Professional Documents
Culture Documents
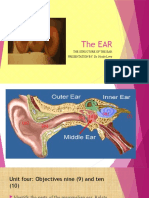
Parts of Human Ear and Their Functions
Uploaded by
Jay SmithCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Parts of Human Ear and Their Functions
Uploaded by
Jay SmithCopyright:
Available Formats
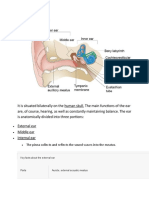
Parts of Human Ear and their functions
Parts
Function/s
Pinna
Auditory Canal Malleus Incus
Collects sound and channels it down the ear. Help determine the direction of sound. Protects internal parts of the ear. Channels sound waves towards the tympanic membrane. Provides a waxy substance to protect and lube the ear. It transmits the sound vibrations from the eardrum to the incus. The incus transmits sound vibrations from the malleus to the stapes, which it is connected to through the incudomalleolar and incudostapedial joint respectively. Vibrate with the same frequency as the sound wave that hits it. Provides an air tight protection between the external and middle ear. To equalize the pressure between the outer and inner ear. These are fluid-filled loops, attached to the cochlea and help in maintaining the balance. Vibrates and passes the compression waves to the inner ear. Transform vestibular information (related to balance) into an egocentric frame of reference based on the position of the head in relation to the body. Sensory apparatus of the inner ear that helps the body maintain its postural equilibrium the actual organ that helps in hearing functions as a sound wave interpreter and converter Keep the cochlear fluids contained within the scala vestibuli and scala tympani. It also functions as a multiplier of the sound waves generated from the oval window membrane.
Tympanic Membrane Eustachian Tube
Semicircular Canals Stapes or Stirrup Vestibular nerve Vestibule Cochlea Round Window
You might also like
- Functions of Parts of The EarDocument1 pageFunctions of Parts of The EarWilda Pado Rivera100% (1)
- The Integumentary System WorksheetDocument3 pagesThe Integumentary System WorksheetEdchel Espeña50% (2)
- Presenting and Analyzing Data VisuallyDocument15 pagesPresenting and Analyzing Data VisuallyTrisha Marieh100% (3)
- Skeletal System Sample Quiz With AnswersDocument4 pagesSkeletal System Sample Quiz With AnswersFlorence Lynn Baisac100% (2)
- The Skeletal System TestDocument6 pagesThe Skeletal System TestCarlo Precioso100% (3)
- Finding Mean, Median, and Mode from Grouped DataDocument2 pagesFinding Mean, Median, and Mode from Grouped DataRowella Catugas100% (3)
- Respiratory System Worksheet Fill-InDocument2 pagesRespiratory System Worksheet Fill-InAnonymous 7QjNuvoCpI90% (10)
- The Skeletal System WorksheetDocument7 pagesThe Skeletal System WorksheetTavon FloydNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System ExamDocument4 pagesReproductive System Examfe jandugan100% (1)
- Animals That Live On LandDocument5 pagesAnimals That Live On Landamihaninternetshop aisNo ratings yet
- English 3 - Week2Document17 pagesEnglish 3 - Week2elleNo ratings yet
- Body Covering of AnimalsDocument16 pagesBody Covering of Animalsmarlon felizardoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System Review WorksheetDocument4 pagesReproductive System Review WorksheetLalaine Angela Denuna86% (7)
- Ethnomedicinal Plants of the MaranaosDocument74 pagesEthnomedicinal Plants of the MaranaosJane Limsan Paglinawan33% (3)
- Mother Tongue 2Document11 pagesMother Tongue 2Gayle LozanoNo ratings yet
- Jose Rizal Educational BackgroundDocument10 pagesJose Rizal Educational Backgroundearlreia100% (2)
- Summative Test No. 2 ScienceDocument2 pagesSummative Test No. 2 ScienceCristita Macaranas Vigo100% (1)
