
10
12
14
16
18
20
Temperature (C)
Vcc Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 13A. Logic "0" (HO) & Logic 1 (LO) & Active SD Input Voltage vs Temperature
Figure 13B. Logic "0" (HO) & Logic 1 (LO) & Active SD Input Voltage vs Voltage
www.irf.com
IR2104(S) & (PbF)
1 1
High Level Output Voltage (V)
High Level Output Voltage (V)
0 .8 0 .6 0 .4 M ax. 0 .2 0 -5 0 -2 5 0 25 50 75 100 125
0 .8 0 .6 0 .4 0 .2 0 10 12 14 16 18 20 M ax.
Temperature (C)
Vcc Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 14A. High Level Output vs Temperature
1
Figure 14B. High Level Output vs Voltage
Low Level Output Voltage (V)
0 .8 0 .6 0 .4 0 .2 0 -5 0 -2 5 0 25 50 75 100 125
Low Level Output Voltage (V)
0 .8 0 .6 0 .4 0 .2 M ax. 0 10 12 14 16 18 20
M ax.
Temperature (C)
Vcc Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 15A. Low Level Output vs Temperature
Offset Supply Leakage Current (A)
500 400 300 200 100 M ax. 0 -5 0 -2 5 0 25 50 75 100 125
Figure 15B. Low level Output vs Voltage
Offset Supply Leakage Current (A)
500 400 300 200 100 0 0 100 200 300 400 500 600
Max.
Temperature (C)
VB Boost Voltage (V)
Figure 16A. Offset Supply Current vs Temperature
Figure 16B. Offset Supply Current vs Voltage
www.irf.com
IR2104(S) & (PbF)
1 50
150
VBS Supply Current (A)
1 20 90 60 M ax . 30 T yp . 0 -50 -25 0 25 50 75 1 00 1 25
VBS Supply Current (A)
120 90 60 30 Ty p. 0 10 12 14 16 18 20
Max .
Temperature (C)
VBS Floating Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 17A. VBS Supply Current vs Temperature
700 700
Figure 17B. VBS Supply Current vs Voltage
Vcc Supply Current (A)
600 500 400 300 200 100 0 -5 0 -2 5 0 25 50 75 100 125 Typ. M ax.
Vcc Supply Current (A)
600 500 400 300 200 100 Typ. 0 10 12 14 16 18 20 M ax.
Temperature (C)
Vcc Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 18A. Vcc Supply Current vs Temperature
30
Figure 18B. Vcc Supply Current vs Voltage
30
Logic 1 Input Current (A)
25 20 15 10 M ax. 5 Typ. 0 -5 0 -2 5 0 25 50 75 100 125
Logic 1 Input Current (A)
25 20 15 10 5 0 10 12 14 16 18 20 M ax. Typ.
Temperature (C)
Vcc Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 19A. Logic"1" Input Current vs Temperature
Figure 19B. Logic"1" Input Current vs Voltage
10
www.irf.com
IR2104(S) & (PbF)
5
Logic "0" Input Current (uA)
Logic 0 Input Current (A)
5 4 3 2 Max. 1 0
4 3 2 Max. 1 0 -50
-25
25 50 75 Temperature (C)
100
125
10
12
14 16 18 VCC Supply Voltage (V)
20
Figure 20A. Logic "0" Input Current vs Temperature
11
VCC UVLO Threshold +(V)
Figure 20B. Logic "0" Input Current vs Voltage
11
VCC UVLO Threshold - (V)
M ax. 10 9 8 7 6 -50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
Temperature (C)
10 Max. 9 Typ. 8 7 6 -50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
Temperature (C)
Typ. Mi n.
Min.
Figure 21A. Vcc Undervoltage Threshold(+) vs Temperature
500
Output Source Current (mA) Output Source Current (mA)
Figure 21B. Vcc Undervoltage Threshold(-) vs Temperature
500 400 300 200 T y p. 100 Mi n. 0 10 12 14 16 18 VBIAS Supply Voltage (V) 20
400 300 200 100 Min. Typ.
0 -50
-25
25 50 75 Temperature (C)
100
125
Figure 22A. Output Source Current vs Temperature
Figure 22B. Output Source Current vs Voltage
www.irf.com
11
IR2104(S) & (PbF)
7 00
Output Sink Current (mA) Output Sink Current (mA)
70 0 60 0 50 0 40 0 30 0 20 0 Mi n. 10 0 0
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 1 00 1 25
6 00 5 00 4 00 3 00 Mi n. 2 00 1 00 0
Temperature (C)
T yp .
Ty p.
