Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Notes Together
Uploaded by
api-216728214Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Notes Together
Uploaded by
api-216728214Copyright:
Available Formats
It is essential for students to know WWII World War II had a big impact on the United States that would
have long term political effects. The nation came together as each American was encouraged to Do Your Part in the war effort. Each and every American was called upon to conserve scarce materials by contributing to scrap metal drives and planting Victory Gardens. However voluntary conservation was not enough and Americans were required to use ration booklets. The economy was finally pulled out of the depression by the war effort as everyone went to work to help win the war. Women, as the homemakers, were responsible for rationing and victory gardens. More women also began to work outside the home in greater numbers. They took the place of husbands, sons and brothers in factories and built airplanes, trucks and ships. Although women faced discrimination, Rosie the Riveter became an icon of the period. Women were expected to return home when the war ended and the soldiers returned to their jobs. Despite hardships, such as discrimination and lack of child care, many women missed the workplace. This wartime experience helped lay the foundation for the womens movement of the 1960s. African Americans demanded the right to wartime jobs and President Roosevelt ordered that they be given opportunity. Many more African Americans moved to cities in the north and on the Pacific coast to work in wartime industries. African Americans made some strides in the military during the war, such as the Tuskegee Airmen; however, they still served in segregated units, as was the experience in previous wars, and were often assigned duties of lesser importance because of racial prejudice that often led those in power to doubt in their capabilities. The role played by African American soldiers in the war and the treatment by whites on the home front during and after the war ended prompted President Truman to order that the army be desegregated after WWII. The experiences of African Americans proving themselves by serving their country at home and abroad (called the double victory campaign) helped to lay the foundation for the Civil Rights movement of the 1960s. Japanese Americans faced the most profound discrimination. Following the bombing of Pearl Harbor, 110,000 Japanese Americans were moved to internment camps in the western deserts of the United States. Made to leave their homes and businesses with little warning or compensation for the loss of their possessions and livelihoods, they were imprisoned behind barbed wire fences without the right to a trial and without proof that they were disloyal. Nonetheless, the Japanese Americans continued to be loyal to the United States. Some of them served with distinction in military units in the European theater. As a result of the war, political boundaries of some nation-states were changed and some governments were altered. The United States established a democracy in occupied Japan. Germany was divided into four zones and occupied by the four Allied powers. Soon the United States, Great Britain and France united their zones and helped to create a democratic government in what later became known as West
Germany. The Soviet Union established a communist government in East Germany. Berlin, the former capital of Germany, was similarly divided although it was located entirely within the Soviet zone. The Soviet Union also set up puppet regimes in the eastern European nations that they liberated from German occupation. Although the United States emerged from the war as a dominant world power, it would soon find itself in confrontation with its World War II ally, the Soviet Union. The Cold War had its roots in differences in wartime priorities between the United States, Great Britain and France, and the Soviet Union.
WWII Notes: Summarize key developments in technology, aviation, weaponry, and communication and their effects on WWII and the United States economy.
New Technology
Airplanes
How Used
Dropped supplies and troops behind enemy lines, dropped bombs Used to destroy Hiroshima and Nagasaki, bought an end to the war Allowed secret messages across enemy lines Gave advanced warning of planes, ships, their location and movement Used to break codes
Atomic Bomb
Codes
Radar
Computers
Key developments in technology, aviation, weaponry, and communication had a significant impact on World War II and on the economy of the United States both during the war years and in the postwar period. With the increase in production necessary to sustain the war effort, the economy of the United States experienced a boost, lifting the nation out of the Great Depression. Medical advances in the treatment of infection and disease such as the first antibiotic,
penicillin have helped to prolong the lives of many Americans and contributed to an aging population. Aviation innovations included improved bombers that were able to fly farther and the use of radar to track these planes and to spot enemy planes. By the end of the war, jets were being developed. After the war, personal and business air travel and the transportation of goods around the world grew significantly because of the technology of the airplane. Secret communications codes developed during the war contributed to the development of computer systems designed to break those codes. The first computers were room-sized machines. The computer industry has grown tremendously in the last 60 years and as a result Americans enjoy almost instant access to information through the use of their personal computers, lap tops, smart phones, tablets and other handheld devices. Advances in weaponry were made in response to wartime needs. The two atom bombs that were dropped on Japan were developed by a team of scientists in the United States who were trying to beat the Germans to the technology. [Although Albert Einstein encouraged President Franklin Delano Roosevelt to establish the Manhattan Project that developed the bomb, he was not involved in the process.] Atomic technology has had a significant impact on the economy of the United States since World War II. The arms race started as a result of Americas exclusive control of the atom bomb. This race to develop new and better bombs and ways to deliver them to the target has resulted in extensive government spending which has both stimulated the economy and focused spending on the military. Peacetime uses of nuclear technology may include a clean and renewable source of energy. However, Americans are cautious about this technology.
