Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2.3 Explain Function: Clo3: Solve Related Problems Critically Using Appropriate Formulae and Concepts. (C3, A1)
Uploaded by
Shaiful AsadOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2.3 Explain Function: Clo3: Solve Related Problems Critically Using Appropriate Formulae and Concepts. (C3, A1)
Uploaded by
Shaiful AsadCopyright:
Available Formats
2.
3 EXPLAIN FUNCTION
CLO3: SOLVE RELATED PROBLEMS CRITICALLY USING APPROPRIATE FORMULAE AND CONCEPTS. (C3, A1 )
1
BA202 Discrete Mathematics
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Describe basic constructions. Explain the properties of following functions:
One-to-one functions Onto functions Composition functions Inverse functions
Describe graphs of the Floor and Ceiling functions.
liyana
JMSK , POLITEKNIK BALIK PULAU
BA202 Discrete Mathematics
FUNCTIONS
Let A and B be nonempty sets. A function A to B is an assignment of exactly one element of B to each element of A . Write as : (Function from A to B) Function sometimes called mapping. (Mapping input to output)
liyana
JMSK , POLITEKNIK BALIK PULAU
BA202 Discrete Mathematics
FUNCTIONS
Assignment of grades in Discrete Mathematic Class = + 1
liyana
JMSK , POLITEKNIK BALIK PULAU
BA202 Discrete Mathematics
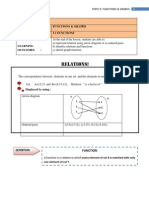
IS THIS A FUNCTION?
R = { (1,a), (2,b), (3,b), (4, c) R is a function from A to B. Exactly one element in B is assigned to every element of A.
liyana
JMSK , POLITEKNIK BALIK PULAU
BA202 Discrete Mathematics
IS THIS A FUNCTION?
R= {(1,a), (2,b), 3,c)} R is not a function Because 4 belongs to A and 4 is not associated with any element of B. R is only a relation but not a function.
liyana
JMSK , POLITEKNIK BALIK PULAU
BA202 Discrete Mathematics
IS THIS A FUNCTION?
R= {(1,a), (1,b), (2,c), (3,c), (4,c) Not function Because 1 belongs to A and 1 is associated with two element of B.
liyana
JMSK , POLITEKNIK BALIK PULAU
BA202 Discrete Mathematics
IS THIS A FUNCTION?
f(x) = {(1,2), (2,3), (3,4)} Funtion Exactly one element in y is associated with every element in x
liyana
JMSK , POLITEKNIK BALIK PULAU
BA202 Discrete Mathematics
TERMS IN FUNCTON
Everywhere defined Domain Codomain Range Image Pre-image/Inverse image
liyana
JMSK , POLITEKNIK BALIK PULAU
BA202 Discrete Mathematics
EVERYWHERE DEFINED
Let f be a function from A to B. Then we say that f is everywhere defined function if Dom(f) = A. In other words, all domain are used.
Everywhere defined
Not everywhere defined
liyana
JMSK , POLITEKNIK BALIK PULAU
10
BA202 Discrete Mathematics
TERMS IN FUNCTION
f is a function from A to B represented by the diagram above: Domain : All element in A
{ Adam, Chou, Ali, Steven, Jacob }
Codomain : All element in B
Codomain : { A, B, C, D, E }
Range : Element in B that associated with element in A
{ A, B, C, E }
liyana
JMSK , POLITEKNIK BALIK PULAU
11
BA202 Discrete Mathematics
TERMS IN FUNCTION
Image : If f(a) = b, the image of a is b f(Adam) = A
The image of Adam is A The image of Jacob is E
Pre-image or inverse image
Pre-image of A are Adam and Steven Pre-image of B is Ali Tambah objek
liyana
JMSK , POLITEKNIK BALIK PULAU
12
BA202 Discrete Mathematics
PROPERTIES OF FUNCTION
One to One Onto Composition Inverse
liyana
JMSK , POLITEKNIK BALIK PULAU
13
BA202 Discrete Mathematics
ONE TO ONE FUNCTION
Function that assign one value in the domain to one value in codomain and Never assign the same value of codomain to two different domain elements. Also known as injective.
