Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FM Eqns2009
Uploaded by
prt24Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FM Eqns2009
Uploaded by
prt24Copyright:
Available Formats
FLUID MECHANICS: LIST OF FORMULAE
Hydrostatic pressure variation with elevation z: Force on surface A due to pressure: F =
A
dp = dz
where
= g
p dA
Tilted surface: F = ( y sin )A = p A where y is the slant distance to the centroid of A I Location of center of pressure: ycp = y + yA Discharge: Q =
A
V dA
or
Q=VA
for constant velocity (similarly for y and z)
u u u u +v +w + x y z t u Local acceleration: ax = t Total acceleration: ax = u Mass ow rate: m =
A
V dA
dBsys d = bdV + bV dA dt dt cv cs dMsys d V da = 0 or Mass conservation: = 0 or dV + = (u) + (v) + (w) dt dt cv t x y z cs d vV dA v dV + Momentum equation: F = dt cv cs d Momentum equation with input/output ports: F= mo vo mi vi v dV + dt cv cs cs Reynolds transport theorem: p1 V2 p2 V2 + 1 1 + z1 + hp = + 2 2 + z2 + ht + hlosses 2g 2g Power used by pump: Ppump = Qghp dVx where = is the dynamic viscosity Surface resistance: = dy d2 u d Differential form of momentum eqn., s is coordinate along ow: 2 = p + z dy ds UL where L is a length scale (e.g., pipe diameter); pipe ow turbulent for Re > 2000 Reynolds number: Re = L V2 Darcy-Weisbach equation: hf = f 2 Dg 64 Resistance coefcient for laminar ow: f = Re f P LV 2 Head loss for non-circular conduits: hf = where P is wetted perimeter. 4 A 2g V2 +y Specic energy in open channels (no head loss, no slope): E1 = E2 where E = 2g Q2 For rectangular channels (width b): E = +y 2gb2 y 2 V Froude number: F r = gy Energy equation:
F IGURE 1: Moody diagram.
You might also like
- MECH 280 Final Exam: Prof. James Olson TA Paul KrochakDocument8 pagesMECH 280 Final Exam: Prof. James Olson TA Paul KrochakirqoviNo ratings yet
- MMAN2600 FormulaeDocument6 pagesMMAN2600 FormulaeAbhishek SharanNo ratings yet
- Appendix A. Formula CollectionDocument4 pagesAppendix A. Formula CollectionsalmanNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesFluid Mechanics Cheat SheettalatbilalNo ratings yet
- Energy Equation DerivationDocument8 pagesEnergy Equation DerivationJohn Eric CabañaNo ratings yet
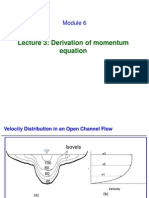
- Lecture 3: Derivation of Momentum EquationDocument33 pagesLecture 3: Derivation of Momentum EquationJanakiSreeramNo ratings yet
- One-Dimensional Flow EquationsDocument14 pagesOne-Dimensional Flow EquationsnandhinidishNo ratings yet
- Hydrodynamics Equation SheetDocument1 pageHydrodynamics Equation SheetsubnautaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Flow in Conduits: Entrance and Developed FlowsDocument43 pagesChapter 8 Flow in Conduits: Entrance and Developed FlowsRicardo ACNo ratings yet
- !! Don't Write On The Formula Sheet Return After The Exam !! FormulasDocument2 pages!! Don't Write On The Formula Sheet Return After The Exam !! FormulasnkchandruNo ratings yet
- Winter School # Finite Volume Method - IDocument35 pagesWinter School # Finite Volume Method - ISreya BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Student Handout 13 2014Document19 pagesStudent Handout 13 2014kietniNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics FormulaeDocument5 pagesFluid Mechanics FormulaeTom HartNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet PHYS 157Document1 pageFormula Sheet PHYS 157Carmen YangNo ratings yet
- EMF FormulaDocument4 pagesEMF FormulaЕвгений КазимировичNo ratings yet
- 2.065/2.066 Acoustics and Sensing: Massachusetts Institute of TechnologyDocument12 pages2.065/2.066 Acoustics and Sensing: Massachusetts Institute of TechnologyKurran SinghNo ratings yet
- Lectures Chapter3 AerodynamicsDocument62 pagesLectures Chapter3 AerodynamicsHermise RajuNo ratings yet
- 2 G 1 1.8 Log 3.7 + 6.9 2 G: Streamline FunctionDocument6 pages2 G 1 1.8 Log 3.7 + 6.9 2 G: Streamline FunctionBao PhanNo ratings yet