Notes on WWII The principal events related to the United States involvement in World War II include the rise of European dictators such as Benito Mussolini in Italy and Adolf Hitler in Germany as a result of the Depression. Hitler used military aggression against the rest of Europe to secure his goals. Japanese also had a militaristic government that was seeking to expand their nations power World War II was fought between the Axis powers (Germany, Italy, and Japan) and the Allied powers (England, France, the Soviet Union, the US, and a many other countries). The major aggressor in WWII was Germany, led by Adolf Hitler. Hitlers Nazi party wanted to take over all of Europe, and quite possibly the world after that! The war began when Germany invaded Poland, and ended with the surrender of Germany and Japan. When Germany invaded Poland, allies Britain and France declared war on Germany. Soon Germany had defeated France and was bombing Great Britain. Germany also invaded the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (U.S.S.R.) even though they were friends. The Americans wanted President Roosevelt to stay neutrality. However President Roosevelt tried to help the British leader, Winston Churchill; and the leader of the Soviet Union, Joseph Stalin, with supplies. After the Japanese bombing of the U.S. Pacific fleet at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii President Roosevelt asked the United States Congress to declare war on Japan. Germany and Italy then declared war on the United States in order to support their ally, Japan, becoming the Axis Powers. The United States, Great Britain, and the Soviet Union became known as the Allied Powers or the Allies. The goal of the Allies was to stop the Axis and defeat them so that they could not invade other countries again. The strategy used by the Allied powers in the European area including the invasions of North Africa and Italy and finally the invasion of Normandy, France. The purpose of the island-hopping strategy in the Pacific area was to invade the Japanese home islands. The invasion of Normandy led to the eventual surrender of the Axis powers in Europe, but the Allied powers continued to struggle against a Japanese army that was determined to fight to the last man. Then President Roosevelt died and Vice-President Harry S Truman became President. As they prepared for the invasion of Japan continued, Einstein tested the worlds first atomic bomb. The decision of whether to risk many more American lives with an invasion of Japan or to use the atomic bombs fell to Truman. The United States dropped two bombs, one on Hiroshima and a second on Nagasaki, which led to the surrender of the Japanese and brought about the end of World War II. The United States entered the war when the Japanese attacked Pearl Harbor, a US naval base in Hawaii. More people died and more damage was done in World War II than in any other war. Millions of Jews and other innocent civilians were killed in Nazi concentration camps. The atomic bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki began the nuclear age. In WWII, soldiers fought with a variety of tanks, guns, airplanes and bombs. Different armies from different nations used different weapons and machines. At the end of the war, two atom bombs were deployed by the United States against Japan. It was the first and only time that nuclear weapons have been used in warfare.
You might also like
- TELESCOPING THE TIMES The United States in World War IIDocument3 pagesTELESCOPING THE TIMES The United States in World War IID KangNo ratings yet
- 101 Amazing Facts about The Second World WarFrom Everand101 Amazing Facts about The Second World WarRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Standard 19 NotesDocument3 pagesStandard 19 Notesapi-248438174No ratings yet
- US Entry into WWII & Global PowerDocument5 pagesUS Entry into WWII & Global PoweralikhanNo ratings yet