liyana
JMSK , POLITEKNIK BALIK PULAU
14
BA202 Discrete Mathematics
ONTO FUNCTION
All element in the domain is assigned to element in domain All elements in codomain has assignment Also known as surjective.
liyana
JMSK , POLITEKNIK BALIK PULAU
15
BA202 Discrete Mathematics
ONE TO ONE CORRESPONDENCE
A function is one to one correspondence if the function satisfy the properties below:
one to one and onto
Also known as bijection.
liyana
JMSK , POLITEKNIK BALIK PULAU
16
BA202 Discrete Mathematics
INVERSE
To define Inverse Function, the function has to be one to one correspondence. A function is not invertible if it is not a one -to-one correspondence, because the inverse of such function does not exist.
It is not a function c is element in the domain but not associated with any element in codomain element a is assigned to two different element in codomain
liyana
JMSK , POLITEKNIK BALIK PULAU
inverse
17
BA202 Discrete Mathematics
INVERSE
To obtain the inverse function, simply reversing the direction of each arrow. For example :
= {(1,a), (2,c), (3,b)} 1 = { (a, 1), (c,2), (b,3) }
liyana
JMSK , POLITEKNIK BALIK PULAU
18
BA202 Discrete Mathematics
INVERSE
= 2 5. Find 1 () .
Let
= 2 5
2 = + 5 =
+5 2 +5 2
1 =
liyana
JMSK , POLITEKNIK BALIK PULAU
19
BA202 Discrete Mathematics
INVERSE
= 2 2 + 5. Find 1 (2) Let = 2 2 + 5 2 2 = 5 2 = =
5 2 5 2 5 2
1 2 =
52 2
= 1.5 = 1.2247
1 =
liyana
JMSK , POLITEKNIK BALIK PULAU
20
BA202 Discrete Mathematics
INVERSE
= + 10. 1 = 12. . Let = + 10 = 10 1 = 10 10 = 12 = 12 + 10 = 22
liyana
JMSK , POLITEKNIK BALIK PULAU
21
BA202 Discrete Mathematics
EXERCISES
Find inverse of = 3 2. Find 1 5 of function = ( 3) 2 Function = 1 = 10
3
2 . 3
Find the value of when
liyana
JMSK , POLITEKNIK BALIK PULAU
22
BA202 Discrete Mathematics
COMPOSITE
Combination of two functions. If we have two functions, f(x) and g(x) the composite of f(x) and g(x) can be denote as : fg(x) f g
liyana
JMSK , POLITEKNIK BALIK PULAU
23
BA202 Discrete Mathematics
COMPOSITE
= 2 + 5 = 3 = 3 = 2 3 + 5 = 2 6 + 5 = 2 1
= 2 + 5 = 2 + 5 3 = 2 + 2
liyana
JMSK , POLITEKNIK BALIK PULAU
24
BA202 Discrete Mathematics
EXERCISES
Given = 4 2 1 and = 3 + 2. Find each of the followings:
i. ii. (5) iii. 1 ()
liyana
JMSK , POLITEKNIK BALIK PULAU
25
BA202 Discrete Mathematics
COMPOSITE
= 2 = 2 4 + 8 Find ()
= 2 4 + 8 2 = 2 4 + 8 Assume = 2 = + 2 = ( + 2) 2 4 + 2 + 8 2 + 4 = 2 + 4
liyana
JMSK , POLITEKNIK BALIK PULAU
26
BA202 Discrete Mathematics
EXERCISE
= 2 = 3 5 Find Solve the equation = 1
liyana
JMSK , POLITEKNIK BALIK PULAU
27
BA202 Discrete Mathematics
GRAPH FUNCTION
Two important function in discrete Mathematics:
Floor Function Ceiling Function
liyana
JMSK , POLITEKNIK BALIK PULAU
28
BA202 Discrete Mathematics
FLOOR FUNCTION
The floor function rounds x down to the closest integer less than or equal to x. Example :
1.5 = 1 1.5 = 2 7 =7 6.9 = 6
liyana
JMSK , POLITEKNIK BALIK PULAU
29
BA202 Discrete Mathematics
FLOOR FUNCTION
Draw a graph for =
liyana
JMSK , POLITEKNIK BALIK PULAU
30
BA202 Discrete Mathematics
CEILING FUNCTION
The ceiling function round x up to the closest integer greater than or equal to x Example :
0.5 = 1 1 =1 2.1 = 3
liyana
JMSK , POLITEKNIK BALIK PULAU
31
BA202 Discrete Mathematics
CEILING FUNCTION
Draw a graph for =
liyana
JMSK , POLITEKNIK BALIK PULAU
32
You might also like
