Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CE 491 - Intro To Matrix Structural Analysis
Uploaded by
fastidious_5Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CE 491 - Intro To Matrix Structural Analysis
Uploaded by
fastidious_5Copyright:
Available Formats
CE 491 INTRODUCTTION TO MATRIX STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS1
INSTRUCTOR: George E. Blandford 161A Raymond Building (859) 257-1855 e-mail: gebland@engr.uky.edu TA: WEB PAGE: Akram Hassan 382 Raymond Building (859) 257-8010 e-mail: akram.hassan@uky.edu http://www.engr.uky.edu/~gebland/ce582
"Our accreditation association and policy of the Graduate School require that there be different assignments and grading criteria for undergraduate students and graduate students in 400G and 500-level courses. For that reason, you will find differences in course requirements and/or grading criteria in this class, posted on the syllabus."
REFERENCES A. Kassimali, Structural Analysis; PWS-Kent; Cincinnati, OH, 1999. (K in course syllabus) Kenneth M. Leet and Chia-Ming Uang, Fundamentals of Structural Analysis, McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, 2002. (L & U in course syllabus) James K. Nelson and Jack C. McCormac, Structural Analysis: Using Classical and Matrix Methods, John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, NJ, 2003 (N & M in course syllabus) W. McGuire, R.H. Gallagher and R.D. Ziemian, Matrix Structural Analysis, Second Edition, John Wiley and Sons, 2000. A. Kassimali, Matrix Analysis of Structures, Brooks/Cole, Cincinnati, OH, 1999. William Weaver, Jr. and James M. Gere, Matrix Analysis of Framed Structures, Second Edition, D. Van Nostrand, New York, NY, 1980. M. Hoit, Computer-Assisted Structural Analysis and Modeling, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1995. T.R. Tauchert, Energy Principles in Structural Mechanics, McGraw-Hill, NY, 1974. COURSE GOALS AND OUTCOMES CE 491 is designed to introduce students to modern topics for analyzing statically indeterminate structures, particularly matrix structural analysis for two-dimensional frame structures. For example, the displacement method of analysis is the overwhelming analysis tool used in modern structural analysis programs. This course will introduce you to this analysis tool and modeling of structural systems and boundary conditions. Furthermore, this course is a prerequisite to the graduate level courses CE 682 Advanced Structural Analysis, CE 684 Slab and Folded Plate Structures, CE 687 Advanced Metal Structures, and CE 782 Dynamics of Structures. At the conclusion of the course, you should be able to:
1
Use the force (flexibility) method to analyze statically indeterminate structures.
The prerequisite for this course is CE 382 Structural Analysis
Use the force method of analysis to solve influence line problems for statically indeterminate structures. Use the displacement (stiffness) method to analyze statically and kinematically indeterminate structural systems. Apply and understand static structural analysis for two-dimensional frame structures including symmetry and antisymmetry boundary conditions.
Such knowledge and capabilities are highly valued in the aerospace, telecommunications, and up-todate structural engineering offices. COURSE GRADE If class participation and attendance are satisfactory, the course grade will be decided using the following weights: Homework Exam #1 Exam #2 Total 25% 35% 40% 100%
ENGINEERING ETHICS It will be assumed that each student subscribes to a professional code of ethics that is the basis for their behavior in class. All exam work, including but not limited to formulation of ideas and methods of approach, must be the work of the student taking the exam. Any and every case where these ethics are violated will be dealt with according to the provisions in the Student Code. The minimum penalty specified by the Student Code for cheating is a failing grade in the course. TEAMS Each student must join a team of two student members. Each team is expected to collaborate and work together on all homework assignments. The team concept will provide students with an opportunity to develop small group interaction skills, mimic the working profession, and should enhance student learning. The instructor will provide you with the team member list next week. HOMEWORK POLICY Homework assignments will be made periodically throughout the semester. All homework assignments involving the solution of problems will be submitted in teams. Each member of the team will submit the completed homework assignment and the team will bundle the completed homework assignments with a paperclip. NOTE: Only one copy of any frame analysis output is required for each team. The instructor will first verify that each team member has submitted a solution for each problem. Solutions that are not submitted or are incomplete will be graded as an n (n = 0 points) for the individual team member who earned that grade. Each team member who has completed the assigned problem will receive the grade given on the evaluated solution. All homework must be submitted at the start of class on the assignment date. Late homework is not acceptable except for unusual circumstances, e.g., an excused absence. Problem solving homework and written text summary homework assignments will be given. No homework will be due on the day
of an exam. Homework will be graded using a letter grade system. The letter grade system is: a = 4 out of 4 points: correct procedure and calculations b = 3 out of 4 points: correct procedure with some calculation errors c = 2 out of 4 points: partially correct procedure and calculations n = 0 out of 4 points: insufficient knowledge or not submitted + = additional point, e. g., b+ = 3.5 out of 4 points SEMESTER EXAMS2 Two semester exams will be given. Exam #1 will last two hours. Exam #2 will be given on Wednesday, May 1 and will last two hours. Exam topics are listed on the course syllabus. Each exam will be open book and notes. SEMESTER GRADING GRADUATE A: B: C: D: E: 90 100 80 89 70 79 NOT AVAILABLE 0 69 UNDERGRADUATE A: B: C: D: E: 85 100 75 84 65 74 55 64 0 63
It is the instructors policy not to return exams in this course.