- Reading Wwii ApushDocument12 pagesReading Wwii Apushapi-297350857No ratings yet
- What Happened After World War II? History Book for Kids | Children's War & Military BooksFrom EverandWhat Happened After World War II? History Book for Kids | Children's War & Military BooksNo ratings yet
- C 25 NotesDocument6 pagesC 25 NotesTrimaan MalikNo ratings yet
- World War II and Its Effects On SocietyDocument9 pagesWorld War II and Its Effects On SocietyAkinyiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 35Document4 pagesChapter 35api-238157510No ratings yet
- International ConflictsDocument31 pagesInternational Conflictsapi-331862987No ratings yet
- USA and The Second World WarDocument5 pagesUSA and The Second World WarТетяна Леонідівна МешкоNo ratings yet
- The Causes of World War 2 History EssayDocument5 pagesThe Causes of World War 2 History EssayEmilianPopescuNo ratings yet
- US History Spring Semester Exam ReviewDocument9 pagesUS History Spring Semester Exam ReviewAlyssa Elaine ParraNo ratings yet
- WWII Essential QuestionsDocument8 pagesWWII Essential QuestionsKJHNo ratings yet
- America in World War II (Presentation) Author Sharyland ISDDocument39 pagesAmerica in World War II (Presentation) Author Sharyland ISDJeremia MaghinangNo ratings yet
- Lecture ch25Document40 pagesLecture ch25api-171412573No ratings yet
- Social CH 2.3,4,5Document13 pagesSocial CH 2.3,4,5RastapipesNo ratings yet
- Ingles UsagbDocument5 pagesIngles UsagbpelosirosnanetNo ratings yet
- MidtermpaperDocument7 pagesMidtermpaperapi-292876362No ratings yet
- CHP 26Document5 pagesCHP 26Daniel LiNo ratings yet
- World War II. America's Motivation and Impact Author Iowa Department of Cultural AffairsDocument32 pagesWorld War II. America's Motivation and Impact Author Iowa Department of Cultural AffairsJeremia MaghinangNo ratings yet
- Effects of World War IIDocument3 pagesEffects of World War IIIrep Princeroy DavisNo ratings yet
- GR 9 US Entering WWIIDocument17 pagesGR 9 US Entering WWIImrgleesonNo ratings yet
- History 261 EssayDocument6 pagesHistory 261 EssayRobert AndersonNo ratings yet
- Pearl Harbor NHD Final DraftDocument15 pagesPearl Harbor NHD Final Draftapi-272925787No ratings yet
- Rakesh Kumar: Second World WarDocument24 pagesRakesh Kumar: Second World Warthakur_rinku75No ratings yet
- WWII AftermathDocument2 pagesWWII AftermathElisa Aguilar YonNo ratings yet
- ch._22_ppt_-_wwii_1941_-_1945Document65 pagesch._22_ppt_-_wwii_1941_-_1945Reagan StoneNo ratings yet
- World War II Study NotesDocument4 pagesWorld War II Study Notesapi-254473256100% (1)
- World War Two Study GuideDocument4 pagesWorld War Two Study GuideJeremy Keeshin100% (8)
- American HistoryDocument3 pagesAmerican Historyale.calafiore1No ratings yet
- A Brief History of ww2Document4 pagesA Brief History of ww2Radu EnacheNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Topics On World War 2Document4 pagesResearch Paper Topics On World War 2s1bebopalyn2100% (1)
- 9th-Cold WarDocument42 pages9th-Cold WarTooba ZaidiNo ratings yet
- PZMJ Ge YP9 WPLNH 6 CHSV IDocument4 pagesPZMJ Ge YP9 WPLNH 6 CHSV Isupriyabharti2207No ratings yet
- Factors Leading to WWII AnalyzedDocument9 pagesFactors Leading to WWII AnalyzedYatharth KohliNo ratings yet
- The Lowdown On The Showdown - World War IiDocument12 pagesThe Lowdown On The Showdown - World War IiIgnatius TisiNo ratings yet
- Global Divides The North and SouthDocument19 pagesGlobal Divides The North and SouthKent Alvin GuzmanNo ratings yet
- World War 3Document1 pageWorld War 3Mateo TeodorNo ratings yet
- U.S Entry Into WWIDocument17 pagesU.S Entry Into WWIEmaan ShahNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgDnh00cJVCLBbRC8a-45mLIP2fELmks9lRUljf 9FTAeid5v58xHqFhUg l10 q72 D7IMlrTE975Fw-yEvVSn54utpb6R90IwRISMplqogByB7LBu9zbZtyt4Document9 pagesACFrOgDnh00cJVCLBbRC8a-45mLIP2fELmks9lRUljf 9FTAeid5v58xHqFhUg l10 q72 D7IMlrTE975Fw-yEvVSn54utpb6R90IwRISMplqogByB7LBu9zbZtyt4CooglyBearNo ratings yet