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsFrom EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- DC Chap1A FunctionsDocument96 pagesDC Chap1A FunctionsRon PascualNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1 GenMath FUNCTIONSDocument15 pagesLESSON 1 GenMath FUNCTIONSCarla Jane MartinNo ratings yet
- EN112 - Functions and Limits 1: Department of Mathematics and Computer ScienceDocument22 pagesEN112 - Functions and Limits 1: Department of Mathematics and Computer SciencePoli KialouNo ratings yet
- Discrete MathematicsDocument4 pagesDiscrete MathematicsxaiiNo ratings yet
- A18 - Exp and Log Fcns VJDocument172 pagesA18 - Exp and Log Fcns VJJeffry RamonidaNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Discretization of Laplace and Poisson EquationsDocument27 pagesFinite Element Discretization of Laplace and Poisson EquationsВладимир СмирновNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Week 1 - Quarter 1 - Gen MathDocument12 pagesModule 1 - Week 1 - Quarter 1 - Gen MathKaru GreyNo ratings yet
- Activity On Forms of QFDocument1 pageActivity On Forms of QFCESAR HERRERANo ratings yet
- wqd10202 Technicalmathii Complex Number PDFDocument33 pageswqd10202 Technicalmathii Complex Number PDFShantha KumarNo ratings yet
- Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson QuizDocument22 pagesWarm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson QuizDrew StrauchNo ratings yet
- Special Functions Supported by EasycalcDocument5 pagesSpecial Functions Supported by EasycalcMichael TaylorNo ratings yet
- Discrete PPT 11 11 22Document143 pagesDiscrete PPT 11 11 22DenjiNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1673761924437 7020266334714414407Document39 pagesOrca Share Media1673761924437 7020266334714414407Kate ComonicalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document18 pagesChapter 1Jhoanna Mae Ibasan IbasanNo ratings yet
- SHT PDFDocument26 pagesSHT PDFUtkarsh RajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Function and RelationDocument25 pagesChapter 5 Function and RelationShina GalvezNo ratings yet
- "MathnotesDocument2 pages"MathnotesDeslisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document55 pagesChapter 2Jacky AKA BrizzardNo ratings yet
- Gen MathDocument5 pagesGen MathFłór GïęłūNo ratings yet
- Functions UpdatedDocument54 pagesFunctions UpdatedviditNo ratings yet
- Chuong 7Document210 pagesChuong 7Đức TríNo ratings yet
- MAT 128 Quantitative Methods Spring 2019 Wednesday 1/16Document4 pagesMAT 128 Quantitative Methods Spring 2019 Wednesday 1/16goflux pwnsNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions Class 12 Notes Maths Chapter 2Document10 pagesInverse Trigonometric Functions Class 12 Notes Maths Chapter 2poda84No ratings yet
- Modeling & SimulationDocument445 pagesModeling & SimulationKflemariam AbayNo ratings yet
- II PUC - Mathematics (TARGET CENTUM) - Question BankDocument68 pagesII PUC - Mathematics (TARGET CENTUM) - Question BankKumkum Kumbarahalli100% (1)
- Module 1 - Week 1 - Gen.-Math-2-FINALDocument12 pagesModule 1 - Week 1 - Gen.-Math-2-FINALKenneth IbarraNo ratings yet
- Review For General Mathematics: Prepared By: Eden G. Aniversario, LPTDocument23 pagesReview For General Mathematics: Prepared By: Eden G. Aniversario, LPTDonzkie YTNo ratings yet
- Week 9 (Sept 21) Exponential and LogarithmicDocument4 pagesWeek 9 (Sept 21) Exponential and LogarithmicdwilfilwqdnxewijdjwefioNo ratings yet
- Maths Functions and Relations HW (Incase Any1 From My Class Wants Them)Document10 pagesMaths Functions and Relations HW (Incase Any1 From My Class Wants Them)ehan.ilrnestersNo ratings yet