CE 491 INTRODUCTTION TO MATRIX STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS
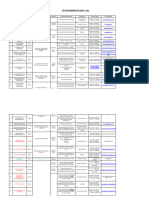
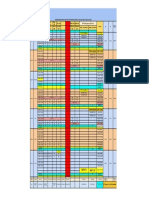
Topic Introduction Review of Linear Algebra Force Method of Analysis Influence Lines for Indeterminate Structures Moment Distribution Analysis Displacement Method of Analysis Two-Dimensional Structures Course Material Appendix B (K) Chapter 13 (K), Chapter 11 (L & U) & Handouts Section 14.1 (K), Chapter 14 (N & M) & Handouts Chapter 16 (K) Sections 16.2 16.3 (L & U), Chapter 17 (K), Chapter 20 (N & M) & Handouts Chapter 10 (K) & Handouts Exam 1 1 1 1 2
Symmetry-Antisymmetry
COURSE DESCRIPTION CE 491 focuses on the flexibility and stiffness methods of analysis using matrix techniques for twodimensional structures.
You might also like
- Intro To Matrix Structural Analysis1Document4 pagesIntro To Matrix Structural Analysis1Ahmad ThaherNo ratings yet
- EAS 207 - ABET - Spring - 20130123Document6 pagesEAS 207 - ABET - Spring - 20130123SyedZain1993No ratings yet
- Syllabus - MEM202 Spring 2009-10Document4 pagesSyllabus - MEM202 Spring 2009-10Vatova JarrandNo ratings yet
- ME 3113 Course PlanDocument3 pagesME 3113 Course PlanxxxtoyaxxxNo ratings yet
- ME5243 Syllabus 1314FDocument3 pagesME5243 Syllabus 1314Fjoe_grnNo ratings yet
- Structures 1Document186 pagesStructures 1Muwaffaq m.100% (1)
- CIVL3206 2014 Semester 2 StudentDocument4 pagesCIVL3206 2014 Semester 2 StudentApril IngramNo ratings yet
- Sum382 12Document7 pagesSum382 12abedejNo ratings yet
- CIV E 321 SyllabDocument2 pagesCIV E 321 SyllabgiorgiNo ratings yet
- Syllabus SP 14 MWFDocument8 pagesSyllabus SP 14 MWFellie<3No ratings yet
- CE 537 SPRSVDocument5 pagesCE 537 SPRSVCarl Justin AzucenaNo ratings yet
- Architectural StructuresDocument462 pagesArchitectural Structuresmatteo_1234100% (1)
- ELGA For CEET311 SyllabusDocument7 pagesELGA For CEET311 SyllabusJoshua HernandezNo ratings yet
- Office Hours: M/W 1:00 - 3:00 or by AppointmentDocument8 pagesOffice Hours: M/W 1:00 - 3:00 or by Appointmentahmed ubeedNo ratings yet
- CE 360 Structural Analysis Course SyllabiDocument3 pagesCE 360 Structural Analysis Course Syllabimagdy bakryNo ratings yet
- Syllabus of Mechanics of MaterialsDocument3 pagesSyllabus of Mechanics of MaterialsAlysson Vany ClochetteNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals, Second Printing (2004) Nob Hill Publishing, 2002 ISBN 0-615-11884-4Document4 pagesFundamentals, Second Printing (2004) Nob Hill Publishing, 2002 ISBN 0-615-11884-4Aline TrindadeNo ratings yet
- 3722013676740Document4 pages3722013676740Mogahid OsmanNo ratings yet
- CE 3010 Syllabus - Summer 2017Document5 pagesCE 3010 Syllabus - Summer 2017PremKumarNo ratings yet
- Sheffield Linear System and Structural AnalysisDocument2 pagesSheffield Linear System and Structural AnalysisphilipyapNo ratings yet
- ES221-2022 FallDocument3 pagesES221-2022 FallAlpay AkpınarNo ratings yet
- MEEN 221 Section 505: Statics and Particle Dynamics: Key InfoDocument5 pagesMEEN 221 Section 505: Statics and Particle Dynamics: Key InfoA SNo ratings yet
- Mee 342 Syllabus GanguliDocument3 pagesMee 342 Syllabus GangulitripsachinNo ratings yet
- Theory of Structures 2 Course OutlineDocument9 pagesTheory of Structures 2 Course OutlineJoshua John Julio100% (1)
- 3rd Sem SyllabusDocument25 pages3rd Sem SyllabusPoornima.M.R KashyapNo ratings yet