- Zoology 1 Lecture: Evolution and Ecology PerspectiveDocument29 pagesZoology 1 Lecture: Evolution and Ecology PerspectiveAngelica Rose EspornaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Questions PDFDocument4 pagesCirculatory System Questions PDFTrajce80% (5)
- Ms. Patricia S. GozonDocument19 pagesMs. Patricia S. GozonsammNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of The Ear: Fact FileDocument5 pagesParts and Functions of The Ear: Fact FileJyoti MeenaNo ratings yet
- The Human EarDocument10 pagesThe Human Earvenkat kandukuriNo ratings yet
- The Ear: The Structure of The Ear PRESENTATION BY: Dr. Nicole LevyDocument31 pagesThe Ear: The Structure of The Ear PRESENTATION BY: Dr. Nicole LevynicoleNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Diagram of The Ear and Its FunctionsDocument14 pagesDiagram of The Ear and Its Functionsmcheche12No ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of the EarDocument10 pagesStructure and Functions of the EarAiza CeciliaNo ratings yet
- The Outer Ear: Collecting Sounds: EarwaxDocument2 pagesThe Outer Ear: Collecting Sounds: EarwaxAlyssa Jane NarvasNo ratings yet
- GL - Day 4Document18 pagesGL - Day 4abdulsalamdharejo2004No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EarDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EarGunel AliyevaNo ratings yet
- Aranilla - Laboratory No. 3Document4 pagesAranilla - Laboratory No. 3Mamamo157No ratings yet
- Bio ProjectDocument23 pagesBio Projectsoumya mazumdarNo ratings yet
- Ear Anatomy FunctionDocument2 pagesEar Anatomy Functionapi-311071858No ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Ear. AreteDocument12 pagesAnatomy of The Ear. AreteBrandon AreteNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy and Physiology of HearingDocument3 pagesThe Anatomy and Physiology of HearingGabriella PatriciaNo ratings yet
- The Human EarDocument2 pagesThe Human EarClarizzel de JesusNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EarDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EarAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of EarDocument2 pagesAnatomy of EarBellarmine JanellaNo ratings yet
- What Are Ears and What Do They DoDocument3 pagesWhat Are Ears and What Do They DoQuin CusayNo ratings yet
- AUDITORY PHONETICSDocument12 pagesAUDITORY PHONETICSruth.pedrajitaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of The Ear Explicated With DiagramsDocument10 pagesStructure and Functions of The Ear Explicated With DiagramsemmanuelNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The EarDocument8 pagesAnatomy of The EarDarkAngelNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EarDocument196 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EarChalsey Jene LorestoNo ratings yet
- Week 16. INDIVIDUAL ASSIGNMENT Review of Ear Ana PhysioDocument2 pagesWeek 16. INDIVIDUAL ASSIGNMENT Review of Ear Ana PhysioSOPHIA PILLENANo ratings yet
- LESSON 1 - EXPLAIN - ACTIVITY 2 - STEP 2 AND STEP 3 - MorenoDocument2 pagesLESSON 1 - EXPLAIN - ACTIVITY 2 - STEP 2 AND STEP 3 - MorenoAiza SaripNo ratings yet
- The Ear and HearingDocument55 pagesThe Ear and Hearingc3rberussNo ratings yet
- Patients With Ruptured or Absent Tympanic Membranes Have Extreme Difficulty in Hearing, and Possibly Even Complete Hearing LossDocument3 pagesPatients With Ruptured or Absent Tympanic Membranes Have Extreme Difficulty in Hearing, and Possibly Even Complete Hearing LossminaNo ratings yet
- Esp EnglishDocument5 pagesEsp EnglishCahyaa NingsiihNo ratings yet
- Ear AnatomyDocument2 pagesEar Anatomyapi-309772427No ratings yet
- Human EarDocument2 pagesHuman EarKristine OlogNo ratings yet
- Parts of The EarDocument5 pagesParts of The EarThons Nacu LisingNo ratings yet
- Parts of the Ear, Eye, Skin and TongueDocument7 pagesParts of the Ear, Eye, Skin and TongueTaryn MitchellNo ratings yet