- USA Ussr Government: Stalin Had Ruled As A Dictator SinceDocument17 pagesUSA Ussr Government: Stalin Had Ruled As A Dictator SinceAmelie SummerNo ratings yet
- U S History7pagepaperroughdraftDocument8 pagesU S History7pagepaperroughdraftapi-237945611No ratings yet
- 2.cold WarDocument43 pages2.cold WarahsanNo ratings yet
- America 5Document2 pagesAmerica 5EINSTEINNo ratings yet
- The Major Causes, Impacts of WWIIDocument6 pagesThe Major Causes, Impacts of WWIIvannesaNo ratings yet
- World War II: MR - Cleggett Luis Torres Mod 3Document4 pagesWorld War II: MR - Cleggett Luis Torres Mod 3Luis TorresNo ratings yet
- The Cold WarDocument13 pagesThe Cold WarFlorin PriboiNo ratings yet
- Cold WarDocument43 pagesCold WarSherman UllahNo ratings yet
- Homework 7-ADocument5 pagesHomework 7-ALandon PeckhamNo ratings yet
- Cold War in AfricaDocument17 pagesCold War in AfricaONAOLAPONo ratings yet
- Research Based English ProjectDocument8 pagesResearch Based English ProjectAnamta KhanNo ratings yet
- Legacyof World War IIDocument4 pagesLegacyof World War IIfantasyunicornoofNo ratings yet
- Further Immigration, Expansion, and IndustrializationDocument4 pagesFurther Immigration, Expansion, and IndustrializationAndra ElisaNo ratings yet
- Key People To Be Identified:: Unit Six: World War IDocument5 pagesKey People To Be Identified:: Unit Six: World War Ibrian huntsonNo ratings yet
- Origins of The CW Tci ReadingDocument8 pagesOrigins of The CW Tci Readingapi-235209117No ratings yet
- 20th Century DevelopmentsDocument7 pages20th Century DevelopmentsAmeenIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Professional Self Assessment FormDocument2 pagesProfessional Self Assessment Formapi-216728214No ratings yet
- Professional Self Assessment 1Document2 pagesProfessional Self Assessment 1api-216728214No ratings yet
- Browns EvaluationsDocument7 pagesBrowns Evaluationsapi-216728214No ratings yet
- Claflin University School of EducationDocument4 pagesClaflin University School of Educationapi-216728214No ratings yet
- Video Consent FormDocument1 pageVideo Consent Formapi-216728214No ratings yet
- Math DataDocument1 pageMath Dataapi-216728214No ratings yet
- Adept Evaluation SummaryDocument1 pageAdept Evaluation Summaryapi-216728214No ratings yet
- Long Range PlanDocument17 pagesLong Range PlanWhitleyHurdNo ratings yet
- Praxis ScoresDocument2 pagesPraxis Scoresapi-216728214No ratings yet
- New EvalsDocument6 pagesNew Evalsapi-216728214No ratings yet
- 1st Time TestDocument5 pages1st Time Testapi-216728214No ratings yet
- 2nd Time TestDocument5 pages2nd Time Testapi-216728214No ratings yet
- TransformationsDocument16 pagesTransformationsapi-216728214No ratings yet
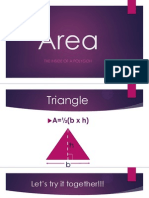
- AreaDocument8 pagesAreaapi-216728214No ratings yet
- AreaDocument8 pagesAreaapi-216728214No ratings yet
- Standards SsDocument3 pagesStandards Ssapi-216728214No ratings yet
- Instructional Strategies WkstsDocument4 pagesInstructional Strategies Wkstsapi-216728214No ratings yet
- StandardsDocument2 pagesStandardsapi-216728214No ratings yet
- Readers TheaterDocument4 pagesReaders Theaterapi-216728214No ratings yet
- Using DataDocument2 pagesUsing Dataapi-216728214No ratings yet
- Video Lesson Plan-Tech Aviation and CommunicationDocument4 pagesVideo Lesson Plan-Tech Aviation and Communicationapi-216728214No ratings yet
- World War II Booklet RubricDocument1 pageWorld War II Booklet Rubricapi-216728214No ratings yet
- PerimeterDocument3 pagesPerimeterapi-216728214100% (1)
- Unit Work Sample-WwiiDocument11 pagesUnit Work Sample-Wwiiapi-216728214100% (1)
- Objective: Test ScoresDocument1 pageObjective: Test Scoresapi-216728214No ratings yet