- Course Outline (January 24) : Catalog DescriptionDocument6 pagesCourse Outline (January 24) : Catalog Descriptionaly_wael71No ratings yet
- MEM255-202045 SyllabusDocument4 pagesMEM255-202045 SyllabusWilliam J. SmithNo ratings yet
- CVEN1300 Course Profile S2-2014Document6 pagesCVEN1300 Course Profile S2-2014Alan TruongNo ratings yet
- 21MAT41 Fourth Sem Maths Syllabus Commomn To All Except CS and ME Allied BranchesDocument4 pages21MAT41 Fourth Sem Maths Syllabus Commomn To All Except CS and ME Allied BranchesSanjana DeshkumarNo ratings yet
- MECE2304 SylDocument6 pagesMECE2304 Syltiger94731897No ratings yet
- 2 EcesyllDocument91 pages2 Ecesyllchavanakshay1812No ratings yet
- 2013 Math 201 A RobbinsDocument3 pages2013 Math 201 A RobbinsMehmed DuhovicNo ratings yet
- Mech 320 Course OutlineDocument7 pagesMech 320 Course OutlineAnonymous jGFOYpNo ratings yet
- Western New England University College of EngineeringDocument5 pagesWestern New England University College of EngineeringdonjuanNo ratings yet
- Utlnghorn1@mail - Utexas.edu: MATLAB Programming For Engineers, S. J. Chapman, Brooks/Cole, Fourth Edition, 2008Document3 pagesUtlnghorn1@mail - Utexas.edu: MATLAB Programming For Engineers, S. J. Chapman, Brooks/Cole, Fourth Edition, 2008bripinkrNo ratings yet
- BEE301Document4 pagesBEE301cshohil300No ratings yet
- Ee 98 Green SheetDocument7 pagesEe 98 Green SheetMultiLogic11No ratings yet
- Engr213t-Outline F2021Document4 pagesEngr213t-Outline F2021Tom ONo ratings yet
- Syllabus For EGR 233: Dynamics of Rigid BodiesDocument4 pagesSyllabus For EGR 233: Dynamics of Rigid BodiesDamn NationNo ratings yet
- 2 EnccsyllDocument90 pages2 EnccsyllMegha ShreeNo ratings yet
- Che 3722012914905Document4 pagesChe 3722012914905nedian_2006No ratings yet
- Syl 2021Document4 pagesSyl 2021DominicNo ratings yet
- CE 360-001: Sustainable Civil Engineering Materials: Digital Commons at NJITDocument9 pagesCE 360-001: Sustainable Civil Engineering Materials: Digital Commons at NJITnasru hajiNo ratings yet
- University of Wyoming College of Business Department of Economics ECON 4230/5230 Intermediate Econometric Theory Spring 2019Document2 pagesUniversity of Wyoming College of Business Department of Economics ECON 4230/5230 Intermediate Econometric Theory Spring 2019Juan Tomas SayagoNo ratings yet
- Cven1300 Course Profile Session 2 2013Document6 pagesCven1300 Course Profile Session 2 2013Jnrules123No ratings yet
- CE 321 Syllabus - Fall 2017Document5 pagesCE 321 Syllabus - Fall 2017Rashid AliNo ratings yet
- Me3281 2013Document3 pagesMe3281 2013joe_grnNo ratings yet
- 2 EtsyllDocument99 pages2 Etsyllshreyasgrade9No ratings yet
- System Dynamics Syllabus MateriaDocument5 pagesSystem Dynamics Syllabus MateriaChristian JgNo ratings yet
- CHE 379/CHE384: Biochemical, Cellular, and Metabolic Engineering: Principles and PracticesDocument4 pagesCHE 379/CHE384: Biochemical, Cellular, and Metabolic Engineering: Principles and PracticesHalil İbrahim ÖzdemirNo ratings yet
- ME 4141 - Machine Design I Syllabus Veazie Print 1 SummerDocument5 pagesME 4141 - Machine Design I Syllabus Veazie Print 1 SummerJacob Todd HewellNo ratings yet
- Circuits SyllabusDocument9 pagesCircuits SyllabusRaymundo GumabongNo ratings yet
- Zhu CE 329 Syllabus SP 2014Document4 pagesZhu CE 329 Syllabus SP 2014sDq746Gwyn6nNo ratings yet