- Problems in Chapter 5 (Control Volume Analysis) : V AnduDocument5 pagesProblems in Chapter 5 (Control Volume Analysis) : V AnduZul ZolkopliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 PDFDocument18 pagesChapter 6 PDFteknikpembakaran2013No ratings yet
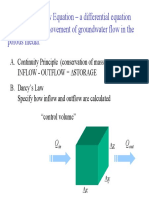
- Groundwater Flow Equation - A Differential Equation That Governs The Movement of Groundwater Flow in The Porous MediaDocument13 pagesGroundwater Flow Equation - A Differential Equation That Governs The Movement of Groundwater Flow in The Porous MediaTNo ratings yet
- 4 Computation of The Free Surface Level in Open Channel FlowDocument7 pages4 Computation of The Free Surface Level in Open Channel Flowjose03No ratings yet
- Vector Calculus II – Gradient, Divergence and Divergence TheoremDocument8 pagesVector Calculus II – Gradient, Divergence and Divergence Theoremgthulasi789193No ratings yet
- WVA 2 Formula Sheet: GeneralDocument2 pagesWVA 2 Formula Sheet: Generalhenk waterbeenNo ratings yet
- Ocean Water Waves IIDocument11 pagesOcean Water Waves IIVivek ReddyNo ratings yet
- Chap 4 Sec2 PDFDocument15 pagesChap 4 Sec2 PDFteknikpembakaran2013No ratings yet
- Compressible Flow EquationsDocument19 pagesCompressible Flow EquationskietniNo ratings yet
- Aero E 541 Midterm Exam 2010 Fall Semester: 1. (30 Points)Document7 pagesAero E 541 Midterm Exam 2010 Fall Semester: 1. (30 Points)Luiz Fernando T. VargasNo ratings yet
- Compressible Flow Through Nozzles and Diffusers: V DT V D V VDocument14 pagesCompressible Flow Through Nozzles and Diffusers: V DT V D V VCamilo SantacruzNo ratings yet
- Things To Know For The Physics GRE: Daniel Beller October 28, 2009Document20 pagesThings To Know For The Physics GRE: Daniel Beller October 28, 2009Arif SolmazNo ratings yet
- CmechDocument10 pagesCmechdaskhagoNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet - Engineering Physics II - Electricity and Magnetism - PHY 303L UT AustinDocument2 pagesFormula Sheet - Engineering Physics II - Electricity and Magnetism - PHY 303L UT AustinJeremy Priest100% (1)
- CH 09Document73 pagesCH 09Vivek Harris88% (8)
- Marc's Formula Sheet for Fall 2019Document1 pageMarc's Formula Sheet for Fall 2019Atif MoeezNo ratings yet
- Principles of Groundwater Flow PDFDocument64 pagesPrinciples of Groundwater Flow PDFJhe TaguinesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Surface Resistance and Boundary Layer FlowDocument22 pagesChapter 9 Surface Resistance and Boundary Layer Flowteknikpembakaran2013No ratings yet
- Compressible Flow PDFDocument90 pagesCompressible Flow PDFOmer TokhNo ratings yet
- Viscous Flow in PipesDocument58 pagesViscous Flow in PipesHarsh SharmaNo ratings yet
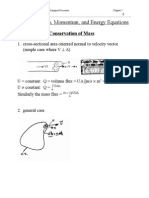
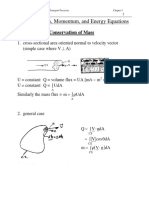
- Chapter 5 Mass, Momentum, and Energy EquationsDocument38 pagesChapter 5 Mass, Momentum, and Energy EquationsAlex GonzalezNo ratings yet
- CHL231 Fluid Mechanics For Chemical Engineers Formula SheetDocument4 pagesCHL231 Fluid Mechanics For Chemical Engineers Formula SheetGarvit GoelNo ratings yet
- 3.7 Governing Equations and Boundary Conditions For P-Flow: 2.20 - Marine Hydrodynamics, Fall 2014Document28 pages3.7 Governing Equations and Boundary Conditions For P-Flow: 2.20 - Marine Hydrodynamics, Fall 2014Felix FisherNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Mass, Momentum, and Energy EquationsDocument38 pagesChapter 5 Mass, Momentum, and Energy EquationsShailesh BhanushaliNo ratings yet
- Potential Flow Theory - 230919 - 100219Document17 pagesPotential Flow Theory - 230919 - 100219rabia elmaakouliNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Fluid FlowDocument10 pagesDynamics of Fluid FlowAnkit RajNo ratings yet
- 2015Document10 pages2015ZaNo ratings yet