- Claflin University School of Education: EDUC 450: Professional Clinical Practice Reflective Lesson Plan ModelDocument3 pagesClaflin University School of Education: EDUC 450: Professional Clinical Practice Reflective Lesson Plan Modelapi-216728214No ratings yet
- Classroom ManagementDocument4 pagesClassroom Managementapi-216728214No ratings yet
- AreaDocument4 pagesAreaapi-216728214No ratings yet
- Video Lesson Plan-Tech Aviation and CommunicationDocument4 pagesVideo Lesson Plan-Tech Aviation and Communicationapi-216728214No ratings yet
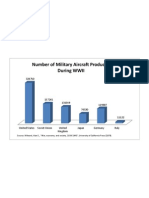
- Aircraft Production Graph WWIIDocument1 pageAircraft Production Graph WWIIsteven_e_kleinNo ratings yet
- WW2 Outline GuideDocument37 pagesWW2 Outline GuideJan muhammadNo ratings yet
- Social Impact of Technology Online Exam 2Document13 pagesSocial Impact of Technology Online Exam 2Venisha Daniels0% (1)
- WWII Timeline AssignmentDocument1 pageWWII Timeline AssignmentwitekmtNo ratings yet
- 7 Wwi - DBQDocument8 pages7 Wwi - DBQMs_Thompson100% (1)
- Factors that Led to WW1Document2 pagesFactors that Led to WW1Kirusaanth SathiyathasanNo ratings yet
- Causes of I World WarDocument4 pagesCauses of I World WaramayalibelulaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 - End of The WarDocument4 pagesLesson 7 - End of The Warapi-295154189No ratings yet
- Christopher Greenwood, The Concept of War in Modern International LawDocument24 pagesChristopher Greenwood, The Concept of War in Modern International LawShrey SomNo ratings yet
- WWII: The Deadliest ConflictDocument2 pagesWWII: The Deadliest ConflictmikaNo ratings yet
- The Most Secret List of Soe Agents: ADocument129 pagesThe Most Secret List of Soe Agents: AeliahmeyerNo ratings yet
- Collocations Unit 39Document3 pagesCollocations Unit 39Đào Gia KhánhNo ratings yet
- Flow Chart AssignmentDocument7 pagesFlow Chart Assignmentzwbennett4No ratings yet
- Von Dach Bern H - Total ResistanceDocument93 pagesVon Dach Bern H - Total ResistanceAlvaro Elizalde100% (1)
- WWII Timeline: Key Events 1939-1945Document2 pagesWWII Timeline: Key Events 1939-1945Viviana GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Ernesto Che Guevara Guerrilla Warfare PDFDocument2 pagesErnesto Che Guevara Guerrilla Warfare PDFAprilNo ratings yet
- Battle of SurabayaDocument6 pagesBattle of Surabayaheri100% (1)
- Korean War Divides PeninsulaDocument8 pagesKorean War Divides PeninsulaMuhammad SajjadNo ratings yet
- Occasional Paper 2 ICRCDocument82 pagesOccasional Paper 2 ICRCNino DunduaNo ratings yet
- Pedido Libros Que No Tiene La LibreriaDocument42 pagesPedido Libros Que No Tiene La LibreriaJose Carlos BenavidesNo ratings yet
- Wwi Main Causes WorksheetDocument2 pagesWwi Main Causes Worksheetapi-263356428100% (2)
- Operational ArtDocument83 pagesOperational Artyasmanyerick100% (11)
- Infiltration Tactics GuideDocument4 pagesInfiltration Tactics GuideChristopher BurkeNo ratings yet
- Frieser PrecisDocument3 pagesFrieser Precisfield_of_mars2176No ratings yet
- MSL 401 Values and Ethics Section 01 - Law of War and Rules of Engagement (ROE)Document18 pagesMSL 401 Values and Ethics Section 01 - Law of War and Rules of Engagement (ROE)EheyehAsherEheyehNo ratings yet
- Name: GP Capt Sameer Pradhan Syndicate: Arihant Words: 545 (75% of Total)Document2 pagesName: GP Capt Sameer Pradhan Syndicate: Arihant Words: 545 (75% of Total)SAMEER PRADHANNo ratings yet
- Generations of Warfare: A History of Tactics and TechnologyDocument9 pagesGenerations of Warfare: A History of Tactics and TechnologysajjadNo ratings yet
- Pitched Battle - WikipediaDocument12 pagesPitched Battle - WikipediadopointtNo ratings yet
- Hitler's Foreign Policy Leads to World War IIDocument4 pagesHitler's Foreign Policy Leads to World War IIShadreck Maganga100% (1)
- (John Buckley) AIR POWER IN THE AGE OF TOTAL WAR ( (BookFi) PDFDocument273 pages(John Buckley) AIR POWER IN THE AGE OF TOTAL WAR ( (BookFi) PDFsohail akbarNo ratings yet