10
12
14
16
18
20
VBIAS Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 23A. Output Sink Current vs Temperature
Figure 23B. Output Sink Current vs Voltage
Case Outlines
8 Lead PDIP
01-6014 01-3003 01 (MS-001AB)
12
www.irf.com
IR2104(S) & (PbF)
D A 5
B
FOOTPRINT 8X 0.72 [.028]
DIM A b c D
INCHES MIN .0532 .013 .0075 .189 .1497 MAX .0688 .0098 .020 .0098 .1968 .1574
MILLIMETERS MIN 1.35 0.10 0.33 0.19 4.80 3.80 MAX 1.75 0.25 0.51 0.25 5.00 4.00
A1 .0040
6 E
5 H 0.25 [.010] A
E
6.46 [.255]
e e1 H K L
8X 1.78 [.070]
.050 BASIC .025 BASIC .2284 .0099 .016 0 .2440 .0196 .050 8
1.27 BASIC 0.635 BASIC 5.80 0.25 0.40 0 6.20 0.50 1.27 8
6X
e e1
3X 1.27 [.050]
A C 0.10 [.004] y
K x 45
8X b 0.25 [.010]
A1 C A B
8X L 7
8X c
NOTES: 1. DIMENSIONING & TOLERANC ING PER ASME Y14.5M-1994. 2. CONTROLLING DIMENSION: MILLIMETER 3. DIMENSIONS ARE SHOWN IN MILLIMETERS [INC HES]. 4. OUTLINE C ONFORMS TO JEDEC OUTLINE MS-012AA.
5 DIMENSION DOES NOT INCLUDE MOLD PROTRUSIONS. MOLD PROTRUSIONS NOT TO EXCEED 0.15 [.006]. 6 DIMENSION DOES NOT INCLUDE MOLD PROTRUSIONS. MOLD PROTRUSIONS NOT TO EXCEED 0.25 [.010]. 7 DIMENSION IS THE LENGTH OF LEAD FOR SOLDERING TO A SUBSTRATE.
8 Lead SOIC
01-6027 01-0021 11 (MS-012AA)
www.irf.com
13
IR2104(S) & (PbF)
LEADFREE PART MARKING INFORMATION
Part number
IRxxxxxx YWW? ?XXXX
Lot Code (Prod mode - 4 digit SPN code) IR logo
Date code
Pin 1 Identifier ? P MARKING CODE Lead Free Released Non-Lead Free Released
Assembly site code Per SCOP 200-002
ORDER INFORMATION
Basic Part (Non-Lead Free) 8-Lead PDIP IR2104 order IR2104 8-Lead SOIC IR2104S order IR2104S
Leadfree Part 8-Lead PDIP IR2104 order IR2104PbF 8-Lead SOIC IR2104S order IR2104SPbF
IR WORLD HEADQUARTERS: 233 Kansas St., El Segundo, California 90245 Tel: (310) 252-7105 This product has been qualified per industrial level Data and specifications subject to change without notice. 4/2/2004
14
www.irf.com
You might also like
- Ids Ips Audit ChecklistDocument1 pageIds Ips Audit Checklisthakim hbNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsFrom EverandSemiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsNo ratings yet
- Sanity ChecksDocument3 pagesSanity Checksswathikomati787067% (3)
- Ir2103 DatasheetDocument12 pagesIr2103 DatasheetToma HaiNo ratings yet
- Irs 2103Document14 pagesIrs 2103Việt LêNo ratings yet
- Ir 2111Document15 pagesIr 2111Kutsal KaraNo ratings yet
- Ir 2101Document14 pagesIr 2101Willard DmpseyNo ratings yet
- Irs2101 (S) PBF: High and Low Side DriverDocument15 pagesIrs2101 (S) PBF: High and Low Side Driverdesin01No ratings yet
- Ir 2111Document15 pagesIr 2111Miltongrimi GrimilNo ratings yet
- Ir2117 Igbt Driver PDFDocument18 pagesIr2117 Igbt Driver PDFismifaizulNo ratings yet
- IR2110/IR2113 : High and Low Side Driver SDocument15 pagesIR2110/IR2113 : High and Low Side Driver SPandu Sandi PratamaNo ratings yet
- IR2110/IR2113 : High and Low Side Driver SDocument15 pagesIR2110/IR2113 : High and Low Side Driver SPepe ModstNo ratings yet
- IR2110/IR2113: High and Low Side DriverDocument16 pagesIR2110/IR2113: High and Low Side DriverguiknopNo ratings yet
- Ir 2105Document12 pagesIr 2105Manuel Villegas AcostaNo ratings yet
- Ir 2110Document17 pagesIr 2110Nguyen KhangNo ratings yet
- Ir 2010Document17 pagesIr 2010Naveed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Ir 2213Document14 pagesIr 2213Lampros LampropoulosNo ratings yet
- Ir 2108Document23 pagesIr 2108robertofurlancriNo ratings yet
- Ir 2109Document25 pagesIr 2109Chavi AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Ir 2184Document24 pagesIr 2184buiphuoclaiNo ratings yet
- Ir 2304Document8 pagesIr 2304Rajo AmehNo ratings yet
- Ir 2127Document16 pagesIr 2127kimonspNo ratings yet