- Day 1Document18 pagesDay 1ALLAN GABRIEL GOJOCONo ratings yet
- Xii Maths Internal Assessment ActivityDocument2 pagesXii Maths Internal Assessment ActivityGangeshNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document17 pagesUnit 2Sagnik GangulyNo ratings yet
- Week 1 General MathematicsDocument10 pagesWeek 1 General MathematicsMarcel Baring ImperialNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Functions in One ShotDocument86 pagesJEE Main Functions in One ShotLNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document1 pageAssignment 2Martin ChengNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Functions & GraphsDocument32 pagesUnit 8 Functions & Graphsحفيظو عبداللهNo ratings yet
- ENGG2420B Assignment 2 Complex Numbers and Functions Complex IntegrationDocument1 pageENGG2420B Assignment 2 Complex Numbers and Functions Complex IntegrationMartin ChengNo ratings yet
- Dot Product of 2-D VectorsDocument2 pagesDot Product of 2-D VectorsmailbabuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Complex NumberDocument28 pagesChapter 1 Complex NumbereliynwanieyNo ratings yet
- Finite Set:: Finite and Infinite SetsDocument12 pagesFinite Set:: Finite and Infinite SetsKuldeep KheemaniNo ratings yet
- HW 3.2.1 Solving Equations Using e and LNDocument3 pagesHW 3.2.1 Solving Equations Using e and LNSanjay SundaramNo ratings yet
- General MathematicsDocument8 pagesGeneral MathematicsCynthia SantosNo ratings yet
- GENMATH FunctionsDocument28 pagesGENMATH FunctionsVictorio MaldicasNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 2 Q. 1 (A) Solve The System of Linear Equation Using Matrices: X+ 2y - 3z 1 2x - y + Z 2 X - Z 3Document23 pagesAssignment No. 2 Q. 1 (A) Solve The System of Linear Equation Using Matrices: X+ 2y - 3z 1 2x - y + Z 2 X - Z 3Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Department of Computer Science, CUI Lahore Campus: CSC102 - Discrete Structures by Mahwish WaqasDocument54 pagesDepartment of Computer Science, CUI Lahore Campus: CSC102 - Discrete Structures by Mahwish WaqasSubhan ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1.05 - Cartesian Product and FunctionsDocument15 pagesLecture 1.05 - Cartesian Product and FunctionsAmelia AmeliaNo ratings yet
- FINAL CORE 3 - General MathematicsDocument82 pagesFINAL CORE 3 - General MathematicsJelamie ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Queen Anne School: General Mathematics Week 1Document8 pagesQueen Anne School: General Mathematics Week 1Monica Joyce NaperiNo ratings yet
- Tos Math IvDocument9 pagesTos Math IvAshley Lamor Kanaku NishimuraNo ratings yet
- FunctionsDocument30 pagesFunctionsRuby WalshNo ratings yet
- Topic:: Understanding Function and RelationDocument28 pagesTopic:: Understanding Function and RelationCarlos Enriquez IVNo ratings yet
- Ch. 5 Functions GraphsDocument41 pagesCh. 5 Functions GraphsTeo Pui KuanNo ratings yet
- WWW - Classpoint.io Join A Class 62815: Click: ClasscodeDocument37 pagesWWW - Classpoint.io Join A Class 62815: Click: ClasscodejayiaNo ratings yet
- Final Exam General Mathematics FinalDocument2 pagesFinal Exam General Mathematics FinalAldyn PintoyNo ratings yet
- 4.6 1 TransformationsDocument4 pages4.6 1 TransformationsBradley SinghNo ratings yet
- Ma1102R Calculus Lesson 20: Wang FeiDocument9 pagesMa1102R Calculus Lesson 20: Wang FeidelsonwiestNo ratings yet
- Genmath Module 1Document19 pagesGenmath Module 1Eunice SiervoNo ratings yet