- April 29Document7 pagesApril 29api-292905822No ratings yet
- Ears HomeworkDocument2 pagesEars HomeworkJonas Zacarias BalingbingNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing in the EarDocument15 pagesThe Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing in the EariwanNo ratings yet
- Troduction: Click On The Image Below For More Information About Each RegionDocument3 pagesTroduction: Click On The Image Below For More Information About Each Regionanon_758251040No ratings yet
- The Ear Is The Organ of Hearing and BalanceDocument2 pagesThe Ear Is The Organ of Hearing and Balancefei zhanNo ratings yet
- Ear AnatomyDocument2 pagesEar Anatomyapi-311370707No ratings yet
- What Is Sound?Document8 pagesWhat Is Sound?Chrisshalyn Sy PinedaNo ratings yet
- The Human EarDocument13 pagesThe Human EarCalvo AdrianNo ratings yet
- (Konsultayo FAQ 2020) RabiesDocument5 pages(Konsultayo FAQ 2020) RabiesJay SmithNo ratings yet
- A Reaction Paper of President Noynoy Aquino 2013 State of The Nation Address.Document2 pagesA Reaction Paper of President Noynoy Aquino 2013 State of The Nation Address.Jay Smith100% (2)
- Torchlight 2 CheatcodesDocument13 pagesTorchlight 2 CheatcodesJay SmithNo ratings yet
- System DeliveryDocument24 pagesSystem DeliveryJay SmithNo ratings yet
- Color: Design'S Most Exciting ElementDocument22 pagesColor: Design'S Most Exciting ElementJay SmithNo ratings yet
- Computer Virus and Anti VirusDocument49 pagesComputer Virus and Anti VirusJay Smith100% (2)
- Application Letter For Applying As A Casual EmployeeDocument1 pageApplication Letter For Applying As A Casual EmployeeJay Smith66% (58)
- Private Institutions Who Helps The Government in Protecting A ChildDocument6 pagesPrivate Institutions Who Helps The Government in Protecting A ChildJay SmithNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report of OJT at Registrar's OfficeDocument61 pagesNarrative Report of OJT at Registrar's OfficeJay Smith87% (119)
- Project PlanDocument6 pagesProject PlanJay SmithNo ratings yet
- Sample Resume For OJT Student (Information Technology)Document2 pagesSample Resume For OJT Student (Information Technology)Jay Smith88% (217)
- Application Letter For OJT StudentsDocument1 pageApplication Letter For OJT StudentsJay Smith87% (86)
- Envelopes and Labels in MS WordDocument19 pagesEnvelopes and Labels in MS WordJay SmithNo ratings yet
- Career Opportunities in IctDocument31 pagesCareer Opportunities in IctJay SmithNo ratings yet
- Agile MethodologyDocument9 pagesAgile MethodologyJay Smith100% (1)
- Basics of Visual FoxPro ProgrammingDocument51 pagesBasics of Visual FoxPro ProgrammingJay Smith72% (36)
- Resignation LetterDocument1 pageResignation LetterJay SmithNo ratings yet
- The Mailings Tab in MS WORDDocument40 pagesThe Mailings Tab in MS WORDJay Smith80% (5)
- The Test Development ProcessDocument20 pagesThe Test Development ProcessJay SmithNo ratings yet
- CSS - Cascading Style SheetsDocument101 pagesCSS - Cascading Style SheetsJay SmithNo ratings yet
- Disaster RecoveryDocument8 pagesDisaster RecoveryJay SmithNo ratings yet
- PollutionDocument37 pagesPollutionJay SmithNo ratings yet
- C++ String FuctionsDocument15 pagesC++ String FuctionsJay SmithNo ratings yet
- Electronic Data InterchangeDocument21 pagesElectronic Data InterchangeJay Smith100% (1)
- Why Bill Gates Is My IdolDocument7 pagesWhy Bill Gates Is My IdolJay Smith100% (1)
- Computerized Enrollment System Case StudyDocument4 pagesComputerized Enrollment System Case StudyJay Smith47% (15)
- Socio Political Ramification On Computer GamingDocument7 pagesSocio Political Ramification On Computer GamingJay SmithNo ratings yet
- Test Case StudyDocument11 pagesTest Case StudyJay SmithNo ratings yet