- Ir2181 Igbt Driver PDFDocument21 pagesIr2181 Igbt Driver PDFismifaizulNo ratings yet
- S2127Document21 pagesS2127RICHIHOTS2No ratings yet
- Ir2121 PDFDocument16 pagesIr2121 PDFMeselao Meselao MeselaoNo ratings yet
- Ir2112 (S) & (PBF) : High and Low Side DriverDocument17 pagesIr2112 (S) & (PBF) : High and Low Side DriverMugahed DammagNo ratings yet
- High and Low Side Driver: Features Product SummaryDocument14 pagesHigh and Low Side Driver: Features Product SummaryFernando Camargo100% (1)
- MC33153 DDocument14 pagesMC33153 DPham LongNo ratings yet
- LM358Document7 pagesLM358llollo21No ratings yet
- Digital Audio Driver With Discrete Dead-Time and ProtectionDocument25 pagesDigital Audio Driver With Discrete Dead-Time and Protectiongotcha75No ratings yet
- Ir 2113Document18 pagesIr 2113rohitsingh2909No ratings yet
- Induction Motor DrivesDocument30 pagesInduction Motor DrivesAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Self-Oscillating Half-Bridge Driver: Ir2153 (D) (S) & (PBF)Document9 pagesSelf-Oscillating Half-Bridge Driver: Ir2153 (D) (S) & (PBF)Zoltán HalászNo ratings yet
- MC33030 MotorolaDocument16 pagesMC33030 MotorolaLuiz EduardoNo ratings yet
- Features Applications: SBOS141Document11 pagesFeatures Applications: SBOS141eslovenitNo ratings yet
- LM723 Voltage RegulatorDocument14 pagesLM723 Voltage Regulatorvanminh91bkNo ratings yet
- BA4911Document17 pagesBA4911Maicon Bruno AlbaNo ratings yet
- Datasheet JFETDocument16 pagesDatasheet JFETaldontetNo ratings yet
- Universal DC/DC Converter: (Top View)Document11 pagesUniversal DC/DC Converter: (Top View)Engine Tuning UpNo ratings yet
- TL062CPDocument12 pagesTL062CPCleison FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Ir 2153Document9 pagesIr 2153Carlos Marinho SilvaNo ratings yet
- 12V DC To 40V DC Converter Circuit DiagramDocument10 pages12V DC To 40V DC Converter Circuit DiagramAhdiat Darmawan LubisNo ratings yet
- FAN7382 High-And Low-Side Gate Driver: Features DescriptionDocument15 pagesFAN7382 High-And Low-Side Gate Driver: Features DescriptionRiza BaduaNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1From EverandNewnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Electricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and PracticeFrom EverandElectricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and PracticeNo ratings yet
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorFrom Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)From EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)No ratings yet
- Analog Circuit Design: A Tutorial Guide to Applications and SolutionsFrom EverandAnalog Circuit Design: A Tutorial Guide to Applications and SolutionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (6)
- Digital Power Electronics and ApplicationsFrom EverandDigital Power Electronics and ApplicationsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Diode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesFrom EverandDiode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Analog Circuit Design Volume 2: Immersion in the Black Art of Analog DesignFrom EverandAnalog Circuit Design Volume 2: Immersion in the Black Art of Analog DesignNo ratings yet
- Optimizing The Load Transient Response of The Buck ConverterDocument7 pagesOptimizing The Load Transient Response of The Buck ConverterNéstor BernalNo ratings yet
- Border-Collision Bifurcations in The Buck ConverterDocument10 pagesBorder-Collision Bifurcations in The Buck ConverterNéstor BernalNo ratings yet
- UP6 15, UP6 20, UP6 25, UP6 30 60Hz: Intellisys Option Dryer Option High Dust Option Outdoor Module Option PORO OptionDocument226 pagesUP6 15, UP6 20, UP6 25, UP6 30 60Hz: Intellisys Option Dryer Option High Dust Option Outdoor Module Option PORO Optionrfg21100% (1)