- P4 Sample Assesment QPDocument11 pagesP4 Sample Assesment QPMirayNo ratings yet
- Conjectura de Birch e Swinnerton-DyerDocument5 pagesConjectura de Birch e Swinnerton-DyerVICENTENo ratings yet
- Math 6 - Q3 - W3 - FINALDocument9 pagesMath 6 - Q3 - W3 - FINALMarlene Tagavilla-Felipe DiculenNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics I 15mat11 Notes PDFDocument165 pagesEngineering Mathematics I 15mat11 Notes PDFRajNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Axler Linear Algebra Done RightDocument35 pagesSolutions To Axler Linear Algebra Done RightJitender Singh71% (7)
- Unit 9 Post Test ReviewDocument3 pagesUnit 9 Post Test Reviewapi-302577842No ratings yet
- Form 5 - Maths - Chapter 2Document38 pagesForm 5 - Maths - Chapter 2Rajeshvaramana Venkataramana50% (2)
- The University of Edinburgh College of Science and EngineeringDocument13 pagesThe University of Edinburgh College of Science and EngineeringLoh Jun XianNo ratings yet
- Matlab Function Ode45Document2 pagesMatlab Function Ode45jack_hero_56100% (1)
- Tut 5Document1 pageTut 5Toufic JrabNo ratings yet
- Hopfield ExampleDocument10 pagesHopfield ExampleSun BirdsNo ratings yet
- Transformations Concept MapDocument1 pageTransformations Concept Maphemof44839No ratings yet
- Revision Notes P3 0 P7Document6 pagesRevision Notes P3 0 P7Nat GariNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7.1 Basic Properties and Laws of LogarithmsDocument10 pagesLesson 7.1 Basic Properties and Laws of LogarithmsKirsten Shayne Maningas100% (1)
- Book 1 ESO GeometricDocument242 pagesBook 1 ESO Geometricurgazu100% (1)
- Daily Lesson Log: TeacherDocument4 pagesDaily Lesson Log: TeacherJoan Ramirez RongaleriosNo ratings yet
- Properties of Integers Operation With Examples and QuestionsDocument3 pagesProperties of Integers Operation With Examples and QuestionsJoepril Tamon Espartero100% (1)
- FALLSEM2019-20 MAT1011 ETH VL2019201004476 Reference Material I 02-Aug-2019 MAT1011 Module 2.1-Laplace Transform Tables 3Document5 pagesFALLSEM2019-20 MAT1011 ETH VL2019201004476 Reference Material I 02-Aug-2019 MAT1011 Module 2.1-Laplace Transform Tables 3vijayNo ratings yet
- PuzzlesDocument13 pagesPuzzlesTakács IstvánNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument8 pagesChapter TwoBiruk YidnekachewNo ratings yet
- Linear Matrix Period in Max-Plus Algebra: Martin GavalecDocument16 pagesLinear Matrix Period in Max-Plus Algebra: Martin GavalecImam FauziNo ratings yet
- Math 211 - Module 1 - Lesson - 2 - Solution To An OrdinaryDocument5 pagesMath 211 - Module 1 - Lesson - 2 - Solution To An OrdinaryJovy AndoNo ratings yet
- The Z TransformDocument44 pagesThe Z Transformbrian mgabiNo ratings yet
- Week 3 PDFDocument20 pagesWeek 3 PDFGerson MisaelNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra Tutorial - Vector NormDocument3 pagesLinear Algebra Tutorial - Vector NormwildanNo ratings yet
- Logs Express 5packDocument10 pagesLogs Express 5packKevinRick B MalicdanNo ratings yet
- 1 Mat070 Module1 SolnDocument94 pages1 Mat070 Module1 SolnJerico MendañaNo ratings yet
- Report 1 حلDocument24 pagesReport 1 حلIslam ElghandourNo ratings yet
- Relations & Functions and Their RepresentationsDocument129 pagesRelations & Functions and Their RepresentationsDeepanshu KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- GATE 2014 Syllabus For CSEDocument2 pagesGATE 2014 Syllabus For CSEAbiramiAbiNo ratings yet