- NCSU CE 214 Syllabus Spring 2023Document17 pagesNCSU CE 214 Syllabus Spring 2023rtestNo ratings yet
- MAE 241 - Syllabus Summer 2011Document5 pagesMAE 241 - Syllabus Summer 2011kostas.sierros9374No ratings yet
- ABET Syllabus CEE 309 2018 (3 Pages)Document3 pagesABET Syllabus CEE 309 2018 (3 Pages)jhgjghNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Methods in Chemical EngineeringDocument4 pagesMathematical Methods in Chemical EngineeringChauhdry Sahab100% (2)
- Getting Started SYS650Document7 pagesGetting Started SYS650Ty SmithNo ratings yet
- 3049269Document82 pages3049269Saulo Marcondes de MouraNo ratings yet
- 3 D ElasticityDocument40 pages3 D ElasticitySantosh GoudarNo ratings yet
- BromsDocument1 pageBromsfastidious_5No ratings yet
- Design of Laterallyloaded PilesDocument85 pagesDesign of Laterallyloaded Pilesfastidious_5No ratings yet
- Working and Reference-1Document2 pagesWorking and Reference-1fastidious_5No ratings yet
- Mayne and PoulosDocument16 pagesMayne and Poulosfastidious_5No ratings yet
- Working and Reference-1Document2 pagesWorking and Reference-1fastidious_5No ratings yet
- Hookah G 2013 CatalogDocument40 pagesHookah G 2013 Catalogfastidious_5No ratings yet
- PCI DWP Binder Ch1Document39 pagesPCI DWP Binder Ch1fastidious_5No ratings yet
- Tutorial ETABSDocument60 pagesTutorial ETABSValentin VrabieNo ratings yet
- PCI Design ManualDocument91 pagesPCI Design ManualNandeesha Ramesh100% (2)
- Advanced Foundation Engineering by VNS Murthy - Civilenggforall PDFDocument821 pagesAdvanced Foundation Engineering by VNS Murthy - Civilenggforall PDFLaritza Elizabeth100% (11)
- Tutorial ETABSDocument60 pagesTutorial ETABSValentin VrabieNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 PP&EDocument62 pagesTopic 4 PP&Efastidious_5100% (1)
- Chapter 1Document23 pagesChapter 1fastidious_5No ratings yet
- Topic 4 PP&EDocument62 pagesTopic 4 PP&Efastidious_5100% (1)
- Topic 4 PP&EDocument62 pagesTopic 4 PP&Efastidious_5100% (1)
- Private Education Loan Applicant Self-Certification: WWW - Fafsa.ed - GovDocument2 pagesPrivate Education Loan Applicant Self-Certification: WWW - Fafsa.ed - Govfastidious_5No ratings yet
- Foundation Analysis and Design-2-Mat Foundation 213Document42 pagesFoundation Analysis and Design-2-Mat Foundation 213aishabarkath786No ratings yet
- PID Controller Design Process: EEC 414 Wri4ng For Electrical and Computer EngineeringDocument11 pagesPID Controller Design Process: EEC 414 Wri4ng For Electrical and Computer Engineeringfastidious_5No ratings yet
- PCI DWP Binder Ch1Document39 pagesPCI DWP Binder Ch1fastidious_5No ratings yet
- PCI DWP Binder Ch1Document39 pagesPCI DWP Binder Ch1fastidious_5No ratings yet
- OU MEM BrochureDocument3 pagesOU MEM Brochurefastidious_5No ratings yet
- 2-8 PetronasDocument33 pages2-8 Petronasfastidious_5No ratings yet
- Solar Catalog Sherwin SolarbusDocument212 pagesSolar Catalog Sherwin Solarbusfastidious_5No ratings yet
- PID Controller Design Process: EEC 414 Wri4ng For Electrical and Computer EngineeringDocument11 pagesPID Controller Design Process: EEC 414 Wri4ng For Electrical and Computer Engineeringfastidious_5No ratings yet
- Eeec 414Document11 pagesEeec 414fastidious_5No ratings yet
- PID Controller Design Process: EEC 414 Wri4ng For Electrical and Computer EngineeringDocument11 pagesPID Controller Design Process: EEC 414 Wri4ng For Electrical and Computer Engineeringfastidious_5No ratings yet