- PHYS2050 2010 2 Curl StuffDocument11 pagesPHYS2050 2010 2 Curl StuffEkky CecilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Water Waves: 6.1 Exact (Nonlinear) Governing Equations For Surface Gravity Waves, Assuming Potential FlowDocument14 pagesChapter 6 - Water Waves: 6.1 Exact (Nonlinear) Governing Equations For Surface Gravity Waves, Assuming Potential Flowamit_bs2002No ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics I Solution 4 Question 1: Problem P2.139: A B B C D DDocument8 pagesFluid Mechanics I Solution 4 Question 1: Problem P2.139: A B B C D Dcartoon_nateNo ratings yet
- Ch. IV Differential Relations For A Fluid Particle: V (R, T) I U X, Y, Z, T J V X, Y, Z, T K W X, Y, Z, TDocument12 pagesCh. IV Differential Relations For A Fluid Particle: V (R, T) I U X, Y, Z, T J V X, Y, Z, T K W X, Y, Z, TAditya GargNo ratings yet
- Incompressible 2D flow field verificationDocument8 pagesIncompressible 2D flow field verificationJames TheeNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument35 pagesFluid MechanicsThabang MaphakisaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - AS102: Class Note No: 10Document31 pagesFluid Mechanics - AS102: Class Note No: 10Pranav KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Airy wave theory dispersion and particle motionDocument18 pagesAiry wave theory dispersion and particle motionsandysrNo ratings yet
- Solution of Assignments For Chapter 3Document5 pagesSolution of Assignments For Chapter 3Sandip GhimireNo ratings yet
- Hay Avar DanaDocument8 pagesHay Avar Danaprt24No ratings yet
- 11 Thyripol Main Project FileDocument11 pages11 Thyripol Main Project FileKirankumar Reddy100% (1)
- Generator Excitation SystemDocument35 pagesGenerator Excitation SystemNitin Sakpal100% (1)
- DVR STG ProtocolDocument8 pagesDVR STG Protocolprt24No ratings yet
- Mechanical EngineeringDocument4 pagesMechanical Engineeringprt24No ratings yet
- Aptitude QuestionsDocument6 pagesAptitude Questionsprt8835800No ratings yet
- Ass AsDocument4 pagesAss AsMukesh BishtNo ratings yet
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (48)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishFrom EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldFrom EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismFrom EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (500)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (409)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- The Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceFrom EverandThe Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (23)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1395)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)From EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (155)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeFrom EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeNo ratings yet
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayFrom EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (125)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceFrom EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityFrom EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (75)
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsFrom EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (94)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldFrom EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (60)
- Starry Messenger: Cosmic Perspectives on CivilizationFrom EverandStarry Messenger: Cosmic Perspectives on CivilizationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (158)
- What is Life?: With Mind and Matter and Autobiographical SketchesFrom EverandWhat is Life?: With Mind and Matter and Autobiographical SketchesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (139)
- The Sounds of Life: How Digital Technology Is Bringing Us Closer to the Worlds of Animals and PlantsFrom EverandThe Sounds of Life: How Digital Technology Is Bringing Us Closer to the Worlds of Animals and PlantsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)