- MSP430 TutorialDocument113 pagesMSP430 TutorialPaulo L. MuñozNo ratings yet
- Circuits Second 2nd Edition Ulaby Maharbiz CH1 SolutionsDocument53 pagesCircuits Second 2nd Edition Ulaby Maharbiz CH1 SolutionsConor Loo33% (3)
- Scaling and Bandwidth-Parameterization Based Controller TuningDocument8 pagesScaling and Bandwidth-Parameterization Based Controller Tuninghamza mesaiNo ratings yet
- OTA MessageDocument11 pagesOTA MessageSachin TiwariNo ratings yet
- HP Mini 210-2120br PC Broadcom Wireless LAN Driver v.5.60.350.23 Pour Windows 7 Download GrátisDocument5 pagesHP Mini 210-2120br PC Broadcom Wireless LAN Driver v.5.60.350.23 Pour Windows 7 Download GrátisFernandoDiasNo ratings yet
- mp-2555sp - mp-3055sp - mp-3555sp RicohDocument4 pagesmp-2555sp - mp-3055sp - mp-3555sp RicohAnonymous WD109UakyNo ratings yet
- Automotive Electronics Sensor Interface CY30 Automotive Electronics Product Information Sensor Interface - CY30Document3 pagesAutomotive Electronics Sensor Interface CY30 Automotive Electronics Product Information Sensor Interface - CY30freddys merchanNo ratings yet
- Quectel OpenCPU User Guide V5.1Document164 pagesQuectel OpenCPU User Guide V5.1Ahmed YousryNo ratings yet
- Speaker - Headset - Earphone Memory Ram Processor MonitorDocument1 pageSpeaker - Headset - Earphone Memory Ram Processor MonitorfaniwardhanaNo ratings yet
- Automatic Street LightDocument11 pagesAutomatic Street Lightbhags7711No ratings yet
- R 2 2 Omniscop FPS Brochure ESDocument7 pagesR 2 2 Omniscop FPS Brochure ESjoseNo ratings yet
- Cisco V6 Exam Answer NotesDocument10 pagesCisco V6 Exam Answer NotesYasin ArafatNo ratings yet
- 10.1.4.8 Lab - Configure ASA 5505 Basic Settings and Firewall Using ASDMDocument40 pages10.1.4.8 Lab - Configure ASA 5505 Basic Settings and Firewall Using ASDMerojasNo ratings yet
- PCPinpad PC-SC UserGuideDocument26 pagesPCPinpad PC-SC UserGuideArief MarlemanNo ratings yet
- Manual FX9500Document78 pagesManual FX9500Gerardo LeyesNo ratings yet
- (CSE-225) Lecture-4 (C++ Part-2)Document8 pages(CSE-225) Lecture-4 (C++ Part-2)Zahin Zami OrkoNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Interfacing: InterfaceDocument21 pagesUnit 3 Interfacing: Interfacechirag khandelwalNo ratings yet
- Test Report (QSK50-G4)Document6 pagesTest Report (QSK50-G4)Mazen SalibaNo ratings yet
- An Optimized Shortest Job First Scheduling Algorithm For CPU SchedulingDocument6 pagesAn Optimized Shortest Job First Scheduling Algorithm For CPU SchedulingDeath AngelNo ratings yet
- HP HWX Reference Architecture On Apollo 4530Document38 pagesHP HWX Reference Architecture On Apollo 4530Madasamy GanapathyNo ratings yet
- Ubuntu 18.04 LTS Desktop InstallationDocument38 pagesUbuntu 18.04 LTS Desktop InstallationJessie DiamanteNo ratings yet
- Datasheet of DS 7616NXI K2 - V4.74.000 - 20230209Document5 pagesDatasheet of DS 7616NXI K2 - V4.74.000 - 20230209Lizzy CortezNo ratings yet
- Jet MaxDocument48 pagesJet Maxiceblue77No ratings yet
- Concurrency Control: R&G - Chapter 17Document24 pagesConcurrency Control: R&G - Chapter 17raw.junkNo ratings yet
- Hyperx Cloud Revolver S FW Update 59035 - 0108 ProcedureDocument2 pagesHyperx Cloud Revolver S FW Update 59035 - 0108 ProcedureTharlys SaoPedro0% (1)
- Axiocam 105 Color - User GuideDocument21 pagesAxiocam 105 Color - User GuideSinan ChenNo ratings yet
- DFNT Protocol Manual p1Document35 pagesDFNT Protocol Manual p1eumetallicaNo ratings yet
- Modbus RTU TCP/IP: HMI SettingDocument2 pagesModbus RTU TCP/IP: HMI SettingGeorge GaitanakisNo ratings yet
- SFC ST Presentation1Document51 pagesSFC ST Presentation1Jose Alberto Herrera OgazNo ratings yet