- Cleveland State University: Campus MapDocument1 pageCleveland State University: Campus Mapfastidious_5No ratings yet
- 2-8 PetronasDocument33 pages2-8 Petronasfastidious_5No ratings yet
- Characteristic of Cause and Effect EssayDocument6 pagesCharacteristic of Cause and Effect EssayMohamad Elias Othman100% (1)
- Portfolio Ready Acpa NaspaDocument10 pagesPortfolio Ready Acpa Naspaapi-448323503No ratings yet
- Narrative Report - Lac Session On RPMS 2020 2021Document4 pagesNarrative Report - Lac Session On RPMS 2020 2021Riza Guste90% (31)
- A.J. Ayer - The Concept of A Person 1963Document288 pagesA.J. Ayer - The Concept of A Person 1963JYDeGroot100% (4)
- Sample SPM SpeechDocument2 pagesSample SPM SpeechAnonymous pOoMwcjNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in ArtsDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in ArtsNiño Ronelle Mateo Eligino83% (70)
- NPTEL Summer and Winter InternshipDocument6 pagesNPTEL Summer and Winter Internshipsankarsada100% (1)
- E-Portfolio DefinitionDocument2 pagesE-Portfolio DefinitioneportfoliosNo ratings yet
- Teaching Productive Skills - WDocument3 pagesTeaching Productive Skills - WGheorghita DobreNo ratings yet
- Auburn Core CurriculumDocument1 pageAuburn Core CurriculumLuisPadillaNo ratings yet
- CBSE School Quality Assessment and AssuranceDocument9 pagesCBSE School Quality Assessment and AssuranceMaxtron MoonNo ratings yet
- Database Prefinal ME TPODocument4 pagesDatabase Prefinal ME TPOडॉ. कनिष्क शर्माNo ratings yet
- AKOFE Life Members - 2012Document27 pagesAKOFE Life Members - 2012vasanthawNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Week 7 Peace EducationDocument19 pagesLesson Plan For Week 7 Peace EducationCDT 3C SandayanNo ratings yet
- 4.HS6251 - Technical English IIDocument159 pages4.HS6251 - Technical English IINeel JhaNo ratings yet
- Illiteracy Thesis StatementDocument4 pagesIlliteracy Thesis Statementsusantullisnorman100% (2)
- q4 Pe 8 Module 2 Week 3. Beta TestedDocument19 pagesq4 Pe 8 Module 2 Week 3. Beta TestedHanelen DadaNo ratings yet
- Self Directed LearningDocument28 pagesSelf Directed LearningDivya Punjwani100% (2)
- History of Indian EducationDocument10 pagesHistory of Indian EducationSayali HaladeNo ratings yet
- RSO UpdatesDocument17 pagesRSO UpdatesKenny AbellanosaNo ratings yet
- English Language Arts Lesson 1 For Unit PlanDocument3 pagesEnglish Language Arts Lesson 1 For Unit Planapi-302696757No ratings yet
- Pop Culture ModuleDocument108 pagesPop Culture ModuleJas Paras100% (1)
- Starfall Kindergarten Lesson Plans Week5Document26 pagesStarfall Kindergarten Lesson Plans Week5Ashley YinNo ratings yet
- English For Public InformationDocument16 pagesEnglish For Public InformationMestika Zuriati100% (2)
- CM 9Document10 pagesCM 9Nelaner BantilingNo ratings yet
- Mapeh - : Physical Education Quarter 1 - Module 2: Striking/Fielding GamesDocument29 pagesMapeh - : Physical Education Quarter 1 - Module 2: Striking/Fielding GamesZedy Gulles82% (11)
- Pi 10 Exam ReviewerDocument5 pagesPi 10 Exam ReviewerJanna TanNo ratings yet
- TIME Table Medical 2022-23 From 24 Apr To 30 AprDocument1 pageTIME Table Medical 2022-23 From 24 Apr To 30 AprAyush KamraNo ratings yet
- Final Usha LexusDocument58 pagesFinal Usha LexusShishir KaushikNo ratings yet
- Translation StudiesDocument18 pagesTranslation StudiesDidier AlexisNo ratings yet